What is fibroid?
Myoma is a benign formation that occurs as a result of the accelerated division of smooth muscle or connective tissue cells in the uterus. Depending on the histological type, leiomyoma, fibroma and mixed tumors (fibromyoma, myofibroma) are distinguished. At present, the exact cause leading to the occurrence of the pathology has not been established, however, there are hormonal and hereditary theories of the appearance of nodes.
The disease most often occurs in premenopausal women, but in recent years the disease has been rapidly growing younger.
It is believed that risk factors leading to the development of uterine fibroids in young women are:
- Poor ecology (polluted air, water), and residents of large cities especially suffer.
- Frequent stress. Psycho-emotional and physical stress.
- Sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work.
- Overweight.
- Taking hormonal drugs.
- Endocrine and cardiovascular pathologies.
Many of these factors cannot be influenced, which is why this gynecological pathology worries many women.
Why doesn't pregnancy occur?
There is an opinion that infertility occurs due to benign tumors of the uterus, since natural fertilization is impossible. However, in reality, this is not the case. Uterine fibroids arise as a hormone-dependent structural disorder, localized in the uterine cavity and leading to disturbances at different stages of conception and gestation.
Nodes in the uterus lead to:
- Impossibility of conceiving a child.
- Spontaneous abortions.
- Premature birth.
- Narrowing and deformation of the birth canal, which is an absolute indication for a caesarean section.
- Postpartum complications occur - heavy uterine bleeding, inflammation of the uterus, sepsis.
What is the likelihood of getting pregnant with uterine fibroids?
The onset, course of pregnancy and the birth itself are affected not so much by the fibroid as by its size, location and the presence of complications. It is necessary to decide on the possibility of natural conception, pregnancy and in vitro fertilization in the presence of nodes in the uterus with the attending physician after a thorough examination.
Artificial insemination for fibroids
Uterine fibroids and their complications are the most common question that worries women who are faced with infertility due to this disease.
Most experts are inclined to believe that it is undesirable to carry out the IVF procedure in the presence of any, even benign, neoplasms, due to:
- The uterine cavity with fibroids is most often deformed, which leads to difficulty in implantation during pregnancy.
- Fibroids are a hormone-dependent pathology, so even small nodes during pregnancy can significantly increase in diameter and affect the developing fetus.
- The birth canal, altered and narrowed by the tumor, prevents the normal advancement of the fetus during natural childbirth.
As a result, in most cases, natural conception with fibroids and IVF is contraindicated.
When planning a pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination and, if necessary, a course of treatment to prepare the body for pregnancy and childbirth.
Why is IVF performed for uterine leiomyoma?
In vitro fertilization is indicated in situations where a woman is unable to conceive a child on her own. The cause may be obstruction of the fallopian tubes, abnormal development of the uterus, endocrine disorders and other pathological conditions that interfere with motherhood. IVF is also possible for some forms of male infertility. Conception in a test tube can be carried out both for married couples and for a single woman - there are no restrictions in the law on this matter.
Obstruction of the fallopian tubes is a common cause of infertility in women.
Uterine fibroids are not an indication for IVF. Gynecologists point out that a benign tumor extremely rarely leads to infertility, and the problem is successfully solved by removing the node. The reason for artificial insemination is another pathology, and fibroids act as a concomitant disease that reduces the chances of a favorable outcome of the procedure.
On a note
Patients of reproductive specialists most often include women of late childbearing age – over 35 years of age. In addition to infertility, fibroids are detected in 5-10% of cases. The tumor itself, according to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, causes infertility in no more than 2% of cases.
Treatment of pathology and pregnancy
Experts have proven that infertility caused by uterine fibroids is reversible and goes away after treatment of the pathology. When planning a pregnancy with fibroids, it is important to consult a doctor and choose the most effective treatment tactics, after which, in most cases, the long-awaited pregnancy occurs.
You can get rid of nodes in the uterus using conservative and surgical methods.
Drug therapy includes:
- Taking gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists (Zoladkes).
- Treatment with combined oral contraceptives (Regulon, Novinet).
- Correction of iron deficiency anemia (iron supplements).
