Modern medicine is developing rapidly, so those pathologies that were previously considered a hopeless diagnosis are now successfully treatable. Especially if the person sought medical help in time.
Today we will talk about neoplasms, one of which is a lump between the vagina and anus. As soon as you discover this tumor in yourself and do not completely understand the reasons for its occurrence, try to visit a specialist as soon as possible, for starters, a gynecologist.
It happens that a woman is embarrassed to go to the doctor with such a problem, but her health may be at risk, so in this case it is worth overcoming her shame, because for a professional, a lump in the perineum is a common disease, like any other.
The sooner the examination is started, the easier it will be to cope with the disease. First, you need to undergo an examination by a gynecologist so that he can exclude or confirm a genital tract infection. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then the gynecologist will prescribe treatment for you. Otherwise, the doctor will refer you to a dermatologist, oncologist, or surgeon.
A lump on the perineum is often a neoplasm of an inflammatory nature, which can be treated with medication. Sometimes it needs to be removed surgically. The choice of option depends on the results of the examination, during which the final diagnosis will be clear.
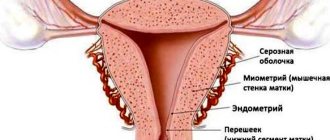
Lump in the perineum
Modern medicine is developing rapidly, so those pathologies that were previously considered a hopeless diagnosis are now successfully treatable.
Especially if the person sought medical help in time. Today we will talk about neoplasms, one of which is a lump between the vagina and anus. As soon as you discover this tumor in yourself and do not completely understand the reasons for its occurrence, try to visit a specialist as soon as possible, for starters, a gynecologist.
It happens that a woman is embarrassed to go to the doctor with such a problem, but her health may be at risk, so in this case it is worth overcoming her shame, because for a professional, a lump in the perineum is a common disease, like any other.
The sooner the examination is started, the easier it will be to cope with the disease. First, you need to undergo an examination by a gynecologist so that he can exclude or confirm a genital tract infection. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then the gynecologist will prescribe treatment for you. Otherwise, the doctor will refer you to a dermatologist, oncologist, or surgeon.
A lump on the perineum is often a neoplasm of an inflammatory nature, which can be treated with medication. Sometimes it needs to be removed surgically. The choice of option depends on the results of the examination, during which the final diagnosis will be clear.
Lymph node If you find a lump in the groin area, then your lymph node is inflamed. There is no danger to life in this situation. Most likely, an infection has entered the body, which caused such a reaction - there is a fight against the enemy. In this case, you should still visit a doctor so that he can identify the cause of the disease.
Abscess. A lump in the perineum or groin can be a consequence of an inflammatory process affecting a woman’s genital organs, both internal and external. A visit to a specialist cannot be postponed, since this pathology is serious.
Hernia. If a woman has to do heavy physical labor or is actively involved in sports, then a tumor in the perineum is a hernia. Its distinctive feature is that it is a soft protrusion located on different sides of the anus.
In addition, such hernias appear due to the fact that during defecation the pressure inside the abdominal cavity increases. Despite the fact that the protrusion can be straightened on your own, you should still visit a gynecologist if in doubt, and then a surgeon if necessary.
Oncology. A lump between the vagina and anus, unfortunately, can mean the development of a cancerous tumor. The doctor will determine this after performing the necessary tests. Remember, the earlier you find a cancerous tumor, the higher the chances of curing this serious disease.
Cyst. Usually teratomas (perineal cysts) are congenital, but due to their small size, a woman is not aware of them. Over time, the tumor grows and fistulas may appear. The only way to get rid of a cyst is through surgery.
Atheroma. A growth between the vagina and anus that occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous glands is called atheroma. This tumor is soft and round in shape. It appears due to metabolic disorders in a woman’s body. It cannot dissolve, so it is advisable to remove it due to the risk of suppuration.
The radio wave method is most often used. The procedure lasts no more than 20 minutes on an outpatient basis. the likelihood of recurrence is negligible if the entire capsule is removed. After the operation, the former location of the atheroma is not noticeable at all - no scars remain.
Once the doctor understands the diagnosis, treatment can begin. Simple pathologies can be cured quite simply and quickly if the woman immediately goes to a medical facility.
A severe lump between the vagina and anus requires longer-term monitoring and treatment. It is important to choose the right medications so that they act as quickly as possible and side effects are reduced to zero.
How to treat an anal boil
Have you been fighting PAPILLOMAS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of papillomas by taking it every day.
The skin has a multi-level structure, and its layers perform different functions. The epidermis is designed to protect against mechanical damage, disease and infection, as well as for thermoregulation. The cause of furunculosis is often associated with various contaminants. A boil is an area of skin that becomes inflamed due to infection. Boils can occur anywhere, including on the genitals and near the anus.
The rectal opening is constantly exposed to fecal matter, which may contain traces of infection. Lack of proper hygiene provokes the appearance of boils.
