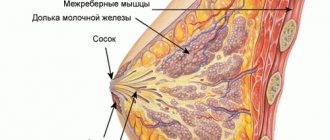
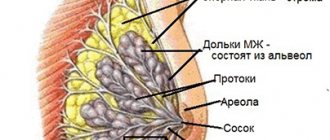
The anatomical and functional basis of the mammary glands are lobules capable of producing a special secretion for feeding a newborn baby: in the postpartum period, glandular tissue in the breast ensures milk production. Breast adenosis is one of the variants of mastopathy, in which the tissue structure is dominated by an increased number (hyperplasia) of glandular lobules in the absence of lactation. The disease most often occurs in young women who delay childbearing and refuse breastfeeding.
ICD 10 diagnosis statistics
ICD 10 (No. 60-64) diseases of the mammary glands are subject to careful statistical analysis. This is one of the reasons why a unified classification was introduced. According to the latest data from the World Health Organization, among the female population of the world, up to 40% of women suffer from mastopathy, and more than half of all cases (up to 58%) are combined with gynecological disorders. Of particular interest is the fact that many breast diseases are also precancerous conditions. The incidence and mortality rate from breast cancer is increasing every year, even despite the enormous advances in medicine in the field of early diagnosis and effective treatment. The lion's share of cases occur in developed countries.
Classification approaches to the diagnosis of ICD No. 10
The internationally accepted classification ICD No. 10 is also used in our country. Based on it, the following are distinguished:
· N 60 – Benign growths of the mammary gland. Mastopathy belongs to this group.
· N 61 — Inflammatory processes. These include carbuncle, mastitis, and abscess.
· N 62 – Breast enlargement.
· N 63 – Unspecified volumetric processes in the chest (nodules and nodules).
· N 64 – Other pathologies.
Each of these diseases has its own causes, characteristic clinical picture, methods of diagnosis and treatment. Let's talk about this now.
Diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the glandular component
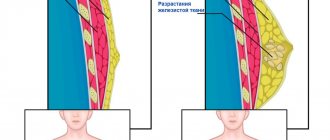
Any variant of the hyperplastic process can become the basis for precancer. Mastopathy of a diffuse or focal nature, in which adenosis occurs in the breast (enlargement of the glandular part of the tissue), is a risk factor for the development of fibroadenoma and diffuse forms of neoplasia of the mammary glands.
Any of the variants of mammary gland adenosis is a borderline state between normal and pathological, occurring in young women (age from 16 to 30 years). It is important to detect the problem in a timely manner in order to prevent the development of dangerous conditions in the breast: the best prevention of adenosis and mastopathy is pregnancy and long-term breastfeeding.
Clinical picture of the diagnosis
The disease can manifest itself with various signs.
But the leading main symptoms can be identified: · Dull pain in the mammary glands, which often tends to intensify before the onset of menstruation. After menstrual bleeding has passed, the pain usually subsides.
· Irradiation – spread of pain beyond the breast. Patients often complain that pain radiates to the shoulder, shoulder blade or arm.
· The presence of a formation in the breast or thickening of its structure. This sign can be identified by patients who are attentive to their health and regularly palpate.
Diagnostics
The doctor begins the examination with a thorough collection of anamnestic data. The doctor asks the patient about the onset of menstruation, its nature, cyclicity, pain, and abundance. Gynecological history is also important, which includes the age at which sexual activity began, the number of pregnancies, miscarriages, abortions, and childbirth. Genealogical data will help to understand whether blood relatives on the female line had similar diseases. All this information helps to establish the correct preliminary diagnosis.
An objective examination will help the doctor identify asymmetry of the mammary glands, and by palpation, determine the presence or absence of neoplasms. Mammologists pay special attention not only to the consistency and structure of the mammary gland, but also to the color, size and condition of the nipples.
Instrumental methods confirm the correctness of the alleged diagnosis or, conversely, refute it and return the doctor to the beginning of the diagnostic search. Most often they resort to mammography and ultrasound of the mammary glands. Additionally, the patient’s blood and urine are studied.
Therapy
Treatment of diseases of the mammary glands No. 60 ICD10 is possible in 2 options. The first is medicinal, which is used for diffuse growths. Hormonal drugs, including oral contraceptives, can achieve good results.
The second method is surgical, which is indicated for the nodular form. The removed lesion is subject to mandatory histological examination to exclude the presence of atypical cancer cells. The prognosis after treatment is favorable.
