Curettage procedure
This operation is performed according to indications, for example, for polyps, endometrial hyperplasia, or if consequences occur after abortion. Curettage is carried out in case of possible changes in the uterus, in case of prolonged bleeding, accompanied by blood clots.
A fairly common cause of uterine curettage can be considered a frozen pregnancy. The material obtained during this procedure must be sent for research. Curettage is a standard procedure for terminating a pregnancy.
https://youtu.be/2FgXtXh9bmM
Consequences of scraping
Curettage of the uterus occurs almost blindly, using special instruments, for this reason violations occur. The doctor performing such a procedure must be able to understand both natural and pathological.
This type of surgery is a unique operation, and it can also have a number of complications. This directly depends on the professionalism of the specialist. The duration of the procedure plays an important role. The rate of surgical intervention performed depends on various types of diseases, processing of instruments and compliance with all rules and regulations.
In women with poor blood clotting, it may appear after curettage, the duration of which may be caused by the presence of hormonal problems. If such surgical intervention is necessary for a number of indications, then it is better to entrust it to a professional specialist who has extensive experience in performing such a procedure.
Monitoring is necessary throughout treatment. This must be done to avoid various kinds of complications and further problems with the genitals. Unsuccessful operations can lead to infertility.
They are observed in almost all women, since curettage is the removal of the entire upper layer of the mucous membrane, which means that the girl’s uterine cavity turns into a huge wound, and therefore such discharge is considered normal. Bleeding after curettage of the uterine cavity does not differ much from the menstrual cycle; it is actually the same, since the uterus begins to reject a layer of the mucous membrane.
Bleeding lasts differently for each woman. It is believed that the norm for bloody discharge is when it lasts no more than 4-5 days, is moderate, and does not have an unpleasant odor. After such an intervention, pain in the lower abdomen and lower back may occur, which occurs due to contraction of the uterus.
When is curettage performed?
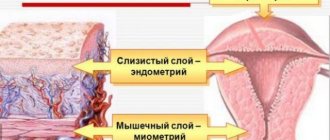
The inner tissue of the uterine cavity is a mucous layer called the endometrium. For some reason, sometimes this fabric needs to be cleaned completely or partially. Such manipulations are carried out surgically using special medical instruments (see photo). This process refers to surgical intervention, and therefore has all the postoperative symptoms and carries a large burden on the body.
Curettage performs a therapeutic and diagnostic function and is used in the following cases:
Pathological bleeding
Complications can arise for a number of reasons. or after other procedures, more often associated with the duration of the operation, and if the standards for processing surgical instruments are violated, poor-quality curettage is considered a common occurrence of complications, this is when particles of the pathological mucous membrane remain in the uterine cavity.
Curettage operations performed using a hysteroscope virtually eliminate the possibility of complications. When using this device, the risk of damage to the muscle layer is reduced, and also provides the opportunity for a specialist to evaluate the quality of the work done.
Bleeding in a girl that is pathological in nature can be distinguished by the following signs:
- How many days does it last (usually more than 10 days).
- An inflammatory process caused by the introduction of harmful bacteria.
- Formation of blood in the uterine cavity, without the possibility of exit.
Discharge is considered pathological if its duration is more than 10 days; this may be due to the remains of unremoved tissue in the uterus. can provoke an inflammatory process that occurs in the endometrium. It occurs when staphylococcus bacteria enter the layer, which means poor-quality processing of medical instruments.
If there are remains of particles of the fertilized egg or other tissues, the discharge has an unpleasant odor.
When blood accumulates in the uterus, women develop a fever and severe pain in the lower abdomen, similar to contractions. On the second day after surgery, the discharge suddenly stops.
In order to eliminate the risk of developing, it is necessary to treat bleeding after surgery. As therapy, special hemostatic drugs are prescribed, as well as drugs that cause the uterus to begin to contract. If the patient gets an infection during curettage, specialists prescribe a course of antibiotics. In rare cases, repeated surgery is resorted to. A hormonal imbalance can be corrected by an endocrinologist.
If bleeding begins after curettage, this is normal. It is important to remember that natural bleeding should not exceed 7-8 days, and end gradually.
Pathological bleeding can be recognized by the following signs:
- If the duration is more than 10 days,
- Heavy bleeding
- Abrupt cessation of discharge
- Bleeding has an unpleasant smell and color,
- Temperature increase,
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen,
- Severe weakness, loss of consciousness.
If you experience any symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Specialists will conduct a full examination and prescribe treatment. If you delay in such situations, severe complications can develop that will be very difficult to stop.
