Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, no matter for what reason, are accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the abdominal area, which are called cramps. They can manifest themselves as a feeling of heaviness, turning into pain, and other extremely uncomfortable conditions.
If we consider spasms as a reaction of the body, this is a spontaneous contraction of the walls of the stomach. This organ has a well-developed muscular system for softening food in order to further transfer it to the next stage of processing in the intestines.
The stomach produces contractile movements independently, and the person does not feel them. But when the organ is exposed to factors not related to digestion, movements resume. Then the contractions bring a feeling of discomfort, because gastric juice is produced, but there is nothing to digest in the stomach.
Causes
Spasmodic pain in the abdomen indicates the presence of serious problems in the body that can subsequently lead to surgical intervention.
There are many reasons why patients feel discomfort. These include:
- pain on the right or in the navel area - this may indicate inflammation of the appendix;
- stagnation of feces in the intestines is accompanied by pain in the left side;
- acute pain in the lower back, a possible cause is renal colic;
- strangulated hernia;
- inflammation of adhesive scars, etc.
The above causes of abdominal pain require a medical examination; you should not self-medicate.
Particular attention should be paid to pregnant women. In recent months, cramps in the lower abdomen may indicate that the pregnancy may be terminated. The pain is accompanied by bloody or liquid discharge; immediate hospitalization is required. But often spasms in expectant mothers appear as a result of diseases of the urinary system: pyelonephritis, cystitis, etc.
If discomfort occurs in the abdominal area, a medical examination is required before treatment.
Discomfort in adults may occur due to liver failure and gallbladder dysfunction, for example, cholecystitis. Bile does not move or its outflow is disrupted. As a result of the ongoing inflammatory processes, the muscles of the bile ducts begin to contract, as do the surrounding muscles.
Cholelithiasis can cause abdominal cramps, but then surgical intervention is certainly required; stones in the gall bladder provoke pain.
Similar symptoms appear with dysfunction of the urinary system, or more precisely, caused by urolithiasis. The stones begin to move along the urinary tract, first the lower abdomen hurts, then the pain radiates to the back, to the intestines, to the groin area.
In infants, abdominal pain is caused by a digestive system that is not fully formed, dysbacteriosis, if the mother took antibiotics before giving birth.
An older child may have a stomach ache for the following reasons:
- intestinal disorders;
- nervous tension at school;
- infection;
- allergies to certain foods;
- inflammatory processes in the urinary system.
Inflammation of the urinary system
Intestinal colic is a common and common cause of abdominal cramps. Adults and children suffer from the disease. Improper diet, dysfunction of the digestive system, intestinal obstruction, which causes intoxication of the body, resulting in painful sensations, diabetes also becomes a source of spasms.
Pulling in the lower abdomen after ovulation - what is it?
Knowing the listed features, we understand the causes of pain directly at the moment of ovulation. But there are times when it comes at a later date, for example, even on the 5th day after ovulation, it pulls in the lower abdomen. Can an ovarian wall rupture be felt for so long? Probably not. The reason here may lie in a more interesting and important moment for the woman - probably, the process of attachment of the embryo to the uterus has occurred. For some, this process is felt 4-7 days after fertilization.
If you have pain, which can be described as mild, nagging, you can expect slight discharge of a pinkish tint. They should pass quickly, no more than a day.
Therefore, if after ovulation the lower abdomen feels tight for a week, you should take care of buying a test and, after waiting another week, analyze the presence of conception. You can also wait for a new cycle and check if your period comes. If you want to find out the cause earlier, you can visit an ultrasound. The doctor will be able to answer the question immediately, because he will clearly see the presence of an embryo.
Classification
Doctors divide pain in the abdominal area into organic and functional.
The first classification of spasms is more common in adults with existing gastrointestinal problems. Functional contractions of the stomach muscles are observed more often in the younger generation. This is due to an immature nervous system and metabolic disorder. In infants, pyloric spasm is observed, requiring immediate medical intervention. This occurs during contractions of the transition zone of the stomach and duodenum, due to dysfunction of the neuromuscular apparatus of the infant’s stomach.