Inflammatory diseases of the breast (N 61)
ICD-10 No. 61 breast diseases include: abscess, carbuncle and mastitis, which is considered the most common pathology in this group.
Mastitis is an inflammatory disease. Breast involvement is often unilateral, and only in rare cases (no more than 10%) spreads to both mammary glands. The cause of the disease is two main factors that overlap one another:
· The first is a violation of the outflow of milk;
· The second is the addition of pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microflora.
Initially, the disease occurs as an aseptic (sterile) inflammation. However, very quickly, literally within a day, under conditions of stagnation of milk secretions and favorable temperatures, the microflora is activated. Thus, the stage of bacterial inflammation begins.
Main symptoms
The clinical picture is almost the same in all women. The first symptom is a sharp increase in temperature to high values (38 – 39 °C). Next comes redness of the skin of one of the mammary glands, and then severe pain. Over time they only intensify. With severe inflammation and lack of timely treatment, sepsis develops very quickly - a deadly complication.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is established on the basis of anamnestic, objective and laboratory data. The medical history reveals that the woman is breastfeeding. As a rule, the risks increase if you constantly attach the baby in the same position. In this case, incomplete emptying of the gland occurs. An objective examination reveals hyperemia of the inflamed gland, its slight enlargement, as well as sharp pain on palpation. A laboratory test in the blood reveals leukocytosis with high values.
Treatment
In the early stages, conservative (medicinal) treatment is also effective. The main condition is careful expression of milk. For these purposes, a breast pump is not the best solution; it is best to do it with your hands. The patient can perform the procedure independently, but often due to severe pain it is necessary to contact specially trained people. Among the drugs, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used. Usually these measures are enough for a complete recovery and further restoration of breastfeeding.
In severe forms of the disease, before prescribing surgical treatment, attempts are made to temporarily stop lactation with the help of special medications. If this method was ineffective, then surgeons take over the treatment.
Other inflammatory diseases of the breast
Carbuncles and abscesses of the mammary gland also occur in clinical practice, but are now becoming less and less common. A carbuncle of the mammary gland, as in any other area of the skin, is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle and sebaceous gland. An abscess is a purulent melting of the mammary gland limited from healthy tissue.
The cause of the disease with carbuncle is a blockage of the sebaceous gland, against the background of which pathogenic microflora has joined. An abscess can develop as a result of hematogenous or lymphogenous spread of infection from other foci.
Both diseases occur with an increase in temperature and an increase in pain in one of the mammary glands.
Treatment is most often performed surgically. The abscess is opened, freed from purulent contents, treated with an antiseptic solution, and then drainage is installed for a while. The patient is prescribed a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics. With timely treatment, the prognosis is always favorable.
ICD 10 - N 63 - diseases of the mammary glands. Education unspecified
It is worth noting that this diagnosis is established not only in women, but also in men, but their ratio to each other is 1:18. Mostly women aged 20 to 85 years are affected, but it is more common between 40 and 45 years old. The mortality rate from the disease is 0%.
Causes
The etiology of the disease is not fully understood.
Clinical picture
At first, the disease has no symptoms at all; this is the so-called latent phase of the disease. The duration of this period varies from person to person and can vary from several months to a year or more. The first symptom is periodic pain in the mammary gland, which may intensify before the onset of menstruation. The pain usually subsides immediately after the end of menstruation.
The biggest mistake patients make is that they do not pay attention to changes in their own body and do not turn to doctors, attributing ailments to hormonal imbalances, the beginning of a new cycle, or the proximity of menopause. Over time, the pain takes on a constant aching character. With careful independent palpation, the patient may detect a formation in the chest, which often serves as a reason to consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
Basic research methods:
· collection of complaints;
· assessment of anamnestic data;
· laboratory research methods (general clinical blood test, general urinalysis, biochemical blood test or test for tumor markers);
· instrumental methods (ultrasound, mammography, biopsy).
Treatment
All breast tumors are subject to surgical treatment. After removal, the biological material in 100% of cases is sent for histological examination, thereby establishing an accurate diagnosis and the need for further treatment.
Classification
According to the degree of growth in the number of cells in the mammary gland and their location, adenosis of the mammary glands is divided into subtypes:
- Local adenosis of the mammary glands. Neoplasms are characterized by a clear localization and lobular structure. Feels good during palpation. There is growth of axillary lymph nodes. When palpated, the lumps are very painful.
