Resection of the uterus is a highly traumatic surgical intervention, which is performed only if there are strict indications. After it, the patient undergoes long-term rehabilitation and endures great discomfort.
It is worth noting that removal of the uterus and appendages provokes the onset of artificial menopause, during which there is a sharp decrease in the concentration of hormones and the cessation of the menstrual cycle. Situations often arise when, after removal of an organ, a woman notices the appearance of discharge from the vaginal area. Let's consider how dangerous such symptoms are, and whether you need to worry about this at all.
Bloody discharge after hysterectomy: normal
A sign of normality can be considered spotting of blood, which is observed in the first weeks after surgery, and its appearance is associated with the natural healing process of surgical sutures of the uterine stump or vagina. The only alarming symptoms are heavy bleeding, as well as those cases when the discharge takes on the appearance of meat slop and acquires an unpleasant, putrid odor. This may indicate infection and inflammatory processes, which, in turn, often leads to sepsis or peritonitis.
If the healing process proceeds without complications, then the bloody discharge from the vagina will stop and the woman will no longer be bothered. However, some women experience slight spotting on the days when they should have their period. This situation does not occur often, but it can still occur.
This situation is explained by the fact that hysterectomy does not always involve the removal of the ovaries, which continue to produce sex hormones. If a woman's uterus is removed in such a way that a stump remains, some endometrial tissue may be retained. That is why on the days of menstruation a woman may experience slight bleeding, which, according to experts, should not be alarmed.
However, doctors warn the woman that removal of the uterus affects the blood supply to the ovaries, and this affects their functioning. The result of this is the approach of menopause, which occurs on average 5 years earlier.
Indications for the cervical excision procedure
- Dysplasia
- Extensive erosion
- Leukoplakia
- Endometriosis
- Cyst
- Scar tissue that leads to deformation of the cervix.
If conservative treatment methods fail or are considered inappropriate, an excision procedure is prescribed.
Preparation for surgery and contraindications
Excision is prescribed only after the woman has passed all the necessary tests and undergone a full examination. There must be colposcopy results, smears taken for flora and cytology, as well as a biopsy with histological examination of the material, a coagulogram, and an electrocardiogram. The patient's general health condition should be satisfactory.
In addition to the absence of sexually transmitted infections and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, the woman at the time of the operation should not suffer from other infectious or viral diseases. The excision procedure is not performed if, according to test results, the patient has extensive cervical cancer or a malignant neoplasm is detected.
Vaginal discharge that should cause concern
Unfortunately, removal of the uterus is a serious stress for the female body, because it affects hormonal levels and symptoms of menopause appear. Often women note the appearance of slight bleeding from the vagina. Their reasons may be:
- Vaginal dryness as one of the symptoms of menopause and, as a consequence, injury to blood vessels during sexual intercourse;
- Inflammatory processes in the vagina, thrush, as well as infectious diseases of the genital organs;
- The appearance of cervical erosion, if the uterus was preserved when the uterus was removed;
- The development of pathological processes in the pelvic organs, for example malignant tumors.
Due to the fact that you began to experience spotting only 4 years after the removal of the uterus, this phenomenon should be a reason to consult a gynecologist and undergo an examination to rule out the presence of life-threatening diseases.
Resection of the uterus is a highly traumatic surgical intervention, which is performed only if there are strict indications. After it, the patient undergoes long-term rehabilitation and endures great discomfort.
It is worth noting that removal of the uterus and appendages provokes the onset of artificial menopause, during which there is a sharp decrease in the concentration of hormones and the cessation of the menstrual cycle. Situations often arise when, after removal of an organ, a woman notices the appearance of discharge from the vaginal area. Let's consider how dangerous such symptoms are, and whether you need to worry about this at all.
After surgery, the woman remains in the hospital for several more days so that she is constantly monitored by the attending physician. In the case of vaginal intervention, this period is up to 10 days, and with laparoscopic surgery, the time in the hospital is reduced to 3 days.