Our readers successfully use Papilite to treat papillomas. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
One home remedy for boils is to take a hot bath, but do not burn yourself. Under the influence of heat, the skin swells and opens faster. Hot compresses work similarly. However, a bath at the same time helps protect against infection. If the boil does not disappear, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment
In case of an infectious disease, it is necessary to clearly identify the causative agent of inflammation. To do this, the woman undergoes a thorough examination: examination on a chair, smears and tests. After receiving the results, antibacterial therapy is prescribed, aimed at combating specific microbes.
A lump in the perineum can cause discomfort in women. In this case, the doctor will suggest ways to eliminate discomfort using special anti-inflammatory drugs. As a result, the tumor will become noticeably smaller. Then you should take care of your immune system to support the body as a whole. Antibiotics are required to avoid complications.
To treat a malignant tumor, the patient is referred to an oncologist. After a detailed study of the situation, the specialist will suggest removing the growth if there is no risk of spreading malignant cells to neighboring tissues. Then a course of chemotherapy is prescribed to completely rid the woman of her illness. A cancer tumor is the most complex pathology and has a lot of nuances in its treatment, so you need to trust your attending physician, discussing the treatment process with him.
If you find a swelling between the vagina and anus, remain calm and believe in a successful outcome of the disease. To do this, you must definitely visit a doctor, undergo all the tests recommended by him and adhere to his prescriptions. If the diagnosis was established correctly, then after a short time you will completely forget about the illness and will continue to live in peace.
source
What can cause pain in the perineum in women?
The perineum is the area between the anus and the vagina. Pain in this place, like in any other place, indicates that something is wrong in the body. This phenomenon does not always threaten health problems, however, there is reason to be wary.
Natural causes of discomfort in the perineum
Pain in the perineum in women is rarely the result of normal physiological processes. They should not cause concern unless they are unbearable and pass quickly.
- Injuries. A bruised or sprained muscle causes serious physical discomfort. Girls often suffer from them after playing sports without proper warm-up. Damage can also occur during a gynecological examination or during active sexual intercourse.
- Pregnancy. The larger the fetus becomes, the more it puts pressure on surrounding tissues. This sometimes causes unbearable pain, but doctors cannot help in such a situation. All that remains is to wait for the child to change his body position. In the later stages, pain in the perineum indicates an imminent birth, and in the early stages it can be a sign of a threatened miscarriage.
- Period. During menstruation, the uterus gets rid of excess blood, endometrial particles and unfertilized eggs. These days, her cervix opens up, which causes nagging pain in the perineum in women. In addition, discomfort is felt in the lower abdomen and lower back. Monthly unbearable pain along with heavy bleeding indicate pathologies of the reproductive organs.
Pain in the perineum as a sign of pathology
Most often, discomfort in the groin area is a sign that all is not well with your health. Usually the matter is not limited to pain; there are other unpleasant symptoms.
- Bartholinitis. Inflammation of the gland, which is located at the base of the labia. The affected area noticeably thickens and increases in size, it can even completely block the entrance to the vagina. Of course, such a neoplasm does not go unnoticed. It interferes with walking and rubs against underwear. The most accurate description of the symptoms is that a dense ball can be felt on the labia.
- Inguinal athlete's foot. A fungal disease that affects the skin in large folds. It occupies large areas, causing constant discomfort. Itchy and flaky spots appear on the epidermis, which merge with each other, forming rings with healthy skin inside and a red border outside.
- Ectopic pregnancy. With this pathology, the fertilized egg is attached not to the wall of the uterus, but inside the appendage. The growth of the fertilized egg provokes tissue stretching and severe pain. Brown discharge is observed. If medical attention is not provided in a timely manner, the pipe ruptures, accompanied by significant bleeding.
- Diseases of the urinary system. The urethra is located above the perineum, and pathological processes in it are reflected by pain in this area. Unpleasant sensations can also be a sign of cystitis or pyelonephritis. Women with such problems experience pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, a frequent urge to urinate, and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. There may be a discharge streaked with blood.
- Intestinal pathologies. Some disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract are associated with constipation. Fullness of the intestines causes a feeling of constriction, and difficult passage of hard feces provokes pain in the anus and perineum.
- Diseases of the reproductive system. Discomfort in the groin area in women often occurs as a result of pathological processes in the uterus and fallopian tubes. The growth of the endometrium, neoplasms on the walls and cervix lead to heavy and irregular menstrual bleeding against the background of severe pain.
- Pinched nerve. Pain in the perineum when sitting in women may indicate a pinched sciatic nerve. In this case, the groin area becomes numb, and there is a sensation of a foreign body in the rectum and vagina. Sitting and lying down provide relief.
- Varicose veins Veins can also expand in the pelvic area. This problem most often affects pregnant women and overweight women. The pathology leads to disruption of the blood supply to the reproductive organs, which is manifested by the following symptoms: acute PMS; perineal sensitivity; cycle disruption; copious discharge; urinary disturbance; feeling of heaviness in the pelvic area.