- Diffuse adenosis of the mammary glands is the first stage of mastopathy. There is no clear localization, it is formed in the tissues of the gland, ducts, nodes. Small tumors can develop into one large tumor. During the premenstrual period, the pain intensifies, the breasts become denser and swell. Women who have not given birth suffer from this disease. If you ignore the first manifestations, long-term treatment of the disease will follow.
- Focal breast adenosis - forms in the ducts of the breast, lining them with cylindrical tissue. Becomes the basis for the formation of nodular mastopathy. In this case, severe premenstrual pain, heaviness and density of the breasts are a concern. It is advisable to remove large adenous lesions so that they do not form a tumor.
- Fibrosing adenosis of the breast is typical for older women. As menopause approaches, the need for glandular tissue decreases and is replaced by fibrous tissue. The pathology is characterized by local periodic pain in the gland area. Small nodules can be felt on the right and left glands; the lesion is elastic and rather small. There is no discharge from the nipples.
According to the nature of the appearance of “extra” cells, adenosis of the mammary glands is divided into:
- Sclerosing adenosis of the breast. The peculiarity of this type of disease is that not individual lumps appear, but the entire breast becomes hard, painful, and the nearest lymph nodes become enlarged. Typical for patients over 35 years of age. The nature of the disease is hormonal imbalance as a result of age-related changes. This pathology requires careful monitoring.
- Adenomyoepithelial and tubular adenosis of the breast - when epithelial cells are scattered chaotically throughout the chest area.
- Apocrine adenosis of the breast takes the form of nodes similar to the lobes of the mammary gland. In such cases, native cells are replaced by other cells with a similar structure.
- Ductal adenosis of the breast prevents the proper formation of the ducts. This form of adenosis is painful, the symptoms are clearly defined.
- Microglandular adenosis of the breast is characterized by the proliferation of epithelial cells in the milk ducts. It is asymptomatic, pain and swelling develop gradually.
- Tumor-like adenosis of the breast has the form of mobile, painful neoplasms.
Other diseases of the breast (N64) ICD10
This group includes:
galactocele - a cyst in the thickness of the mammary gland, filled with milk;
· involutive change after breastfeeding;
· secretion from the nipple outside the lactation period;
· inverted nipple;
· Mastodynia is a condition that is perceived subjectively. It is characterized by discomfort in the chest. They may be present constantly or periodically.
Prevention of breast diseases
Propaganda for the prevention of breast diseases occupies a priority place in working tactics among gynecologists and oncologists. This should include social advertising, various medical brochures, preventive conversations with patients at appointments, increasing the popularity of a healthy lifestyle, as well as the approval of World Breast Cancer Day.
To minimize the risk of developing the disease, and not to miss it at an early stage, you should adhere to the following rules:
· refusal of smoking and drinking alcohol;
· treatment of acute diseases, as well as prolongation of the remission phase of chronic ones;
· undergoing preventive examinations, especially over the age of 35;
· performing independent palpation of the mammary glands at home at least once every 4-6 months.
Prevention
The most effective prevention against breast diseases is to perform its natural function - feeding the baby milk.
Also have a positive effect:
- pregnancy, breastfeeding for at least six months
- refusal of abortion
- refusal of uncontrolled use of contraceptives
- regular sex life
- correct, gentle lifestyle
- regular visits to a mammologist
Adenosis of the mammary gland is well treated if diagnosed in a timely manner. But do not underestimate the seriousness of the disease. As a result of the development of the disease, serious consequences are possible, including breast cancer. It is necessary to undergo regular examination by a specialist (at least once every six months) and when the first signs of illness appear. Such a simple rule will help protect the health, and maybe even the lives of women and mothers!
Benign breast dysplasia according to ICD-10 or mastopathy
ICD-10, (No. 60-No. 64) breast diseases. Benign mammary dysplasia according to ICD-10 or mastopathy is a disease of the mammary glands (benign tumor). It appears as a result of tissue proliferation due to various hormonal disorders and there are 2 types: nodular (single compaction) and diffuse mastopathy (with multiple nodes). Mastopathy occurs mainly in women of reproductive age. This phenomenon is easy to explain. Every month, periodic changes occur in a young body under the influence of the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which affect not only the menstrual cycle, but also the tissue of the mammary glands (stimulation and inhibition of cell division, respectively). Hormonal imbalance causing excess estrogen leads to tissue proliferation, i.e. to mastopathy. ICD-10, (No. 60-No. 64) breast diseases. The disease can also be caused by untimely production of prolactin, the lactation hormone (normally it appears during pregnancy and breastfeeding). The development of mastopathy can be provoked by vitamin deficiency, trauma, abortion, hereditary predisposition, chronic diseases, etc. You can feel the appearance of mastopathy yourself. It causes pain in the mammary gland, accompanied by breast enlargement, swelling and hardening. Sometimes there may be discharge from the nipples. If such signs are detected, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Treatment of mammary adenosis
There are two known ways to treat such breast diseases: conservative and surgical.
