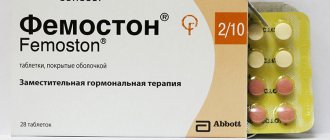
The best drugs for menopause
What are the best pills for menopause? This is the question most often asked by women who have crossed the age of 45-60. Popular drugs that a specialist can prescribe are Angelique and Femoston.
These products have one task - to enable a woman to accept all the symptomatic manifestations of postmenopause and, if possible, reduce them. But at the same time, the composition of medications has certain differences.
Femoston, Angelique can be classified as replacement therapy; they contain hormones (estrogens, gestagens), the concentration of which decreases during menopause. The appointment is carried out after the woman has completely stopped menstruating (after a certain time).
The manufacturer is Femoston - Dutch, Angelique is produced by Germany. These two companies have rightly gained the trust of the Russian consumer. If you compare the price, then Angelique will be a little more expensive.
Answering the question of what is the best remedy for menopause is not so simple. It should be understood that there is no one drug that would suit any woman.
The most suitable medication is one that helps reduce side effects that occur during menopause (for example, increased sweating). It should be borne in mind that a remedy that helped one woman may not bring relief and even harm another.
Angelique
Active substance:
Drospirenone*, Estradiol* (Drospirenone*, Estradiol*)
Pharmgroup:
Estrogens, gestagens; their homologs and antagonists in combinations
Average price in pharmacies
| Name | Manufacturer | average price |
| Angelique n28 tablet p/capt/sheath | BAYER | 1320.00 |
| Angelique micro 0.00025+0.0005 n28 tablet p/film/shell | BAYER | 1320.00 |
Analogs for the active substance:No data on synonyms | Application area:Age-related skin changes Dysfunction of the gonads Menopausal osteoporosis Menopausal syndrome Menopause symptom Violation of keratinization processes Ovarian dysfunction Non-functioning ovaries Osteoporosis in menopause Osteoporosis in menopause Osteoporosis in postmenopause Osteoporosis in the postmenopausal period Postmenopausal osteoporosis Osteoporosis due to estrogen deficiency Osteoporosis in postmenopausal women Osteoporosis in postmenopausal women Osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and after hysterectomy Primary ovarian dysfunction Perimenopausal osteoporosis Postmenopausal period Increased dry skin Postmenopausal osteoporosis Post-acne Postmenopausal osteoporosis Postmenopause Postmenopausal osteoporosis Postmenopausal bone demineralization Premenopausal period Decreased function of the gonads Decreased skin elasticity Skin cracks Cracks in the skin Erosion Estrogen deficiency |
Angelique and Femoston for menopause: composition
In the pharmacy chain, both drugs are available in blisters containing 28 tablets. Femoston and Angelique contain the active female sex hormone - estrogen. The difference is in the composition of female steroid hormones - gestagens, involved in the functioning of the ovaries, hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
The steroid hormones included in Angelica are represented by drospirenone, and in Femoston - dydrogesterone. In addition to the active ingredients, the products also contain excipients.
Briefly about the composition. Estradiol is the main component that is similar to estrogen both chemically and biologically. Capable of reducing the manifestations of menopause (vegetative, psycho-emotional):
- hyperhidrosis;
- migraine;
- sleep disorders;
- irritability;
- skin aging;
- drying of mucous membranes.
This component helps to normalize metabolic processes in bone tissue, which helps prevent the development of osteoporosis during menopause.
However, in addition to their positive properties, estrogens can lead to the growth of the endometrium, thereby provoking cancer of the lining of the uterus. In order to reduce the possible risk, both drugs taken during menopause include synthetic progestogens - progestins (drospirenone, dydrogesterone).
What is better during menopause: indications for the use of drugs
Taking into account the fact that the composition of the products is almost the same, the indications for their use are also identical. Manufacturers inform you how long after the last menstruation you should start taking it; a woman can also check this information with a gynecologist.
Femoston and Angelique for menopause are prescribed for the purpose of:
- replenish the lack of female hormones;
- prevention of osteoporosis during menopause;
- normalization of calcium metabolism;
- treatment of osteoporosis in women, in case of contraindications to taking non-hormonal drugs.
Femoston and Angelique for menopause: instructions
In order for the specialist to correctly select the product and its dosage, the woman must report the date of her last menstruation. The hormonal drug is taken after a day.
It is advisable to choose the most favorable and convenient time for taking pills, and correlate it with your daily routine and habits. Medicines must be taken continuously, i.e. open and start taking a new package the day after the previous one is finished.
If for some reason the dosage hour was missed, it is advisable to take the pill as quickly as possible. If it is impossible to take the medicine within 24 hours, a double dose is not needed.
If a woman is prescribed other hormonal drugs, in order to prevent the occurrence of unpleasant phenomena, she should first complete the course of taking the previous medication. If a woman is menstruating, the first day of taking the product should be agreed with a specialist.
Taking femoston during menopause (1/10 or 2/10). First, tablets that do not contain dydrogesterone are taken. They will be marked -1 on the packaging. In the next 2 weeks - with gestagen content, mark on the blister - 2.
Contraindications
The identity of the composition of the drugs also determines the similarity of contraindications for taking the drugs.
Of course, during menopause a woman cannot be pregnant or breastfeeding, but these conditions fall into the prohibited category of using Femoston and Angelica.
Both drugs are prohibited if a woman has:
- bleeding (uterine, vaginal), which have any etiology;
- diseases of oncohematological type;
- threats of blood clots or in the presence of thromboembolic conditions;
- disorders of the liver or kidneys;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- disturbances in porphyrin metabolism;
- individual intolerance to certain components included in the preparations.
A woman must notify her doctor if she has:
- arterial hypertension;
- metabolic syndrome;
- fibroids or endometriosis;
- asthma;
- atherosclerosis;
- migraine attacks;
- cholelithiasis;
- epilepsy.
Angelique Micro in Moscow
pharmachologic effect
Angelique Micro contains 17β-estradiol, chemically and biologically identical to endogenous human estradiol, and the synthetic progestogen drospirenone. 17β-estradiol provides hormone replacement during and after menopause. The addition of drospirenone provides control of bleeding and counteracts the development of estrogen-induced endometrial hyperplasia.
Effects of estradiol
The decline of ovarian function, accompanied by a decrease in the production of estrogen and progesterone, leads to the development of menopausal syndrome, which is characterized by vasomotor and organic symptoms. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is indicated to treat these symptoms.
Of all natural estrogens, estradiol is the most active and has the greatest affinity (binding strength) for estrogen receptors. Target organs for estrogen include, but are not limited to, the uterus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, vagina, mammary glands, and bones (osteoclasts).
Other effects of estrogens include decreased blood insulin and glucose concentrations, receptor-mediated vasoactive effects, and receptor-independent effects on vascular smooth muscle cells. Estrogen receptors have been identified in the heart and coronary arteries.
Oral administration of natural estrogens has advantages in cases of hypercholesterolemia due to a more favorable effect on lipid metabolism in the liver.
Estrogen monotherapy has a dose-dependent stimulating effect on mitosis and endometrial proliferation, etc. thus, increases the incidence of endometrial hyperplasia and, consequently, the risk of developing endometrial cancer. To avoid the development of endometrial hyperplasia, a combination with irogestagens is necessary.
Effects of drospirenone
Drospirenone has pharmacodynamic effects very similar to natural progesterone.
Progestogenic activity
Drospirenone is a potent progestogen with a central inhibitory effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. In women of reproductive age, drospirenone has a contraceptive effect; When drospirenone is administered as a single drug, ovulation is suppressed. The threshold dose of drospirenone to suppress ovulation is 2 mg/day. Complete transformation of the endometrium previously exposed to estrogen occurs after taking a dose of 4 or 6 mg/day for 10 days (= 40-60 mg per cycle).
Continuous hormone replacement therapy with Angeliq Micro allows you to avoid regular “withdrawal” bleeding that is observed with cyclic or phase HRT. During the first months of treatment, bleeding and spotting are quite common, but over time their frequency decreases.
Antimineralocorticoid activity
Drospirenone has the ability to competitively antagonize aldosterone. Women who received drospirenone in addition to estradiol in a clinical study reported less peripheral edema than those who took estradiol alone.
Antiandrogenic activity
Like natural progesterone, drospirenone has antiandrogenic properties.
Effect on carbohydrate metabolism
Drospirenone does not have any glucocorticoid or antiglucocorticoid activity and has no effect on glucose tolerance or insulin resistance. When using the drug Angeliq Micro, glucose tolerance is not impaired.