If women have pain in the perineum, do not put off visiting a gynecologist. Unpleasant sensations in this place are often a signal of the development of a pathological process. The source of the problem can be in any organ of the pelvic floor, so it is important to pay attention to accompanying symptoms for a correct diagnosis.
Loading…
Source: https://uginekologa.com/boli-v-promezhnosti-u-zhenshhin.html
Swelling. between the anus and vagina
Consultation
Good morning, 2 days ago a swelling appeared between the anus and the vagina, but it was clearly growing at first, the swelling was only on the left and now on the right and has increased, closer to the anus there is some kind of white leg on palpation, painful sensations are felt at first I thought hemorrhoids began to smear with heparin ointment, now I see that it’s not it helps, I need to go to the gynecologist and apparently urgently, there is no painful sensation during defecation and urination, but it’s just difficult to walk and I can’t sleep, the best position is sitting, there are some painful sensations until you start to move, is there a possibility that I have a cold? on cold days I ran in autumn boots and was frozen, thanks in advance for your answer
Guaranteed response within an hour
Doctors' answers
It can be either a boil or a fistula. To accurately establish a diagnosis, you need to go to a proctologist for an examination, but you also need to rule out other intestinal pathologies. The examination should include: a digital examination by a proctologist, if the doctor deems it necessary to undergo further examination - sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, etc. Treatment depends entirely on the diagnosis and stage of advanced disease. If drug treatment does not help you, then doctors may suggest surgical treatment. Do not self-medicate. If only the symptoms are removed and not treated comprehensively, the disease may be complicated by strangulation or the addition of a secondary infection, and this may result in surgical intervention.
Katerina Dyakonova
Thank you very much, yesterday I was at the gynecologist, she looked and said I need to see a surgeon and prescribed Vishnevsky and started applying antibiotics to Vishnevsky during the day, changed the bandage 3 times in the evening, the abscess opened as it became easier, the pain almost went away on Monday I’ll go to the surgeon, tell me, after the abscess breaks, can I continue to use it Vishnevsky ointment? When I wash myself only with warm water, I’m afraid I’ll use soap, maybe I’ll make things worse... it’s just that even after washing, the ointment still remains a little, that is, it’s not completely washed off with water. Can I wash with soap or leave it as is with just water? thank you in advance)
It is best to treat the wound not with ointment, but with antiseptics in the form of solutions - hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine, octenisept in a dilution of 1: 6, and so on. Before treating the wound, hygiene is performed with water, but you can use soap, but be sure to wash off the soap suds. After the wound has dried a little, you can use an antibiotic ointment (tetracycline, gentamicin, etc.). Further treatment tactics will depend entirely on the diagnosis made by the surgeon.
source
INTERNAL LUMBE BETWEEN ANUS AND VAGINA
Branch No. 2 of State Budgetary Healthcare Institution “GP No. 12 DZM” (GP No. 77) of the Russian Federation. Moscow, Tsandera str., 9 building 1 skype: shapych Sign up for a consultation +7 (903) 169-0222 https://www.shaposhnikov.net
Medical
Moscow, Bolshaya Molchanovka, building 32 building 1
e-mail; tel.: 8-910-434-17-86;
Sign up for a consultation: 8-926-294-50-03; (495)223-22-22.
Make an appointment, st. Myasnitskaya, 19
Consultations in personal messages and by telephone NOT provided.
About treatment in absentia In accordance with Russian legislation (Article 70 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 323-FZ “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation”), only the attending physician has the right to prescribe treatment .
“Making a diagnosis without an in-person examination of the patient is not only illegal, but also carries a direct threat of harm to the life and health of citizens. Remote monitoring of the patient’s health status is prescribed by the attending physician after an in-person appointment.” Roszdravnadzor.
source
Causes of vulvovaginitis
Bacterial vulvovaginitis
Irritative vulvovaginitis
The cause of this form of vulvovaginitis is mechanical irritation of the woman’s external genitalia and vagina.
The most common factors that lead to irritation of the vulva and vagina are:
- frequent masturbation;
- foreign bodies of the vagina;
- too frequent sexual intercourse;
- wearing ill-fitting, uncomfortable underwear;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
Vulvovaginitis due to helminthiasis
With helminthiases (enterobiasis - pinworm parasitism, ascariasis), worms often leave the intestine and crawl onto the skin in order to lay eggs. They are able to penetrate the vagina and lead to the development of an inflammatory process in it.
Vulvovaginitis with decreased immunity
Vulvovaginitis due to improper use of antibiotics
Allergic vulvovaginitis
Specific vulvovaginitis
Vulvovaginitis in diabetes mellitus (diabetic vulvovaginitis)
If diabetes mellitus remains for a long time without effective treatment, then over time it leads to complications in the form of damage to small vessels. If blood flow in the vessels of the female genital organs is disrupted, vulvovaginitis develops. In the future, an infection joins the blood flow disturbances.