Conservative treatment
In the initial stages, mammary adenosis is almost always treated medically. But for this, the disease must be diagnosed and localized in time.
The most common methods and procedures:
- vitamin therapy - taking vitamins at the right periods of the menstrual cycle, most relevant for girls
- hormone therapy (to restore endocrine balance)
- sedative homeopathic medicines
- herbal remedies
- improvement of lifestyle (elimination of bad habits, healthy eating), diet
Diffuse adenosis is usually treated with hormonal therapy. A combination of gestagens + contraceptives (oral) is used. If the disease is not advanced, this method is used for 6 months.
The main drugs used in therapeutic treatment:
- Lindinet 30 - eliminates clinical signs of mastopathy, normalizes menstrual function in patients
- Norkolut
- Pregnin
- Duphaston
- 1% oil solution of Progesterone
The drugs are prescribed between the 16th and 25th day of the menstrual cycle. The use of drugs relieves pain and eliminates lumps in the mammary glands, and discharge from the nipples stops.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes contraceptives Zhannine, Silhouette, the main substance of which is dienogest. This hormone has the same effectiveness as progesterone, only it is synthetic.
Mastodinon, a homeopathic medicine, is also popular. But experts say that treatment with this drug does not bring clear positive results. It should be prescribed in combination with hormone therapy. Separately, it can be used by young patients or at the first signs of mastodynia.
Surgery
With focal adenosis, surgical intervention becomes necessary. The nodular lesion does not respond to traditional treatment; postponing surgery is quite dangerous. The procedure consists of resection of the damaged area and removal of the pathological node. At the slightest possibility of the formation of a malignant tumor, histological examination is used. For a complete recovery, vitamins A, C, E, P, B1, B2, B9, calcium and magnesium supplements are prescribed.
Traditional medicine
There are traditional medicine methods that give good results in the fight against adenosis. But they can only be used if approved by a doctor. These are mainly infusions of burdock roots, horse chestnut and walnuts. When treating more serious, cystic mastopathy, compresses at home can be a good addition to hormonal therapy. Compresses made from table salt, magnesia (Epsom salt) and cabbage leaves are mainly used. The components of these substances have anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory properties and have virtually no contraindications (except allergies). Making compresses is simple:
- Dissolve 2-3 tablespoons of salt in a liter of warm water
- dilute a spoonful of magnesia in a small amount of water
- apply to natural fabric, apply to the sore breast
- Apply clean cabbage leaves to the gland, secure all compresses well
ICD-10, (No. 60-No. 64) diseases of the mammary glands according to the International Classification of Diseases
Mastopathy is treated medicinally with the help of hormonal (gestagens, estrogen inhibitors, antiestrogens, androgens, used according to the International Classification of Diseases, ICD-10) and non-hormonal drugs Mabusten. Surgical intervention is used for nodular mastopathy and is diagnosed in two types: sectoral resection (in which the tumor is removed along with the breast area) and enucleation (only the tumor is removed). The operation is indicated if there is a suspicion of breast cancer, the tumor is rapidly growing or there is a single cyst. Lifestyle affects a speedy recovery. During the treatment period, it is better to limit the consumption of tea and coffee, include more vegetables and fruits containing vitamins in the diet, give up bad habits, thermal procedures (for example, in a bathhouse or sauna), and wear comfortable underwear. Diagnosis (by a mammologist) consists of several stages: palpation of the mammary glands in a lying and standing position, examination of the nipples, palpation of the lymph nodes and thyroid gland;
• mammography – x-ray of the mammary glands; • Ultrasound to accurately determine the structure and location of the tumor in the breast; • biopsy – examination of tissue for oncogenes; • hormonal studies, liver examination and consultation with specialists (gynecologist, oncologist).
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms of adenosis appear, you need to consult a mammologist. He will conduct a survey, examine the breast, and prescribe further research methods. Based on them, a residual diagnosis can be made. The main known diagnostic methods:
- mammography
- cytological examination
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the breast and lymph nodes
- mammoscintigraphy
- tissue biopsy
- tomography (CT, MRI)
- aspiration, excisional biopsy (mandatory puncture of the tumor)
- blood test to determine hormonal levels