What is fertility, fertile period, fertile days
Fertility is the ability to become pregnant and give birth to a healthy child.
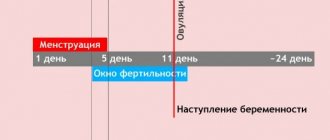
Fertile days (period) are several days in the menstrual cycle that occur before ovulation and directly on this day. The maximum chances of conception occur 5 days before ovulation, as well as on the day of its occurrence. This period of time is fertility.
Ovulation is the moment when a mature egg is released from the ovarian follicle into the fallopian tube and its further movement towards the uterus. According to doctors, the greatest chance of pregnancy is the day before ovulation. In this case, sperm can live in the vagina for several hours, and in the uterus for approximately 5 days. After ovulation occurs, the egg has a day to fertilize.
The menstrual cycle lasts on average 28 days, and ovulation occurs in the middle.
This calculation is an average; as a rule, a woman has individual deviations in her cycle.
Age and fertility
The ability to conceive in both boys and girls appears during puberty. The beginning of the fertile age of the fair sex will be marked by the onset of ovulation and menstruation. However, over the years, reproductive function undergoes changes. Fertility decreases as the body ages, and after menopause, women can no longer become pregnant naturally.
In modern society, infertility associated with age-related changes in the reproductive system has become increasingly common. There are many reasons why many girls begin to start families only after 30 years. Today women have more opportunities to take care of themselves and monitor their health, but all this does not exclude an age-related decline in reproductive function. It is important to understand that fertility declines as a woman ages due to the natural process of a reduction in the number of eggs in the ovaries. And this process can begin much earlier than most women expect.
OVULATION AND MENSTRUAL CYCLE
During their reproductive years, women experience regular menstrual cycles, during which the process of ovulation occurs monthly. At the beginning of each cycle, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), produced in the pituitary gland, stimulates a group of follicles in both ovaries to grow. Usually only one of these follicles matures and releases an egg (ovulates), the rest stop growing and are destroyed. Pregnancy occurs when an egg is fertilized and implants in the lining of the uterus (endometrium). If pregnancy does not occur, the endometrium is released as menstruation and the cycle resumes.
At the beginning of adolescence, girls experience “wandering” ovulation, which leads to irregular menstruation, but by the age of 16, as a rule, a stable periodicity of menstruation is established. From this time on, the female cycle will remain stable, ranging from 26 to 35 days.
Unlike men, whose bodies produce sperm throughout their lives, a woman is born with a constant number of eggs with follicles contained in the ovaries. So, at birth, a girl develops about a million follicles. By puberty, this number is reduced to about 300,000. Of all the remaining follicles, about 300 reach ovulation during reproductive years. The remaining follicles are not used during ovulation, but are used only as they undergo a natural, sequential process of degeneration called atresia.
As women age, fertility declines due to natural age-related changes that occur in the ovaries. From about 30-40 years old, you can notice that the cycle has become shorter. Over time, ovulation begins to disappear, periods become increasingly rare until they stop completely. It is believed that the stage of menopause occurs when a woman does not menstruate for a year. It is believed that women who like to smoke a cigarette or two experience menopause a year earlier than non-smoking women.
FERTILITY IN AGING WOMEN
The best reproductive years for women are considered to be 20-30 years of age. Fertility gradually begins to decline by the age of 30, and this trend is especially pronounced after 35 years. Each month, a healthy woman of childbearing age has a 20% chance of becoming pregnant. That is, for every hundred childbearing 30-year-old women who try to get pregnant on the first try, only 20 will succeed, the remaining 80 will have to try their luck again. By age 40, this probability is less than 5%. Thus, less than 5 out of 100 women can successfully conceive in any given month.
As we said, women remain fertile until menopause, the average age of which is 51 years. However, most women fail to conceive a child at the age of forty. These indicators apply to both those who are trying to get pregnant the traditional way and those who are undergoing infertility treatment, including in vitro fertilization (IVF). Stories broadcast in the media can lead women and their partners to the mistaken idea that no matter what, they can be guaranteed to become pregnant using procedures such as IVF. But we should not forget that a woman’s age still affects the likelihood of a cure for infertility. The quality and quantity of eggs gradually decrease with age, which causes a decline in female fertility.
FERTILITY IN AGING MEN
Unlike the early decline in fertility that is observed in women, in men the change in reproductive function occurs much later. Although sperm quality declines somewhat as a man ages, this is generally not a problem until a man reaches 60 years of age. Although problems in men are not as sudden and noticeable as in women, changes in reproductive and sexual functioning also occur as they age.