Diabetic vulvovaginitis is very difficult to treat.
The division of vulvovaginitis into different types depending on the cause of the disease is quite arbitrary. During examination, an association consisting of different types of microorganisms is most often detected in the vagina. And even if the disease initially has non-infectious causes, over time, as a rule, an infection still develops.
Factors that contribute to the development of vulvovaginitis
There are a number of factors that may not themselves be the cause of vulvovaginitis, but facilitate its occurrence:
- non-compliance with the rules of hygiene of the female external genitalia: infrequent washing, infrequent change of linen, use of dirty toilets, promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- diaper rash, which occurs in the folds of the external genitalia due to obesity;
- abrasions, scratching, injuries, use of personal hygiene products that irritate the skin and mucous membrane of a woman’s external genitalia;
- skin diseases such as eczema and psoriasis;
- prolapse and prolapse of the uterus and vagina;
- diseases of the rectum: fissures, hemorrhoids, anal fissures;
- boils, carbuncles, phlegmons, abscesses and other foci of purulent inflammation in the perineal area;
- pregnancy;
- the use of contraceptives made on the basis of hormones, especially those with a high content of estrogens;
- the use of cytostatics - drugs that are used to treat malignant tumors;
- radiation therapy for cancer;
- taking medications made on the basis of adrenal hormones (glucocorticoids);
- ovarian dysfunction;
- any decrease in immunity that is associated with severe injuries, surgical interventions, infections, tumors, etc.
If at least one of these factors is present in a woman’s life, then the likelihood of vulvovaginitis increases.
Removal of genital (pointed) warts in women and men
- Causes of genital warts
- Signs (symptoms) of genital warts
- Locations of genital warts
- Methods for diagnosing genital warts
- Methods for removing genital warts
- Preparations for removing warts on intimate places
- Prevention
The appearance of papillomas and warts on the skin is associated with infection with HPV (human papillomavirus). The location of the formations depends on where the virus entered the body. If HPV enters the body through the genitals, various types of formations (genital warts) may appear in these areas.
The disease may not manifest itself in any way for a long period of time, but the negative effects on the body, reducing its defenses, lead to the fact that genital formations begin to actively appear and grow. In this case, removal of genital warts is a more complex and lengthy process.
Causes of genital warts
The main source of HPV infection is sexual, but there are cases where infection occurred through contact through household contact.
Our readers successfully use Papilite to treat papillomas. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
There are a number of negative factors due to which the virus is activated, resulting in warts appearing on the skin:
Signs (symptoms) of genital warts
The formations may not cause any concern, but sometimes the patient may complain of discomfort in the affected area. This manifests itself especially intensely during sexual intercourse, with mechanical impact on the neoplasm.
Genital warts are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Itching, burning in places of their formation;
- Inflammation, redness of the skin in the immediate vicinity of the tumor;
- Unpleasant sensations, pain;
- Bleeding when exposed to papilloma;
- Discharge from the genitals with an unpleasant odor.
At the initial stage of development, genital warts are small in size, but if the disease is not treated, over time the formations increase in size and connect with each other. There is also active formation and growth of new warts.
Locations of genital warts
In women, genital warts appear:
- Most often in the area of the vaginal opening;
- In the inner part of the vagina;
- In the area between the anus and vagina;
- In the anal area;
- On the surface of the cervix;
- In the urethra (rarely).
Photo: genital warts in women and men
Locations of genital warts in men:
- In the area of the foreskin of the penis;
- Near the anus;
- On the head of the penis;
- On the skin of the scrotum.
Methods for diagnosing genital warts
Diagnosis of genital warts usually involves visual inspection of the affected area.
In this case, methods such as cytological examination of the affected area and smear are used.
Methods for removing genital warts
Today, the only way to completely remove it is surgically. To achieve a more successful result, the patient is prescribed medication. How are warts and genital warts removed?
If there are few warts and they are small in size, they are removed using a laser scalpel. This method is also used when the tumor is located in a hard-to-reach place (other removal methods cannot be used in this situation).
Sometimes genital warts are removed using a carbon dioxide laser. This method is not so effective; it is used quite rarely (in extreme cases when the use of other methods is impossible). During the removal process, a patch of dead tissue forms near it, on which warts can form again. This method is combined with the use of immunomodulatory agents.
Preparations for removing warts on intimate places
There are 4 groups of medications used to treat genital warts on intimate places:
- Immunomodulatory agents (Anaferon, Arbidol) activate the body's defenses, help fight infections, as a result of which the appearance of new genital warts stops and the growth of those that already exist stops.
- Antiviral drugs (Panavir, Viferon, oxolinic ointment) are able to penetrate into the deep layers of the skin, destroying the root of the tumor, preventing its reappearance in this area of the skin.