Other properties
Observational studies suggest that among postmenopausal women, the incidence of colon cancer is reduced when using HRT. The mechanism of action is still unclear.
Pharmacokinetics
Estradiol
Absorption
After oral administration, estradiol is quickly and completely absorbed. During absorption and first pass through the liver, estradiol undergoes significant metabolization, for example, into estrone, estriol and estrone sulfate. After oral administration, the bioavailability of estradiol is about 5%. The maximum plasma concentration of estradiol, approximately 16 pg/ml, is usually achieved 2-8 hours after taking the tablet. Food intake does not affect the bioavailability of estradiol.
Distribution
After oral administration of Angeliq Micro, a gradual change in the concentration of estradiol in the blood plasma is observed over 24 hours. Due to the circulation of estrogen sulfates and glucuronides in a wide range on the one hand, enterohepatic recirculation on the other, the half-life of estradiol is a complex parameter, which depends on all these processes and is in the range of 13-20 hours after ingestion.
Estradiol binds nonspecifically to serum albumin and specifically to sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). The free fraction of estradiol in plasma is approximately 1-2%, and the fraction of the substance bound by SHBG is in the range of 40-45%. Following oral administration, estradiol induces the formation of SHBG, which affects the distribution of serum proteins, causing an increase in the SHBG-bound fraction and a decrease in the albumin-bound and unbound fractions, indicating a non-linearity in the pharmacokinetics of estradiol after administration of Angeliq Micro. The apparent volume of distribution of estradiol after a single intravenous injection is about 1 l/kg.
Metabolism
Estradiol is metabolized primarily in the liver, and also partially in the intestines, kidneys, skeletal muscles and target organs. These processes are accompanied by the formation of estrone, estriol, catechol estrogens, as well as sulfate and glucuronide conjugates of these compounds, each of which has significantly less estrogenic activity or no estrogenic activity at all. Plasma estrone concentrations are 6 times higher than estradiol. Plasma concentrations of estrone conjugates are 26 times higher than the corresponding concentrations of free estrone.
Elimination
Estradiol clearance from plasma is about 30 ml/min/kg. Estradiol metabolites are excreted by the kidneys and intestines with a half-life of approximately 24 hours.
Equilibrium concentration
With daily use of the drug Angeliq Micro, the equilibrium concentration of estradiol in the blood plasma is achieved after approximately 5 days. On average, the concentration of estradiol in blood plasma ranges from 12 pg/ml (minimum level) to 29 pg/ml (maximum level).
Drospirenone
Absorption
After oral administration, drospirenone is rapidly and completely absorbed. Bioavailability after oral administration is 76-85%. Food intake does not affect the bioavailability of drospirenone.
Distribution
The maximum plasma concentration of drospirenone, approximately 3.35 ng/ml, is achieved approximately 1 hour after single and multiple doses of 0.25 mg of drospirenone. After this, a biphasic decrease in the concentration of drospirenone in plasma is observed with a final half-life of about 35-39 hours. Drospirenone binds to serum albumin and does not bind to SHBG and corticoid-binding globulin. About 3-5% of the total plasma concentration of drospirenone is not bound to protein.
Metabolism
After oral administration, drospirenone is largely metabolized. The main metabolites in human plasma are the acid form of drospirenone and 4.5-dihydro-drospirenone-3-sulfate. Both metabolites are formed without the participation of the cytochrome P450 system. Based on in vitro data, drospirenone is slightly metabolized by the cytochrome P450 3A4 system.
Elimination
Plasma clearance of drospirenone is 1.2-1.5 ml/min/kg. Some part of the received dose is excreted unchanged. Most of the dose is excreted by the kidneys and intestines in the form of metabolites in a ratio of 1.2:1.4 with a half-life of about 40 hours.
Equilibrium concentration
Equilibrium concentration is achieved after approximately 10 days of daily use of the drug Angeliq Micro. Due to the long half-life of drospirenone, the steady-state concentration is 2-3 times higher than the concentration after a single dose.
Indications
- Hormone replacement therapy for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause in women with a non-removed uterus.
Dosage regimen
If a woman does not take estrogen or switches to Angeliq Micro from another combination drug for continuous use, then she can begin treatment at any time.
Patients who switch to Angeliq Micro from a combination drug for a cyclic HRT regimen should begin taking it after the end of the current cycle of therapy.
Each package is designed for 28 days of use.
One tablet should be taken daily. After finishing taking 28 tablets from the current package, the next day they begin taking tablets from a new package of Angeliq Micro (continuous HRT), taking the first tablet on the same day of the week as the first tablet from the previous package.
The tablet is swallowed whole with a small amount of liquid. Tablets are taken regardless of meals. The time of day a woman takes the drug does not matter, however, if she started taking the pills at a specific time, she should continue to do so at that time.
The forgotten pill should be taken as soon as possible. If more than 24 hours have passed after the usual dosing time, you should not take an additional tablet. If you miss several tablets, you may develop bleeding from the vagina.
Use in certain groups of patients
In children
The drug is contraindicated for use in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
In the elderly
There are no data indicating the need for dose adjustment in elderly patients. Information on the use of the drug in women aged 65 years and older is presented in the “Special Instructions” section.
For liver dysfunction
In women with mild to moderate liver dysfunction, drospirenone is well tolerated.
The drug is contraindicated for use in women with severe liver dysfunction (see section “Contraindications”).
For impaired renal function
A small increase in drospirenone exposure was observed in women with mild to moderate renal impairment but is not expected to be clinically significant.
The drug is contraindicated for use in women with severe renal impairment (see section “Contraindications”).
Side effect
The most common adverse drug reactions (ADRs) observed when using Angeliq Micro were breast tenderness, bleeding from the genital tract, and abdominal pain (in less than 2% of patients).
Irregular bleeding usually disappears with long-term therapy. The frequency of bleeding decreases with increasing duration of treatment.
Serious adverse reactions include arterial and venous thromboembolic complications and breast cancer.
ADRs described in clinical studies using Angeliq Micro are presented in the table below. To determine the frequency, the following concepts are used: very common (> 1/10), common (from > 1/100 to < 1/10), infrequent (from > 1/1,000 to < 1/100) and rare (from > 1 /10,000 to <1/1,000).
| Class of organ systems | Very frequent | Frequent | Infrequent |
| Mental disorders | emotional lability | ||
| Nervous system disorders | migraine | ||
| Vascular disorders | venous and arterial thromboembolic complications* | ||
| Gastrointestinal disorders | stomach ache | ||
| Genital and breast disorders | breast pain (including breast discomfort) bleeding from the genital tract | cervical polyp breast cancer** |
In clinical studies, adverse events were coded using the MedDRA dictionary. Different MedDRA terms that reflect the same medical phenomenon were grouped into one adverse event to avoid duplication or ambiguity in reporting the true effect.
* The concept of “venous and arterial thromboembolic complications” includes the following medical terms: peripheral deep vein occlusion, thrombosis and embolism/occlusion of pulmonary vessels, thrombosis, embolism and infarction/myocardial infarction/cerebral infarction and stroke, excluding hemorrhagic.
** Data on the relationship with the use of the drug were obtained from post-marketing observations; Frequency data are obtained from clinical studies using the drug Angeliq Micro.
Also about venous and arterial thromboembolic complications, breast cancer and migraine, see the sections “Contraindications” and “Special instructions”.
One placebo-controlled study reported adverse reactions occurring at a frequency of >2%: headache (6% of patients treated with Angeliq Micro and 5% of patients treated with placebo), nausea (3.3% and 1.1%, respectively), diarrhea ( 2.2% and 0.6%, respectively), vulvovaginal candidiasis (5.5% and 0.6%, respectively), peripheral edema (2.2% and 1.1%, respectively).
Adverse reactions that occur in isolated cases or symptoms that develop very long after the start of therapy and which are considered to be associated with the use of drugs from the group of combination drugs for continuous hormone replacement therapy are listed below:
- liver tumors (benign and malignant);
- hormone-dependent malignant tumors or hormone-dependent precancerous diseases (if it is known that the patient has such conditions/diseases, this is a contraindication to the use of Angeliq Micro)
- cholelithiasis;
- dementia;
- endometrial cancer;
- arterial hypertension;
- liver dysfunction;
- hypertriglyceridemia;
- changes in glucose tolerance or insulin resistance;
- increase in the size of uterine fibroids;
- reactivation of endometriosis;
- prolactinoma;
- chloasma;
- jaundice and/or itching associated with cholestasis;
- the occurrence or worsening of conditions/diseases for which the relationship with the use of HRT has not been clearly proven: epilepsy; benign diseases of the mammary glands; bronchial asthma; porphyria; systemic lupus erythematosus; otosclerosis; chorea;
- in women with hereditary angioedema, exogenous estrogens may exacerbate symptoms;
- hypersensitivity (including symptoms such as rash and urticaria).
