Laser therapy in gynecology is actively used to treat pathologies of various origins. Treatment is prescribed for infertility, condylomas, cervical erosion, menstrual irregularities, during pregnancy complicated by toxicosis and fetoplacental insufficiency, and other pathologies. Laser therapy can replace severe and traumatic surgical interventions. It is carried out only by a doctor, as it requires the skill of a doctor. It is not possible to carry out treatment on your own.
When pills are not enough
Uterine fibroids are hormonally sensitive neoplasms. At an early stage, it is possible to carry out conservative therapy with low-dose monophasic oral contraceptives, and in adulthood with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, Mifepristone, Gestrinone. This treatment is effective for neoplasms up to 3 cm in size. If the nodes exceed this parameter, connective tissue begins to predominate in them, which loses the ability to decrease in volume. Therefore, in this case, surgical intervention is necessary.
Other indications for surgical treatment are:
- rapid growth of nodes;
- ineffectiveness of drug treatment;
- subserous or submucosal nodes on the stalk;
- interstitial fibroids larger than 3 cm, deforming the uterine cavity.
Radical surgery is performed in premenopausal patients. Indications for it are:
- uterine size greater than 14-16 weeks of pregnancy;
- frequent anemic bleeding;
- dysfunction of neighboring organs;
- cervical location of myomatous nodes;
- node power failure;
- suspicion of sarcoma;
- tumor growth in postmenopause.
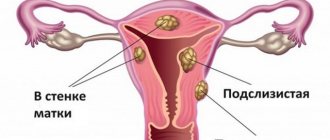
Types and locations of uterine fibroids
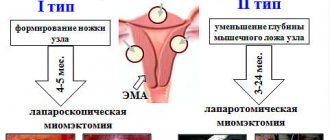
At a young age, organ-preserving operations are performed, which will allow, after a recovery period, to become pregnant and give birth to a child. Traditionally, fibroids are removed in several ways:
- laparotomy - through a wide incision in the abdominal cavity;
- laparoscopy - using a video camera and surgical equipment inserted into the abdominal cavity through 3 punctures;
- vaginally - with submucosal fibroids.
Laparotomy access is used in cases where the location of the neoplasm and its subsequent enucleation will not allow adequate comparison of the wound edges for hemostasis and subsequent scar formation. But recently it has been resorted to less frequently due to the advent of modern surgical methods, including laser removal.
Briefly about pathology
Myoma is a hyperplastic benign disease. It is sensitive to hormonal levels and is able to respond to it by slowing down or accelerating growth. According to autopsy results, myomatous nodes are found in 80% of women, but clinical manifestations of pathology are observed only in 30% of cases.
For unknown reasons, in the muscle layer of the uterus, some cells begin to actively divide and form nodes. The latter can be located under the mucous layer, have a stalk, be located in the thickness of the main tissues or under the outer serous membrane. Their localization determines the clinical manifestations of the disease. It can be:
- Bleeding;
- Heavy menstruation;
- Signs of compression of neighboring organs;
- Torsion of the leg of the knot;
- Necrosis of fibroids.
Pros of laser fibroid removal
Laser radiation is a directed beam of waves of different lengths that pass through a certain gaseous environment and are capable of targeting tissue, causing damage to the required volume of pathologically altered structures, and coagulating blood vessels. The beam does not come into direct contact with tissue, therefore, when using it, the risk of infection is significantly lower, unlike a surgical scalpel.
Laser removal of fibroids can be performed using any access method. Laparotomy will allow the use of a laser for any location of the nodes. Special flexible light guides deliver the laser beam through laparoscopic units.
The method minimizes the risk of bleeding. The peculiarity of radiation is that when the tissue is simultaneously cut, the vessels are sealed. They coagulate more accurately than when using bipolar or monopolar coagulators. The surgical field remains dry, which does not impair visibility. After completion of the operation, the risk of adhesions is reduced, since one of the reasons for the postoperative formation of adhesions is the exudate that forms during the intervention.
The advantages of laser removal of fibroids are as follows:
- good hemostasis;
- local effect and no damage to healthy tissues;
- high stability and ablasticity;
- minimal possible invasiveness;
- the possibility of performing the operation using open and laparoscopic access;
- laser operation in air;
- effective contact and non-contact vaporization and thermocoagulation.
Modern lasers are well compatible with endoscopic and laparotomy equipment. A surgical laser, which is used for abdominal operations, is effective in the abdominal cavity and does not require the creation of a special gas composition of the environment.
Approach to choosing a treatment method for uterine fibroids
Myoma is a benign formation, but it requires therapy. During the reproductive period, the growth of nodes leads to infertility. In older women who no longer plan to have children, fibroids are often combined with endometrial hyperplasia and are accompanied by bleeding. In rare cases, nodes can become malignant.
Today, many gynecologists believe that fibroids never become malignant, and uterine sarcoma is an independent pathology. This theory has not been proven, so doctors still maintain oncological vigilance in the case of fibroids. Both diseases have a similar clinical picture, and before choosing one or another treatment tactic, the doctor must be sure that the tumor is exclusively benign.