Moreover, in the stronger sex there is no age limit at which a man cannot become a father, as proven by gentlemen of 60-70 years of age who managed to successfully conceive offspring with their younger partners. However, as men age, testicles tend to become smaller and softer, sperm structure changes, and sperm motility tends to slow down. Aging men often develop diseases that can adversely affect their reproductive and sexual functions. Moreover, with age there is a higher risk of gene defects in sperm. However, it is worth noting that not all men experience significant changes in reproductive or sexual function as they age, especially not men who have maintained good health for many years.
In any case, if a man has problems with sexual desire or erection, he needs to seek treatment from a urologist. Decreased libido may also be associated with low testosterone levels.
EGG QUALITY
As women age, they become less likely to get pregnant and more likely to miscarry as the quality of the eggs decreases as the number of remaining eggs decreases in number. Such changes are most pronounced in women closer to forty years of age. For this reason, a woman's age is the most accurate test of egg quality.
Important changes in the quality of eggs associated with the presence of hereditary abnormalities and the frequency of past diseases are called aneuploidy (the content of too many or too few chromosomes in the egg). During reproduction, a normal egg should consist of 23 chromosomes, then in total the embryo will contain 46 chromosomes. As we age, more and more eggs have either too many or too few chromosomes. This means that the number of chromosomes in the embryo will also be either more or less than the required value. Most people know that Down Syndrome is a process that results in the embryo having an extra chromosome. However, most embryos with too many or too few chromosomes do not result in pregnancy or result in miscarriage. This situation explains the lower chance of getting pregnant and the higher chance of miscarriage in adult women.
NUMBER OF EGGS
A decrease in the number of follicles containing eggs in the ovaries is called “loss of ovarian reserve.” Women begin to lose ovarian reserves before they become infertile and before they stop having regular periods. Since women are born with the same set of follicles that they will have throughout their lives, the number of waiting follicles is gradually depleted. As ovarian reserves dwindle, the follicles become less and less receptive to IVF and require more and more stimulation of the egg to mature and ovulate. At first, periods may move closer together, resulting in shorter cycles of 21 to 25 days each. As a result, the follicles become unable to function properly for stable ovulation, leading to long, irregular cycles. Declining ovarian reserve is usually associated with age and occurs due to the natural loss of eggs and deterioration in the quality of the remaining eggs. However, ovarian reserve may also decrease in younger women. This often occurs due to smoking, a hereditary predisposition to premature menopause, and previous ovarian surgery.
INFERTILITY AND AGED MOTHERHOOD
Infertility is diagnosed if a woman fails to become pregnant after a year of unprotected sexual relations (including without the use of oral contraceptive methods). However, if the woman is 35+, the examination should be carried out after 6 months of unsuccessful attempts to conceive a child. If couples have obvious medical problems that affect their inability to conceive, such as absence of periods (amenorrhea), sexual dysfunction, inflammatory diseases, or previous surgery, they are advised to begin infertility evaluation immediately.
A fertility test usually involves determining your ovulation period, examining the fallopian tubes, cervix, and uterus itself. The male partner will need to undergo a spermogram (sperm analysis). Most tests can be completed within one month. After the examination is completed, the necessary treatment is prescribed. It is very important to monitor your overall health. A preliminary consultation with a specialist often also gives a positive result. Doctors may suggest a course of necessary therapy before pregnancy begins, as there are increased risks for older women.
For example, women who have medical conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes should consult their doctor before trying to conceive, as symptoms of these conditions may worsen during pregnancy. Additionally, children born to women after age 35 have a higher risk of being born with the wrong number of chromosomes. Therefore, women at risk during pregnancy may be recommended to undergo a special examination.
It is better for women to discuss the existing risks with their doctor or genetic counselor before planning a pregnancy. The screening may include prenatal testing after specific screening for certain congenital anomalies. Currently, amniocentesis and chorionic villus biopsy are used to identify pathologies. Blood tests and ultrasound are also used as diagnostic tests. As practice shows, most parents want to find out as much information as possible about pregnancy in order to be able to make an informed decision.
TREATMENT OPTIONS AND ALTERNATIVES
Assisted reproductive technologies
When determining the cause of infertility, doctors may suggest special treatment. However, sometimes there are cases in which no specific problem can be found and the cause of infertility is considered “unknown”. For undiagnosed infertility, or when traditional treatments have not worked, assisted reproductive technologies, such as superovulation using intrauterine insemination (IUI) technology and in vitro fertilization (IVF), can be used. In the IUI cycle, infertility treatment is carried out using drugs to increase the number of eggs in the ovaries. When these eggs are ready to ovulate, the partner's selected sperm is placed directly into the woman's ovaries. This procedure is called intrauterine insemination (IUI) technology and does not cause any discomfort. IVF is the procedure of retrieving an egg and fertilizing it with the partner's sperm in the laboratory, then the finished embryo is placed in the uterus. In each of these procedures, sperm from a donor may be used instead of the sperm of the woman's partner.