For more information about serious adverse events associated with hormone replacement therapy, see the "Special Instructions" section.
Contraindications for use
Taking Angeliq Micro is contraindicated in the presence of any of the conditions/diseases listed below. If any of these conditions/diseases occur while taking Angeliq Micro, you should immediately stop using the drug.
— pregnancy or breastfeeding (see section “Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding”);
- bleeding from the vagina of unspecified etiology;
- confirmed or suspected diagnosis of breast cancer or a history of breast cancer;
— confirmed or suspected diagnosis of a hormone-dependent precancerous disease or a hormone-dependent malignant tumor;
- liver tumors currently or in history (benign or malignant);
- severe liver diseases;
- severe kidney disease currently or in history or acute renal failure (until normalization of renal function indicators);
- acute arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism (for example, myocardial infarction, stroke), angina pectoris;
- deep vein thrombosis in the acute stage, venous thromboembolism (including pulmonary embolism) currently or in history;
— the presence of a high risk of venous and arterial thrombosis (see section “Special instructions”);
- identified predisposition to venous or arterial thrombosis, including resistance to activated protein C, antithrombin III deficiency, protein C deficiency, protein S deficiency, hyperhomocysteinemia, antibodies to phospholipids (anticardiolipin antibodies, lupus anticoagulant);
- adrenal insufficiency;
- untreated hyperplasia;
- porphyria;
- severe hypertriglyceridemia;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug Angeliq Micro;
- children and adolescents up to 18 years of age;
- congenital lactase deficiency, lactose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Carefully :
Angelique Micro should be prescribed with caution in the following diseases: congenital hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert, Dubin-Johnson and Rotor syndromes), cholestatic jaundice or cholestatic itching during a previous pregnancy, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, diabetes mellitus (see "Special Instructions").
It is necessary to take into account that estrogens alone or in combination with gestagens should be used with caution in the following diseases and conditions: the presence of risk factors for the development of thrombosis and thromboembolism in a family history (thromboembolic complications in close relatives at a young age), the presence of risk factors for the development of estrogen-dependent tumors (for example, 1st degree relatives with breast cancer), history of endometrial hyperplasia, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, obesity, systemic lupus erythematosus, dementia, gallbladder disease, retinal vascular thrombosis, moderate hypertriglyceridemia, edema in chronic heart failure, severe hyiocalcemia, endometriosis, bronchial asthma, epilepsy, migraine, liver hemangiomas, hyperkalemia, conditions predisposing to the development of hyperkalemia, taking medications that cause hyperkalemia - potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, ACE inhibitors, apgiotheisin II receptor antagonists and heparin.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
HRT is contraindicated during pregnancy or while breastfeeding. If pregnancy is detected while taking Angeliq Micro, the drug should be discontinued immediately.
Small amounts of sex hormones can be excreted in breast milk.
Use in children
The drug is contraindicated for use in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
Overdose
Acute toxicity studies have not revealed a risk of acute side effects when accidentally taking the drug in quantities many times higher than the daily therapeutic dose.
In clinical studies, the use of drospirenone up to 100 mg or combined estrogen/progestin drugs containing 4 mg estradiol was well tolerated.
Symptoms that may occur in case of overdose: nausea, vomiting, bleeding from the vagina.
There is no specific antidote, treatment is symptomatic.
Drug interactions
Long-term treatment with drugs that induce liver enzymes (for example, some anticonvulsants and antimicrobial drugs) may increase the clearance of sex hormones and reduce their clinical effectiveness, resulting in irregular bleeding. A similar property to induce liver enzymes has been found in hydantoins, barbiturates, primidone, carbamazepine and rifampicin, and the presence of this feature is also suggested in oxcarbazepine, topiramate, felbamate and griseofulvin. Maximum enzyme induction is usually observed no earlier than 2-3 weeks, but it may then persist for at least 4 weeks after discontinuation of the drug.
In rare cases, against the background of concomitant use of certain antibiotics (for example, penicillin and tetracycline groups), a decrease in the concentration of estradiol was observed.
The main metabolites of drospirenone are formed in plasma without the participation of the cytochrome P450 system. Therefore, the effect of inhibitors of the cytochrome P450 system on the metabolism of drospirenone is unlikely. However, CYP3A4 inhibitors (eg, cimetidine, ketoconazole, etc.) may inhibit the metabolism of estradiol.
Interaction of the drug AnzhelikMicro with other drugs
Based on in vitro interaction studies, as well as an in vivo study in female volunteers taking 3 mg of drospirenone per day in combination with omeprazole, simvastatin or midazolam, it can be concluded that a clinically significant interaction of drospirenone with cytochrome P450 on the metabolism of other medicinal substances is unlikely.
Pharmacodynamic interaction with antihypertensive drugs and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
An increase in serum potassium concentration with the combined use of Angeliq Micro and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or antihypertensive drugs is unlikely. The combined use of the above three types of drugs may lead to a slight increase in serum potassium concentrations, more pronounced in women with diabetes mellitus.
Interaction with alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption during HRT may increase circulating estradiol concentrations.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
On prescription.
Storage conditions and periods
At a temperature not higher than 30°C. Keep out of the reach of children. Shelf life: 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Use for liver dysfunction
In women with mild to moderate liver dysfunction, drospirenone is well tolerated.
The drug is contraindicated for use in women with severe liver dysfunction
Use for renal impairment
A small increase in drospirenone exposure was observed in women with mild to moderate renal impairment but is not expected to be clinically significant.
The drug is contraindicated for use in women with severe renal impairment
special instructions
Angeliq Micro is not used for contraception.
If pregnancy is suspected, you should stop taking the pills until pregnancy is ruled out (see section “Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding”).
If any of the following conditions/diseases or risk factors are present or worsening, before starting or continuing to take Angeliq Micro, you should evaluate the individual risk-benefit ratio of treatment, taking into account the possible need to discontinue it.
When prescribing HRT to women who have several risk factors for the development of thrombosis or a high degree of severity of one of the risk factors, the possibility of mutually enhancing the effect of risk factors and the prescribed treatment on the development of thrombosis should be taken into account. In such cases, the total value of the existing risk factors increases. If there is a high risk, Angeliq Micro is contraindicated.
Venous thromboembolism
A number of controlled randomized as well as epidemiological studies have revealed an increased relative risk of developing venous thromboembolism (VTE), i.e. deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, against the background of HRT. Therefore, when prescribing Angeliq Micro to women with risk factors for VTE, the risk-benefit ratio of treatment should be carefully weighed and discussed with the patient.
High risk factors for developing VTE include individual and family history (the presence of VTE in close relatives at a relatively young age may indicate a genetic predisposition) and obesity with a body mass index of more than 30 kg/m2. The risk of VTE also increases with age.
The possible role of varicose veins in the development of VTE remains controversial.
The risk of VTE may temporarily increase with prolonged immobilization, “major” elective and post-traumatic operations, or major trauma. In case of prolonged immobilization or planned surgery, the drug should be stopped 4-6 weeks before surgery; resumption of use is possible only after the woman’s motor activity is completely restored.
Treatment should be stopped immediately if symptoms of thrombotic disorders appear or if their occurrence is suspected.
It is necessary to assess the ratio of individual risk and benefit of treatment in women using HRT drugs in conjunction with anticoagulants.
Arterial thromboembolism
Randomized controlled trials with long-term use of conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) and medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) did not provide evidence of a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system. Large-scale clinical trials of the combination of CLE and MPA revealed a possible increase in the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) in the first year of use, followed by a lack of beneficial effect. One large clinical trial using CLE alone found a potential reduction in the incidence of CAD among women aged 50–59 years, but no overall benefit in the overall study population. As a secondary outcome, two large clinical trials using CLE either alone or in combination with MPA found a 30-40% increase in the risk of stroke. It is therefore unknown whether this increased risk applies to HRT preparations containing other types of estrogens and irogestogens or to non-oral routes of administration.
