Hormonal contraceptive patch
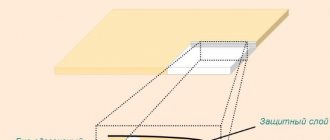
Evra, a remedy that prevents unplanned conception, is an adhesive square that looks like a regular adhesive plaster. For its manufacture, a thin material of synthetic origin and flesh color is used. The Evra hormonal patch has three layers:
- First
. It is a fabric-based adhesive tape that is directly attached to the skin. - Second
. This layer contains synthetic sex hormones. - Third
. The top protective layer is breathable. Its task is to protect the active substances from moisture and contamination.
The Evra patch contains synthetic hormones that suppress ovulation, provoke structural changes in the endometrium and make cervical mucus more viscous. Due to its thickness, the movement of sperm is disrupted, and the proliferation of pathogenic flora is also prevented. This contraceptive option is suitable for women with one sexual partner.
The contraceptive patch has its advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include the following facts:
- Ease of use;
- high level of efficiency;
- need to be glued only once a week;
- does not cause discomfort.
The Evra patch has certain disadvantages that cannot be ignored:
- hormones can affect weight;
- does not protect against sexually transmitted infections;
- irritation may occur;
- possible side effects;
- After discontinuation, you need to wait until you become pregnant.
There are a number of features that should be considered when using the contraceptive patch:
- The protective effect of this remedy occurs on the first day of the uterine cycle. When using the patch in the middle of the cycle, additional methods of contraception are required during the first week after application.
- When there is a break after removing the Evra patch (the fourth week of the cycle), the contraceptive effect will continue.
- If a woman used hormonal pills before gluing the patch, then the interval after finishing taking them and before gluing the product should be no more than seven days. When more than a week has passed, before starting to use the patch, you should make sure that conception has not occurred.
- The hormonal patch can be used on the day of the abortion, but only if the pregnancy is no more than 12 weeks. If more than 5 days have passed since the termination of pregnancy, then the product should be applied only on the first day of menstruation. When the pregnancy was more than 12 weeks, the patch can be used only after a month.
- During the first three months of using this product, brownish discharge may appear. If after this time the problem does not disappear, you should definitely consult a doctor.
- If after a break, that is, the fourth week, a woman forgets about gluing the contraceptive, then she needs to remember the day when the error was corrected, from which the report will begin. It is recommended to use additional protection methods during the week.
- If the second or third contraceptive has not been replaced, then after sticking on the new patch, you should remember the day and start a new report from it, that is, three weeks with a break. During the first week, additional methods of protection should be used.
- When the remedy is not used in the fourth week, and menstruation has not occurred, but the patch does not come off, and it is replaced in a timely manner, then you should not stop using the remedy. If menstruation does not occur after two cycles, then be sure to consult a doctor.
- An urgent appointment with a gynecologist is necessary if pregnancy occurs while using hormonal medications. Then be sure to stop using the patch.
Hormonal patch for pregnancy - effectiveness
According to information provided by the manufacturer, this contraceptive provides protection in 99.4% of cases. Independent expert commissions present slightly low figures, for example, experiments have shown that the Evra transdermal patch will be 92% effective, but these are also high levels of protection that many other methods are simply incapable of. The difference between the values of the manufacturers and the commission is explained by the fact that, as it turned out, if a woman weighs more than 90 kg, then the chance of getting pregnant increases significantly.
Evra patch – when does your period start?
After a three-week course of using this contraceptive, you need to take a week's break, during which menstruation begins. In most cases, this occurs on the second or third day after withdrawal. The new Evra contraceptive patch must be applied after seven days, even if menstruation has not yet ended. Longer breaks are undesirable, as the chance of getting pregnant will increase.
Pregnancy after Evra patch
If a woman plans to become a mother, then she should prepare for this event. Doctors recommend abandoning hormonal contraceptives three months before the expected conception. During this time, the woman’s hormonal system will be restored, the menstrual cycle and ovarian function will stabilize. Experts have studied the relationship between the Evra patch and pregnancy, so if a woman misses the time to apply a new patch, then after two days the risk of conception will increase.
What to do?