With any of the treatment options, the woman’s age directly affects the onset of pregnancy. Among women over 40 years of age, the likelihood of successful intrauterine insemination is less than 5% per cycle. In comparison, the success rate for women aged 35 to 40 is approximately 10%. IVF is considered a more productive technology, but the success rate among women 40+ is relatively low, only 20% per cycle.
Egg donation
If other treatments have failed, the woman is over 42 years of age, or suffers from Ovarian Failure Syndrome (Premature Ovarian Failure), also known as early menopause, treatment options are narrowed. In this case, egg donation, which is the use of eggs from female donors aged 20-30 years, is considered a fairly successful procedure. The high likelihood of becoming pregnant with a donor egg confirms that age-related egg quality is the primary barrier to conception in older women. If you are over 40, then the likelihood of successfully becoming pregnant using an IVF cycle using a donor egg is much higher, but many couples or single women around forty years of age prefer to use their own eggs, although the likelihood of getting pregnant in this case is lower. By the age of 43, the chance of becoming pregnant through IVF is less than 5%, and by the age of 45, the only reasonable rational alternative is the use of a donor egg.
In this treatment, the egg donor takes drugs to stimulate the production of many eggs in the ovaries. At the same time, the egg recipient (the woman who receives the donor egg) receives hormone therapy to prepare her ovaries to receive fertilized eggs (embryos). After receiving the eggs from the donor, they are fertilized with the partner's sperm in the laboratory. A few days after this, the embryos are placed in the recipient's uterus. Any of the embryos that are not used can be frozen (cryopreserved) for later use.
IVF egg donor gives women the opportunity to become pregnant, give birth and experience the joy of motherhood. However, one must understand that a child conceived in this way will not be genetically related to the woman who gave birth to him. At the same time, he will have a biological connection with the father and the egg donor. Many programs recommend counseling to ensure that all parties to the egg donation agreement understand the ethical, legal, psychological and social aspects of the issue. Since the success of the procedure is highly dependent on the quality of the donor's eggs, ideal donors are women between the ages of 20 and 30 with proven fertility.
DELAYED MATERNITY
Women who want to delay childbearing until after age 38 may consider methods such as embryo freezing after IVF or egg retrieval and freezing for later use. The success of embryo freezing (crypoconservation) is well known, but it requires the woman to have a male partner or to use donor sperm. Egg freezing to delay motherhood is a promising new technology. However, there is a problem with using voluntary egg freezing. As a woman gets older, the end result of her assisted reproductive technology cycle is less and less successful.
PRE-IMPLANTATION GENETIC SCREENING
New technologies are currently being developed that will allow embryos to be tested for chromosomal abnormalities. This method is applied to embryos created using IVF. It may be especially useful for older women. In preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD), a small number of cells are taken from each embryo and tested. Chromosomally correct embryos are selected for transplantation into the mother's uterus. It is expected that this procedure will lead to a high rate of pregnancy and transfer of embryos with genetic abnormalities.
CONCLUSION
Fertility naturally declines as you age. Despite the fact that the timing of the decline in fertility and the onset of menopause in women varies significantly, this period occurs in the life of every representative of the fair sex. Typically, fertility begins to decline around age 30 and declines noticeably at age 35. Women who decide to delay pregnancy until age 35 or later should be realistic about their chances of success and have information about their options for conceiving and, if necessary, using fertility treatment. By reviewing all the options and understanding her needs and goals, a woman and her partner can make the best decision.
Fertility age
Nature has designed it in such a way that a person is ready for offspring only during a certain period of life. In men, reproductive function continues until old age, but in women this period is not so long. A representative of the fair sex can become pregnant and carry a baby only until menopause.
Fertility in women lasts on average from 15 to 49 years of age. Therefore, you should not postpone pregnancy for a long time, since the prognosis for conception is more favorable at a young age.
Calendar method
The fertile period in women is determined quite simply. It is necessary to divide the number of days of the menstrual cycle in half, and add 2 days before and after to the resulting value.
For example, if a girl’s menstrual cycle is 30 days, then dividing this figure in half, we get 15. The period favorable for conceiving a child is in this example from the 13th to the 17th day.