Endometrial cancer
With long-term estrogen monotherapy, the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia or carcinoma increases. The addition of drospirenone prevents the development of endometrial hyperplasia caused by estrogen. If there is a history of endometrial hyperplasia, estrogens alone or in combination with gestagens should be used with caution.
Mammary cancer
Clinical and observational studies have found an increase in the relative risk of developing breast cancer in women using HRT for several years. This may be due to earlier diagnosis, accelerated growth of an existing tumor during HRT, or a combination of both factors. The relative risk increases with duration of therapy but may be absent or reduced with estrogen-only treatment. This increase is comparable to the increased risk of breast cancer in women with a later onset of natural menopause, as well as with obesity and alcohol abuse. The increased risk gradually decreases to normal levels over several years after stopping HRT.
The increased risk of breast cancer has been suggested based on the results of more than 50 epidemiological studies (risk ranges from 1 to 2).
Two large randomized trials of CLE alone or in combination with MPL reported estimated risk ratios of 0.77 (95% confidence interval: 0.59 to 1.01) or 1.24 (95% confidence interval: 1.01 to 1.54) after approximately 6 years of use HRT. It is unknown whether this increased risk also applies to other HRT drugs. HRT increases mammographic breast density, which in some cases may have a negative effect on X-ray detection of breast cancer.
When prescribing Angeliq Micro to women with risk factors for estrogen-dependent tumors (for example, first-degree relatives with breast cancer), the risk-benefit ratio of treatment should be carefully weighed and discussed with the patient.
Ovarian cancer
A study of estrogen in combination with a progestin showed a statistically non-significant increase in the risk of ovarian cancer. The relative risk of developing ovarian cancer with conjugated estrogens with MPA compared with placebo was 1.58 (95% confidence interval: 0.77-3.24) after a median follow-up of 5.6 years. The absolute risk of conjugated estrogens with MPA compared with placebo was 4 versus 3 cases per 10,000 woman-years. Long-term use of estrogen-only HRT (5-10 years) was associated with a slightly increased risk of ovarian cancer. Long-term use of combination HRT drugs may have the same or slightly lower risk of developing ovarian cancer.
Liver tumor
During the use of sex hormones, which also include drugs for HRT, in rare cases benign, and even more rarely, malignant liver tumors were observed. In some cases, these tumors have led to intra-abdominal bleeding, which is life-threatening. If there is pain in the upper abdomen, an enlarged liver, or signs of intra-abdominal bleeding, the differential diagnosis should take into account the possibility of a liver tumor.
Cholelithiasis
It is known that estrogens increase the lithogenicity of bile. The risk of developing cholelithiasis increases 2-4 times when treated with estrogen.
Dementia
There is limited clinical trial data on a possible increased risk of dementia in women starting CLE-containing medications aged 65 years or older. As observed in studies, the risk may be reduced if CLE-containing HRT medications are started in early menopause.
Other conditions/diseases
Treatment should be stopped immediately if migraine-like pain or frequent and unusually severe headaches appear for the first time, as well as if other symptoms appear that are possible precursors of a thrombotic stroke of the brain.
The relationship between HRT and the development of clinically significant arterial hypertension has not been established. A slight increase in blood pressure has been described in women taking HRT; clinically significant increases are rare. However, in some cases, if persistent clinically significant arterial hypertension develops while taking HRT, discontinuation of HRT may be considered.
In renal failure, the ability to excrete potassium may be reduced. Taking drospirenone does not affect the concentration of potassium in the blood plasma in patients with mild to moderate forms of renal failure. The risk of developing hyperkalemia cannot theoretically be excluded only in the group of patients in whom the concentration of potassium in the blood plasma before treatment was determined at the upper limit of normal, and who additionally take potassium-sparing drugs.
For mild liver dysfunction, including various forms of hyperbilirubinemia, such as Dubin-Johnson syndrome or Rotor syndrome, medical supervision is necessary, as well as periodic liver function tests.
If liver function indicators deteriorate, Angeliq Micro should be discontinued.
In case of recurrence of cholestatic jaundice or cholestatic itching, which was observed for the first time during pregnancy or previous treatment with sex hormones, taking Angeliq Micro should be stopped immediately.
Special monitoring of women is necessary when triglyceride concentrations increase. In such cases, the use of HRT may cause a further increase in the concentration of triglycerides in the blood, which increases the risk of acute pancreatitis.
Although HRT may affect peripheral insulin resistance and glucose tolerance, there is usually no need to change the treatment regimen of diabetic patients when undergoing HRT. However, women with diabetes should be monitored when undergoing HRT.
Some patients may develop undesirable effects of estrogen stimulation, such as abnormal uterine bleeding. Frequent or persistent pathological uterine bleeding during treatment is an indication for examination of the endometrium in order to exclude an organic disease.
Under the influence of estrogens, uterine fibroids can increase in size. In this case, treatment should be stopped.
It is recommended to discontinue treatment if endometriosis relapses during HRT.
If prolactinoma is suspected, this disease should be excluded before starting treatment. If prolactinoma is detected, the patient should be under close medical supervision (including periodic assessment of prolactin concentrations).
In some cases, chloasma may occur, especially in women with a history of chloasma during pregnancy. During treatment with Angelique Micro, women with a tendency to develop chloasma should avoid prolonged exposure to the sun or ultraviolet radiation.
The following conditions/diseases may occur or worsen during HRT, and women with these conditions/diseases should be under medical supervision when undergoing HRT: epilepsy; benign breast tumor; bronchial asthma; migraine; porphyria; otosclerosis; systemic lupus erythematosus, chorea minor.
In women with hereditary forms of angioedema, exogenous estrogens may cause or worsen symptoms of angioedema.
Preclinical safety data
Preclinical data from routine repeated-dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenicity and reproductive toxicity studies do not indicate a particular risk to humans. However, it should be remembered that sex hormones can promote the growth of certain hormone-dependent tissues and tumors.
Medical examination and consultation
Before starting or resuming taking the drug Angeliq Micro, you should familiarize yourself in detail with the patient’s medical history and conduct a general medical and gynecological examination. The frequency and nature of such examinations should be based on existing standards of medical practice with the necessary consideration of the individual characteristics of each patient (but not less than once every 6 months) and should include measurement of blood pressure, assessment of the condition of the mammary glands, abdominal and pelvic organs, including cytological examination of the cervical epithelium.
Impact on laboratory results.
Taking sex hormones can affect biochemical indicators of liver, thyroid, adrenal and kidney function, plasma concentrations of transport proteins such as sex hormone-binding globulin and lipid/lipoprotein fractions, indicators of carbohydrate metabolism, coagulation and fibrinolysis.
Angelique Micro does not have a negative effect on glucose tolerance.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
Not found.
pharmachologic effect
A combined two-phase drug for hormone replacement therapy, containing micronized 17β-estradiol as an estrogenic component and dydrogesterone as a gestagenic component. Both components are analogues of female sex hormones (estradiol and progesterone).
Estradiol replenishes the deficiency of estrogen in the female body after menopause and provides effective relief of psycho-emotional and vegetative menopausal symptoms, such as hot flashes, increased sweating, sleep disturbances, increased nervous excitability, dizziness, headache, involution of the skin and mucous membranes, especially the genitourinary system (dryness) and irritation of the vaginal mucosa, pain during sexual intercourse).
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) with Femoston® prevents bone loss in the postmenopausal period caused by estrogen deficiency.
Taking Femoston® leads to a change in the lipid profile towards a decrease in the level of total cholesterol and LDL and an increase in HDL.
Dydrogesterone is a gestagen, effective when taken orally, which completely ensures the onset of the secretion phase in the endometrium, thereby reducing the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia and/or carcinogenesis (increased with the use of estrogens). Dydrogesterone does not have estrogenic, androgenic, anabolic or glucocorticoid activity.
Instructions:
Clinical and pharmacological group
23.042 (Anti-climacteric drug)
Release form, composition and packaging
The tablets are greyish-pink, round, biconvex, film-coated, with “DL” embossed in a regular hexagon on one side.
| 1 tab. | |
| estradiol (as hemihydrate) | 1 mg |
| drospirenone | 2 mg |
Excipients: lactose monohydrate, corn starch, pregelatinized corn starch, povidone K25, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, macrogol 6000, talc, titanium dioxide, red iron oxide dye.
28 pcs. - blisters (1) - cardboard packs. 28 pcs. - blisters (3) - cardboard packs.
pharmachologic effect
Anticlimacteric drug.