Abdominal muscle spasms
This is one of the types of spastic pain caused by disruption of the digestive system, stress, and unhealthy lifestyle. A sharp contraction of the abdominal muscles can also be caused by an unexpected fright. Damage to internal organs, colic in the liver, in the genitourinary system, damage to the pancreas, stomach diseases. Colic in the intestines can be caused by lipid metabolism disorders, diabetes mellitus, and porphyrin disease. When spasms occur, the internal organs of a person and the circulatory system passing through the abdominal cavity are affected. Often the pain syndrome is associated with the appendix; when it becomes inflamed, the organ begins to contract, causing pain.
Tonic spasms
Tonic pain is characterized by prolonged muscle tension. Such syndromes are accompanied by persistent hypertonicity of the abdominal muscular system, with the development of dense, painful muscle areas called trigger points. The movement of the damaged muscle decreases, it begins to shorten and become denser. When you try to put pressure on the compacted area, pain occurs that spreads to other parts of the human body: in the lower back, arm, leg.
The causes of tonic spasms are associated with injuries, prolonged static muscle tension, and emotional stress.
The danger of tonic pain lies in the fact that with constant pain, a person gets used to constant contractions and stops paying attention. But pain is a protective function of the body, warning of problems with the normal functioning of internal organs. Inattention to such spasms can lead to the development of complex diseases:
- the damaged muscle is not provided with sufficient blood flow, which means that blood circulation to nearby organs is impaired;
- the body works “idle”, supplying the seal with an increased amount of oxygen and nutrients;
- the presence of a damaged area and untreated leads to a negative effect on the psyche, physiology and the body system as a whole;
- the muscle in which the disorder occurred does not perform musculoskeletal functions.
Clonic spasms
This is a spontaneous muscle contraction, but occurs in periods (periods of tension and periods of muscle relaxation). The body begins to twitch involuntarily.
The cause of such spasms may be renal failure, dysfunction of the adrenal glands, uremia, or intoxication.
The use of medications to help a patient with an attack of clonic muscle contractions is not recommended. The doctor prescribes medications, taking into account the specific effects of specific drugs on the body of an individual patient. It is permissible to provide first aid before the arrival of doctors: lay him down on a level place, put something soft under his head, try to prevent the person from injuring himself.
Pathological nature of seizures
Involuntary contractions in the abdomen caused by diseases are often accompanied by a complex of unpleasant symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract.
Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract
Spasms and pain are observed in the following diseases:
- Gastritis. Spasms are most often localized in the left abdominal area and radiate into the chest. Less often, acute pain radiates to the back, and most often appears on an empty stomach.
- Stomach ulcer. Spastic pains usually appear after eating, and sometimes hunger cramps occur. The pain is located in the upper or middle abdomen and may radiate to the side. Antispasmodics do not help with such pain; special medications are required.
- Intestinal diseases. Spasms constantly accompany acute or chronic colitis, dysbacteriosis, and occur with intestinal obstruction. The muscles can contract in the left hypochondrium, on the right, below and on the side, because the intestines occupy a significant area of the abdomen. Additional symptoms include: acute pain, gas formation, bloating, nausea.
- Cholecystitis, pancreatitis and liver diseases. In this case, the pain is accompanied by spasms on the right or left, under the ribs. Symptoms are often associated with excessive production or stagnation of bile: sour taste, yellow tongue, rotten egg burps, changes in urine color and odor.
- Appendicitis. Inflammation of the appendix of the cecum is difficult to confuse with other diseases, because the pain in this disease is unbearable, accompanied by high temperature, spreading to the hips, back, and sternum. There is a concept of chronic appendicitis, in which inflammation is accompanied by moderate spasms and the absence of suppuration (due to fatty foods, spicy dishes, stress or alcohol).
- Helminths. The symptoms combine a whole group of unpleasant symptoms; they can manifest themselves as spasms and a sensation of movement, pain appears when large parasites move. Symptoms of acute intoxication are observed, and sometimes skin rashes occur.
- Inflammation of the spleen. The pain is on the left side. When combined with inflammation of the stomach or pancreas, the symptoms “move” to the right side.
Spasms can also appear with severe food or chemical poisoning.