Women note that the first day is the hardest because there is pain along the incision and in the abdomen. For this reason, the patient may be prescribed analgesics, both non-narcotic and narcotic.
24 hours after surgery, it is important to resume independent movement, which will allow the intestines to work properly and prevent the development of adhesions.
It happens that the rehabilitation period is delayed due to the development of complications, which include:
After surgery, you may experience some bloody or brown discharge for 14 days, which is normal. This is explained by the restoration process that occurs in the area of the stump and vagina. In case of longer-lasting discharge, you must inform your attending physician, who will conduct an examination and decide on the need for additional examination.
The patient should be alert to the following during the postoperative period:
- excessive discharge;
- have a bright red color;
- pus is detected;
- there are clots.
Bloody discharge is normal, but if it contains dark mucus and a sharp putrid odor, then one can judge the development of complications that require urgent intervention by medical personnel. The main reason for what is happening is the inflammatory process that occurs in the sutures and turns into peritonitis or even sepsis.
If during the operation the cervix was preserved, and the discharge becomes more abundant every day, then the patient should report this situation to her doctor, who will rule out the development of an inflammatory process. It is necessary to pay attention to the frequency of changing the gasket. If this happens more than once every 2 hours. The volume of fluid released is also important, because bleeding in the postoperative period is an alarming signal and in some cases requires repeat laparotomy.
After surgery, menstruation is out of the question. In the case where the ovaries were preserved, slight bleeding may occur during menstruation.
Women have to slightly adjust their usual way of life. In order for the healing period to be as comfortable as possible, it is important to listen to the recommendations of your doctor, which include the following:
- First of all, after the operation, the patient puts on a special bandage;
- stay at maximum rest for several weeks or even months and do not perform heavy physical work;
- Sexual contact is prohibited, as it can cause bleeding.
- yoga;
- Pilates;
- bodyflex;
- shaping;
- swimming
The start of classes should not be earlier than 90 days after surgery and in the absence of any complications. If the patient notices any discomfort or discharge, she must tell her doctor about what happened.
Also, for 5 weeks after surgery the following is prohibited:
- wash in the bathroom (shower only);
- swim in a pool or open pond, go to a bathhouse or sauna.
It is imperative to keep your genitals clean. For better recovery, it is recommended to follow a simple diet. It includes vegetables, fruits, which are high in fiber, wholemeal bread and porridge.
- alcohol of any strength;
- fatty and fried foods;
- tea and coffee;
- carbonated drinks.
It is best to drink clean water, natural juices, fruit drinks. To improve immunity, you can, on the recommendation of your doctor, purchase complexes of vitamins and minerals at the pharmacy.
All the unpleasant symptoms that accompany the removal of the uterus and ovaries include the onset of menopause. It provokes some changes in the functioning of the whole organism. To maintain your physical and psychological condition, you can take hormonal and non-hormonal medications, prescribed exclusively by your attending physician.
Prevention of complications
After any surgical intervention, which includes hysterectomy of the uterus, the main rule is to prevent bleeding and pathological discharge from the vaginal cavity. To do this, each patient after undergoing surgical treatment is recommended to follow certain rules aimed at her self-preservation.
- You should not lie in bed for a long time - the early start of physical activity in moderate quantities has a beneficial effect on the course of the recovery period, the normalization of metabolic processes and the activation of reparation processes, which will contribute to the accelerated healing of the wound surface.
- Do not overload a weakened body. Physical activity should be adequately dosed, not to the point of exhaustion, but until the first manifestations of mild fatigue.
- During the recovery period, lifting weights is prohibited. Maximum cargo weight 1-3 kg.
- It is worth getting rid of bad habits. Smoking has adverse effects on the body. Nicotine entering the body promotes the development of a reflex spasm of blood vessels, while alcohol, on the contrary, expands them, after which a sharp spasm occurs. Products with excessive carbohydrate content (sweets) contribute to the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the walls of arteries and veins, and a sedentary lifestyle contributes to the formation of thrombosis.