The drug Angelique® contains estrogen - estradiol, which is identical to natural 17β-estradiol. The drug Angeliq® also contains a spironolactone derivative - drospirenone, which has a progestational, antigonadotropic and antiandrogenic, as well as antimineralocorticoid effect.
Angeliq® is a combination drug for hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for postmenopausal menopausal disorders (natural menopause, hypogonadism, castration or premature ovarian failure), including vasomotor symptoms (such as hot flashes, increased sweating), sleep disturbances, decreased mood , irritability, atrophic changes in the genitourinary tract in women with a unremoved uterus. Continuous hormone replacement therapy with Angeliq® avoids regular withdrawal bleeding, which is observed with cyclic or phase HRT.
Estradiol replenishes the deficiency of estrogen in the female body after menopause and provides effective treatment of psycho-emotional and autonomic menopausal symptoms (such as hot flashes, increased sweating, sleep disturbances, increased nervous excitability, irritability, palpitations, cardialgia, dizziness, headache, decreased libido , muscle and joint pain); involution of the skin and mucous membranes, especially the genitourinary system (urinary incontinence, dryness and irritation of the vaginal mucosa, pain during sexual intercourse).
Estradiol prevents bone loss caused by estrogen deficiency, which is mainly associated with suppression of osteoclast function and a shift in the process of bone remodeling towards bone formation. Long-term use of HRT has been shown to reduce the risk of peripheral bone fractures in women after menopause. When HRT is discontinued, the rate of bone mass decline is comparable to that characteristic of the period immediately after menopause. It has not been proven that HRT can restore bone mass to premenopausal levels.
HRT also has a beneficial effect on the collagen content of the skin, as well as its density, and may also slow down the formation of wrinkles.
In addition, due to the antiandrogenic properties of drospirenone, Angeliq® has a therapeutic effect on androgen-dependent diseases such as acne, seborrhea, androgenic alopecia.
Drospirenone has antimineralocorticoid activity, increases the excretion of sodium and water, which can prevent increased blood pressure, weight gain, edema, breast tenderness and other symptoms associated with fluid retention. After 12 weeks of using the drug Angeliq®, a slight decrease in blood pressure was observed (systolic - on average by 2-4 mm Hg, diastolic - by 1-3 mm Hg). The effect on blood pressure was more pronounced in women with arterial hypertension. After 12 months of using the drug Angeliq®, the average body weight remained unchanged or decreased by 1.1-1.2 kg.
Drospirenone is devoid of any androgenic, estrogenic, glucocorticosteroid and anti-glucocorticosteroid activity and does not affect glucose tolerance or insulin resistance. This, combined with its antimineralocorticoid and antiandrogenic effects, gives drospirenone a biochemical and pharmacological profile similar to natural progesterone.
Taking Angeliq® leads to a decrease in total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol, as well as a slight increase in triglyceride levels. Drospirenone reduces the increase in triglyceride concentrations caused by estradiol.
The addition of drospirenone prevents the development of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer.
Observational studies suggest that among postmenopausal women, the incidence of colon cancer is reduced when using HRT. The mechanism of action is still unclear.
Pharmacokinetics
Estradiol
Suction
After taking the drug orally, estradiol is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Subjects to a “first pass” effect with the formation of estrone, estriol and estrone sulfate. Bioavailability when taken orally is about 5% and is independent of food intake. Cmax of estradiol in serum is approximately 22 pg/ml and is achieved after 6-8 hours. Food intake does not affect the bioavailability of estradiol.
Distribution
Binds to albumin and sex steroid binding globulin (GSBS). The free fraction of estradiol in serum is approximately 1-12%, and bound SHPS is 40-45%. The apparent Vd after a single intravenous injection is about 1 l/kg.
After repeated use, the concentration of estradiol is approximately 2 times higher than after a single dose, while Css varies from 20 pg/ml to 43 pg/ml. After discontinuation of use, levels of estradiol and estrone return to baseline values within approximately 5 days.
Metabolism
Estradiol is metabolized primarily in the liver, partially in the intestines, kidneys, skeletal muscles and target organs with the formation of estrone, estriol, catechol estrogens, as well as sulfate and glucuronide conjugates of these compounds, which have significantly less estrogenic activity compared to estradiol or are completely inactive .
Removal
Serum clearance of estradiol is about 30 ml/min/kg. Estradiol metabolites are excreted in urine and bile. T1/2 is approximately 24 hours.
Drospirenone
Suction
After oral administration, drospirenone is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability is 76-85% and does not depend on food intake. Food intake does not affect the bioavailability of drospirenone.
Distribution
After a single or multiple dose of 2 mg, Cmax in serum is reached after 1 hour and is about 22 ng/ml. After this, a biphasic decrease in the concentration of drospirenone in the serum is observed with a final half-life of about 35-39 hours. Drospirenone binds to albumin and does not bind to SHBG and corticoid-binding globulin (CBG); about 3-5% is the free fraction.
Due to the long T1/2 Css is achieved after 10 days of daily use of the drug Angeliq® and exceeds the concentration after a single dose by 2-3 times.
Metabolism
The main metabolites are the acid form of drospirenone and 4,5-dihydro-drospirenone-3-sulfate, which are formed without the participation of isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system.
Removal
The serum clearance of drospirenone is 1.2-1.5 ml/min/kg. Some part of the received dose is excreted unchanged. Most of the dose is excreted by the kidneys and through the intestines in the form of metabolites in a ratio of 1.2:1.4; T1/2 - about 40 hours.
Dosage
If a woman is not taking estrogen or switching to Angeliq® from another combination drug for continuous use, she can begin treatment at any time. Patients who switch to Angeliq from a combination drug for cyclic HRT should begin taking it after the end of withdrawal bleeding.
Each package is designed for 28 days of use.
The drug should be taken daily, 1 tablet. After finishing taking 28 tablets from the current package, start a new package of Angelique® the next day, taking the first tablet on the same day of the week as the first tablet from the previous package.
The tablet is swallowed whole with a small amount of liquid.
The time of day a woman takes the drug does not matter, but if she starts taking the pills at a specific time, she should continue to do so at that time.
If you miss a dose, take the missed tablet as soon as possible. If more than 24 hours have passed after the usual dosing time, you should not take an additional tablet. If you miss several tablets, vaginal bleeding may develop.
Overdose
Acute toxicity studies have not revealed a risk of acute side effects when accidentally taking the drug in quantities many times higher than the daily therapeutic dose. In clinical studies, the use of drospirenone up to 100 mg or combined estrogen/progestin drugs containing 4 mg estradiol was well tolerated.
Symptoms that may occur in case of overdose: nausea, vomiting, bleeding from the vagina.
Treatment: there is no specific antidote; if necessary, symptomatic therapy is carried out.
Drug interactions
Long-term treatment with drugs that induce liver enzymes (for example, some anticonvulsants and antimicrobial drugs) may increase the clearance of sex hormones and reduce their clinical effectiveness. A similar property - to induce liver enzymes - has been found in hydantoins, barbiturates, primidone, carbamazepine and rifampicin, and the presence of this feature is also suggested in oxcarbazepine, topiramate, felbamate and griseofulvin. Maximum enzyme induction is usually observed no earlier than 2-3 weeks, but it may then persist for at least 4 weeks after discontinuation of the drug.
In rare cases, a decrease in estradiol levels has been observed during concomitant use of certain antibiotics (for example, penicillins and tetracyclines).
The main metabolites of drospirenone are formed in plasma without the participation of the cytochrome P450 system. Therefore, the effect of inhibitors of the cytochrome P450 system on the metabolism of drospirenone is unlikely. However, CYP3A4 inhibitors (eg, cimetidine, ketoconazole) may inhibit the metabolism of estradiol.
Based on in vitro interaction studies, as well as an in vivo study in female volunteers taking omeprazole, simvastatin and midazolam as markers, it can be concluded that the effect of drospirenone 3 mg on the metabolism of other medicinal substances is unlikely.
The use of Angelica in women receiving antihypertensive therapy (for example, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, hydrochlorothiazide) may slightly increase the antihypertensive effect.
An increase in serum potassium levels when taking Angelica in combination with NSAIDs or antihypertensive drugs is unlikely. The combined use of the above three types of drugs may lead to a slight increase in serum potassium levels, more pronounced in women with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Excessive alcohol consumption during HRT may increase circulating estradiol levels.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
HRT is contraindicated during pregnancy or breastfeeding. If pregnancy is detected while taking Angeliq®, the drug should be discontinued immediately.
Small amounts of sex hormones can be excreted in breast milk.