In your case, smoking and being overweight pose an additional risk of side effects, which include nausea and changes in the perception of smells. However, a two-week period of use does not allow us to say with certainty whether these symptoms are a manifestation of side effects. In addition, the drug cannot be stopped in the middle of the cycle. It is advisable to wait until the fourth week - the week of “rest” - and observe whether the discomfort decreases after o. Your body needs to adapt to artificially administered hormones. Typically, such manifestations disappear within 1 - 2 cycles. However, if the intensity of the discomfort increases, inform your gynecologist.
Best regards, Ksenia.
How to use the Evra patch?
The contraceptive provides an effect for four weeks, so a new copy is attached to the skin for three weeks, and then a break is taken for a week. At this time, menstruation occurs, which indicates that the hormones have stopped working. The instructions for the Evra patch indicate that seven days after removing the old product, a new one must be applied.
If you do not take a week-long break, you can delay menstruation for a certain period of time, so the longer the product is on the body, the longer there will be no menstrual bleeding. It should be borne in mind that gynecologists do not recommend using the Evra bad patch for a break longer than three menstrual cycles. If, for certain reasons, after the end of the first week of the monthly cycle the patch was not replaced, then this should be done as quickly as possible, taking additional local contraception for ten days.
How to apply Evra patch?
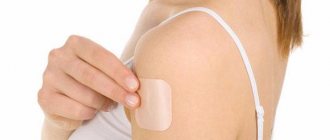
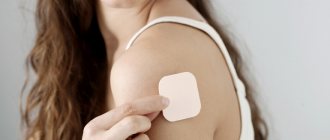
Using this contraceptive is very simple, so first take it out of the package, remove the protective film and stick it on the selected place. It is important that the Evra contraceptive patch fits tightly and evenly to the skin. The effectiveness of the product is significantly reduced if folds, bends are formed and an incomplete fit is observed. The manufacturer recommends monitoring the tightness of the patch to the skin every day, since this determines how many hormones will enter the bloodstream, that is, effectiveness.
Where to glue the Evra patch?
The protective agent is applied to clean and dry skin, which should not be pre-lubricated with cream or other care products. It is important to know where it is best to apply the Evra patch, so the following areas of the body are considered suitable: buttocks, the outer surface of the upper third of the shoulder, the stomach and the area of the shoulder blade. The contraceptive should be placed in places where clothing does not rub. The mammary glands, places where there is hair and folds are not suitable for the patch. It is important that there is no damage to the selected area of skin.
The Evra patch has come off - what to do?
The surface of the patch is covered with a special glue, which differs in composition from the usual medical composition, so it holds well and can even be wetted. If the Evra contraceptive patch has come off, then you need to calculate the approximate time of what happened, and if another 48 hours have not passed, then you can reattach it. When the sticky surface deteriorates, the patch should be replaced with a new one, and the replacement is carried out according to a schedule. If more than two days have passed, use a new product, and consider this day the first in the cycle.
Cancellation of the Evra patch
According to reviews and opinions of doctors, in most cases, menstruation normalizes already in the first cycle, after stopping the use of this remedy. Rarely, ovarian hyperinhibition may occur, which is manifested by the absence of menstruation for six months or more. This condition does not require treatment, and the function will be restored on its own. As for ovulation, after using the Evra patch, it takes a month to normalize it.
special instructions
Before starting to use the transdermal patch Evra ®, it is necessary to collect a detailed medical history regarding immediate relatives, including data on heredity, and exclude pregnancy.
A general (including blood pressure measurement, breast examination, mammography) and gynecological examination should be performed. If a hereditary predisposition to venous thromboembolism is suspected (if a brother, sister or parent has venous thromboembolism), the woman should be referred for consultation with a specialist.
When prescribing the transdermal Evra ® patch, it is necessary to take into account the likelihood of thromboembolic complications (thrombophlebitis, venous thromboembolism, including pulmonary embolism, cerebrovascular diseases and retinal vascular thrombosis). At the slightest manifestation of symptoms of any of these diseases, the use of the transdermal Evra ® patch should be stopped immediately. Several epidemiological studies have been conducted assessing the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) among women using the Evra ® transdermal patch in comparison with women taking various oral contraceptive drugs. The probable index of VTE occurrence among women using the Evra ® transdermal patch ranged from 0.9 (the risk does not increase) to 2.4 (the risk increases by 2.4 times).