You should not start self-medicating with drugs or using traditional medicine methods. Only a gynecologist will help identify the true cause of prolonged bleeding, prescribe treatment or repeat surgery.
Curettage or abrasion is one of the most traumatic procedures for the uterine mucosa. But for many specialists it remains a kind of “gold standard” for abortion, diagnosis of inflammatory processes, and sometimes it is done, as they say, just in case (after a medical abortion before a control ultrasound).
Although now there are analogues of curettage that are safer for women’s reproductive health, it is still often used in medical practice. Therefore, every woman should know about the goals, possible complications and consequences of the procedure. Discharge after curettage of the uterine cavity can be of different colors, consistency and strength. Knowing their norm, in particular, how many days they should go, will help to avoid the development of complications and will make it possible to consult a doctor in time.
No bleeding
Sometimes it happens that after curettage of the uterine cavity, bleeding does not appear at all. This sign is unfavorable and should alert both the medical professional and the woman herself.
The reason why there is no discharge may be blood clots that form in the uterine cavity (hematometer). Sometimes a bruise forms on the neck, which disrupts the normal outflow of liquid contents from the cavity.
Very often inflammation occurs, then the woman’s nagging pain in the abdomen intensifies, her temperature rises, and her general health worsens.
Such changes require immediate medical attention.
Specifics and consequences of curettage
Attention!
The information on the site is presented by specialists, but is for informational purposes only and cannot be used for independent treatment. Be sure to consult your doctor!
Content
Brown discharge after curettage (curettage, cleaning) of the uterus is a phenomenon considered normal. Do not forget that cleaning the uterus is an invasive surgical procedure, accompanied by various complications.
The presence of brown discharge after curettage is considered a physiological norm, but in some cases it may indicate the development of pathology.
Scanty and copious discharge
Another situation is if the bleeding is either heavy or scanty, lasts longer than the agreed period, the stomach periodically pulls, the pain radiates to the side, back, while chills and general malaise are felt. These symptoms may indicate a hormonal imbalance, erosive processes, ineffective removal of foci of endometriosis, polyps and even neoplasms of various etymologies.
A common ailment after curettage, in particular abortive, is endometritis, inflammation of the uterus. It develops as a result of infection during the cleaning process, poor antiseptic treatment, and also due to non-compliance with the rules of the rehabilitation period. It is important that as a result of surgical intervention, the woman’s body and immunity are weakened, its resistance is low, and therefore the uterine cavity is susceptible to unhindered attack by pathogenic organisms. This is how inflammation develops.
Causes of discharge
The cleansing procedure involves completely removing the upper (functional) layer of the endometrium of the uterus. After curettage, the woman experiences bleeding, reminiscent of menstruation. The difference is that during curettage the mucous membrane is removed within a short time - the procedure lasts no more than 20 - 40 minutes. It depends on the purpose for which the woman was prescribed uterine cleaning.
In some cases, curettage is performed in the middle of the menstrual cycle. If the procedure is timed to coincide with the beginning of menstruation, the inner surface of the uterus after cleaning is an open bleeding wound. It requires recovery, which takes some time - approximately one menstrual cycle - 1 month. It is during the period of regeneration of endometrial tissue that a woman experiences brown discharge.
But the process of restoring the endometrium after curettage of the uterus does not always proceed without problems. Complications after cleaning may include:
- development of secondary bacterial infection;
- inflammation of the endometrium;
- inflammation initiated by the remaining particles of the embryo or its tissues, as well as pieces of the mucous membrane.
In this case, uterine discharge will not only have a brown color, but also differ from the norm in consistency and smell. Such discharge will last much longer.
Normal indicators
The appearance of discharge from the uterus after surgery is a natural and natural process. Since the functional layer of the endometrium (the inner lining of the uterus) is removed during curettage, a bleeding wound remains in this place. The uterus always bleeds after diagnostic curettage. The nature of bleeding after surgery normally does not differ from that during menstruation.
Discharge appears immediately after curettage of the uterus. Their intensity can vary - from scanty bleeding to heavy bleeding. The duration depends on the extent of the surgical intervention and the individual characteristics of the woman’s body.
Normal discharge from the uterus has the following features:
- Moderate intensity.
- They consist mainly of fresh blood.
- No unpleasant smell.
- Gradually the blood is replaced by lighter ichorous secretions.
- Further, the amount of ichor gradually decreases.
- After a few more days, the daubing completely stops.
- The discharge may be accompanied by mild nagging pain in the lower abdomen. The pain may radiate to the lower back. The cause of these pains is the contraction of the muscles of the uterus.