- It is necessary to normalize your diet, eat more fresh vegetables, fruits, poultry and dairy products. Thanks to this diet, the patient will receive the necessary amount of vitamins and proteins, with which, as a rule, certain problems arise due to excessively fatty and large amounts of sweet foods.
When discharged from the hospital, it is necessary to discuss in advance with a specialist the question of whether there may be discharge after removal of the uterus and what its nature should be. The main thing is to remember that any changes in the discharged fluid and the patient’s well-being should be discussed in a timely manner with the attending physician to prevent undesirable consequences.
Life after resection
Despite the fact that the patient's life undergoes significant changes, it is possible to adapt to them. You can find a large number of horror stories about this on the Internet. The first of them concerns sex life. It is important to understand that the areas that are responsible for pleasure from sexual intercourse are located at the entrance to the vagina, and not in the uterus, so removal of the organ does not affect orgasm.
Patients report pain only when there is a scar in the vagina, which occurred during radical hysterectomy. After surgery, there is a risk of formation of adhesions, which are indicated by the appearance of:
- flatulence;
- dyspeptic phenomena, which occur very often;
In order to minimize the chance of their occurrence, it is important to return to movement as soon as possible after surgery. The doctor may also recommend antibiotics and anticoagulants.
The period after surgery is never easy, but if you follow all the recommendations, you can go through this period as quickly and painlessly as possible and return to your normal lifestyle.
Hysterectomy is a procedure that is performed on the strict recommendation of a doctor. After removal of the uterus, discharge bothers the woman for a long time. After all, its consequences are often even more serious than the operation itself. So, they no longer resemble menstruation, during which the stomach often feels tight or the lower back hurts, but in any case, it is necessary to pay attention to how this discharge passes.
There are a number of other consequences that you will have to learn to live with after the procedure.
The first day after surgery is the hardest
Most often, women have their uterus removed if they are diagnosed with cancer of the uterus or cervix. Also among the reasons for surgical intervention are heavy bleeding, benign tumors that appeared after menopause, severe prolapse of the uterus, and gynecological pathologies.
Of course, surgery is considered as the last treatment option that cannot be avoided. In such cases, the patient cannot choose, but must adhere to the doctor's recommendations.
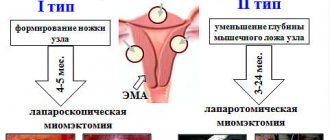
The operation can be performed using various methods depending on the severity of the disease, the location of the tumor and other factors:
- abdominal method - in this case the uterus is removed through an incision in the abdomen;
- vaginal – all manipulations are carried out through the vagina and the stitches are invisible after the operation;
- laparoscopic - small incisions are made in the lower abdomen through which they operate.
With any of these methods, the woman is in the hospital for five to ten days. The first day after the procedure is considered the most difficult, because the woman has severe stomach pain, it is difficult for her to move, she needs to stick to a diet, and problems with stool may appear.
After removal of the cervix, the patient may have complications that must be paid attention to. These include:
- Inflammatory processes in the area of the surgical suture.
- Painful urination.
- Bleeding.
- Peritonitis.
- Hematomas in the abdominal area.
- the discharge has a sharp unpleasant odor, which is either rotten;
- blood clots appeared;
- the discharge became bloody;
- The discharge has intensified and requires frequent changes of the pad. There can be 2-3 pads per hour.
All these complications can be diagnosed by a doctor during the patient’s hospital stay. During the time that a woman is in the hospital, many of these complications go away with proper care.
Discharge can last a whole month
Vaginal discharge may continue after discharge.
So, if a woman notices that the discharge has become bright red or with blood clots, she should urgently consult a doctor, as this may indicate internal bleeding.