- General strengthening therapy (taking vitamin and mineral complexes).
Under the influence of hormonal drugs, myomatous nodes stop growing and can also shrink, thereby facilitating conception.
Surgical treatment for tumors in the uterus is indicated when drug therapy is ineffective, as well as for large (uterine size over 12 weeks of pregnancy) and rapidly growing nodes. Surgical interventions include FUS ablation, uterine artery embolism, node resection and hysterectomy.
The scope of intervention is determined by a gynecologist. The choice of surgical method depends on the size and location of the pathological process, as well as on the presence of complications in the woman.
Stimulation of ovulation in an IVF cycle with uterine fibroids
When stimulating superovulation in an IVF treatment cycle for a history of uterine fibroids, the following schemes are used:
- Long protocol - includes the use of daily injections of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (a-GnRH) agonist diferelin, decapeptyl, suprefact, subcutaneously into the navel area, starting from the 19-22nd day of the menstrual cycle (mid-luteal phase).
- A short protocol of GnRH a is administered simultaneously with gonadotropic drugs from the 2-3rd day of the menstrual cycle.
- The use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists (ant-GnRH) orgalutran, citrotide, in combination with gonadotropins.
IVF after surgery
Is IVF done for fibroids after surgery, and what difficulties will you encounter?
This is a question that concerns women who have undergone surgery on the uterus. Only a gynecologist can answer this question and assess the possibility of artificial insemination. The likelihood of success of the procedure depends on the condition of the woman, the volume and effectiveness of the operation performed.
The most effective organ-preserving surgical interventions for fibroids include:
- Embolization of the uterine arteries. A method in which a special substance is injected through the femoral artery into the vessels supplying blood to the tumors, blocking their lumen. As a result, the nodes decrease in size and “shrink out.” The advantages of this operation include its high efficiency, painlessness and quick recovery period.
- FUS ablation is a method, the essence of which is the coagulation of the myomatous node with focused ultrasound waves. The clinical effectiveness of the method depends on the location and histological structure of the node.
Patients, after the operations, are subject to dynamic monitoring for a year. In the absence of complications, recurrence of fibroids and other contraindications, they can undergo the IVF procedure.
What determines whether IVF is done for uterine fibroids?
When deciding on the possibility and feasibility of IVF, specialists rely on the following factors:
The number of myomatous nodes, their size and location play a decisive role when deciding on the possibility of IVF. If the procedure is not possible, the doctor may refer the patient for treatment or myomectomy.
From the growth and direction of development of intramural myomatous medium and small sizes. This is determined by examination via ultrasound. If the nodes grow towards the uterine cavity, their negative impact on the course of pregnancy can be significant - during gestation, in the first trimesters, the nodes can increase up to 25%. If the node grows outward, then its negative impact on the course of pregnancy will be insignificant.
From the age of the patient. Often, women in late reproductive age simply do not have time for fibroid treatment and rehabilitation, since the time factor plays against them. If a woman does not have time for treatment, the doctor may decide on IVF, despite the presence of nodes.
The patient’s medical history, which includes data on the number of births and pregnancies; in case of infertility, its duration and treatment performed. In cases where all other causes except fibroids are excluded, surgery may be required.
Additional factors such as concomitant diseases, the general condition of the woman, etc.
In what cases is IVF not possible?
Unfortunately, even with the treatment of uterine fibroids, in some cases the artificial insemination procedure is not performed.
IVF is an expensive operation that doctors will not perform if the chances of successful implantation of the embryo, its full gestation and childbirth do not exceed 20%.
Artificial insemination is contraindicated if:
- Large neoplasms, accompanied by heavy bleeding and deforming the uterine cavity and cervical canal.
- Scars on the uterus left after resection of nodes.
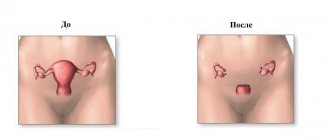
- Hystrectomy (during this operation, the entire uterus is completely removed, making pregnancy impossible).
You need to decide on the possibility of an IVF procedure with your doctor on an individual basis, 3 months after the operation. It is believed that during this time the disturbed hormonal levels are restored and the examination will be as informative as possible.