If the postoperative period proceeds according to the described “scenario”, this is a sign that healing is occurring normally.
Duration
Brown discharge after curettage of the uterus, even in the absence of complications, can last 10-20 days. Gynecologists allow bleeding of varying intensity for 14-21 days after cleansing if the woman is not bothered by pain and the consistency and smell of the discharge is normal. It all depends on the reasons for which the cleaning was carried out - it could be an abortion, diagnostic curettage, a frozen pregnancy, or a disease of the uterus.
But there are other factors that directly affect the duration of bleeding. This:
- the presence of other pathologies of the organs of the pelvic region;
- quality of the manipulation performed;
- total volume of removed endometrium.
Brown discharge will last the shortest time after diagnostic curettage: no more than 10 days. They will last longer after an abortion - they can be observed for 14-21 days. And if we consider the volume, it will be more significant than after a diagnostic cleansing of the uterus. But the longest possible discharge should be expected after curettage of the uterine cavity to remove a frozen pregnancy. In this case, light bleeding may last up to three weeks.
There are several criteria that gynecologists rely on when assessing the norm and deviation of bleeding.
- During the first few hours after cleaning the uterus, they are profuse and red in color, representing typical bleeding.
- Then the discharge becomes lighter and decreases in volume.
- Before its completion, the discharge turns brown, resembling a “daub.” Its appearance indicates the beginning of the restoration of cyclic production of sex hormones and the completion of regeneration of the endometrial layer.
Yellow discharge with or without odor
The bright yellow color of the discharge after manipulation indicates infection and the beginning of the inflammatory process.
If a woman does not yet feel an unpleasant odor of discharge or pain, this does not at all mean that the recovery of the uterus is progressing well. In this case, you need to contact a gynecologist for further therapy.
If a faint yellowish tint is the result of a gradual decrease in the intensity of secretion, then there is no cause for concern.
The discharge may also smell due to the development of inflammation due to infectious diseases. For example, bacterial vaginosis or candidiasis (thrush). Their symptoms are complemented by discomfort in the vaginal area: itching, burning. Bleeding after brushing is accompanied by yellow, white or gray mucus. Such ailments are transmitted both sexually and develop against the background of a disturbance in the composition of the microflora, which is inherent in the postoperative period in women.
Norm and pathology
A sign of a well-performed uterine cavity curettage is not only the duration of the brown discharge, but also its quality. In the absence of pathology, they must have the following characteristics:
- have a small volume and medium degree of density;
- do not have an unpleasant odor;
- do not contain clots.
If at the beginning the discharge is almost completely identical to blood, then towards the end of the recovery period it becomes brown.
A rich dark brown shade indicates the release of residual clotted blood, and should not frighten a woman.
If curettage of the uterine cavity was carried out in violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis, or the woman did not follow the recommendations of doctors during the recovery period, then various complications may develop.
When brown discharge also has a sharp, unpleasant odor, this symptom may indicate the following:
- development of infection caused by both opportunistic and pathogenic pathogenic flora with the formation of endometritis, as well as ascending infection;
- hematometer;
- remnants of parts of the fertilized egg in the uterus and their necrosis.
Inflammatory processes after cleaning can lead to peritonitis and sepsis - life-threatening conditions.
With prolonged brown discharge - more than 21 days - with a significant volume remaining, one can suspect:
- development of hormonal imbalance;
- poorly performed curettage;
- presence of problems with blood clotting.
A significant amount of brown discharge is also a pathology, since it should decrease. The development of uterine bleeding, typical of hematometra, is indicated by the need to change the sanitary pad every two to three hours. In addition, the discharge also contains clots. This symptom may also indicate injury to the walls of the uterus.
If brown discharge has yellowish or green impurities, then this is a symptom of the development of a bacterial infection. Pinkish-brown is a typical sign of inflammation. When white inclusions appear in the discharge, we can talk about the beginning of suppuration. Discharge from the genital tract with the consistency of meat slop with a pungent odor signals endometritis.
What discharge is considered normal and what signals pathology?
For health, it is not only the duration of the discharge that matters, but also what it is. Normally, bloody mucus from the genital tract should meet the following criteria:
- be moderate in volume;
- not have a nauseating odor;
- be a uniform mass without clots.
The color of the discharge varies from red to brown. The more time passes from the moment of manipulation, the closer their shade is to the second option. Dark brown discharge after curettage is detected closer to the end of the mucosal restoration process, when the remnants of coagulated blood come out.
