The growths formed by the glandular uterine epithelium are called polyps. As a rule, they appear when there is a hormonal imbalance in the female body or chronic pathologies of the reproductive system. These formations must be eliminated, since there is a risk of their degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
In the early stages of polyp development, you can try to remove it using hormonal therapy. Treatment is carried out:
- oral contraceptives, provided that the polyp is less than 10 mm and the woman is not older than 35 years;
- antibiotics, if a flora analysis reveals a chronic infection that caused the appearance of a polyp;
- progesterone-containing agents (Utrozhestan, Duphaston), when endocrine changes are noted;
- preparations containing iron for heavy bleeding;
- differelin if the patient is over 35 years old.
Drug therapy lasts up to 6 months. If it does not give the desired result, surgical treatment is performed.
To avoid complications caused by surgery, you need to know what kind of discharge there is after removal of a polyp in the uterus and how much of it should be normal.
What is the operation
There are two main ways to get rid of benign growths:
- Polypectomy – removal of a polyp by curettage or unscrewing. This operation should only be performed by an experienced specialist.
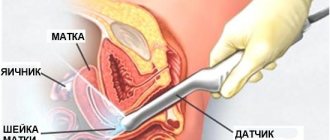
- Hysteroscopy of endometrial polyp is the most popular method. The procedure goes like this: an endoscope equipped with a microcamera, as well as a set of microsurgical instruments, are inserted into the cervix. Internal tissues and genital organs are not injured. Microsurgery allows you to eliminate the polyp and perform curettage of the uterus correctly, without complications.
It is not enough to carry out one procedure to eliminate the formation. After this, diagnostic curettage is required.
Surgery is followed by restorative treatment. Here it is necessary to take into account the patient’s age and the cause of the polyps. The examination is carried out only by the attending physician. He also prescribes antibiotics.
After surgery, many women are bothered by spotting. If they are accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, you should urgently consult a doctor. It is necessary to exclude possible complications due to severe cervical spasm.
What is a polyp?
Polypous formation is an abnormally enlarged endometrial lining. The disease develops as a result of impaired function of the hormonal system and long-term inflammatory diseases. 2 types are most often diagnosed:
- Ferrous. Formed due to hypertrophied endometrium. There are no specific symptoms; there may be spotting and mild pain. Hormone therapy is prescribed for therapeutic purposes.
- Fibrous. The connective tissue structure predominates; the formations contain few blood vessels and endometrial glandular tissue. Appear after childbirth, gynecological operations, abortions. The main treatment is surgery, and after the polyp is removed, antibiotics and hormonal drugs are prescribed.
Postmenopausal age is dangerous due to the development of pathology against the background of atrophic changes in the endometrium. In patients with an unfavorable medical history, a polyp in the uterus sometimes degenerates into a malignant neoplasm.
Factors influencing discharge
The fluid that appears after excision of the polyp may vary. Only the doctor determines whether the discharge is with signs of pathology or normal. They are directly related to the rate of wound healing and tissue regeneration.
There are several factors that influence the nature of the discharge:
- Appearance and size of the polyp. The larger the tumor, the greater the number of blood vessels it contains. The volume and thickness of the leg also matters.
- Inflammation. It begins when the genital tract becomes infected with a bacterial infection. In this case, yellow or greenish discharge appears that has an unpleasant odor. Usually they are abundant and do not stop for a long time.
- Vascularization is the degree of blood supply to an organ or growth. That is, the more vessels, the stronger the bleeding after polyp removal.
- Methods for eliminating growths. The least damage occurs with laser cauterization or cryodestruction (freezing). Unscrewing the stem or scraping the uterine cavity are traumatic procedures. After such an intervention, heavy discharge may occur that lasts for a long time.
- Ingrown legs. If the formation is deeply embedded, it will be quite difficult to remove it. During surgery, healthy blood vessels may be damaged. Therefore, the period after surgery is characterized by long-term discharge.