Side effects
During the first few months of therapy, breakthrough bleeding and spotting may occur (> 10%). The frequency of bleeding decreases with the duration of therapy. A very common symptom is breast pain (>10%). The incidence of adverse events was classified as follows: often (≥1/10, <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1000, <1/100), rare (<1/10,000).
From the reproductive system: often - benign neoplasms of the mammary gland, enlarged mammary glands, enlarged uterine fibroids, benign neoplasms of the cervix, menstrual irregularities, discharge from the genital tract; uncommon - breast cancer, endometrial hyperplasia, benign neoplasms of the uterus, fibrocystic mastopathy, diseases of the uterus, ovaries, cervix, pelvic pain, vulvovaginal disorders, vaginal candidiasis, vaginitis, vaginal dryness; rarely - salpingitis.
From the digestive system: often - abdominal pain, nausea, abdominal enlargement; Uncommon: gastrointestinal disorders, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, dry mouth, bloating, perversion of taste, abnormal liver test results; rarely - cholelithiasis.
From the hematopoietic system: rarely - anemia.
From the side of the central nervous system: often - depression, emotional lability, irritability, headache; uncommon - migraine, sleep disturbances, anxiety, decreased libido, paresthesia, impaired ability to concentrate, dizziness; rarely - vertigo.
From the organ of vision: infrequently - eye diseases, visual impairment.
On the part of the hearing organ: rarely - ringing in the ears.
From the cardiovascular system: uncommon - palpitations, embolism, thrombophlebitis, venous thrombosis, edema, arterial hypertension, varicose veins.
From the respiratory system: infrequently - shortness of breath.
Dermatological reactions: uncommon - skin and hair diseases, acne, alopecia, itching, rash, hirsutism.
From the side of metabolism: infrequently - changes in body weight (loss or increase), anorexia, increased appetite, hyperlipidemia.
From the musculoskeletal system: infrequently - pain in the limbs, back pain, arthralgia, muscle spasms; rarely - myalgia.
From the urinary system: infrequently - diseases and infections of the urinary tract.
Other: often - asthenia, local edema; uncommon - generalized edema, chest pain, malaise, increased sweating; rarely - chills.
The following adverse events have been reported in connection with taking HRT drugs: erythema nodosum or multiforme, chloasma, purpura, breast tenderness and tension, increased fatigue, contact lens intolerance.
In women with arterial hypertension, in clinical studies on the use of the drug Angeliq, the following adverse events were noted, possibly associated with taking Angeliq: heart failure, atrial flutter, prolongation of the QT interval, cardiomegaly, hyperkalemia, increased blood aldosterone levels.
Storage conditions and periods
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Shelf life: 5 years.
Indications
— hormone replacement therapy for menopausal disorders in postmenopause;
— prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to start HRT if you have any of the conditions listed below. If any of these conditions occur during HRT, you should immediately stop using the drug.
- vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology;
- confirmed or suspected breast cancer or a history of breast cancer;
— confirmed or suspected diagnosis of a hormone-dependent precancerous disease or a hormone-dependent malignant tumor;
- benign or malignant liver tumors (including in history);
- severe liver diseases;
- severe kidney disease currently or in history or acute renal failure (until normalization of renal function indicators);
- acute arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism (including those leading to myocardial infarction, stroke);
— deep vein thrombosis in the acute stage, venous thromboembolism currently or in history;
- pulmonary embolism;
- severe hypertriglyceridemia;
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Angeliq® should be prescribed with caution in the following diseases: arterial hypertension, congenital hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert, Dubin-Johnson and Rotor syndromes), cholestatic jaundice or cholestatic pruritus during previous pregnancy, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, diabetes mellitus.
It is necessary to take into account that estrogens alone or in combination with gestagens should be used with caution in the following diseases and conditions: smoking, hypercholesterolemia, obesity, systemic lupus erythematosus, dementia, gallbladder disease, retinal vascular thrombosis, moderate hypertriglyceridemia, edema in chronic heart disease insufficiency, severe hypocalcemia, endometriosis, bronchial asthma, epilepsy, migraine, porphyria, liver hemangiomas, hyperkalemia, conditions predisposing to the development of hyperkalemia, taking drugs that cause hyperkalemia (potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists and heparin) .
special instructions
Angeliq® is not used for contraception.
If contraception is necessary, non-hormonal methods should be used (with the exception of calendar and temperature methods). If you suspect pregnancy, you should stop taking the pills until pregnancy has been ruled out.
If any of the following conditions or risk factors are present or worsening, the individual risk-benefit ratio of treatment should be assessed before starting or continuing HRT.
Venous thromboembolism
A number of controlled randomized as well as epidemiological studies have revealed an increased relative risk of developing venous thromboembolism (VTE) during HRT, i.e. deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. Therefore, when prescribing HRT to women with risk factors for VTE, the risk-benefit ratio of treatment should be carefully weighed and discussed with the patient.
Risk factors for developing VTE include individual and family history (the presence of VTE in first-degree relatives at a relatively young age may indicate a genetic predisposition) and severe obesity. The risk of VTE also increases with age. The possible role of varicose veins in the development of VTE remains controversial.
The risk of VTE may temporarily increase with prolonged immobilization, “major” elective and trauma surgeries, or major trauma. Depending on the cause or duration of immobilization, the question of the advisability of temporarily stopping HRT should be decided.
Treatment should be stopped immediately if symptoms of thrombotic disorders appear or if their occurrence is suspected.
Arterial thromboembolism
Randomized controlled trials with long-term use of conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) and medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) did not provide evidence of a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system. In large-scale clinical trials of this compound, a possible increase in the risk of coronary heart disease in the first year of use was identified, followed by a lack of beneficial effect. One large clinical trial using CLE alone found a potential reduction in the incidence of CAD among women aged 50–59 years, but no overall benefit in the overall study population. As a secondary outcome, two large clinical trials using CLE as monotherapy or in combination with MPA found a 30-40% increase in the risk of stroke. It is therefore unknown whether this increased risk applies to HRT products containing other types of estrogens and progestogens or to non-oral routes of administration.
Endometrial cancer
With long-term estrogen monotherapy, the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia or carcinoma increases. Studies have confirmed that the addition of gestagens reduces the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer.
Mammary cancer
Clinical trial data and observational studies have found an increase in the relative risk of developing breast cancer in women using HRT for several years. This may be due to earlier diagnosis, accelerated growth of an existing tumor during HRT, or a combination of both factors.
The relative risk increases with duration but may be absent or reduced with estrogen-only treatment. This increase is comparable to the increase in the risk of breast cancer in women with each year of delay in the onset of natural menopause, as well as with obesity and alcohol abuse. The increased risk gradually decreases to normal levels within a few (but most of five) years after stopping HRT.
The increased risk of breast cancer has been suggested based on the results of more than 50 epidemiological studies (risk ranges from 1 to 2).
According to research, breast cancer detected in women taking HRT is usually more differentiated than in women not taking it.
Evidence regarding the spread of breast cancer beyond the breast is controversial.
Two large randomized trials of CLE alone or chronically combined with MPA reported estimated risk ratios of 0.77 (95% CI: 0.59–1.01) or 1.24 (95% CI: 1.01–1.54) after approximately 6 years of HRT use. . It is unknown whether this increased risk also applies to other HRT products.
HRT increases mammographic breast density, which in some cases may have a negative effect on X-ray detection of breast cancer.
Liver tumor
During the use of sex steroids, which include drugs for HRT, in rare cases benign, and even more rarely, malignant liver tumors were observed. In some cases, these tumors have resulted in life-threatening intra-abdominal bleeding. If there is pain in the upper abdomen, an enlarged liver, or signs of intra-abdominal bleeding, the differential diagnosis should take into account the possibility of a liver tumor.
Cholelithiasis
It is known that estrogens increase the lithogenicity of bile. Some women are predisposed to developing gallstones when treated with estrogen.
Dementia
There is limited clinical trial data with CLE-containing products showing a possible risk of increased numbers of women with this condition when starting hormone replacement therapy at age 65 years or older. The risk may be reduced if HRT is started early in menopause, as has been observed in studies. It is not known whether this applies to other HRT products.
Other states
Treatment should be stopped immediately if migraine-like or frequent and unusually severe headaches appear for the first time, as well as if other symptoms appear - possible precursors of a thrombotic stroke of the brain.