The risk of vascular complications is increased in women with thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins and varicose veins, as well as in obesity (body mass index more than 30 kg/m2).
Conditions of prolonged immobilization or surgical interventions on the lower extremities, obesity, or a family history of thromboembolic complications can increase the risk of developing venous thromboembolic complications. In this regard, it is recommended to stop using hormonal contraceptives 4 weeks before surgery (for planned surgery) and for two weeks after emergency surgery, as well as during and after prolonged immobilization.
Some epidemiological studies have found an increased risk of breast cancer with long-term use of combined hormonal contraceptives, especially at a young age, before the first pregnancy. Some studies have shown that taking hormonal contraceptives is associated with an increased risk of developing cervical tumors, including cancer.
Women using combined contraceptives may develop benign liver adenomas, which can cause life-threatening intra-abdominal bleeding. The risk of their occurrence increases after 4 or more years of use.
We recommend reading: Subclinical hypothyroidism: treatment, symptoms, causes
In case of severe pain in the upper abdomen, liver enlargement or symptoms of intra-abdominal bleeding, differential diagnosis should be carried out to exclude a liver tumor.
If pharmacologically uncontrolled arterial hypertension occurs in women while using combined hormonal contraceptives, the drug should be discontinued; use of the transdermal patch can be resumed after normalization of blood pressure.
Hormonal contraceptives may affect certain endocrine function tests, liver function markers, and blood components:
- concentrations of prothrombin and coagulation factors VII, VIII, IX and X increase; antithrombin III levels decrease; protein S levels decrease; platelet aggregation increases;
- the content of thyroxine-binding globulin increases, which causes an increase in the concentration of total thyroid hormone. The binding of free triiodothyronine (T3) by the ion exchange resin decreases, as evidenced by an increase in the concentration of thyroxine-binding globulin, the concentration of free thyroxine (T4) does not change;
- Plasma levels of other binding proteins may be elevated;
- The concentrations of sex hormone-binding globulins increase, which leads to an increase in the concentrations of total circulating endogenous sex hormones. At the same time, the concentrations of free or biologically active sex hormones decrease or remain unchanged;
- concentrations of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and triglycerides increase, while the LDL-C/HDL-C ratio may remain unchanged;
- glucose tolerance decreases;
- serum folate concentrations decrease, which may have potentially clinically significant consequences if pregnancy occurs soon after discontinuation of a hormonal contraceptive. Currently, all women who are aware of their folic acid deficiency are advised to take it in early pregnancy.
Combined hormonal contraceptives may affect peripheral insulin resistance and glucose tolerance, but there is no evidence that changes in diabetes mellitus therapy are necessary while using combined hormonal contraceptives. At the same time, the health status of women with diabetes mellitus should be carefully monitored, especially at the early stage of using the transdermal Evra ® patch.
There are clinical observations of cases of retinal vascular thrombosis associated with the use of hormonal contraceptives. Oral contraceptives should be discontinued if unexpected transient, partial or complete loss of vision occurs; attacks of blurred vision or diplopia; swelling of the papilla or disruption of the integrity of the retinal vessels. Appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic measures must be taken immediately.
Chloasma: Women who have experienced facial hyperpigmentation during pregnancy should avoid exposure to sunlight or artificial ultraviolet light while using the Evra ® transdermal patch, as such hyperpigmentation may not be completely reversible.
Women should be informed that the Evra ® transdermal patch does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases. When using combined hormonal contraceptives, spotting and spotting may occur, especially in the first 3 months of contraception. If, in cases of long-term use of the transdermal patch Evra ® in accordance with the recommendations, acyclic bleeding is observed for a long time or such discharge occurs after previous regular cycles, then other reasons should be taken into account in addition to the use of the transdermal patch. It is necessary to remember about non-hormonal causes of disruption of the cycle of drug use and examine the woman more carefully to exclude organic diseases and pregnancy.
There may be no menstrual withdrawal bleeding in some women during the period free from the use of the transdermal Evra ® patch. If a woman violated the instructions for use in the period preceding the first failed menstrual-like withdrawal bleeding, or if she did not have two menstrual-like withdrawal bleedings after interruptions in the use of the transdermal patch, then pregnancy must be ruled out before continuing to use the transdermal patch Evra ® .