- Vitamin complexes help not only restore immunity, but also improve the condition of the skin, promoting its speedy healing.
- External use products containing components that have a detrimental effect on neoplasm tissue, promoting its death.
Symptoms of vulvovaginitis
General symptoms of vulvovaginitis
Symptoms of acute vulvovaginitis:
- itching and burning in the genital area, which intensifies during urination;
- pain in the external genital area;
- redness, swelling of the vulva;
- pain in the lower abdomen, which can sometimes radiate to the sacrum;
- vaginal discharge, most often purulent;
- painful intercourse;
- difficulty urinating, which is sometimes accompanied by difficulty defecating;
- general weakness;
- if vulvovaginitis is caused by E. coli, then liquid discharge from the vagina is yellow-green in color and has an unpleasant odor.
Symptoms of chronic vulvovaginitis:
Symptoms of specific types of vulvovaginitis
| Form of the disease | Symptoms |
|
|
|
|
| Against the background of redness, swelling, itching and burning, pain, white curdled discharge from the vagina occurs. Bubbles appear in the vulva area, which burst, leaving behind erosions. In the future, crusts remain at the site of erosion. |
|
|
|
|
| A characteristic manifestation of human papillomavirus vulvovaginitis is genital warts, which appear on the skin and mucous membranes in the area of the external genitalia and anus. Gradually they grow, merge with each other, and sometimes reach such large sizes that they resemble tumors. At the same time, sexual intercourse is greatly difficult. |
| Vulvar tuberculosis is very rare. Very painful ulcers appear, which are located on the labia minora and clitoris. |
| Vulvovaginitis is accompanied by severe itching, burning, and redness. The discharge is usually liquid and transparent. Symptoms occur during contact with the allergen. Later, infection and corresponding symptoms appear. |
| Caused by tissue malnutrition. It is characterized by the appearance of erosions and ulcers on the affected areas of the skin and mucous membrane. Later, an infection occurs. |
Causes of neoplasms
The concept of “lump in the vagina” includes any tumor-like formation located on the inner surface of the vagina, labia, or perineum. There are two groups of reasons leading to the development of the disorder.
Physiological reasons
In almost 70% of cases, the appearance of any irregularities in the genital area is associated with natural processes in the body and does not require mandatory medical or surgical treatment. Most often, the cervix is mistaken for a tumor when the vaginal walls prolapse in young mothers. The likelihood of developing the disorder increases with multiple pregnancies, repeated and traumatic births, and the birth of a large baby.
In most cases, the cervix returns to its natural position on its own within 6-8 weeks.
To prevent and eliminate the consequences of prolapse of the vaginal walls, Kegel gymnastics is used, which includes exercises for squeezing and relaxing the intimate muscles at different speeds and intensity.
Other factors that lead to cervical displacement include:
- Connective tissue diseases;
- Obesity;
- Endocrine disorders;
- Chronic severe cough;
- Excessive or insufficient physical activity.
Diagnosis of vulvovaginitis
Laboratory methods for diagnosing vulvovaginitis
| Methodology | Essence and indications | What can it reveal? |
| General blood analysis. | It is not directly related to vulvovaginitis, but should be prescribed to all patients with suspected inflammatory diseases. Allows you to exclude pathological processes of other origin. | With vulvovaginitis, a general blood test does not reveal any pathological changes. |
| General urine analysis. | Prescribed to all women with suspected vulvovaginitis. General clinical routine examination. Allows you to identify the inflammatory process. | With vulvovaginitis, a general urine test reveals an increased content of leukocytes. |
| Bacterioscopy of vaginal discharge. | It is performed on all women with suspected vulvovaginitis. Allows you to confirm or refute the bacterial nature of vulvovaginitis. They take smears or vaginal discharge, stain them in a special way and examine them under a microscope. | During the inflammatory process, leukocytes are visible. The bacteria and viruses that caused the disease become visible. It is possible to identify helminths in vulvovaginitis caused by parasitic worms. |
| Bacteriological research. | The vaginal discharge is taken and placed on a special nutrient medium. | Bacteriological research makes it possible to identify the pathogen that led to the development of the disease. In addition, its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs can be determined. |
| Analysis for helminth eggs. | The analysis makes it possible to identify in the material the eggs of parasitic worms that caused the disease. Often, scrapings from the skin in the perineal area are taken for examination. | The material obtained from the patient is examined under a microscope. In this case, helminth eggs are visible. |
| PCR (polymerase chain reaction). | Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a laboratory test that makes it possible to isolate the DNA of the pathogen and multiply it into a large number of copies. As a result, researchers obtain a large amount of genetic material and can accurately identify the pathogen. | The study makes it possible to accurately determine the type of pathogen that led to the development of vulvovaginitis. |
| Testing for STIs (sexually transmitted infections). | A study of the woman's vaginal discharge and blood is carried out. Various laboratory tests are used that are aimed at diagnosing different types of sexually transmitted infections. The study is conducted in adult women who are sexually active. | This group of tests allows you to confirm or exclude sexually transmitted diseases. |
Instrumental research methods for vulvovaginitis
| Research method | Goals and indications | What helps to identify? |
| Vaginoscopy. | Internal examination of the vagina using special mirrors. It is mandatory to be carried out by a gynecologist if the patient is suspected of vulvovaginitis. | The condition of the vaginal mucosa is assessed: redness, swelling, erosion, and hemorrhage are detected. If there is a foreign body in the vagina, it can be detected and removed. |
| Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound). | An ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs is performed: the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, bladder, etc. Usually, during diagnosis, a transvaginal examination is also performed using a special sensor, which is inserted through the vagina. | Ultrasound allows one to distinguish vulvovaginitis from inflammatory processes in the uterus and its appendages (adnexitis). Using this study, it is possible to identify the tumor process at an early stage. |
Cervical canal papilloma: how to diagnose and treat the disease
Such a neoplasm as cervical canal papilloma occurs quite often in gynecology. The cervical canal is the area that is located between the vagina and the cervix. Both single and multiple polyps can form in it.