Factors influencing the success of artificial insemination
Scientists have not been able to find out exactly why uterine fibroids reduce the effectiveness of IVF even in the case of small intramural and subserous formations. The following factors are expected to influence:
- Violation of contractility of the myometrium - the muscular layer of the uterus, which provokes termination of pregnancy;
- Changes in the condition of the uterine mucosa. The embryo cannot penetrate the endometrium and dies in the early stages;
- Poor blood circulation in the uterus. Obstacles are created to the normal functioning of the placenta, the nutrition of the fetus and its oxygen supply are disrupted. Possible fetal death, premature birth;
- Hormonal disorders that interfere with the normal course of pregnancy.
This is interesting
Foreign literature provides scientific research data according to which the effectiveness of IVF for interstitial fibroids is reduced to 60%. At the same time, other data appeared according to which small-sized formations have virtually no effect on the outcome of artificial insemination. A 2007 study confirmed that fibroids that do not distort the uterine cavity do not worsen the prognosis. Women aged about 40 years old with nodes measuring up to 4 cm took part in the testing.
In vitro fertilization for untreated fibroids
Is it possible to do IVF for fibroids that have not been treated?
A frequent question that arises among representatives of the fair sex who, for some reason, have not undergone a course of conservative therapy and surgical intervention.
In this case, the artificial insemination procedure is associated with a high risk for both mother and child and is performed extremely rarely. IVF is possible if:
- The nodes in the uterus are small (up to 3 cm in diameter) and do not grow under the influence of hormones.
- The neoplasms do not deform the uterine cavity and the cervical canal (most often these are fibroids located in the intermuscular layer or under the serous membrane).
In any case, pregnancy with uterine tumors requires constant monitoring by an obstetrician-gynecologist. This is due to the fact that under the influence of hormonal levels, which change with each month of gestation, fibroids can increase in size and be accompanied by complications that threaten both the mother and the unborn child.
Myomectomy – to do or not?
Preliminary surgical removal of myomatous nodes is indicated in the following situations:
- Submucosal formations that deform the uterine cavity. According to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, submucosal tumors of any location are subject to removal;
- Subserous and interstitial formations larger than 4 cm.
Myomatous nodes that tend to grow or are larger than 4 centimeters require removal before the IVF procedure.
Surgery may also be recommended for smaller fibroids that tend to grow toward the uterine cavity. Many gynecologists send patients with nodes larger than 3 cm for myomectomy. The decision is made individually, based on the number of nodes and the location of the tumor, as well as the patient’s age.
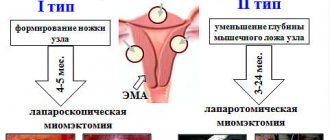
Myomectomy involves removing the tumor while preserving the uterus. Before IVF, surgery is usually performed laparoscopically - through small punctures in the abdominal wall. Submucosal tumors are removed during hysteroscopy. Planning a pregnancy using IVF is allowed 6-12 months after minimally invasive surgery. If abdominal surgery was performed, the conception of a child is delayed for 1.5-2 years.
It is important to know
After surgical correction, you should not delay pregnancy planning for more than 1.5 years, unless there are special indications for it. Recurrence of fibroids worsens the prognosis of IVF.
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive method of treating uterine fibroids, after which you can begin the in vitro fertilization procedure after six months.
An alternative to myomectomy may be a uterine artery embolization procedure. UAE stops blood flow in the vessels feeding the fibroid, after which the formation regresses. The technique is used for multiple myomatous nodes, when excision of the tumor is problematic and dangerous for the woman. After UAE, you can plan to conceive a child after 6-12 months.
It is important for women planning a pregnancy against the background of left fibroids to know: after successful IVF, under the influence of progesterone, the tumor will grow and can increase by 25%. The growth of the node is observed in the first and second trimesters. In the third trimester, stabilization and even reduction of fibroids in size is observed.