Normally, the consequences of polyp removal should appear within 7-10 days. Brown discharge indicates that the patient has normal blood clotting. If they continue longer than necessary, consult a doctor.
Often women do not pay attention to the signals that the body sends. They wait until the discharge goes away on its own or mistake it for menstruation. In fact, during this period you need to be examined by a specialist.
Recovery period
As a rule, recovery after hysteroscopy does not take much time and occurs relatively easily, without much effort on the part of the woman. And yet, since the patient may experience watery or bloody discharge from the genital tract for 2–4 weeks after the procedure, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Every day a woman should perform thorough hygiene of the external genitalia and also use sanitary pads.
- During this period, nothing should be inserted into the vagina. This includes not only hygiene items, but also medications or medical procedures (tampons, suppositories, douching).
- Until vaginal discharge stops, a woman should abstain from intimacy with her sexual partner.
- Thermal procedures (bath, sauna, solarium), swimming in open bodies of water (river, pond, lake) and taking baths should be avoided. Of the water procedures, only washing in the shower is allowed.
Only a doctor can say with certainty how serious a deviation from the norm some discharge is. Of course, there is no need to panic out of the blue. But if all patients went to see a gynecologist on time, then many serious complications could be avoided.
Main types of discharge
Medicine knows 4 options for discharge after removal of polyps:
- Physiological, within normal limits. As the wound heals, there are fewer and fewer of them. If the operation is less traumatic, such discharge may last 1 or 2 days. Their daily volume is approximately 50 ml. The liquid is sticky, transparent or pink in color (ichor). When the wound heals, the discharge stops.
- Uterine bleeding. If, during excision of a polyp, large vessels located on the wall of the organ are damaged, bleeding occurs. Usually it is fresh, bright red, and stands out a little. Sometimes dark clots left after surgery come out. If bleeding continues for more than 3-4 days, you should immediately seek help.
- Purulent discharge after polyp removal. They have a yellow-green tint and do not lighten, but on the contrary, become cloudy. Accompanied by an unpleasant odor. This indicates an infection caused by staphylococcus, streptococcus or sexually transmitted diseases. If you miss the problem, the development of sepsis, peritonitis or infertility is likely.
- Putrid discharge. They begin when clostridia enter the uterus, causing a putrefactive infection. In an oxygen-free environment, the reproduction of these organisms occurs rapidly. A woman experiences sharp pain in the lower abdomen. This liquid foams and has an unpleasant odor. In this case, medical intervention is urgently required.
The menstrual cycle after excision of the polyp is not restored immediately. For a month, a woman who has had a polyp removed should not be sexually active, visit the bathhouse or gym, lift heavy objects, or take medications that stimulate bleeding, such as aspirin. Conception is contraindicated for 6 months from the date of surgical treatment.
What discharge should be there after hysteroscopy and is considered normal?
In most women, after hysteroscopy, the discharge looks like a scanty daub consisting of particles of mucus and ichor. However, the appearance and characteristics of this phenomenon vary depending on what type of procedure was used. The characteristics of the female body can also play a role: the appearance and nature of the smear after hysteroscopy may differ depending on the degree of blood clotting, the ability to regenerate and existing diseases.
Experts say that after diagnostic hysteroscopy, during which only an examination of the uterine cavity is carried out, the volume of ichor is small. Most often it is a pinkish, slightly watery discharge streaked with blood. Similar smearing fractions are also released during a diagnostic procedure involving taking a smear or scraping from the surface of the endometrium.
More abundant and brightly blood-stained lochia are associated with hysteroresectoscopy, after which a wound remains on the endometrium after removal of fibroids, polyps or other neoplasms. The appearance of discharge of this nature is considered normal consequences resulting from surgical hysteroscopy. During a therapeutic procedure, such as resectoscopy or diagnostic RDV of the uterine cavity, many small vessels of the endometrium may bleed. At the same time, there is a discharge very similar to normal menstruation. After a few days they turn brown, indicating normal healing.
Important! A slight spasm and nagging pain that accompany bleeding are considered normal if they occur in the first 1-3 days after hysteroscopy.