The relationship between HRT and the development of clinically significant arterial hypertension has not been established. A slight increase in blood pressure has been described in women taking HRT; clinically significant increases are rare. However, in some cases, if persistent clinically significant arterial hypertension develops while taking HRT, discontinuation of HRT may be considered. In women with high blood pressure, there may be a slight decrease in blood pressure while taking the drug Angeliq®. In women with normal blood pressure, significant changes in blood pressure are not expected.
In renal failure, the ability to excrete potassium may be reduced. Taking drospirenone does not affect serum potassium concentrations in patients with mild to moderate forms of renal failure. The risk of developing hyperkalemia cannot theoretically be excluded only in the group of patients whose serum potassium concentration before treatment was determined to be at the upper limit of normal, and who additionally take potassium-sparing drugs.
For mild liver dysfunction, incl. Various forms of hyperbilirubinemia, such as Dubin-Johnson syndrome or Rotor syndrome, require medical supervision, as well as periodic liver function tests. If liver function tests worsen, HRT should be discontinued.
If cholestatic jaundice or cholestatic pruritus recurs, first observed during pregnancy or prior treatment with sex steroid hormones, HRT should be stopped immediately.
Special monitoring is required for women with moderately elevated triglyceride levels. In such cases, the use of HRT may cause a further increase in blood triglyceride levels, which increases the risk of acute pancreatitis.
Although HRT may affect peripheral insulin resistance and glucose tolerance, there is usually no need to change the treatment regimen of diabetic patients when undergoing HRT. However, women with diabetes should be monitored when undergoing HRT.
Some patients under the influence of HRT may develop undesirable manifestations of estrogen stimulation, for example, abnormal uterine bleeding. Frequent or persistent pathological uterine bleeding during treatment is an indication for examination of the endometrium in order to exclude an organic disease.
Under the influence of estrogens, uterine fibroids can increase in size. In this case, treatment should be stopped.
It is recommended to discontinue treatment if endometriosis relapses during HRT.
If prolactinoma is suspected, this disease should be excluded before starting treatment.
In some cases, chloasma may occur, especially in women with a history of chloasma during pregnancy. During HRT, women prone to chloasma should avoid prolonged exposure to the sun or ultraviolet radiation.
The following conditions may occur or be aggravated by HRT and women with these conditions should be under medical supervision when undergoing HRT: epilepsy, benign breast tumor, bronchial asthma, migraine, porphyria, otosclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, chorea minor.
In women with hereditary forms of angioedema, exogenous estrogens may cause or worsen symptoms of angioedema.
Preclinical safety data
Preclinical data from routine repeated-dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenicity and reproductive toxicity studies do not indicate a particular risk to humans. However, it should be remembered that sex steroids can promote the growth of certain hormone-dependent tissues and tumors.
Medical examination
Before starting or resuming HRT, a woman is recommended to undergo a thorough general medical examination (including examination of the pelvic organs, abdomen and blood pressure measurement) and gynecological examination (including examination of the mammary glands and cytological examination of cervical mucus), and exclude pregnancy. In addition, disorders of the blood coagulation system should be excluded. Control examinations should be carried out periodically. The scope of additional studies and the frequency of follow-up examinations are determined individually. Typically, follow-up examinations should be carried out at least once a year.
Impact on laboratory results
Taking sex steroids can affect the biochemical parameters of the liver, thyroid gland, adrenal glands and kidneys, the plasma content of transport proteins, such as globulin that binds sex hormones and lipid/lipoprotein fractions, indicators of carbohydrate metabolism, coagulation and fibrinolysis. Angeliq® does not have a negative effect on glucose tolerance.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Not found.
Use for renal impairment
The use of the drug is contraindicated in case of severe kidney disease until laboratory parameters are normalized (including in medical history).
Use for liver dysfunction
The use of the drug is contraindicated for benign or malignant liver tumors (including a history), severe liver diseases.
Angeliq should be prescribed with caution for congenital hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert, Dubin-Johnson and Rotor syndromes), cholestatic jaundice or cholestatic itching. If liver function tests worsen, HRT should be discontinued.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
The drug is available with a prescription.
Pharmacokinetics
After taking the drug orally, micronized estradiol is easily absorbed.
Metabolism and excretion
Estradiol is metabolized in the liver to form estrone and estrone sulfate. Estrone sulfate undergoes intrahepatic metabolism.
Glucuronides of estrone and estradiol are excreted primarily in the urine.
In the human body, dydrogesterone is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Metabolized completely. The main metabolite of dydrogesterone is 20-dihydrodydrogesterone, present in urine mainly as a glucuronic acid conjugate.
Complete elimination of dydrogesterone occurs after 72 hours.
Dosage regimen
Femoston® 1/10 is taken 1 tablet per day (preferably at the same time of day) without interruption, regardless of meals.
In the first 14 days of a 28-day cycle, take 1 white tablet daily (from half the package with an arrow marked with the number “1”) containing 1 mg of estradiol, and in the remaining 14 days - 1 gray tablet daily (from half the package with an arrow marked "2") containing 1 mg of estradiol and 10 mg of dydrogesterone.
Femoston® 2/10 is taken 1 tablet per day (preferably at the same time of day) without interruption, regardless of meals.
In the first 14 days of a 28-day cycle, take 1 pink tablet daily (from half the package with an arrow marked "1") containing 2 mg estradiol, and in the remaining 14 days - 1 light yellow tablet daily (from half a package with an arrow marked “2”) containing 2 mg of estradiol and 10 mg of dydrogesterone.
Side effect
From the reproductive system: possible soreness of the mammary glands, breakthrough bleeding, pain in the pelvic area; sometimes - changes in cervical erosion, changes in secretion, dysmenorrhea; rarely - enlarged mammary glands, premenstrual-like syndrome; in some cases (0.1-1%) - a change in libido.
From the digestive system: possible nausea, flatulence, abdominal pain; sometimes - cholecystitis; rarely (0.01-0.1%) - impaired liver function, in some cases accompanied by asthenia, malaise, jaundice or abdominal pain; very rarely - vomiting.
From the central nervous system: headache, migraine (1-10%); sometimes (0.1-1%) - dizziness, nervousness, depression; very rarely - chorea.
From the cardiovascular system: sometimes - venous thromboembolism; very rarely - myocardial infarction.
From the hematopoietic system: very rarely (
Angelique micro
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
HRT is contraindicated during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
If pregnancy is detected while taking Angeliq Micro, the drug should be discontinued immediately. Small amounts of sex hormones can be excreted in breast milk.
Use for liver dysfunction
In women with mild to moderate liver dysfunction, drospirenone is well tolerated.
The drug is contraindicated for use in women with severe liver dysfunction
Use for renal impairment
A small increase in drospirenone exposure was observed in women with mild to moderate renal impairment but is not expected to be clinically significant.
The drug is contraindicated for use in women with severe renal impairment
Use in children
The drug is contraindicated for use in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
special instructions
Angeliq Micro is not used for contraception.
If pregnancy is suspected, you should stop taking the pills until pregnancy is ruled out (see section “Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding”).
If any of the following conditions/diseases or risk factors are present or worsening, before starting or continuing to take Angeliq Micro, you should evaluate the individual risk-benefit ratio of treatment, taking into account the possible need to discontinue it.
When prescribing HRT to women who have several risk factors for the development of thrombosis or a high degree of severity of one of the risk factors, the possibility of mutually enhancing the effect of risk factors and the prescribed treatment on the development of thrombosis should be taken into account. In such cases, the total value of the existing risk factors increases. If there is a high risk, Angeliq Micro is contraindicated.
Venous thromboembolism
A number of controlled randomized as well as epidemiological studies have revealed an increased relative risk of developing venous thromboembolism (VTE), i.e. deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, against the background of HRT. Therefore, when prescribing Angeliq Micro to women with risk factors for VTE, the risk-benefit ratio of treatment should be carefully weighed and discussed with the patient.
High risk factors for developing VTE include individual and family history (the presence of VTE in close relatives at a relatively young age may indicate a genetic predisposition) and obesity with a body mass index of more than 30 kg/m2. The risk of VTE also increases with age.
The possible role of varicose veins in the development of VTE remains controversial.
The risk of VTE may temporarily increase with prolonged immobilization, “major” elective and post-traumatic operations, or major trauma. In case of prolonged immobilization or planned surgery, the drug should be stopped 4-6 weeks before surgery; resumption of use is possible only after the woman’s motor activity is completely restored.
Treatment should be stopped immediately if symptoms of thrombotic disorders appear or if their occurrence is suspected.