If the procedure for any reason leads to complications, they may manifest themselves as the following symptoms:
Visit doctor
If the brown discharge after curettage does not meet the physiological norm either in appearance or in volume, then the woman is recommended to visit a gynecologist’s office as soon as possible.
Brown discharge after cleaning the uterus is especially dangerous when the following symptoms occur:
- increase in body temperature to high levels;
- prolonged pain syndrome that cannot be relieved with painkillers;
- deterioration in general health.
A dangerous sign is the complete cessation of bleeding within several hours or days after the procedure. The cause of this condition is hematometra - the accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity caused by the cessation of its physiological outflow. This can occur as a result of spasms of the cervix, as well as in the presence of blood clotting pathology. Additional signs of hematometra include severe pain in the lower abdomen and increased body temperature.
Brown discharge that appears a month after cleaning the uterus is a reason to contact a gynecologist. They can be either another menstruation or a sign of a developed infection of the female reproductive system.
If you have any doubts about your well-being after curettage, you should seek medical help. If the smell or consistency of brown discharge changes, only a gynecologist should treat it, and self-medication should be excluded.
Discharge after curettage is normal; another thing is how long it lasts and what consistency it has. This procedure involves cleaning the uterine cavity with a special instrument to remove the upper mucous layer of its lining. It is otherwise called gynecological cleansing, or curettage.
The uterus is a pear-shaped muscular organ consisting of a cervix, isthmus and fundus. The cervical canal is located in the cervix, through which menstrual blood is excreted and sperm penetrate. The endometrium lines the cavity of the organ; this mucous membrane differs from others in that it has the ability to secure a fertilized egg. During the curettage procedure, the superficial functional layer of the endometrium is removed. The procedure is carried out 2-3 days before the start of menstruation, under anesthesia. Contraindications are acute inflammatory processes, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disorders, and blood diseases. Curettage is not performed if a woman has vaginitis or colpitis.
When is it time to see a doctor
If postoperative discharge does not correspond to the norm purely in appearance and volume, and lasts longer than usual, these are already sufficient reasons to visit a gynecologist. It’s even worse when they are complemented by a feeling of well-being:
- abdominal pain that is not relieved by pills;
- raising and maintaining high temperature;
- general loss of strength.
An equally dangerous sign is the absence of discharge or its abrupt cessation 1 to 2 days after the start. This happens when the contents separated from the wound surface are retained inside the uterus due to stenosis of the cervix or the formation of a hematoma on it. All this is also accompanied by pain and fever.
Bloody discharge a month after curettage also dictates the need to visit a doctor. It may be the next menstruation, but there is also a possibility that inflammation has occurred in the reproductive organs. And not necessarily only in the uterus.
Causes of the phenomenon
Discharge after curettage of the uterine cavity is a normal condition. During the operation, the top layer of the endometrium is removed, the same happens during menstruation. Therefore, bleeding after curettage can last the same period as regular periods.
How much blood flows after the procedure depends on the woman’s condition. The discharge should not be heavy; after hysteroscopy it lasts from 5 to 7 days. Further, after cleaning the uterus, they acquire a smearing character. In total, the duration of the discharge is a maximum of 10 days. Throughout the entire period, the woman will experience minor pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. Such discomfort is caused by curettage and contraction of the uterus and is also considered normal.
The relationship between types of cleaning and discharge
Women often ask their doctor whether the intensity and duration of bleeding depends on the reason for cleaning the uterus.
After removal of the endometrium and fertilized egg due to the death of the embryo, the uterus is cleaned very abundantly. Discharge after abortive curettage performed for short periods will last from 10 to 14 days. If, for medical reasons, the termination of pregnancy was performed in the later stages, bleeding after RDV will be long.
Discharge after diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is a small amount of blood, which disappears about a week after the manipulation. Normally, by the 10th day there should be no traces of blood on the pad.
Any terms that relate to the duration of cleansing the uterus are very arbitrary. The body of each representative of the fair sex is unique, so it is impossible even for an experienced gynecologist to predict anything. Doctors can only guess the duration of uterine cleansing based on their experience.
Pathological signs
In what situations is discharge after hysteroscopy considered pathological? You should be careful:
- If the discharge continues for more than 10 days. This may be evidence of hormonal imbalance. Prolonged bleeding exhausts a woman and can develop anemia.
- If the blood after scraping has an unpleasant odor, then an infection may be present.
- A sudden stop in discharge may indicate that blood clots have formed in the uterus. At the same time, the body temperature will rise, the pain in the lower abdomen will intensify.