If the discharge is scanty and seems to be “smeared”, this is the norm: this is how the suture heals after surgery. You should consult a doctor if:
All these symptoms may indicate that an inflammatory process has begun, which can lead to sepsis if you do not seek help in time. Remember, heavy bleeding from the genital tract after such an operation is a dangerous symptom!
However, some doctors note that discharge after removal of the uterus is a normal process that can last a whole month.
The main thing is that their frequency should not increase. Discharge may occur due to the fact that the activity of the ovaries is not affected and the influence of sex hormones on the cervix occurs.
Life after surgery!
Often, in order to save the patient from postoperative complications, doctors prescribe certain recommendations, following which you can quickly return to your normal pace of life.
There are a number of factors that frighten women who have undergone this operation. Many people think that they will become more masculine, their hair growth will increase, their voice will change, and the sensations during sex will be different. All these are far-fetched thoughts. So, if a woman only had her uterus removed and her ovaries were preserved, she will still experience sexual desire and will enjoy sex even more. After all, she will get rid of the pain in the lower abdomen, and the risk of getting pregnant will now not play a role for her. Often, women after a hysterectomy become even more relaxed in bed.
Separately, I would like to emphasize that after such an operation, life expectancy increases and the woman will not be susceptible to uterine cancer, and today, during a sharp increase in oncology among the population, this says a lot.
Of course, the postoperative period is not honey, it will be difficult to learn to live without a uterus, and this takes time. The main thing is to watch yourself during this time - do not miss important symptoms that may indicate a deterioration in your condition. Discharge after hysterectomy should not be abundant or too long! Remember that it is because of bleeding that a woman sometimes has to go back to the operating table. Be attentive to yourself!
The operation to remove the uterus (hysterectomy or hysterectomy) is one of the most common in the practice of operative gynecology.
It is carried out when all other possible treatment methods have demonstrated their ineffectiveness, and when it comes to saving the patient’s life. In some cases, during this surgical procedure, in addition to the uterus, the ovaries and fallopian tubes are also removed. Let's consider the consequences of the operation and recovery after hysterectomy.
Recovery after hysterectomy: first 24 hours
The first postoperative day is especially difficult. At this time, the woman feels quite severe pain inside the abdomen, as well as in the area of the sutures, which is not surprising, since there are wounds both inside and outside. To relieve pain, the doctor prescribes narcotic and non-narcotic painkillers.
The patient's lower limbs are bandaged with elastic bandages or in compression stockings (prevention of thrombophlebitis).
Doctors are of the opinion that the patient needs to be active after surgery. It is better for her to get out of bed earlier (in a few hours - a maximum of a day). Such physical activity perfectly “accelerates the blood” and promotes normal intestinal function.
During the first day after surgery, the doctor prescribes a gentle diet, which includes broths, pureed food and liquids (still mineral water, weak tea, fruit drinks). Such a treatment table gently stimulates intestinal motility and promotes early (1-2 days) spontaneous bowel movement. Independent stool indicates the normalization of intestinal function, which indicates the possibility of switching to familiar foods.
The abdomen after surgery remains sensitive and painful, usually from 3 to 10 days - everything will depend on the woman’s sensitivity threshold to pain. It should be noted that the more actively the patient behaves after surgery, the sooner her normal state is restored and the lower the likelihood of possible complications.
How long can the discharge last?
After removal of the uterus and ovaries, not too much bleeding may be present for up to 20-30 days, gradually becoming sanguineous in nature. If there was only hysterectomy, then every month there will be discharge from 3 to 6 days (menstruation). Their duration depends on the woman’s cycle. If the appendages are removed, menstruation stops.
During the first week and a half, a woman has more noticeable discharge. But keep in mind that the number of them is individual for each woman. The intensity also depends on how much the lady moves, whether she lifts weights, etc. If you take care of yourself and follow all the rules, the wound will heal faster. After 2-3 weeks, the discharge changes color and turns brown, which indicates that the healing process is coming to an end.