Stomach cramps caused by pathologies rarely remain without additional symptoms. You can suspect the disease by nausea, fever, acute pain that does not go away for more than 1-2 days, heartburn, belching, and bad breath.
Gynecological factors in women
Abdominal cramps may be associated with inflammation of the uterus and appendages. Usually accompanied by intense pain, sometimes the temperature rises, and spotting appears:
- Adnexitis - develops due to inflammation or infection, can appear on one or both sides.
- Ectopic pregnancy - the fertilized egg does not reach the uterus, remains in the tube, spasms intensify over time and cause unbearable pain.
- Apoplexy (damage to blood vessels) of the ovary - most often observed during ovulation as a result of too active sexual activity or physical activity, the girl loses strength, may faint, and the bleeding is quite severe.
- Endometriosis – pain is localized in the area just below the navel, but can radiate to other parts of the abdomen.
- Adhesive processes - develop due to the gluing of organs after surgery or prolonged inflammation. The pain is similar to that that develops before menstruation and is accompanied by digestive disorders.
- Inflection of the cyst - occurs after physical activity. The pathology is accompanied by weakness, swelling of the ovary and pain, nausea, and fever.
Pain and cramps can be observed due to kidney disease, prolapse, inflammation or the appearance of stones (sand). With cystitis, pain occurs during urination, and cramps appear in the very lower abdomen.
Symptoms
Symptomatic phenomena accompanying spasms can be serious. It is worth paying special attention to the signs:
- the duration of the muscle contraction period is more than 60 minutes;
- loss of consciousness due to pain;
- pale skin;
- the person has not urinated for more than 10 hours;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- the patient has difficulty breathing;
- Pregnant women experience vaginal bleeding;
- increased body temperature, a person has a fever;
- There is blood in the stool and vomit.
If a woman has pain on the left side, the cause may be an ectopic pregnancy. In this case, an ambulance is called immediately.
Lower abdominal cramps in women
For the fair sex, spasm has long been a faithful companion, appearing at least once a month. Although some “lucky ones” receive his attention much more often. Due to the fact that cramps in the lower abdomen in women most often appear before, at the beginning, and maybe in the middle of the cycle (it all depends on individual characteristics), they are well aware of the reasons for which such ailment may appear and what remedies can be used to treat it It's preferable to fight. Menstrual pain is a common but treatable phenomenon.
Some cramps in the lower abdomen in women, accompanied by specific symptoms, may appear due to exacerbation of chronic diseases. Diseases of the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and the appearance of neoplasms often provoke painful conditions. During pregnancy, periodic cramping spasms cannot be avoided, as they can be disturbing for various reasons.
Lower abdominal cramps in women: causes
If you need to determine for yourself what causes cramps in the lower abdomen in women in a particular case, then it is worth distinguishing between their symptoms, since depending on the specific characteristics of the body and the presence of chronic diseases, they can vary significantly. If we omit menstrual pain, the process of pregnancy and associated ailments, we can identify the following reasons:
- Spasm of the piriformis muscle. Due to the fact that the muscle can compress the joint, this leads to dull pain. In this case, constant muscle tension can lead to hemorrhoids and arthrosis. In addition, as a result of its improper functioning, fibrosis may occur, which worsens to a greater extent after childbirth.
- Inflammatory processes occurring in the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Spasms in the lower abdomen are of a long-lasting, “aching” nature. They intensify with significant physical exertion, hypothermia, and physical proximity. In complicated cases, the development of adhesions in the pelvis begins.
- Disparity. Spasms and pain appear in the lower abdomen and vaginal area during intimacy. This can lead to further fibrosis of the vagina, as a result of severe tears during childbirth.
- Displacement of the uterus during abortion followed by muscle twisting.
Almost all cramps in the lower abdomen in women are caused by diseases and problems related to the reproductive organs. If they begin to appear with enviable regularity, then an immediate examination by a gynecologist is required and a correct diagnosis is made.
Lower abdominal cramps during pregnancy
If a expectant mother experiences cramps in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, then this condition should be treated with special care. They can often indicate serious problems. Often, such prerequisites can serve as a clear sign of spontaneous abortion. In some cases, this condition can also appear during an ectopic pregnancy (tubal abortion). In this case, it is necessary to urgently contact a gynecologist, since there is still an opportunity to save the child.