What is cervical canal papilloma
The neoplasm is pinkish or red in color. This is due to the fact that the growth is in the path of blood flow. If it is violated, the wart may change color to brownish-violet.
There are several types of such polyps:
- Glandular. It is formed from the glandular tissue of the endometrium, usually it does not exceed one centimeter.
- Fibrous. This type of growth is formed from fibrous tissue. The fibrous tissue is quite dense, so the wart is easy to notice during ultrasound examination.
- Mixed. This type of neoplasm is formed simultaneously from glandular and fibrous tissue.
Causes of cervical canal papilloma
In most cases, it is not possible to establish the exact cause of the development of pathology. There are many factors and comorbidities that go into diagnosing the disease. Most doctors are inclined to believe that the cause of the pathology is hormonal.
Most often, this disease appears in women over 40 years of age. As menopause approaches, a woman's body begins to experience serious hormonal changes that can negatively affect a woman's sexual health.
There are the following risk factors leading to the development of the disease:
In some cases, a neoplasm appears without apparent reasons or prerequisites.
Symptoms of cervical canal papilloma
Symptoms are not always pronounced with a disease such as cervical canal papilloma. You can use a photo to familiarize yourself with the disease. In most women, signs of polyps, if present, can be confused with symptoms of other diseases.
There are the following signs of the presence of growths:
- Regular pains, they do not torment a woman constantly, but come in attacks. Pain occurs only if the size of the wart becomes about two centimeters.
- Blood from the vagina after sexual intercourse. This happens because during sexual relations the polyp can become seriously damaged and begin to bleed.
- Menstrual irregularities. When a growth appears, a disruption of the menstrual cycle occurs. Most often this is a hormonal problem, which can be caused by the same reason as cervical papilloma.
- Vaginal discharge. With such a neoplasm, they may have the character of mucus or leucorrhoea. Therefore, this disease may be confused with thrush.
Treatment of vulvovaginitis
General recommendations given by the doctor for vulvovaginitis:
Medicines used for vulvovaginitis
| A drug | Mechanism of action | Indications and contraindications for use |
| Amoxiclav | A drug that includes an antibiotic (amoxicillin) and a substance that enhances its effect (clavulanic acid). It has an effect on many types of microorganisms. | The drug is available in the form of tablets for oral administration. Use of amoxiclav in children:
Use of amoxiclav in adults:
Treatment is continued for 5 to 10 days. Source : M. D. Mashkovsky “Medicines. A manual for doctors." 15th edition, revised and expanded, Moscow, “New Wave”, 2005. |
| Cefazolin | A broad-spectrum antibiotic that is effective against most types of pathogenic microorganisms. Available in powder form, intended for dissolution in liquid and injection. | The required amount of Cefazolin powder is dissolved in water for injection or saline. Use in children:
Use in adults:
Treatment is continued for 5 to 10 days. Source : M. D. Mashkovsky “Medicines. A manual for doctors." 15th edition, revised and expanded, Moscow, “New Wave”, 2005. |
| Ceftriaxone | Broad-spectrum antibiotic from the cephalosporin group. It has an effect on many types of microorganisms. It is used in powder form, which is diluted in saline or water for injection. | Ceftriaxone injections are given to adults and children over 12 years of age. 1–2 g of the drug is administered once a day. Treatment is continued for 5 to 10 days. Source : M. D. Mashkovsky “Medicines. A manual for doctors." 15th edition, revised and expanded, Moscow, “New Wave”, 2005. |
| In order for antibiotic therapy to bring maximum effect, antibiotics are prescribed only after the sensitivity of the pathogens to the drugs has been established (determined during a bacteriological study). Combinations of antibacterial agents are often prescribed. For specific infectious vulvovaginitis, specific medications are prescribed (see below). | ||
| Iodoxide | Suppositories containing iodine and povidone are two antiseptics that destroy pathogens. Iodoxide is capable of destroying most types of bacteria, fungi, and viruses. | Treatment of acute vulvovaginitis:
Treatment of subacute and chronic vulvovaginitis:
Source : Vidal Directory, 2008 |
| Betadine | A medicinal product made on the basis of the active substance Povidone-Iodide. An antiseptic that destroys many bacteria, fungi, viruses, including the HIV virus. For vulvovaginitis it is used in the form of suppositories. | Treatment of acute vulvovaginitis:
Treatment of subacute and chronic vulvovaginitis:
Source : Vidal Directory, 2008 |
| Vaginal douching | Douching is washing the vagina with medicinal solutions. Solutions of various medicinal substances are used as washing liquids. | Typically, douching is carried out 1 - 2 times a day. The average duration of treatment is 1 week. Poses in which vaginal douching is performed:
A small amount of solution is drawn into the syringe, after which the tip is inserted into the vagina and pressed on the bulb. The douching solution must be preheated in a water bath. |
| Tantum Rose | Antiseptic prepared on the basis of benzydamine hydrochloride. Available in the form of a ready-made solution for douching or in the form of a powder for dissolution. | For douching, use approximately 140 ml of Tantum Rose solution. Injected into the vagina using a syringe 2 times a day, preheated in a water bath. Treatment is continued for at least 10 days. Source : Vidal Directory, 2008 |
| Baths with solutions of boric acid, soda, potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide. | Baths with antiseptics are effective against pathogens that cause the development of vulvitis. | They are used depending on the doctor's prescription. The usual bath duration is 10 minutes. |
| Anesthetic ointment (Anastezin-UVI, Anestezin-UVI, Anestezin, Benzocaine) | A medicinal product in which the active ingredient is the anesthetic benzocaine (a substance from the same group as novocaine). It is a symptomatic remedy that eliminates pain and itching. | Apply to the skin and mucous membrane at the site of localization of unpleasant sensations 1 – 2 times a day. Source : Vidal Directory, 2008 |
| Ointments and creams with glucocorticoids - hormones of the adrenal cortex. | Glucocorticoids are hormones that can suppress immune and allergic reactions. Therefore, for vulvovaginitis, local remedies with glucocorticoids are used for severe symptoms of inflammation: burning, itching, redness, swelling. | The group includes a large number of different drugs. The appointment is made by the attending physician. |
Herbal Blend:
| Mix all plants in equal proportions. Take 12 grams of the resulting mixture. Pour two cups of boiling water and then heat in a water bath for 15 minutes. Let it brew for 2 hours, strain. These plants have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. | Take the decoction orally three times a day after meals in an amount of 100 ml. |
Herbal Blend:
| Take two tablespoons of the mixture, place in a thermos and pour boiling water (400 ml). Leave overnight. | Take 100 ml of infusion 3 times a day. |
Herbal Blend:
| Mix all the plants, take 12 g of the resulting mixture. Pour two glasses of cold water and let it brew for 6 – 8 hours. Then heat, but do not bring to a boil. Cool. Strain. | The resulting infusion should be drunk at one time before meals, about 30 minutes. |
Herbal Blend:
| Take 5 g of each medicinal plant. Mix and chop thoroughly. Pour a glass of boiling water. Then heat in a water bath for 10 minutes. | Take the decoction warm in an amount of 100 ml 3 times a day before meals. |
| Chamomile flowers and Potentilla erecta herb. | Take 5 grams of both herbs. Pour boiling water over it. Leave overnight. Strain. | Use the resulting infusion for vaginal douching. Inject 150 ml of infusion into the vagina using a syringe 1 – 2 times a day. |
| Folk remedies for vulvovaginitis can be used only as prescribed by a doctor and only as an addition to the main method of treatment. | ||
There is a lump in the vagina
In most cases, a lump in the vagina or in the external genital area does not pose a threat to the life and health of a woman. Treatment depends on the causes of the pathology, the general clinical picture and the size of the tumor.
Lump in the vagina
The appearance of bulky lumps in the intimate area in women is a common gynecological problem.
Most often, such formations do not pose a serious danger and respond well to treatment.
Let's consider what diseases a lump in the vagina or on the external genitalia may be a sign of.
Causes of neoplasms
The concept of “lump in the vagina” includes any tumor-like formation located on the inner surface of the vagina, labia, or perineum. There are two groups of reasons leading to the development of the disorder.
Physiological reasons
In almost 70% of cases, the appearance of any irregularities in the genital area is associated with natural processes in the body and does not require mandatory medical or surgical treatment.
Most often, the cervix is mistaken for a tumor when the vaginal walls prolapse in young mothers.
The likelihood of developing the disorder increases with multiple pregnancies, repeated and traumatic births, and the birth of a large baby.