During bleeding, it is necessary to use pads that are changed as often as possible to prevent infection. Tampons are strictly prohibited.
The nature of the discharge and its quantity changes over time:
| Period | Quantity | Hue |
| First 1-2 days | Abundant | Red |
| 3,4,5 day | Less abundant | Burgundy |
| 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 days | Sparse | Dark brown |
| 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 days | Scarce | Brown |
| 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 days | Scarce | Light brown |
| 20 days or more, but not longer than 40 days | Scarce | There is ichor in clear discharge |
After 30-40 days, normal clear cervical mucus appears.
Recovery after hysterectomy: medications
Antibiotics - often, for the purpose of prevention, an antibacterial course is prescribed, since the patient’s internal organs during the operation had contact with air, and, consequently, with all kinds of infectious agents. Treatment with antibiotics continues for 7 days.
Anticoagulants - during the first 2 to 3 days, the doctor usually prescribes anticoagulants (drugs that thin the blood) to protect against blood clot formation and thrombophlebitis.
Intravenous infusions - during the first day after a hysterectomy, infusion treatment (drip infusion of intravenous solutions) is prescribed in order to replenish the volume of circulating blood, since the operation is usually accompanied by significant blood loss.
How to prepare for surgery?
A complete examination is very important, especially if cervical cancer is suspected. To the usual urine and blood tests, colposcopy, a biopsy, tomography (magnetic resonance, or MRI, positron emission scan, or PET, and computer), and a blood test for tumor markers are added.
When the operation has already been scheduled, you need to cleanse the intestines (a laxative is prescribed for 2-3 days), as well as shave the pubic and perineal hair. If there is inflammation (acute, exacerbation of chronic), it must first be treated.
Early complications after hysterectomy
The course of the early period after surgery is considered smooth if there are no complications at all. Early postoperative complications may include the following:
- inflammatory process on the skin in the area of the postoperative scar (swelling, redness, purulent discharge from the wound, as well as suture dehiscence);
- cramps or pain during urination caused by traumatic urethritis (damage to the mucous membrane of the urethra);
- bleeding of varying degrees of intensity;
- pulmonary embolism is a dangerous complication that causes blockage of the branches or the artery itself, and this is fraught with pulmonary hypertension, pneumonia and even death in the future;
- peritonitis - inflammation of the peritoneum, spreading to other internal organs, dangerously with the possible appearance of sepsis;
- hematomas (bruises) near the stitches.
Discharge
Bloody discharge after hysterectomy, reminiscent of “daub,” is always observed, especially during the first 10 to 14 days after surgery. This symptom is caused by the healing of sutures in the area of the uterine stump or in the vaginal area.
If the patient’s discharge pattern changes after hysterectomy: an unpleasant, putrid odor appears, the color is similar to the color of meat liquid, you should immediately consult a doctor. It is possible that inflammation of the sutures in the vaginal area has developed, which is fraught with the appearance of sepsis and peritonitis.
Bleeding from the genital tract after surgery is a very alarming signal and indicates the need for repeat surgery.
Types of discharge
After removal of the uterus, it is possible to encounter several types of discharge. Spotting that lasts for two weeks will be considered normal. Excessive discharge or discharge that is bright red in color should cause alarm.
There should be no discharge with a purulent component during the postoperative period. There should also be no discharge containing a large number of clots. Any deviation from the norm in vaginal discharge after removal of the uterus should be perceived as a pathology, which is a complication after surgery.
If the discharge is dark mucus with an unpleasant putrefactive odor, it is imperative to carry out an examination and repeated surgical intervention. The presence of such discharge may indicate suppuration of the sutures. If the situation is not corrected in time, the patient may develop peritonitis or sepsis. The consequences of such complications are very difficult to predict. Both sepsis and peritonitis are very difficult to cure, and both conditions can cause the death of the patient.