In order not to miss her fertile days, a woman should keep a calendar in which she will mark the start and end dates of her period. Based on the data obtained, it will be possible to approximately calculate the period during which conception is most possible. However, the calendar method has significant drawbacks: unfortunately, not every female body works stably, like a clock. Very often, representatives of the fair sex complain about changes in the length of the monthly cycle. It is also necessary to take into account that in certain cycles there may not be ovulation at all.
This method is perfect for girls with a clear monthly cycle and excellent memory, who will not forget to mark the necessary dates on the calendar.
How to calculate fertile days for a woman
The menstrual cycle varies in length for different women. Individual calculation of the fertile period allows you to more accurately determine the day of ovulation, which significantly increases the chances of conception. Fertility in women can be calculated in several ways.
The calendar method involves maintaining a calendar of the fertile period. In this case, it is necessary to note the date of the first and last days of menstruation, as well as the middle of the cycle. It is at this time that ovulation usually occurs. A significant drawback of this calculation method is that it is only suitable for those who have a stable menstrual cycle. If the duration of the cycle is variable, then it is almost impossible to calculate the fertile period using this method.
The calendar method of determining fertile days is no more than 60% effective.
A representative of the fair sex, who listens carefully to her body, notices that some changes occur in it with a certain frequency. Thanks to such observation, you can recognize fertile days. During this period, the nature and volume of vaginal mucus changes. During the fertile period, it becomes more abundant and looks similar to egg white.
This is due to the fact that a woman’s body adapts to the most favorable time for conception. At the same time, fertility can also manifest itself with other symptoms: nagging pain in the lower abdomen and increased sensitivity of the mammary glands.
If such symptoms are not typical for a woman in each cycle, then this may indicate the presence of an infection.
The fertile period can also be calculated by measuring basal temperature. The method involves regularly measuring basal temperature in the rectum or vagina. This should be done in the morning immediately after sleep, without turning over. Also, to ensure the reliability of the results obtained, it is better to use the same thermometer all the time.
It is important when using this method to measure basal temperature at the same time. Its meaning can be influenced by sex, drinking alcohol, any illness or nervous shock. Daily measurement data must be entered into a table. The fertile period begins with a slight increase in basal temperature, which remains at this level for several days. At this time, ovulation occurs.
You can determine fertile days using a special test that is sold in pharmacies. They should be started approximately 5 days before the expected moment of ovulation. This test works similarly to a pregnancy test, and detects luteinizing hormone.
Before using the ovulation test, you should read the instructions that come with it. Testing is carried out daily at the same time once or twice a day. You need to collect urine in a clean container and place the test strip in it for a certain time. Just before ovulation, the amount of luteinizing hormone increases sharply, which is what the test monitors.
A positive test result indicates that fertility is now high, that is, the female body is ready for fertilization.
What factors influence female fertility?
The main ones are:
- Hormone levels. The chance of getting pregnant is influenced by a woman’s hormonal background; a lack or excess of certain hormones will be an obstacle to childbearing.
- Lifestyle. Tobacco and alcohol abuse, as well as lack of sleep and stress negatively affect the ability to become pregnant.
- Age. The most favorable range for the first pregnancy is 20-26 years. As age increases, the number of cycles without ovulation increases, and fertility decreases.
- Weight. Being underweight or overweight negatively affects both health in general and fertility in particular.
- Surgical interventions or diseases of the reproductive system.
If we consider the female menstrual cycle, we can highlight the most important moment in it - the day of ovulation.
Unfortunately, determining this day with maximum accuracy at home is very difficult, so people often pay attention to fertility days. These are the days on which conception is most possible. As a rule, this is 2 days before ovulation and 2 after. Each woman can determine her fertile period for herself based on her specific indicators. But it is better if a specialist helps her with this.
Fertility days can also be viewed from a medical perspective. The finished egg, which has left the follicle - the place where it was formed, awaits fertilization in the fallopian tube. By nature, the egg does not live long - about 12 hours or a little longer. Spermatozoa retain greater viability compared to eggs, therefore, entering the fallopian tubes a few days before the arrival of the egg, they are able to wait for it. Based on the above facts, doctors who help plan pregnancy recommend having sex every day, starting 2-3 days before ovulation, as well as several days after. This mode of sexual activity will allow sperm to wait for the release of a mature egg.
What can cause fertility problems?
Doctors include factors affecting fertility: a woman’s age over 30 years, excess weight, abnormal development of the egg, genital tract infections, inflammatory processes and other reasons. It is advisable that if a woman is infertile, she should be examined not only by a gynecologist, but also by an endocrinologist and a nutritionist.