In most cases, the cervix returns to its natural position on its own within 6-8 weeks.
To prevent and eliminate the consequences of prolapse of the vaginal walls, Kegel gymnastics is used, which includes exercises for squeezing and relaxing the intimate muscles at different speeds and intensity.
Other factors that lead to cervical displacement include:
- Connective tissue diseases;
- Obesity;
- Endocrine disorders;
- Chronic severe cough;
- Excessive or insufficient physical activity.
In approximately 5-7% of cases, persistent weakness of the pelvic floor muscles can lead to regular prolapse and injury to the anterior or posterior vaginal vault, pathologies of the urinary system, and partial tissue necrosis due to circulatory disorders. Such patients are advised to undergo surgery to restore the shape and position of the internal genital organs.
Pathological causes
The main pathological causes leading to the formation of lumps in the intimate area include the following:
- Violation of hygiene rules;
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- Wearing tight or synthetic underwear;
- Microtraumas leading to disruption of the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, followed by infection and inflammation;
- The presence of foci of chronic infection in the body;
- Regular hypothermia;
- Avitaminosis;
- Chronic stress;
- Some systemic diseases.
Symptoms and treatment of pathologies
Let's consider the manifestations of the main diseases, accompanied by the formation of seals and tumors in the vagina. If you suspect any violation, you should immediately contact a gynecologist.
Bartholinitis
A common gynecological pathology is inflammation of the large (Bartholin's) gland located near the entrance to the vagina. Bartholinitis is caused by pathogenic microorganisms (staphylococci, gonococci, trichomonas, E. coli) that penetrate the gland through its excretory duct with infected discharge from the vagina or urethra.
The disease is accompanied by significant swelling and redness of the skin around one of the labia minora. On palpation, a painful round or oblong compaction is felt.
Complex treatment consists of the following activities:
- Elimination of the underlying cause of the infection (most often antibiotic therapy is required as prescribed by a doctor);
- Cold compresses on the affected area (several times a day for 35-40 minutes);
- Application of tampons moistened with local anti-inflammatory drugs (Levomekol, ichthyol ointment);
- Physiotherapy on the 3-4th day from the onset of the disease (magnetic therapy, UHF).
When an abscess forms, immediate surgical treatment is required, which consists of opening it and removing the pus. In case of frequent relapses, it is recommended to completely remove the Bartholin gland.
Paraurethritis (skineitis)
Inflammation of the paraurethral glands and ducts is caused by the same pathogenic microorganisms as bartholinitis. The general clinical picture often corresponds to cystitis or urethritis. The main symptoms are discomfort during urination and sexual intercourse, pain in the perineum, the formation of lumps and abscesses near the urethra or vaginal opening.
Treatment consists of antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating drugs. In severe cases, surgery is required.
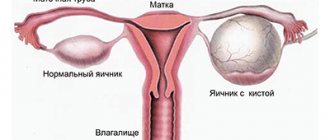
Vaginal cyst
A painless round lump is most often located on the left or right side of the vaginal wall. A cyst is a sac of connective or muscle tissue filled with viscous serous or mucous contents. The pathology can be congenital or acquired as a result of injury to the internal surfaces of the organ.
The disease most often has an asymptomatic course and is detected during a routine gynecological examination.
Many patients are interested in the question of whether it is necessary to remove a cyst in the vagina. The main indication for surgical intervention is the large size of the formation, which causes discomfort to the woman or interferes with natural delivery.
Boils and abscesses
Purulent formations appear as a result of microtrauma during sexual intercourse or wearing uncomfortable underwear. In this case, a hard, painful lump often appears in the perineum between the anus and vagina.
For minor inflammation, patients are prescribed wound-healing creams or ointments for topical use. If the abscess hurts and continues to grow, it may need to be opened surgically.
Benign tumors
True benign neoplasms include fibroids, myomas, fibromyomas and lipomas that form in different layers of the vagina. Tumors are most often localized along the anterior wall of the vagina and do not cause any discomfort. Sometimes there are periodic pains, moderate discomfort and a sensation of a foreign body in the genital tract.
Despite the low risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor, it is recommended to remove all tumors surgically within the boundaries of unchanged tissue.
Oncological pathologies
Carcinoma poses the greatest threat to the life and health of the patient. In most cases, oncology is asymptomatic, but some women may be bothered by the following symptoms:
- Scanty intermenstrual bleeding;
- Discharge of a pathological nature (thick, foamy, with an unpleasant odor, inclusions of mucus and pus);
- Pain syndrome of different nature.
If any alarming signs appear, you should contact a specialist. Diagnostics includes an examination in a gynecological chair and an ultrasound, which makes it possible to detect dangerous pathologies at an early stage. If necessary, a biopsy and other clinical tests are performed.
Source: https://DrLady.ru/disease/shishka-vo-vlagalishhe.html