The choice of treatment method depends on three factors:
- Fibroids size;
- Woman's age;
- The desire to preserve reproductive function.
At a young age, therapeutic techniques are aimed at maximizing the preservation of fertility. Therefore, if hormonal therapy is ineffective, surgical methods are used that allow preserving the reproductive organ. For this purpose, FUS ablation and laser removal of nodes are used. If surgery is resorted to, it is preferable to use a laparoscopic approach. Laparoscopy is less traumatic than laparotomy. This shortens the postoperative period and the patient’s rehabilitation time.
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) is used if a woman wishes to preserve reproductive function. Impaired blood flow in the uterine arteries leads to necrosis of the nodes. Relapse after UAE is extremely rare. Most women do not have problems conceiving a child or carrying a pregnancy after the procedure.
Uterine artery embolization (UAE). The main essence of the method is to block the blood flow in the vessels of the fibroids due to emboli (special drugs), which are introduced through a catheter through the femoral vein to the uterine arteries.
Radical surgery (hysterectomy) is indicated in the following situations:
- Large fibroids that compress neighboring organs and disrupt their function;
- In adulthood, when pregnancy is no longer planned.
Hysterectomy in young women is performed without removing the appendages, so as not to cause symptoms of premature menopause. In premenopausal patients, especially with altered ovaries, the operation also includes removal of the appendages.
Types of hysterectomy: 1. Subtotal (supravaginal amputation with preservation of the cervix and appendages) 2. Total (hysterectomy with preservation of the vagina and appendages) 3. Radical (Wertheim operation with preservation of only 2/3 of the vagina).
Laser removal of uterine fibroids is a gentle option for myomectomy, which has a number of advantages over other methods..
Advantages of laser therapy:
- Painless procedure;
- No bleeding;
- No rough scar tissue is formed;
- Minimum operation time;
- Laser sterility;
- Short postoperative period.
Laser removal of fibroids is carried out for the following indications:
- Infertility of a woman in the absence of other causes other than fibroids;
- Miscarriage;
- A single node measuring up to 10 cm;
- Multiple nodes up to 5 cm in diameter.
Contraindications to the procedure:
- Large nodes;
- Presence of cancer;
- Decompensation of severe chronic diseases.
But even after laser therapy for fibroids, the risk of tumor recurrence remains.
Mechanism of action of the emitter
In gynecology, various types of laser systems are used, but a neodymium laser is suitable for surgery in the pelvic cavity. It generates optical radiation using quantum transitions between different energy states of Nd3+ ions, which are placed in a condensed matrix containing yttrium aluminum garnet crystals.
Scheme of how fibroids are removed with a laser
In surgical practice, continuous or pulsed laser radiation is used. Depending on the power level, the type of effect on tissue differs:
- 1-5 W – coagulation of small vessels;
- 5-20 W – shallow cuts, evaporation of pathological foci;
- 20-100 W – deep cuts.
The neodymium laser operates in the infrared range with a wavelength of 1.06 microns, which is invisible to the eye. In any operating mode, this laser has high efficiency. High-power radiation is capable of cutting tissue up to 6-8 mm in depth. A neodymium laser can coagulate many large neoplasms in gynecology, including uterine fibroids.
The potassium titanium phosphate crystal produces radiation in the green spectrum, and the coagulating effect is more pronounced here. Therefore, this type of laser is used in operations on organs with a large number of blood vessels or in cosmetology.
Contraindications
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Therefore, contraindications may be associated with both laser exposure and the effects of anesthesia. It is not recommended to perform surgery in the following conditions:
- acute inflammatory processes in the body;
- increased body temperature;
- allergic reactions in the active phase;
- unstable hemodynamics;
- severe forms of bronchial asthma;
- surgery on a full stomach.
Intervention is allowed for diabetes mellitus and other endocrine pathologies, if they are compensated. If the patient has suffered a myocardial infarction or acute cerebrovascular accident, surgery is postponed until the full recovery period (at least 6 months).
Preparation rules
Laser removal of fibroids is carried out as planned. In the preoperative period, careful preparation is necessary to reduce the likelihood of complications, both during the intervention and in the postoperative period.
A standard examination is carried out, which includes:
- clinical blood and urine tests;
- biochemical blood test assessing liver function, protein balance, ionic composition of blood;
- glucose level – necessary for early detection of hyperglycemia, which worsens the prognosis of any intervention;
- hemostasiogram – reflects the state of the blood coagulation system;
- a smear from the vagina to determine the degree of purity; if there are signs of inflammation, sanitation is carried out;
- Pelvic ultrasound – necessary to assess the condition of fibroids, its size and location;
- ECG - shows the work of the heart, necessary to eliminate the risks of anesthesia.
It is also recommended to pre-sanitize the oral cavity and any other foci of chronic infection that may become active in the postoperative period. Before the operation itself, the patient is examined by an anesthesiologist to exclude pathological conditions that may be a contraindication for giving anesthesia.