- If there is a lot of discharge in volume and there is no tendency to reduce bleeding.
How many days the uterine healing process will take largely depends on the purpose for which the curettage was performed and how much material was removed. It is of great importance how well and sterile the operation was performed. Brownish discharge after cleaning the uterus during a frozen pregnancy lasts the longest, on average 8-20 days, but in the end it should go away without a trace.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed drugs that stop bleeding and contract the uterus. To avoid infectious diseases, antibacterial agents are prescribed. All medical instructions must be followed. It is recommended to include beef liver, red meat, apples and pomegranates in your diet. Physical activity and hard work should be limited. 2 weeks after the operation, you must visit a gynecologist to monitor the recovery process. The examination will show the state of the uterine tone. If necessary, hormone therapy is prescribed.
How to prevent complications from occurring
Complications during the rehabilitation period arise against the background of decreased immune defense, as well as hormonal imbalances. To protect yourself as much as possible from a long recovery period, you must follow simple rules:
- Do not leave the hospital for at least 24 hours after cleaning.
- For 7 days after curettage, observe bed rest.
- Avoid excessive physical activity.
- Protect yourself from stressful situations.
- Don't freeze.
- Follow all recommendations of the gynecologist.
- Use therapy aimed at maintaining the body's protective resources.
- Promptly undergo repeated ultrasounds to assess repair processes.
Women who are periodically observed by a gynecologist after surgery are maximally protected from complications. Therefore, it is so important not to ignore the need to visit doctors. Patients who went to the hospital for a consultation may not have to worry about their health in the future.
Curettage of the uterus is an unpleasant but necessary operation, which is sometimes impossible to do without. The procedure, which is performed by highly qualified specialists, very rarely causes complications that require appropriate treatment. However, discharge after cleansing is a natural and completely normal process that cannot be avoided.
The task of every woman is to control the nature, color and duration of the discharge. Many people do not know what to do if their health changes for the worse during the recovery period. In such a situation, there is only one way out - to seek help from specialists. Only a doctor can give a real assessment of the state of women’s health, as well as prescribe adequate therapy.
Possible complications
Gynecological curettage is performed blindly and involves a certain risk. The technique of curettage is identical to abortion. When the deep layers of the endometrium are damaged, the risk of scar formation in place of the ciliated cylindrical cells increases. As a result, the embryo loses the ability to attach to the mucous surface of the uterus. A woman should have an idea of what risks and complications this procedure may entail. The experience and professionalism of the doctor performing the operation is very important.
The first menstruation after curettage will occur approximately a month after curettage. Menstrual flow may vary in abundance and duration.
In some cases, women experience hormonal disorders, expressed in the absence of menstruation. A delay of up to one and a half months is considered normal. If it is not caused by an inflammatory process, the doctor may prescribe hormonal drugs to restore ovarian function. It is not recommended to plan pregnancy within 6-7 months after the procedure. In the case where curettage was carried out due to a frozen pregnancy, it is necessary to identify the cause of the incident, carry out proper treatment and plan the pregnancy in consultation with specialists.
Uterine bleeding is possible; as a rule, it appears in women with poor blood clotting. If the pads are changed more often than every 3 hours, and the discharge is profuse, the doctor will prescribe an Oxytocin injection.
Cervicitis
Yellow discharge after curettage can occur with cervicitis. The pathology is an inflammation of the cervical canal. The reason may be:
The following types of cervicitis that form after curettage are distinguished.
In general, the disease can be asymptomatic. The appearance of yellow purulent discharge after curettage indicates an acute form of inflammation.
The woman also receives the following complaints:
In some cases, after cleaning and the development of cervicitis, an increase in temperature may be observed.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor, in addition to yellow discharge, notes swelling and redness of the part of the cervix that extends into the vagina. Minor hemorrhages and ulcerations may also be detected.
If left untreated, the pathology becomes chronic. The yellow discharge becomes less abundant, but contains blood. A woman feels a constant aching pain in the lumbar region during sexual intercourse.
Diseases associated with blood retention in the uterus
Hematometra is a disease characterized by impaired blood flow from the uterine cavity. The cause may be polyps in the cervical canal or the presence of myomatous nodes in the uterus. The disease is recognized by the abrupt cessation of discharge after the curettage procedure, literally a day or two after the operation. The pain syndrome is of a paroxysmal nature, intensifying with physical stress. Fever and nausea may be present. If the inflammatory process develops, the pain spreads to the lumbar region, and the temperature rises sharply.