In some women, discontinuation of hormonal contraceptives may provoke the absence of menstrual-like “withdrawal” bleeding or rare menstrual-like bleeding, especially if it was present before starting hormonal contraception.
If the use of the transdermal Evra ® patch causes skin irritation, then you can glue a new transdermal Evra ® patch to another area of the skin and wear it until the next day of replacement. Only one transdermal patch can be used at a time.
The Evra ® transdermal patch must not be damaged or cut. If the Evra ® transdermal patch is damaged (the shape is changed, part of the transdermal patch is cut off, or there are other visible damages), then the effectiveness of the contraceptive effect may be reduced.
In women weighing 90 kg or more, contraceptive effectiveness may be reduced.
Smoking while using the transdermal Evra ® patch increases the risk of side effects from the cardiovascular system (see section "Side Effects"). Women using the Evra ® transdermal patch are strongly advised to refrain from smoking.
The safety and effectiveness of the transdermal Evra ® patch have been established only for women from 18 years of age to menopause.
While using the transdermal Evra ® patch, women must undergo regular preventive medical examinations. The frequency and scope of these examinations should be based on appropriate guidelines, and should also be individually selected for each woman based on the clinical picture, but at least once every six months.
Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and machines The transdermal patch Evra ® does not affect or only slightly affects the ability to drive a car and other machines.
Evra patch - contraindications
For contraception to be effective, its use must be coordinated. The "Evra" patch, the use of which should be in accordance with the rules, has its contraindications:
- period of pregnancy and lactation;
- hypertension;
- problems with blood vessels;
- diabetes;
- oncology;
- uterine bleeding;
- age under 18 and over 35 years;
- frequent headaches;
- smoking.
Evra patch for endometriosis
One of the most inexplicable diseases among the fair sex is endometriosis, in which cells of the inner layer of the uterus appear in atypical places, for example, in the ovaries, cervix, tubes, and so on. Many women have noticed that the Evra hormonal patch is not only an excellent protection against unwanted pregnancy, but also helps in the presence of this disease. However, doctors do not use this method of treatment, prescribing other methods.
Advantages
Among the numerous innovative contraceptive drugs, the Evra hormonal patch has significant advantages:
- you need to change the contraceptive once a week, taking pills is a daily procedure,
- the contraceptive effect of the patch lasts about 2 days, for tablets this period is 12-24 hours,
- the menstrual cycle is normalized, pain during menstruation is reduced, discharge in the middle of the uterine cycle is much less common than when taking hormonal pills,
- the contraceptive effect of the drug remains in case of disorders of the digestive system,
- the risk of malignant neoplasms in the uterus and ovaries is significantly reduced,
- dosed and uniform supply of hormones into the blood, there are no concentration jumps that are observed when taking oral contraceptives,
- reliable fixation, does not come off during intense physical activity and water procedures,
- simplicity and ease of use.
Evra patch - side effects
Since protection is provided by hormones, the risk of side effects cannot be ruled out.
- Problems may arise in the functioning of the nervous system, as evidenced by sleep disturbances, drowsiness and decreased performance.
- Hormone surges have an impact on the activity of the cardiovascular system.
- The following side effects of the Evra patch are possible: hypertension, circulatory problems, thrombosis, increased blood density and coagulability.
- Some women experience discharge and bleeding, as well as pain. Cycle disturbances are also possible.
- The effect of the product may affect the functioning of the digestive system.
- The possible development of individual tolerance cannot be excluded. More often, an allergy to the Evra patch manifests itself in the form of urticaria.
Side effect
The most common side effects observed in clinical trials were breast discomfort, headache, application site reactions and nausea. The most common side effects leading to discontinuation of the Evra ® transdermal patch were application site reactions, breast discomfort (including breast discomfort and pain, breast swelling), nausea, headache and emotional lability. Also during clinical studies, the following side effects were observed, identified in less than one percent of patients: galactorrhea, a symptom complex similar to premenstrual syndrome, changes in vaginal secretion, insomnia, changes in libido.