Abdominal muscles
The human abdominal wall consists of several types of muscles. The abdominal muscles perform important functions. The main highway of our body is supported by the abdominal muscles.
The peritoneum is responsible for intestinal motility, controls internal abdominal pressure, and helps maintain the placement of internal organs in appropriate positions.
Any weakening or damage to the peritoneum leads to muscle strain. This especially affects women after 50 years of age, who stop taking care of their physical shape long before that.
The most unpleasant thing that can await a woman is prolapse of the internal genital organs. Simply put, prolapse of the internal pelvic organs.
Modern medicine offers patients to use a bandage for prolapse; you can even buy it on the Internet. But this is not a reason to give up daily exercise and training, but a reason to think about your health and take all measures to preserve it.
Characteristic discharge during ovulation
When the lower abdomen pulls after ovulation, specific discharge is also observed, characterized by the following moments:
- The mucus is liquefied due to the action of the hormone, which “splashes out” after the rupture of the bubble. Before this, the cervical mucus was very thick and blocked the entrance to the uterus to prevent the passage of sperm in the absence of a cell here. At the moment the cell enters the genital tract, the mucus changes its structure and characteristics, creating an optimal environment for the movement of male cells. The mucus is thick, transparent, viscous. There is an abundance that is not typical for other periods of the cycle. Therefore, the woman immediately understands that ovulation has arrived. Due to the rupture of the follicle, shades of brown may appear in the mucus. If there are only a few of them and they disappear after a couple of days, the process went well. If the shades are bright, bloody, and last a long time, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Causes of abdominal muscle strain
The main cause of abdominal muscle strain is excessive tension. This can happen due to excessive overvoltage when too much load is applied. Excessive tension can also be caused by injury or sudden abnormal movement of the body along its axis. This typically occurs due to lifting, pushing, or pulling heavy objects.
Sports activities can cause tension in the abdominal muscles. Peritoneal spasm can occur during breaststroke, ice skating, or playing hockey. Abdominal spasms can occur when an obese person tries to perform movements that are unusual for him.
Even minor deviations from the norm, such as a hacking cough or continuous sneezing, can cause tension and spasm of the abdominal muscles.
Excessive tension in the fibers leads to micro tears and can cause injury. In the case of severe deformation, the muscle burdened by spasm may be partially or completely torn from the ligament. Which will lead to internal bleeding or a hernia.
Types of pain
Tension or spasm can be broadly divided into three types of pain. It all depends on the severity of the sprain and muscle damage.
- The first type of muscle tension is a condition when the abdominal muscles contract relatively weakly. This does not entail any serious restrictions in movement. It is enough for a person to straighten up and take his usual body position for the spasm to subside.
- The second type of muscle tension is a condition where the pain is moderate. Tension of the abdominal wall muscles during a spasm does not allow a person to turn the torso by twisting the body.
- The third type of tension is accompanied by severe pain in the abdominal wall. Muscle spasms cause such severe pain that even basic movements become difficult to perform.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the cause of abdominal tension can generally only be done through a physical examination. Indirect signs of tenderness, such as swelling, functional loss of muscle strength in a specific area, indicate injury to the abdominal muscles.
Home ab exercise machine
Home ab exercise machine
Withstands loads of up to 300 kg and does not break when bent.
A muscle rupture, a hernia and the presence of a gap felt upon touch, upon palpation, clearly indicate the presence of an injury. Hardware diagnostics will help make a more accurate diagnosis. This includes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound or CT.
How many days does your stomach hurt after ovulation?
The stomach pain may be the most severe on the first day the cage comes out.
Sometimes this process can be felt for several hours. Nagging pain lasts up to a maximum of 2 days. p, blockquote 29,0,0,0,0 —>
If this condition does not stop for 3-4 days or more, this may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the female genital organs.
p, blockquote 30,0,0,0,0 —>
Pain on the 5th day after ovulation is a clear sign that you should immediately consult a doctor. Either pregnancy will be confirmed if there was sexual intercourse a few days before the ovulatory process, or some disease may be detected. In any case, the examination cannot be postponed for a long time.
p, blockquote 31,0,0,0,0 —>
Treatment
Treatment for cramps depends on the underlying cause. Possible options include:
Home Remedies
To treat abdominal cramps, it is recommended to drink water or sports drinks in moderation.
