What are uterine fibroids?
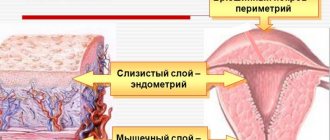
Uterine fibroids are represented by a round node.
Uterine fibroids are a very common disease of the uterus. It is a compaction in the form of a benign tumor, which is formed from muscle tissue. Depending on the stage of development, its size increases. After week 11, the size of the lump is considered large.
The causes of this disease are not fully understood. During its development, the cells of the muscular layer of the uterus actively divide and form compactions. Most scientists agree that the accelerated division of uterine cells is associated with the influence of the hormone estrogen.
This disease occurs quite often, the risk of its occurrence is very high. About 20% of women over 37 years of age suffer from a disease such as large uterine fibroids. Moreover, often not one, but several lumps appear, during which it is quite difficult to get pregnant.
Intercostal neuralgia: causes
This unpleasant disease can develop for many reasons. “Most often, intercostal neuralgia is caused by problems with the spine and the musculo-ligamentous system: osteochondrosis, osteoporosis, herniated intervertebral discs, muscle spasms, inflammation of the intercostal muscles,” says Vladimir Khomutov. “Also, the development of intercostal neuralgia can be caused by injuries, tumors, or taking medications that have a neurotoxic effect.” Some diseases and infections can lead to neuralgia, for example, ARVI, multiple sclerosis, diabetes mellitus, rheumatism, tuberculosis, shingles. It must be said that intercostal neuralgia is extremely rarely caused by just one factor. Most often, this is a whole complex of unfavorable circumstances that arise simultaneously or sequentially.
Why does uterine fibroid occur?
The mechanism of occurrence of this disease is not fully understood. Its education may be affected by:
- Hereditary factors;
- Abortion;
- Stress;
- Excess body weight.
However, most experts agree that the main cause of this disease is hormonal imbalance. It is possible to get pregnant with this disease, but it is quite difficult.
The greatest risk of this disease occurs in women of childbearing age; as a rule, it is determined by chance. However, with the development of this disease the following signs may appear:
- Copious discharge;
- Lower abdominal pain;
- Frequent urge to urinate.
Is it possible to diagnose the disease using ultrasound?
Most often, this disease manifests itself spontaneously and occurs without any special symptoms. The most effective method for detecting it is ultrasound. In order to diagnose fibroids at an early stage, it is enough to undergo an ultrasound examination once a year. The essence of the method is that ultrasonic waves are reflected from tissues.
Many women are concerned about the question of whether pregnancy can be confused with fibroids? Indeed, it is quite difficult to distinguish the disease at the initial stage from pregnancy, therefore, in order to confirm the diagnosis and not confuse it, specialists prescribe a number of additional studies. After all, getting pregnant with this disease is not easy.
The maximum accuracy of diagnosis can be confirmed by:
- Palpation;
- Analyzes;
- Ultrasound.
The main feature that allows you to distinguish fibroids from pregnancy is the phase of the cycle at which the study is carried out. As a rule, experts recommend conducting studies on the 5th or 7th day after the end of menstruation.
In any case, if there is any doubt about the correctness of the diagnosis, the specialist will prescribe additional tests in order to minimize the risk. After a complete examination, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Why does bronchitis occur with coronavirus? Could it be a sign of infection?
Bronchitis with coronavirus is not the main form of the disease; it is not considered as a typical sign of infection. A new infectious agent preferentially invades and multiplies in places with a high concentration of special receptors. They are located in the nasal passages and the lower part of the bronchi, the thinnest branches (bronchioles), so coronavirus does not cause bronchitis, but bronchiolitis.
Since the symptoms are very similar, the patient is often given an initial diagnosis of bronchial inflammation, and then, after a tomography and examination of swabs from the nose and throat, a coronavirus infection is found.
If the patient actually suffers from acute bronchitis caused by other viruses (parainfluenza, adenovirus) or bacteria, then it cannot turn into coronavirus. Rarely, it also happens that a new infectious agent joins existing active inflammation (co-infection). Therefore, at first there was the wrong tactic when patients were tested for influenza, but if the result was positive for coronavirus, they were not examined.
Symptoms, how it progresses
Bronchiolitis with coronavirus occurs with symptoms of a dry cough and fever, but the most typical sign of damage to the smallest bronchioles is shortness of breath. At first it occurs during physical activity, and then it increases and appears with any activity. Usually, frequent and shallow breathing is accompanied by attacks of hacking cough, and the sputum does not come out at all or a meager amount of transparent sputum is released.