To eliminate hematometra, it is necessary to remove accumulated blood clots from the uterine cavity using a probe inserted into it. If an inflammatory process is diagnosed, then antibacterial therapy is first carried out, and only then the organ is released from the accumulated secretions.
Endometritis is inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus. After scraping, the inner surface of the organ becomes an open wound, as a result of which the ingress of microbes develops an inflammatory process. Endometritis is accompanied by elevated body temperature, sharp pain in the lower abdomen, and discharge mixed with pus. Signs of intoxication may be present - headache, nausea, general weakness. Treatment includes taking antibacterial drugs and washing the organ cavity with antiseptic solutions.
Uterine perforation is the most dangerous complication. It can occur when the uterus is deformed and its cervix cannot dilate. In this case, suturing and drug therapy are necessary.
The risk of complications after curettage is approximately 13%. However, such a procedure is simply necessary in some cases. In order to avoid adverse consequences, you should find a professional doctor. Taking care of a woman’s health is her future, her ability to bear and give birth to a healthy child.
Curettage of the uterine cavity is performed in some cases for the diagnosis and treatment of gynecological diseases. This procedure is low-traumatic, but after it is performed the patient requires a recovery period. A woman should be prepared for the fact that after cleaning the uterus there will be bleeding. How long this will last depends on the purpose for which and under what circumstances the procedure was performed.
Causes and signs of pathology
Discharge from the uterine cavity may be pathological. Such changes may be due to:
- The presence of diseases of the genitourinary organs.
- Violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis during curettage and in the postoperative period.
- Poor scraping quality.
- Insufficient amount of removed endometrium.
Pathological discharge can be recognized by characteristic signs. These include the following changes:
- The bleeding is massive even several hours after cleaning (a woman needs more than 1 pad per hour).
- The discharge acquires a strong, unpleasant odor.
- Outwardly, they look like meat slop. Such signs indicate the addition of an infection and the development of an inflammatory process.
- Bleeding may suddenly stop when a hematometra forms.
- The woman’s general condition changes: the temperature rises, weakness and malaise develop. Nausea and vomiting may occur.
- The patient feels severe cramping pain in the lower abdomen.
- Gradually, the pain can spread to the entire abdomen and radiate to the lower back, hips and perineum. The pain cannot be relieved by taking antispasmodic drugs.
- With prolonged bleeding, anemia develops.
One of the most serious complications after cleaning is uterine bleeding. It can develop if a woman has a blood clotting disorder. This type of bleeding is more intense and lasts longer. It can pose a serious threat to the health and life of a woman.
What is uterine cavity curettage, why and how is it performed?
Curettage (curettage) is a procedure for removing part of the endometrial layer. Curettage is performed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. In the first case, endometrial cells are sent to the laboratory to be examined for the presence of atypical elements. Diagnosis of the inner layer of the uterus is necessary in case of severe bleeding for an unknown reason, as well as in the detection of tumors on the endometrium. In this case, the gynecologist uses a hysteroscope to examine the organ and makes scrapings.
As a therapeutic measure, cleaning is carried out in the following situations:
- inflammation of the endometrium;
- polyps;
- bleeding, including during menopause;
- menstrual irregularities;
- pathologies of the cervix;
- miscarriage;
- frozen pregnancy;
- consequences of an unsuccessful abortion;
- the presence of placenta particles in the uterus after childbirth.
Before curettage, it is necessary to perform an OAC, a blood test for coagulation, and a smear examination of the vaginal flora. Three days before the procedure, you should stop using vaginal suppositories, intimate hygiene products, gels, ointments, etc. Two days before the procedure, you should avoid sexual intercourse. If a woman is taking medications, you should tell your doctor about this: their use may need to be reduced or discontinued. On the day of surgery, you should limit the amount of food and liquid you consume.
The procedure consists of several stages:
- The patient lies down in the gynecological chair. The doctor administers a local anesthetic to eliminate pain during the procedure.
- A speculum and a hysteroscope are inserted into the cervix. The gynecologist examines the walls of the uterus, assessing their condition.
- Curettage is carried out using a special medical instrument, similar to a small spoon with a long handle - a curette. This device cuts off excess endometrial tissue or removes the remains of the embryo after an artificial termination or a frozen pregnancy.
Upon completion of the procedure, patients feel pain in the lower abdomen, which can last for several days. This is a normal phenomenon: the uterus contracts, cleaning itself. Analgesics can be used to reduce pain. Also, over the course of several days, clots may be released, which decrease every day and after about 10 days should disappear completely. After the operation is completed, sexual intercourse should be avoided for a month.