Normal fertility is greatly influenced by the lifestyle a woman leads. She needs to eat well, get enough sleep, follow all the rules of personal hygiene, and not engage in casual intimate relationships. You need to be healthy not only for the sake of conception, but also in order to bear a healthy baby. To plan a pregnancy, you need to understand what fertile days are and learn how to calculate them.
Fertile days and ovulation may be absent. This is influenced by the following factors: hormonal imbalance or deterioration of the thyroid gland. Natural disorders include the lactation period - breastfeeding. Since the list of root causes is not small, you need to see a doctor to find out.
How to increase fertility in women?
It would seem, what is needed for conception? If you have a sexual partner, then pregnancy will not take long to occur. But, unfortunately, not everything is as simple as we would like. The hormonal background of the female body constantly undergoes various changes. This is what causes frequent mood swings. Even slight increased nervous arousal can affect a woman's ability to become pregnant.
Here are some tips that we hope will be useful to you if you want to improve your fertility:
- Watch your kilograms. Both excess and lack of fat negatively affect ovulation. With an increased number of fat cells, the body turns on the process of producing hormones that interfere with the normal functioning of the ovaries. A lack of fat, on the contrary, inhibits the production of necessary hormones that are directly related to this process. As a result of such changes, the periodicity of the menstrual cycle is disrupted, and with it the regularity of ovulation. Physical activity will help control excess weight. But you should be careful not to overdo it here either. Very often, professional athletes experience irregularities in their monthly cycle. This happens due to overstrain of the body, which causes hormonal imbalances.
- Eat right. For a woman’s health, a balanced and proper diet plays an important role. The female body needs foods rich in protein, iron, zinc and vitamin C. Their deficiency delays the onset of menstruation, therefore, ovulation occurs less frequently. By the way, athletes often suffer from zinc deficiency. Sufficient amounts of animal protein are found in meat, eggs, fish and dairy products. Vegetarians can be advised to eat legumes with rice, as well as include soy products in their diet.
- Give up cigarettes. It has long been proven how smoking ages a woman’s body. The chemicals contained in cigarettes harm some functions of the reproductive system. If we consider the ovaries of a 30-year-old woman who smokes, their functional capacity is comparable to the capabilities of the ovaries of a 40-year-old woman. This indicates early decline of the body. But if a woman stops smoking, she will have every chance of restoring some functions of the reproductive system.
- Keep track of your cycle duration. The norm is considered to be an interval of 25-35 days. If the gap between menstruation is longer, for example, 42 days, then ovulation will occur according to the cycle. To calculate your fertile days and plan conception, you need to calculate the day of ovulation. It is considered the most fertile day of the cycle. The days preceding the start of the process are also favorable for conception. The fertile period is 4-5 days before the egg is released from the ovary. After the process is completed, the probability of conception is reduced to zero. Usually, to roughly calculate the day of ovulation, the length of the cycle is divided in half. Suppose if the cycle is 28 calendar days, then the probable day of ovulation will occur on the 14th day from the start of bleeding. But since an accurate calculation is needed, it is worth using a special test that shows the days of approaching ovulation. This test is sold in all pharmacies. Another way is to measure your basal temperature daily.
- Stay calm. Danish scientists conducted research and came to the conclusion that during psychological stress, the hormonal background becomes similar to that which the body experiences during increased physical activity. You need to teach yourself to get out of this state using methods of meditation, relaxation or yoga. Swimming helps many people relieve stress. It’s a good idea to remember your hobbies, which can replace going to a psychotherapist.
- Avoid alcoholic drinks. Alcoholic drinks change the level of the hormone estrogen in the blood. It is he who is responsible for a woman’s fertility and the ability to maintain pregnancy in the early stages. Insufficient estrogen levels prevent the implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterine cavity. However, according to scientists, one glass of wine with dinner will not harm a woman’s health and reproductive ability. It is also worth paying attention to drinks that contain caffeine. American obstetricians and gynecologists believe that more than 2 cups of black coffee per day contributes to miscarriage. Therefore, in order to bear and give birth to a healthy child, you should give up alcohol and coffee.
- Take initiative in your intimate life. It has long been proven that irregularities in the menstrual cycle most often occur in women who do not have regular sex life.
- Avoid douching. There is a special microflora in the vagina that performs a protective function. During douching, this layer is washed off and there is a risk of developing bacterial vaginosis.
We hope that our recommendations will be useful to you. But they cannot replace a consultation and face-to-face examination by a qualified specialist, as they contain general information.