Many people get relief from home remedies. Pregnant women should talk to their doctor before using home remedies as they may be inappropriate or dangerous for use during pregnancy.
Home remedies that are effective:
- Rest. People experiencing cramping due to pulled muscles will find relief by resting their abdominal muscles while avoiding abdominal exercises.
- Warm. Applying a heating pad to the stomach relaxes the muscles and relieves pain.
- Massage. Gentle massage of the abdominal muscles improves blood flow and relieves pain.
- Hydration. Drinking plenty of water helps avoid dehydration, which can cause or worsen cramps. Sports drinks that replenish electrolytes are also beneficial, but should be used in moderation as they are often high in sugar.
- Epsom salt baths. Warm baths using Epsom salts are a popular home remedy for cramps and spasms. Warm water relaxes muscles, and Epsom salts contain a lot of magnesium, which helps with muscle spasms.
- Peppermint oil is considered an antispasmodic. It has an effect by reducing the influx of calcium into smooth muscle cells. It reduces abdominal pain. Peppermint oil is well tolerated. The most common side effect is heartburn.
Drug treatment
Both over-the-counter and prescription medications help with abdominal cramps. Use depends on the underlying cause of the spasms.
Types of medications that are recommended:
- Aminosalicylates, corticosteroids. Used to treat forms of IBD (inflammatory bowel disease.
- Antacids, inhibitors (PPIs). These medications reduce levels of stomach acid, which contributes to the cramping associated with gastritis.
- Antibiotics. They are prescribed for bacterial infections that cause gastritis and gastroenteritis.
- Antispasmodic drugs. Bentyl (dicyclomine), Hyoscyamine. People with IBS (irritable bowel syndrome) experience a reduction in cramps when using these medications.
- Painkillers. Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and acetaminophen (Tylenol) relieve pain.
What to do to relieve pain?
to consult a gynecologist about taking painkillers The modern assortment presented on pharmacy counters includes dozens of varieties of medications that are designed specifically to relieve pain. However, such drugs do not eliminate possible diseases.
You can get rid of the symptom using the following methods:
- common over-the-counter drugs (Aspirin, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Ketorol);
- specialized products (Nurofen, Butadione, Brufen);
- Regular intake of vitamins will make it easier to endure the process of ovulation and menstruation;
- the abdominal area can be slightly warmed with a heating pad or towel;
- It is recommended to drink more fluid;
- the diet should be varied with fresh juices, fruits, vegetables and other food products that contain a large number of vitamins of various groups;
- if the date of ovulation is known, then for a couple of days before and after the process of releasing the egg, it is better to avoid strong physical activity;
- relaxing baths with oils or herbs (melissa and flower oil are very relaxing).
REFERENCE! According to medical statistics, every fifth woman out of a hundred experiences nagging pain in the lower abdomen every month during the period of fertility.
General treatment features
The main treatment is to reduce swelling, pain and bleeding. Treatment of the abdominal muscle is complicated, first of all, by the fact that complete relaxation in this area is impossible.
Therefore, a person should take a lying position in which the abdomen does not stretch. This will relieve the pain to some extent. The duration of treatment directly depends on the severity of the injury.
In the first two types of tension, applying ice is enough to relieve pain.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs relieve pain within the first two days.
If the pain is significant, the doctor may prescribe pain-relieving injections. Sometimes an elastic bandage is loosely wrapped around the abdomen to limit movement and provide relief.
Muscle rupture is considered a serious injury and cannot be avoided without surgical intervention.
Abdominal muscle strain can be avoided by strengthening your abdominal muscles with proper exercises.
Watch the video: strengthening abdominal muscles for beginners
It is equally important to perform these exercises correctly. If possible, do this under the guidance of a good trainer. And then tension, spasms, sprains will not be scary for you.
Source
Abdominal cramps can bother anyone. The main reason is a contraction of smooth muscles, however, various diseases have specific features that determine the individual clinical picture.