According to indications, the uterus can be removed along with the cervix, but sometimes doctors preserve the cervix. If, in the presence of a cervix, after resection of the uterus, the discharge becomes more abundant, urgent medical intervention is required. Such discharge is a sign of the presence of an inflammatory process in the cervix. Normally, gaskets are rarely changed. If you have to change the pad every two hours, this is a serious reason to inform your doctor about what is happening.
After resection of the uterus, it is imperative to pay attention to the volume of discharge. If the discharge is abundant and has a bright red color, then this is a sign of beginning bleeding. Any internal bleeding poses a great danger, since it is very difficult to stop, and the consequences of large blood loss can pose a serious threat to the patient’s life. In this case, a repeat laparotomy is performed.
After removal of the uterus, menstruation is absent in its usual form. If the ovaries have been preserved, minor bleeding may occur from time to time. Their formation occurs approximately at the same time as menstruation began before the operation. These secretions are the result of the work of the ovaries and the remains of the uterus forming a stump. These discharges are very similar to those that were during menstruation, but their volume is small.
Suture infection
When a postoperative suture becomes infected, the overall body temperature increases to 38 degrees. The patient's condition, as a rule, does not suffer. Prescribed antibiotics, as well as antiseptic treatment of sutures, are quite sufficient to relieve this complication.
The postoperative dressing is changed for the first time and the wound is treated the next day after the operation, then the dressing is carried out the next day. It is advisable that the seams be treated with a solution of Curiosin (10 milliliters 350-500 rubles), which ensures gentle healing; It is also an excellent prevention of the formation of keloid scars.
Peritonitis
The appearance of peritonitis usually occurs after a hysterectomy, which was performed for emergency reasons, for example, necrosis of a myomatous node.
In this case, the woman’s condition worsens sharply:
1. The temperature rises to 39 - 40 degrees.
2. There is a pronounced pain syndrome.
3. There are signs of peritoneal irritation.
In this case, massive antibiotic therapy is performed (2-3 drugs are prescribed) and infusion of colloidal and saline solutions.
Prognosis after hysterectomy
Hysterectomy not only has no effect on a woman’s life expectancy, but even significantly improves its quality. Having forever gotten rid of the problems associated with diseases of the uterus and/or appendages, having forgotten forever about the issue of contraception, many women literally blossom.
More than half of the patients talk about liberation and increased libido. A woman is not granted disability after removal of the uterus, since the operation does not reduce her ability to work. A disability group is assigned only in the presence of severe uterine pathology, as well as when hysterectomy was followed by radiation or chemotherapy, which significantly affected the woman’s ability to work and health.
Hysterectomy or surgery to remove the uterus is a fairly common operation that is performed based on special health conditions. If we look at medical statistics, a third of women over 45 years of age were referred by a gynecologist for this operation. The only thing that scares almost all women is the consequences that await the patient after removal of the uterus.
Postoperative period
The postoperative period is the time after surgery, which borders on the stage of complete recovery. Usually there is an early postoperative period, when the patient, after removal of the uterus, is still in the hospital under the close supervision of a doctor. The duration of this period depends on the patient’s condition, age, and the body’s restorative forces. After a woman has had her uterus or appendages removed, the patient must stay in the gynecological department for about 10 days. As soon as her stitches are removed, the second postoperative period begins.
The first day after surgery is very difficult for any woman. During this period, the woman feels pain in the abdomen itself and at the site of the stitches. This is not surprising, because the person is left with an open wound. If each of us experiences incredible pain when cutting a finger, then what can we say about an operation to remove the uterus. To relieve this pain syndrome, that is, reduce it, the woman is prescribed painkillers. Even before the operation, the woman’s lower limbs are bandaged with elastic bandages to prevent thrombophlebitis from forming. A woman should not lie in bed for several days. Recently, doctors have welcomed getting up early, literally a few hours after surgery. This is necessary so that the patient’s motor activity is restored, blood begins to circulate through the pelvic organs and at the same time the intestines begin to work. Diet is also a very important point that absolutely every patient must follow. In the first few days after surgery, it is advisable to eat liquid food, namely chicken broth, pureed vegetables, weak tea, and also drink more water. It is this type of therapeutic nutrition that helps a person to have bowel movements about 2 times a day.