In what cases is curettage performed?
The internal cavity of the uterus is lined with a layer of endometrium. If fertilization of the egg does not occur, every month this layer is naturally rejected and uterine bleeding occurs - menstruation. This is how the uterus periodically cleanses itself, preparing for a new potential conception. For some reasons, situations arise when the inner shell needs to be cleaned. For this purpose, a surgical method is used - curettage.
If your doctor has prescribed a cleaning, you should be aware that this is a surgical procedure and will require a long recovery period.
Cleansing the uterus is used as a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure, which is carried out for the following pathologies:
- Thinning or thickening of the inner layer of the uterus.
- Spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
- Disruption in the menstrual cycle.
- Endometriosis.
- Incomplete completion of abortion using vacuum aspiration.
- Biopsy.
- Diseases of the cervix.
- Inflammatory pathologies.
- Presence or suspicion of a neoplasm of any nature.
Why is there discharge after cleaning?
This article talks about typical ways to solve your issues, but each case is unique! If you want to find out from me how to solve your particular problem, ask your question. It's fast and free
!
Cutting off part of the inner layer of the uterus causes bleeding. The larger the area of the organ that is treated, the more blood flows. This is the norm, because such a procedure makes the uterine layer an open wound that will heal over time.
If hysteroscopy was done for diagnostic purposes, the discharge is usually scanty and lasts up to 4 days after curettage. If there has been therapeutic curettage, especially after a miscarriage or termination of pregnancy, the bleeding is more profuse and prolonged. In this case, it is advisable to take hemostatic medications.
What should the discharge be like after curettage and how long does it last normally?
Discharge after cleaning the uterine cavity occurs like normal menstruation. Normally, it lasts about 10 days, at first it bleeds profusely, then more and more sparingly. Finally, there is brown discharge after curettage, which indicates the healing process of the uterus. Then it stops bleeding and begins to “smear” with a light color.
How long does the discharge last? The maximum bleeding period should not exceed 10 days while taking hemostatic drugs. The presence of clots in the first days is allowed, but the discharge after cleaning the uterus should not have an unpleasant odor. Yellow or green color of the discharge indicates pathology, the addition of a bacterial infection. If your body temperature increases, you should consult a doctor.
Duration of discharge
The amount of discharge after curettage will depend on the condition of the body. If the cleaning was done according to all the rules and recovery occurs normally, the total duration does not exceed 10 days. When curettage is performed on the eve of menstruation, the duration of bleeding is approximately equal to that during menstruation. Usually in such cases it is applied for no more than 5-6 days.
If the procedure was carried out in the cervical canal of the uterus, the discharge will be very short-lived. If bleeding lasts too long (more than 10-20 days), this may indicate a hormonal imbalance in the woman’s body.
Complications after cleaning the uterus
If bleeding after curettage does not stop after 10 days and pain remains in the uterus and lower back, this may indicate the presence of complications. In this case, you should not delay your visit to the gynecologist.
Curettage can cause the following complications:
- Heavy scarlet bleeding (in an hour a large pad is completely filled) with a large number of clots, accompanied by severe or moderate pain in the uterine area. In this case, paleness of the skin and loss of consciousness are possible. In such cases, there will be no brown discharge, since the symptoms indicate that the patient has problems with blood clotting. This situation requires emergency medical attention. To prevent such cases, a blood clotting test is done before surgery.
- Hematometra is a situation where blood cannot leave the uterus. This picture is usually observed with cervical spasm. Signs of hematometra are an increase in temperature from 37°C, an unpleasant odor from the vagina, severe pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back. A mandatory symptom is that in the first days after the procedure, the discharge is scanty or absent at all.
- Inflammation of the endometrium. This complication is accompanied by a temperature much higher than 37°C – values can reach up to 39°C. In this case, the patient experiences chills, pain in the lower abdomen, and general malaise. Endometritis develops as a result of the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms on the inner layer of the uterus. Yellow discharge is possible. This situation also requires hospitalization and drug therapy.
- Infertility. The most rare complication, almost never encountered in women who have undergone uterine cleansing.
Upon completion of curettage, complications do not arise provided that the patient follows all the doctor’s recommendations. During the recovery period, you cannot perform heavy physical work or play sports. It is important to take medications prescribed by the gynecologist (analgesics, hemostatic agents, antibiotics to avoid fever and the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria after curettage).
The main criteria for assessing the condition after surgery
It must be remembered that there are 4 criteria for discharge that help keep the situation under control - color, abundance, duration and consistency.