In patients infected with coronavirus, the disease can also occur in the form of bronchitis without fever, or an increase to 37.1-37.5 will persist for no more than 1-3 days. In such patients, severe weakness, increased breathing and heart rate during physical activity come to the fore. Shortness of breath and a feeling of constriction in the chest further progresses. With the development of pneumonia, these symptoms are accompanied by bluish skin, and possible suffocation without connecting the patient to a ventilator.
Diagnostics
In order to make a diagnosis and distinguish viral bronchitis from coronavirus infection, an examination is carried out:
- computed tomography, if not possible, radiography;
- swabs from the throat and nose for coronavirus RNA (PCR diagnostics);
- sputum analysis (if available);
- complete blood count, biochemistry (including ferritin, C-reactive protein), coagulogram;
- pulse oximetry (testing of oxygen levels in the blood);
- determination of bronchial function (spirometry).
Treatment
With the development of bronchitis and bronchiolitis due to coronavirus, bed rest is indicated; if there is no pneumonia, then treatment is carried out at home. Patients are recommended:
- plenty of warm drinks (1.5-2 times more than usual);
- a gentle diet, mainly dairy-vegetable;
- mandatory smoking cessation;
- maintain high humidity in the room, because dry air makes the cough worse;
- interferon instillation or spraying (Genferon, Grippferon);
- for removing phlegm - Ambroxol, soda inhalations, and for a hacking cough, Stoptussin;
- for bronchospasm, inhalation with Salbutamol, Berodual.
If there is shortness of breath, compression in the chest, and the level of oxygen in the blood drops, then hospitalization in a hospital where drugs with antiviral and immunomodulatory effects are used (for example, Kaletra, Plaquenil). If there are signs of a bacterial infection, antibiotics are added to therapy. If respiratory failure develops, oxygen is supplied through a mask or a tube is inserted into the trachea and the patient is transferred to artificial ventilation.
Does fibroids affect hCG levels?
Most women, when symptoms of this disease occur, wonder whether it can be confused with pregnancy. Determining pregnancy using a home test is one of the most accurate. The test determines pregnancy by the presence of a special hormone, hCG, in the blood, and fibroids are a benign neoplasm that is caused by hormonal imbalance. The hormone estrogen influences the formation of compactions, and progesterone, on the contrary, reduces their development. That is why fibroids do not affect the production of hCG and thus false positive test results are excluded.
The normal hCG level in the blood serum of a non-pregnant woman is less than 10 IU/ml, except in cases where the woman has tumor processes (fibroids).
Signs of early pregnancy
The symptoms of premenstrual syndrome are very similar to early pregnancy. A pregnant woman’s body begins to actively produce progesterone, a hormone necessary to prepare the body for bearing a baby.
The main signs of pregnancy in the early stages include:
- increased breast sensitivity;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased fatigue;
- fatigue;
- mood swings.
In general, pre-term pregnancy symptoms are a lot like PMS, so it can be quite difficult to distinguish one from the other.
Impact of the disease on the period after childbirth
This disease carries a certain risk of various complications during the postpartum period. Due to its influence, a woman may experience various early and late complications. However, there is a chance to get pregnant and give birth without complications even with such an illness; it all depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
Early complications include:
- Bleeding;
- Compaction of the placenta.
The later ones include:
- Stretching of the uterus;
- Infectious diseases.
Symptoms of complications are very common and include:
- Painful sensations;
- Bloody discharge.
Can uterine fibroids or pregnancy be confused?
Small myomatous nodes, located in the tissues of the uterus and growing outward, in most cases develop without clearly recognizable symptoms. It is with this course of fibroids that there is a possibility of confusion. The question arises - pregnancy or uterine fibroids, how to distinguish these two conditions. The first weeks after conception, as a rule, pass without any special symptoms. The notorious toxicosis does not happen to everyone and begins later, when the fertilized egg penetrates the endometrium of the uterus. The only signs of early pregnancy may be general weakness, slight dizziness, and drowsiness. With fibroids of significant size growing inside the cavity, a woman may experience the following symptoms:
- uncharacteristic bleeding during the intermenstrual period;
- heavy, prolonged menstruation;
- uterine bleeding of varying intensity;
- pronounced signs of anemia due to blood loss;
- impaired urination and constipation due to pressure from nodes on neighboring organs;
- nagging aching pain in the lower abdomen or side (in the area where the node is located);
- enlargement of the abdomen due to the growth of the myomatous node.