It was noted that the increased activity of the patient after removal of the uterus increases her chances of successful treatment and recovery.
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is a resection, amputation of the main organ of female reproduction. This term refers to uterine excision. Sometimes the situation requires the simultaneous removal of the cervix, tubes, appendages, and ovaries. The operation is performed when a woman’s life is at risk, usually due to oncology. The diagnosis involves removing what contains cancer cells, otherwise there is a risk of a new tumor appearing. Therefore, excision of the affected areas is a vital necessity. Doctors are always considering options for organ preservation. Other prerequisites for the operation cannot be excluded.
Indications for removal
This includes pathologies in which normal functioning of the uterus is impossible, and the prognosis is not reassuring:
- Progressive polyposis. The walls of the organ are covered with polyps so that removing the formations individually is impossible. Some types of polyps are harbingers of cancer, and today it is impossible to cure the pathology with medication;
- Fibroma is a benign formation in the muscles of the uterus. For women who are planning a pregnancy in the future, laparoscopic removal of the fibrous node is used. The danger of a tumor is tissue torsion or necrosis. The risk of cancer is 1%. Complications of pathology - indication for removal;
- Uterine fibroids are also a benign tumor. Malignancy - 2%. Possible tissue necrosis and torsion of the node;
- Prolapse, severe prolapse of the uterus;
- Endometriosis is a pathology of the inner lining. In severe cases that cannot be treated conservatively, surgery is used. Options are possible without removing the organ;
- Purulent inflammation of the endometrium;
- Injuries that occur during gynecological manipulations;
- Fusion of the placenta with the wall of the uterus;
- Organ rupture during childbirth. A clear sign is a blue discoloration of the navel area. The operation is urgently needed, the consequence is death from blood loss;
- Removal of the ovaries is prescribed if there is a cyst in its tissues.
Surgical methods
The operation is performed laparoscopically, through punctures, when a small area is to be removed. For example, with small fibroids, organ prolapse, endometriosis. Complex cases require an open method through abdominal dissection. Based on what is removed, the procedure involves the following methods:
- Supravaginal amputation or subtotal hysterectomy. Part of the cervix, appendages, ovaries, and vagina are left behind. Prescribed for endometriosis, early stage cancer, fibroids.
- Extirpation or total hysterectomy. The cervix must be removed along with the uterus. Used for polyposis, endometrial oncology, postpartum complications, and cancer of this area.
- Wertheim's method. The appendages, the upper third of the vagina, the lymph nodes and, accordingly, the uterus are excised. A method that is used in severe cancer cases.
Complications after hysterectomy
The two main dangers during this period are bleeding and peritonitis. Both conditions can lead to death. The risk persists for a week or 10 days after hysterectomy. Broken sutures cause bleeding. The discharge is bright red, liquid, copious. Or with a lot of dark clots. To prevent this, a corrective procedure is urgently carried out. The wound is sutured, the inflammation is removed with medications.
Peritonitis is suppuration of the sutures after surgery on the uterus. Manifested by symptoms of severe intoxication: nausea, vomiting, pale skin, acute abdominal pain, increased body temperature. The discharge from the suture and vagina is purulent. The abdominal cavity is urgently opened, the surgical site is washed with antiseptic drugs, and drains are installed. The patient is prescribed a course of antibacterial therapy.