Types of surgery
Surgery to remove fibroids is planned based on the diagnostic results. The patient undergoes a gynecological examination, transvaginal ultrasonography, and undergoes standard blood, urine and smear tests. If necessary, an MRI is done. A biopsy specimen must be taken for morphological examination to exclude malignancy of the tumor.
Currently, medicine has reached a high level of development, allowing organ-conserving surgery to remove fibroids. Moscow clinics use several options, which determine the price of the operation:
- Cavity or open.
- Laparoscopic.
- Hysteroresectoscopic.
- Arterial embolization.
- Hysterectomy.
The tactics are chosen individually, taking into account the number of nodes (one or several), shape and size, as well as location (intermuscular nodes, submucosal, subperitoneal, interligamentous, cervical).
Open myomectomy
To remove fibroids using the classic cavity (open) method, an incision is made on the anterior wall of the peritoneum with an average length of 10 cm to provide surgical access. The incision can be either vertical or horizontal. In the latter case, the incision made by an experienced surgeon remains almost invisible after the operation. An operation performed in this way is justified for large tumors and inconvenient localization for other types of interventions.
Disadvantages of traditional operations: a suture on the abdomen, which can be performed inaccurately, possible blood loss, trauma, the use of general anesthesia, and an extended rehabilitation period. If the tumor is located inside the uterus, then postoperative scars will remain on the organ, which will complicate conception and pregnancy. Abdominal gynecological operations are performed less and less frequently.
Progress of the laser fibroid removal procedure
The process of starting a laser fibroid removal operation differs little from conventional surgery. Premedication is given 30 minutes before surgery. Its goal is to reduce autonomic symptoms that may appear during the intervention or induction of anesthesia. Antihistamines and tranquilizers are administered to stabilize the nervous system, and atropine is administered to reduce gastric secretion.
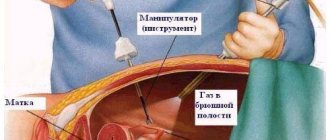
When using laparoscopic access, small skin incisions are made at three points in the abdomen through which guide tubes are inserted. Carbon dioxide is also pumped through them, which is necessary to expand the abdominal cavity and make manipulation easier.
An endoscopic camera is inserted through one of the tubes and transmits the image to the screen. Using manipulators, the doctor identifies the myomatous node and brings a laser emitter to its base. The vessels feeding the tumor are cauterized with a laser. The fibroid is held in place with a clamp, and its stalk is coagulated using a laser. After cauterization, the node is removed through a special uterine marcellator. Surgeons assess the condition of the abdominal cavity and remove instruments. After suturing the skin incisions, the patient is removed from anesthesia and transferred to the department.
Ways to improve surgical results
Any operation in the abdominal cavity increases the likelihood of adhesive disease. Even after the laser removal method, there is a risk of developing a tissue reaction and the formation of an inflammatory effusion, after which fibrin threads will remain in the pelvis - the basis for future adhesions. To prevent such a complication, some surgeons at the last stage of the operation insert a special mesh into the abdomen, which dissolves after some time.
Another way is to use suppositories with distreptase. This enzyme promotes the resorption of fresh adhesions. It is also recommended to get out of bed early and diet to prevent constipation.
But we must remember that removing fibroids surgically or with a laser does not eliminate the causes of pathology. Therefore, there is always a risk of relapse.
Hysteroresectoscopic myomectomy
Hysteroresectoscopy refers to minimally invasive operations to remove uterine fibroids. The technique is indicated for excision of intracavitary and endometriotic uterine nodes. The operation is performed through the vagina using a hysteroscope. Instruments and a device are inserted into the vagina, the node is cut off, the wound is cauterized with an electrocoagulator or treated with an antiseptic.
The method allows you to remove nodes with a hard-to-reach location.
Disadvantages: if the removal of uterine fibroids is performed poorly, infection and the development of inflammation, bleeding, uterine spasm, a high risk of relapse, and excessive damage to the endometrium cannot be ruled out, which poses a threat of infertility. The operation is common, the price is reasonable.
What alternative is there
Removing a myomatous node using laser technology is not always possible. Some women have contraindications to laser radiation or anesthesia. In this case, the doctor may suggest alternative treatment methods:
- UAE is uterine artery embolization, a destructive type of intervention in which a vascular surgeon injects a special suspension through the uterine artery under ultrasound control. It clogs the uterine arteries that feed the tumor, which causes its death.
- FUS ablation is the effect of focused ultrasound on the node, which is carried out under MRI control. Ultrasound waves cause destruction of tumor tissue, and it gradually decreases in size. If the intervention is carried out on time, the fibroid resolves completely.
- Cryomyolysis is a abdominal operation in which a liquid nitrogen solution is used to destroy fibroids. After the procedure, there is a low risk of the formation of rough scars and deformation of the uterine cavity.
Removal of fibroids with a laser is not yet used in all clinics. This method is still being studied, tested and improved. But studies show that laser treatment can reduce the incidence of postoperative complications, including infectious ones, and reduce the manifestations of pain. Surgery time is saved, women need a smaller dose of anesthesia, which has a beneficial effect on their overall health.