It is necessary to assess the ratio of individual risk and benefit of treatment in women using HRT drugs in conjunction with anticoagulants.
Arterial thromboembolism
Randomized controlled trials with long-term use of conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) and medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) did not provide evidence of a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system. Large-scale clinical trials of the combination of CLE and MPA revealed a possible increase in the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) in the first year of use, followed by a lack of beneficial effect. One large clinical trial using CLE alone found a potential reduction in the incidence of CAD among women aged 50–59 years, but no overall benefit in the overall study population. As a secondary outcome, two large clinical trials using CLE either alone or in combination with MPA found a 30-40% increase in the risk of stroke. It is therefore unknown whether this increased risk applies to HRT preparations containing other types of estrogens and irogestogens or to non-oral routes of administration.
Endometrial cancer
With long-term estrogen monotherapy, the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia or carcinoma increases. The addition of drospirenone prevents the development of endometrial hyperplasia caused by estrogen. If there is a history of endometrial hyperplasia, estrogens alone or in combination with gestagens should be used with caution.
Mammary cancer
Clinical and observational studies have found an increase in the relative risk of developing breast cancer in women using HRT for several years. This may be due to earlier diagnosis, accelerated growth of an existing tumor during HRT, or a combination of both factors. The relative risk increases with duration of therapy but may be absent or reduced with estrogen-only treatment. This increase is comparable to the increased risk of breast cancer in women with a later onset of natural menopause, as well as with obesity and alcohol abuse. The increased risk gradually decreases to normal levels over several years after stopping HRT.
The increased risk of breast cancer has been suggested based on the results of more than 50 epidemiological studies (risk ranges from 1 to 2).
Two large randomized trials of CLE alone or in combination with MPL reported estimated risk ratios of 0.77 (95% confidence interval: 0.59 to 1.01) or 1.24 (95% confidence interval: 1.01 to 1.54) after approximately 6 years of use HRT. It is unknown whether this increased risk also applies to other HRT drugs. HRT increases mammographic breast density, which in some cases may have a negative effect on X-ray detection of breast cancer.
When prescribing Angeliq Micro to women with risk factors for estrogen-dependent tumors (for example, first-degree relatives with breast cancer), the risk-benefit ratio of treatment should be carefully weighed and discussed with the patient.
Ovarian cancer
A study of estrogen in combination with a progestin showed a statistically non-significant increase in the risk of ovarian cancer. The relative risk of developing ovarian cancer with conjugated estrogens with MPA compared with placebo was 1.58 (95% confidence interval: 0.77-3.24) after a median follow-up of 5.6 years. The absolute risk of conjugated estrogens with MPA compared with placebo was 4 versus 3 cases per 10,000 woman-years. Long-term use of estrogen-only HRT (5-10 years) was associated with a slightly increased risk of ovarian cancer. Long-term use of combination HRT drugs may have the same or slightly lower risk of developing ovarian cancer.
Liver tumor
During the use of sex hormones, which also include drugs for HRT, in rare cases benign, and even more rarely, malignant liver tumors were observed. In some cases, these tumors have led to intra-abdominal bleeding, which is life-threatening. If there is pain in the upper abdomen, an enlarged liver, or signs of intra-abdominal bleeding, the differential diagnosis should take into account the possibility of a liver tumor.
Cholelithiasis
It is known that estrogens increase the lithogenicity of bile. The risk of developing cholelithiasis increases 2-4 times when treated with estrogen.
Dementia
There is limited clinical trial data on a possible increased risk of dementia in women starting CLE-containing medications aged 65 years or older. As observed in studies, the risk may be reduced if CLE-containing HRT medications are started in early menopause.
Other conditions/diseases
Treatment should be stopped immediately if migraine-like pain or frequent and unusually severe headaches appear for the first time, as well as if other symptoms appear that are possible precursors of a thrombotic stroke of the brain.
The relationship between HRT and the development of clinically significant arterial hypertension has not been established. A slight increase in blood pressure has been described in women taking HRT; clinically significant increases are rare. However, in some cases, if persistent clinically significant arterial hypertension develops while taking HRT, discontinuation of HRT may be considered.
In renal failure, the ability to excrete potassium may be reduced. Taking drospirenone does not affect the concentration of potassium in the blood plasma in patients with mild to moderate forms of renal failure. The risk of developing hyperkalemia cannot theoretically be excluded only in the group of patients in whom the concentration of potassium in the blood plasma before treatment was determined at the upper limit of normal, and who additionally take potassium-sparing drugs.
For mild liver dysfunction, including various forms of hyperbilirubinemia, such as Dubin-Johnson syndrome or Rotor syndrome, medical supervision is necessary, as well as periodic liver function tests.
If liver function indicators deteriorate, Angeliq Micro should be discontinued.
In case of recurrence of cholestatic jaundice or cholestatic itching, which was observed for the first time during pregnancy or previous treatment with sex hormones, taking Angeliq Micro should be stopped immediately.
Special monitoring of women is necessary when triglyceride concentrations increase. In such cases, the use of HRT may cause a further increase in the concentration of triglycerides in the blood, which increases the risk of acute pancreatitis.
Although HRT may affect peripheral insulin resistance and glucose tolerance, there is usually no need to change the treatment regimen of diabetic patients when undergoing HRT. However, women with diabetes should be monitored when undergoing HRT.
Some patients may develop undesirable effects of estrogen stimulation, such as abnormal uterine bleeding. Frequent or persistent pathological uterine bleeding during treatment is an indication for examination of the endometrium in order to exclude an organic disease.
Under the influence of estrogens, uterine fibroids can increase in size. In this case, treatment should be stopped.
It is recommended to discontinue treatment if endometriosis relapses during HRT.
If prolactinoma is suspected, this disease should be excluded before starting treatment. If prolactinoma is detected, the patient should be under close medical supervision (including periodic assessment of prolactin concentrations).
In some cases, chloasma may occur, especially in women with a history of chloasma during pregnancy. During treatment with Angelique Micro, women with a tendency to develop chloasma should avoid prolonged exposure to the sun or ultraviolet radiation.
The following conditions/diseases may occur or worsen during HRT, and women with these conditions/diseases should be under medical supervision when undergoing HRT: epilepsy; benign breast tumor; bronchial asthma; migraine; porphyria; otosclerosis; systemic lupus erythematosus, chorea minor.
In women with hereditary forms of angioedema, exogenous estrogens may cause or worsen symptoms of angioedema.
Preclinical safety data
Preclinical data from routine repeated-dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenicity and reproductive toxicity studies do not indicate a particular risk to humans. However, it should be remembered that sex hormones can promote the growth of certain hormone-dependent tissues and tumors.
Medical examination and consultation
Before starting or resuming taking the drug Angeliq Micro, you should familiarize yourself in detail with the patient’s medical history and conduct a general medical and gynecological examination. The frequency and nature of such examinations should be based on existing standards of medical practice with the necessary consideration of the individual characteristics of each patient (but not less than once every 6 months) and should include measurement of blood pressure, assessment of the condition of the mammary glands, abdominal and pelvic organs, including cytological examination of the cervical epithelium.
Impact on laboratory results.
Taking sex hormones can affect biochemical indicators of liver, thyroid, adrenal and kidney function, plasma concentrations of transport proteins such as sex hormone-binding globulin and lipid/lipoprotein fractions, indicators of carbohydrate metabolism, coagulation and fibrinolysis.
Angelique Micro does not have a negative effect on glucose tolerance.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
Not found.
Instructions for use
Femoston is a combination drug that is used for hormonal replacement treatment .
In the composition of the drug, estradiol is its estrogenic component, and dydrogesterone is a gestagenic component.
Estradiol acts as a component that compensates for the lack of estrogens (hormones) after the onset of menopause and provides the necessary treatment for vegetative and psycho-emotional manifestations :
- hyperhidrosis (increased sweating);
- feeling of "hot flashes";
- lack of oxygen in brain tissue;
- restless sleep;
- migraine;
- dryness of the vaginal mucosa, etc.
Estradiol can cause cyclic processes in the tissues of the vagina, cervix and uterus itself, due to which their elasticity will be maintained at the proper level, as well as the tone of the genitourinary tract. This component of the drug is aimed at preventing damage to the integrity of bones and loss of their strength, helping to preserve bone tissue.
Indications for use
Femoston is used for:
- the need for hormonal replacement treatment during the physiological onset of menopause or its development after surgical treatment
- prevention of changes in bone density in women after menopause.