Other pathological conditions in the first days after removal of the uterus:
- Severe swelling and redness of the skin;
- The appearance of purulent or bloody discharge on the external scar;
- Pain in the urethra;
- Pulmonary embolism is a blockage of the corresponding artery that leads to death. Develops as a result of the movement of a blood clot into this area, provoked by surgery;
- Sepsis is a consequence of peritonitis, a blood infection that leads to death.
Attention! Prescription of painkillers is mandatory in the postoperative period. The noticeable pain that is typical for such patients increases the recovery time of the body.
Therapy after surgery
Treatment after surgery is the use of antibiotic therapy. After all, after the operation, and even during it, the patient’s internal organs were exposed to bacteria and various infections. The course of antibiotic treatment is approximately 7 days. It is very important to use anticoagulants - these are drugs that thin the blood and prevent blood clots.
Blood may be infused intravenously, since the operation to remove the uterus is accompanied by heavy blood loss of up to 500 ml. The early period of rehabilitation is considered quite smooth if there are no pathological complications at this stage.
Subtotal hysterectomy
Surgeries to remove the uterus are the second most common in gynecology after cesarean section. No matter how sad it may be, in a number of cases, when conservative therapy does not lead to the cure of a particular disease of the uterus, gynecologists are forced to act radically, excising the diseased organ from the body. There are several types of this operation, differing both in the number of reproductive organs removed and in the surgical approaches (laparotomy, vaginal or laparoscopic).
One of the most effective methods is subtotal hysterectomy, which involves removing the body of the uterus while maintaining the integrity of the cervix. Depending on the nature of the pathology, the uterus is removed with or without appendages. In gynecological practice, typical, low or high amputation of the uterus is also known.
Complication after hysterectomy surgery
After removal of the uterus, the following postoperative symptoms are possible:
- Swelling of the skin;
- Redness of the skin;
- Discharge of pus from a postoperative scar on the skin;
- If the urethra is damaged, problems with urination begin;
- Pain when urinating;
- Bleeding from the suture of varying intensity - it can be dark or scarlet in color; There are clots of scarlet blood in the discharge.
- Pulmonary embolism is a very dangerous and severe complication that leads to blockage of the artery. As a result, this is fraught with pulmonary hypertension. This can eventually develop into pneumonia and be fatal.
- Inflammatory process of the abdominal cavity, leading to damage to internal organs, the development of the disease develops into sepsis.
So, if a woman experiences severe bleeding in the first few days after removal of the uterus, then this is considered normal and not pathology. There is no need to worry or be afraid of this phenomenon. You need to wait about 2 weeks for the discharge to stop on its own. Discharge from the vagina can be explained by the fact that the sutures are tightened after the operation and since the operation was performed directly in the area of the uterus or vagina, the mucous membrane is gradually rejected.
If you have unpleasant, foul-smelling, putrefactive discharge, as well as a consistency reminiscent of slop, you should urgently consult a doctor. Most likely, the patient began an inflammatory process of the sutures directly in the vagina itself. This phenomenon is fraught with the development of peritonitis and sepsis. If a woman has very heavy bleeding, then serious measures must be taken.
Penetration of infection into the seam
If the postoperative suture becomes infected, the patient’s body temperature rises and her general well-being worsens. To relieve (stop) this condition, it is enough to take a course of antibiotics and re-treat the sutures. The postoperative dressing must be changed using Curiosin solution, due to which the wound heals quickly and a scar begins to form.
If a woman develops peritonitis after removal of the uterus, then the patient’s general well-being worsens. The temperature rises sharply to 40 degrees. The pain syndrome is very pronounced. Since the signs of irritation of the abdominal cavity are very pronounced, it is impossible to do without infusion of saline solutions. If a positive effect is not achieved, then in this case, it will be necessary to resort to relaparotomy, that is, completely amputate the uterus and then rinse the abdominal cavity with antiseptics and install drainage. If you follow the doctor’s recommendations, change the dressing in a timely manner, and take a course of antibiotics, then the consequences after removing a woman’s uterus will disappear.