These signs of the disease can appear in various combinations, so the question of whether uterine fibroids can be confused with pregnancy is quite justified. After all, aching pain and abdominal enlargement are characteristic of both conditions. How to distinguish fibroids from pregnancy is not a difficult question for a specialist. The first difference is the uneven surface of the uterus with fibroids. During pregnancy, the uterus increases evenly throughout its entire volume; with fibroids, this can only happen if the nodes are located internally or interstitially. External localization of the nodes results in an enlargement of the uterus with characteristic local protrusions on the surface. Therefore, to the question whether tuberous fibroids can be confused with pregnancy, the answer is obvious - no. Even during a gynecological examination, a gynecologist will suspect the presence of neoplasms due to uneven enlargement of the uterus. Hidden and internal nodes are more difficult to identify; special research methods are used for this.
Diagnosis of fibroids: preparation for the procedure, main signs
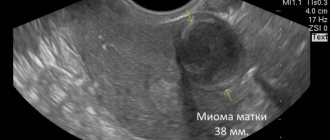
For uterine pathologies, ultrasound is used quite often as one of the most effective and accurate diagnostic methods. It is actually very simple to distinguish the development of the disease from the process of conception and fetal development. This does not even require any additional procedures - an ordinary study is enough.
Basically, when fibroids are suspected, transabdominal and transvaginal diagnostics are used. These methods make it possible to increase the accuracy of determining the size and nature of the tumor, predict the dynamics of its development and the possibility of developing into a malignant formation. In addition, it is very important to monitor the cycle of treatment measures and regulate them in a timely manner.
When preparing for an ultrasound scan of fibroids, the patient is advised to avoid stressful situations for some time and follow a certain diet aimed at removing excess salts and fluids from the body. Preparation for ultrasound of the uterus is an independent medical procedure, the implementation of the algorithm of which guarantees the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosis.
In addition, it is of great importance to eliminate factors of possible biological damage.
In order to determine when to do an ultrasound for fibroids, you need a qualified specialist. Under no circumstances should you resort to a variety of artisanal methods of diagnosis and treatment.
It is worth noting the following echo signs of uterine fibroids:
- enlarged uterus;
- uneven contours of the uterine cavity;
- displaced median M-echo;
- ovoid, round shape of tissue formations, which are characterized by increased echogenicity;
- pathogenic formations penetrating deep into the myometrium or into the uterine cavity.
However, the given signs are only the most general, and may change in a specific case of pathology.
In order to diagnose the exact form and stage of development of the disease, it is necessary to do a series of complex studies that require special medical equipment and professional training.
Diagnosis and treatment methods for fibroids
During a gynecological examination, the doctor collects an anamnesis, which includes the patient’s complaints, classification of symptoms and the examination itself. Myoma can be immediately identified in the presence of characteristic and accompanying symptoms, as well as in cases where the formation has reached a significant size. A characteristic sign of fibroids is high density of the uterus; during pregnancy, such a sign occurs only with increased tone, hypertonicity. Multiple myomatous nodes on the surface of the uterus also give a clearly defined picture of the disease. In all other cases, instrumental diagnostic methods are required.
Often it is enough to conduct an ultrasound examination of the uterus and pelvic organs. Only a layman can doubt and wonder whether fibroids or pregnancy can be distinguished on an ultrasound. An experienced, qualified specialist will immediately determine the difference. The fertilized egg or embryo is always localized in the endometrial tissues and has a clear attachment to the mucous membrane. Fibroids have a completely different appearance, shape and response to the echo signal.
If a woman is concerned about whether fibroids could be pregnancy, she just needs to go to a specialized clinic and undergo an ultrasound. If myomatous formations of any type and location are detected, treatment must be started immediately. Fibroids are a progressive disease that rarely stops at one or the same size. The growth of myomatous nodes is fraught with serious complications and may lead to the need for surgical intervention. If detected early, fibroids can be stabilized with hormonal therapy and undergo degeneration using the uterine artery embolization (UAE) method.
How can you determine the cause of the problem for sure?
In order to determine what exactly is the cause of the malaise: PMS or pregnancy, you need to wait for menstruation. If it does not occur within the expected period, then, most likely, conception has occurred. You can verify this using an express pregnancy test.
If you don't have the patience to wait for your expected menstruation date, you can do a blood test to determine your human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level.
It is the increase in hCG levels after a delay that pregnancy tests respond to, but the level of the hormone in the blood rises much faster. Already on the 10th day after fertilization, the analysis will show with almost 100 percent accuracy whether you are pregnant or not.