After endometrial polyp removal
Discharge during hysteroscopy of an endometrial polyp can be either watery with an admixture of ichor or bloody. Their characteristics will depend on which polyp was removed:
- removal of small tumors on a thin stalk causes the release of clear or slightly colored mucus within 1-3 days:
- excision of large pedunculated polyps provokes short-term, scanty bleeding, followed by the transformation of the daub into watery mucus;
- after hysteroresectoscopy of a wide-based polyp, regardless of its size, in the first 1-3 days the patient releases about 50 ml of blood.
Gynecologists pay attention: if on the first day a clot comes out of the genital tract along with the mucous lochia, there is no reason for alarm. Removal of a polyp is almost always accompanied by the release of blood, which can clot in the cavity of the organ and then come out naturally.
After scraping
As a rule, discharge after hysteroscopy with curettage resembles normal menstruation. In the first days, patients may experience pain in the abdomen and lower back. In general, this is normal, because as a result of curettage, almost the entire inner surface of the uterus is an open wound that can hurt.
Normally, the release of blood and mucus continues until secretion is restored after curettage. It usually takes about 3-5 days. In rare cases, endometrial bleeding continues for up to 10 days. The intensity of bleeding decreases over time, turning into a brown spot.
Menstruation after polyp removal
If the tumor is located on the cervix, the operation is not very stressful for the body, so the resumption of the menstrual cycle occurs quickly. But the first menstruation will be scanty. This is due to the use of antibiotics prescribed to prevent inflammation. Intermenstrual bleeding ends, but immediately after the removal of the polyp, small discharge should begin, which lasts about 10 days. Timely release of fluid is necessary to avoid the inflammatory process.
If we are talking about removing an endometrial polyp located inside the uterus, your periods will return to normal after 30-40 days. What matters here is the patient’s age and the number of growths. The more polyps and the larger the surgical area, the more likely it is to delay menstruation. The cycle may not recover for a long time after curettage, since in this case all layers of the endometrium are affected. It is important that postoperative bleeding does not last more than 10 days. Otherwise, part of the formation remains in the uterine cavity and repeated intervention is necessary.
There are several other reasons why menstruation does not come on time after polyp removal. In the absence of dangerous symptoms, such as pain and fever, the problem is most likely stress or antibiotic therapy. But taking hormones, such as progesterone, will correct the situation.
After the tumors are eliminated, the nature of the cycle changes. There are no longer excessively heavy periods, pain disappears, brown and clear discharge between menstruation disappears.
Even with an ideal course of the postoperative period, the patient’s compliance with all the precautions listed above is mandatory. Only then will the cycle be restored, and later the woman will not have difficulties with pregnancy and bearing a child. Polyps are often the cause of temporary infertility, so it is better to remove them immediately if prescribed by a doctor.
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPLICATIONS
The main cause of complications during the rehabilitation period is an unsuccessful operation. The consequences of inaccurate surgical intervention can be:
- uterine bleeding;
- infection of the uterine cavity;
- endometrial diseases;
- air embolism;
- infertility.
One of the dangerous consequences of surgical intervention may be perforation of the uterine walls during probing or inept expansion of the cervical canal (cervix). Also, a consequence of careless intervention can be a violation of the integrity of the intestines - damage to the intestines. These surgical errors can occur due to an unclear image of the internal organs on the monitor during the removal of tumors.
Endometritis may appear as a result of infection of the uterine cavity during examination. Symptoms of endometritis are severe pain accompanied by high fever and bleeding with purulent discharge. In this case, antibiotics and detoxification therapy are used.
Air embolism is an extremely rare occurrence in practice. This pathology can be fatal. The cause of the disease is the pumping of air into the uterine cavity along with a medical solution.
The consequences of infection after hysteroscopy and laparoscopy appear on the third day. The patient feels severe pain in the lower abdomen, there is copious discharge mixed with pus and an unpleasant odor. This pathology is typical in the case of surgery against the background of existing inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.