Color and smell
Proper healing of wounds in the uterus can be determined by the change in color of the marks on the pad.
Brown
The appearance of a brown spot is a sign that the blood is rapidly clotting, and this portends a quick restoration of the reproductive organ.
Yellow
If the cleansing was carried out due to the death of the fetus, disturbances in the body’s reparative processes often occur. In such patients, the discharge has a watery structure with suspicious inclusions, it is quite abundant, and is characterized by a characteristic yellowish tint and a rotten odor. The change in color of the secreted secretion occurs due to the fact that a special inflammatory fluid comes out of the uterus. It consists of formed elements, blood and water.
Yellow marks on the gasket are an alarming signal that indicates the presence of an acute inflammatory process.
This liquid provides an ideal habitat for a large number of microorganisms. During their life, nitrogen-containing compounds are released, which cause a foul odor.
Pink
Pink discharge after endometrial scraping is a clear sign that blood clotting is impaired. Patients who are concerned about pinkish marks on the pad should consult a hematologist with complaints.
Unpleasant aroma
A rotten smell is another very dangerous symptom. It appears due to volatile compounds that bacteria produce during their life.
Abundance
After surgery, the amount of discharge should be the same as during menstruation. The woman will notice that every day the pad can be changed less and less, and by the end of the week the need to use these hygiene products will disappear.
If the blood volume during “critical” days is approximately 180 mg, then after curettage it is allowed to exceed this figure by 1.5 times.
If you need to change the pad too often (less than 3 hours), you should definitely consult a doctor - this condition can cause anemia.
Lack of bleeding is also a cause for concern. The reason for this is either an incorrectly performed operation; or a hematometer; or exacerbation of a gynecological disease; or hormonal imbalance.
Duration
Many women wonder how many days after RDV of the uterine cavity the bleeding continues. Another marker that allows us to judge the success of regeneration processes is the duration of bleeding. Normally, the discharge will last 10 days: on the 7th–8th day there is very little of it, and on the tenth it disappears completely. If this period is exceeded, you should consult a gynecologist for advice.
Consistency
The nature of the discharge should be similar to menstrual. After cleaning, due to the death of the fertilized egg, traces of a brown or bright red color with endometrial particles can be seen on the pad. The discharge after curettage of fibroids has a similar consistency and should also have a normal smell.
Even if curettage was performed for diagnostic purposes, there should be no significant difference in the nature of the discharge, and any pathological changes are a reason for a visit to the gynecologist.
When will the menstrual cycle resume?
How long should it take after curettage for menstruation to come? Usually menstruation comes after 24–35 days. In this case, the discharge after curettage should be the same as before the procedure: without an abundance of clots or unpleasant odor, of moderate duration and intensity, and not spotting. At the end of the recovery period, the discharge turns brown. The menstrual cycle will improve 2-3 months after the procedure. If this does not happen, you should contact a specialist to find out how to treat such a deviation.
If curettage was performed during a frozen pregnancy before the 12th week, then menstruation will begin in 4–8 weeks. If the fetus “frozen” in the 2nd–3rd trimester, your period will come in 6–8 weeks, just like after an abortion. Repeated untimely bleeding does not normally occur after cleaning. If after some time it starts to bleed again, the doctor will recommend hemostatic agents and order an examination.
Abortive cleansing
Abortive curettage in case of artificial termination of pregnancy is used at 10–12 weeks and is considered the least safe method. It is carried out in two stages. The first, dilatation, involves widening the cervical canal with surgical instruments or special drugs (which is less effective). The second stage, curettage - cleaning the cavity and walls of the womb using a curette - a medical surgical spoon. The process is painful, therefore it is performed under general anesthesia in the absence of contraindications.
Cleaning a frozen pregnancy is carried out in the same way if the fetus froze and remained in the womb, as well as if the miscarriage took place partially. About discharge after curettage of a frozen pregnancy, read the article at the link.
It happens that pharmabortion or vacuum aspiration did not provide a complete termination of pregnancy. The remaining embryo particles must be removed to avoid sepsis of adjacent tissues. This process is carried out through cleaning.
When is conception possible?
Gynecologists advise waiting to conceive after an abortion or a frozen pregnancy for at least six months. Why so long? The body needs this period for rehabilitation. It is important to wait until the menstrual cycle is restored and the reproductive system is functioning properly. This time can be used for active preparation for pregnancy, including giving up bad habits, taking folic acid, and leading a healthy lifestyle. In this way, you can increase the chances of conceiving again as quickly as possible and bearing a healthy child.