We recommend reading: Formula for calculating free testosterone, how and why
The frequency of adverse effects was classified as follows:
- Very common ≥ 1/10
- Common ≥ 1/100 and - Uncommon ≥ 1/1000 and - Rare ≥ 1/10000 and - Very rare
The following undesirable effects were noted:
- Common: skin reactions at the site of application (burning, dryness, scarring, bruising, photosensitivity, peeling, swelling, crusting, paresthesia, bleeding, inflammation, induration, atrophy, excoriation, loss of sensation, infection, ulcer, eczema, nodule formation, pustules , discharge, abscess, tumor growth, erosion, unpleasant odor), fatigue, malaise.
- Uncommon: irritation, peripheral edema, hypersensitivity;
Disorders of the central and peripheral nervous system:
- Very common: headache;
- Common: dizziness, migraine;
- Very rare: cerebrovascular accidents (including transient cerebrovascular accidents; ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, cerebral vascular occlusions and stenoses), migraine with focal neurological symptoms, subarachnoid hemorrhage, dysgeusia.
Cardiovascular system disorders:
- Uncommon: arterial hypertension;
- Rarely: venous thrombosis; thrombophlebitis of the veins of the extremities;
- Very rare: myocardial infarction, arterial thrombosis and thromboembolism, hypertensive crisis.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
- Very common: nausea;
- Common: abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, bloating;
- Very rare: colitis
Disorders of the reproductive system and mammary glands:
- Very often: a feeling of discomfort in the mammary glands, enlargement of the mammary gland, swelling, pain, swelling, increased sensitivity, fibrocystic changes in the mammary glands;
- Common: painful withdrawal bleeding, uterine spasms, vaginal discharge;
- Uncommon: breast tumors, galactorrhea, dry mucous membrane of the vagina and vulva, discharge from the genital tract;
- Rarely: absence of menstrual-like bleeding, rare menstrual-like bleeding;
- Very rare: cervical dysplasia, scanty/heavy menstrual-like bleeding, acyclic bleeding, suppressed lactation.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues:
- Common: itching, skin reactions, acne;
- Uncommon: alopecia, allergic dermatitis, erythema, chloasma, eczema, photosensitivity reactions, urticaria;
- Rarely: generalized itching, erythematous rash, itchy rash;
- Very rare: angioedema, erythema multiforme, erythema nodosum, exfoliative rash, seborrheic dermatitis.
Metabolic and nutritional disorders:
- Common: weight gain
- Very rare: hyperglycemia, increased appetite, insulin resistance.
Hepatobiliary disorders:
- Uncommon: cholelithiasis, cholecystitis;
- Very rare: cholestasis, liver damage, cholestatic jaundice.
Visual disorders:
- Very rare: intolerance to contact lenses.
Mental disorders:
- Often: emotional instability, anxiety, affect, aggressiveness, depression, tearfulness;
- Uncommon: insomnia, changes in libido;
- Very rarely: anger, frustration.
Neoplasms benign, malignant and of unknown etiology (including cysts and polyps):
- Rarely: uterine leiomyoma;
- Very rare: breast cancer, cervical cancer, breast fibroadenoma, liver adenoma, liver tumors.
From the musculoskeletal system
- Common: muscle cramps.
Infections and infestations:
- Common: fungal infections of the vagina;
- Very rare: pustular rash.
Changes in laboratory parameters
- Very rarely: changes in the concentration of cholesterol in the blood, changes in the concentration of glucose in the blood, an increase in the concentration of low-density lipoproteins.
Instructions for use
The hormonal combination patch is glued to the skin once every 7 days. It is necessary to start using it on the first day of menstruation. Every week it is necessary to replace the contraceptive with a new one. The package contains 3 patches, which are intended for a month; accordingly, after three weeks you need to take a break from using the patch. Menstruation usually occurs during this time.
Many women wonder how to use a contraceptive patch, on which part of the body should it be glued? In fact, there are quite a lot of options; you can glue it on the shoulder, shoulder blade, hips or buttocks. The location of the patch does not play a special role, but you should pay attention to some tips:
- The use of the patch is strictly prohibited on the décolleté area and mammary glands.
- The skin should be free of obvious damage, allergic rash or irritation.
- There should be no folds in the area where the patch is located.
- The patch should be positioned so that contact with clothing is minimal.