From the practice of a gynecologist
Svetlana, 35 years old, talks about how she managed to give birth to a child with uterine fibroids. A woman was taken into IVF with two subserous myomatous nodes – 1.5 and 2 cm. After stimulation of ovulation (“short protocol”) the nodes increased in size to 2 and 4 cm, respectively. Fertilization was successful; one embryo implanted on the first attempt. The fibroid continued to grow actively, but due to its subserous location, it did not affect the course of pregnancy. During a planned caesarean section, the nodes were removed after the fetus was delivered.
Sometimes, during a planned caesarean section, specialists also remove myomatous nodes.
Choosing an artificial insemination protocol
If the specialist has given the go-ahead for IVF, it is necessary to choose a protocol with a minimum dosage of hormonal drugs that may affect the disease. The effectiveness of the procedure depends on the size and location of the residual formation.
Pregnancy with artificial insemination occurs the first time in 38% of cases with:
- Myomatous nodes (up to 3 cm in diameter) that do not deform the uterine cavity.
- The location of the formation on the posterior wall of the uterus.
- Fibroma, the growth of which does not depend on the level of female sex hormones in the blood.
The IVF procedure itself for fibroids has no special features and consists of the stages of stimulation, puncture, fertilization and attachment.
In most cases, uterine fibroids, with timely and correct treatment, are not a contraindication for the artificial insemination procedure. It is very important to regularly undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist, with the aim of early detection and timely treatment of pathology, which increases the chances of a successful pregnancy naturally and with IVF.
The effect of myomectomy on IVF results
Briefly about in vitro fertilization
IVF after surgical myomectomy is a set of measures aimed at stimulating reproductive functions. Prescribed to married couples diagnosed with infertility, when the expected pregnancy does not occur within a year, subject to regular sexual activity and complete abstinence from contraception.
The procedure consists of several stages:
- stimulation of the ovaries to obtain several follicles in one cycle, for this they use hormonal preparations containing follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, chorionic gonadotropitis, ultimately obtaining from 5 to 12 eggs;
- collection of material - eggs are removed by puncture, under local or general anesthesia; the optimal way to donate sperm is called masturbation;
- cultivation - fertilization of an egg in a laboratory, the material is placed in a test tube with a liquid identical in composition to that found in the fallopian tubes and uterus;
- When the embryos reach 3 or 5 days of age, they are transferred.
When is IVF performed after myomectomy?
Myomectomy and IVF are quite compatible. Most women who undergo surgery become pregnant and bear children under the constant supervision of reproductive specialists. IVF can be performed without myomectomy under the following conditions:
- if the tumor is small (no more than 3 cm), does not deform the body of the uterus, does not interfere with the normal attachment and development of the embryo,
- if resection causes scarring, which will significantly reduce the chances of conception.
In any case, IVF after myomectomy is prescribed no earlier than one year later, since it is during this period that the pathology most often recurs.
The effectiveness of IVF after myomectomy
The effectiveness of IVF performed after myomectomy depends on the diameter and location of the fibroid and, accordingly, the location of the scar after surgery.
- Subserous localization - the tumor grew from the outer part of the uterus and after its removal the scar is small and not rough.
- Intramural - the formation was located in the middle muscle layer, and after its resection the damage was deeper and more extensive.
- Submucosal - located in the submucosal layer, which after resection loses its integrity. This affects the attachment of the embryo.
It is noted that when removing submucosal and intramural formations larger than 5 cm, the effectiveness of the procedure decreases by 4 times.
Features of gestation
There is no convincing evidence that the effectiveness of IVF after myomectomy manipulation decreases. But scarring after surgery negatively affects pregnancy, which is manifested in the following:
- impaired blood supply to the fetus,
- placenta accreta or abruption,
- scar rupture
- fetal malnutrition,
- sudden termination of pregnancy or premature birth,
- disruption of labor.
Statistics
According to research results provided by one of the reproductive clinics, IVF statistics after myomectomy are as follows:
- the age of the patients who took part in the study was 23–39 years;
- the pregnancy rate in patients as a result of IVF after myomectomy was 19%, spontaneous abortion in 34%;
- The pregnancy rate in patients with fibroids was 21%, and the pregnancy rate was 48%.
Conclusion: the advisability of myomectomy before IVF is determined individually for each case.