Lower abdominal cramps in men
We can say that cramps in the lower abdomen in men are not a rare phenomenon, but very common. Due to the fact that many representatives of the stronger sex do not lead the healthiest lifestyle, certain diseases can often accompany them. The main reasons for their appearance are the following conditions and diseases:
- Acute cystitis.
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Prostatitis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Neoplasms in the genital organs.
The main problem in this case is that the patient cannot understand until the very end what was the prerequisite for the development of the disease state. And only when cramps in the lower abdomen in men become acute do they seek medical help. But in some cases it may already be too late.
How to relieve spasms in the lower abdomen
In pharmacology, there are many antispasmodics and painkillers. But, it is clear to say that only a specialist who has established a diagnosis can help in each specific case. Therefore, if you want to know how to relieve a spasm in the lower abdomen, you should first of all consult with specialists and not take medications uncontrollably.
Spasms in the lower abdomen have a different nature. But equally, they all need to be diagnosed. A timely visit to a specialist will help you cope with many problems and teach you how to deal with all diseases correctly.
Source
Causes
Abdominal cramps can occur under various pathological conditions. The most common are:
- Increased gas formation. Typically, the deviation develops when the diet is violated (consuming large amounts of legumes, cabbage, juices and carbonated drinks). The increasing volume of air in the intestines causes overstrain and stretching of the smooth muscles, which, trying to return to their original position, contract.
- Impaired movement of feces. With constipation, food particles accumulate in separate parts of the large and small intestines and put significant pressure on its walls. Increased afferent impulses cause muscle contraction. With diarrhea, the mechanism is reversed - significant secretion of fluid into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract promotes hypermotility, which manifests itself externally as spastic pain.
- Stress and neuropsychic disorders. Against the background of these conditions, discoordination of the activity of the central nervous system develops. As a result, inadequate efferent impulses to various parts of the gastrointestinal tract occur.
- Acute inflammatory processes. The affected intestinal wall reacts reactively to the movement of feces and the muscles contract.
- Renal colic. Any disorders of the kidneys can excite local pain receptors (in the ureters, bladder, pyelocaliceal system). Due to the irradiation of excitation, muscle cells contract.
- Uterine disorder. The reproductive organ is a large muscle in our body. With various pathologies (from neoplasms to menstrual irregularities and infections), spasms of the intestines and abdomen may occur.
- Spasms of the sphincters (esophageal, Oddi) and cystic ducts. In pathologies, usually caused by dysregulation and the appearance of hyperplastic processes, “muscle valves” begin to work inadequately, which is expressed by pain.
- Gastric colic. The presence of open lesions of the organ leads to the fact that gastric juice irritates the stomach wall and causes sharp pain, in response to which the stomach wall contracts.
- Changes in normal intestinal microflora. The growth of opportunistic and pathogenic microflora contributes to the development of inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane, and their toxins cause spasms and contractions of the smooth muscles of the abdomen.
Types of spasms
Depending on the number of areas involved, pain can be:
- limited (no more than 1 square abdomen);
- widespread (2 or more quadrants).
Depending on the duration:
- periodic (quickly arise and stop);
- constant (pursues all the time).
According to the severity of pain there are:
- low intensity;
- medium intensity;
- expressed.
Painful sensations, in some cases, can disrupt a person’s normal functioning (inability to change body position, move, etc.) Accordingly, spasms can be:
- with impaired functioning;
- without disruption of life.
There are also:
- with irradiation;
- without irradiation.
Irradiation is the spread of pain beyond the affected segment due to the close proximity of nerve fibers innervating different parts of the body.
Possible diseases and symptoms
The reasons leading to abdominal cramps are many, the most common ones are presented in the table.
| Name of pathology | Clinical picture |
| Acute intestinal infection, toxic infections | Spastic pain - in the initial stages. Then nausea and vomiting follow. The pain becomes constant and becomes acute. Possible fever and dehydration |
| Acute appendicitis | In the initial stages, spasms are observed in the epigastric region. Then they gradually descend into the iliac region of the abdomen on the right and are replaced by aching, dull or sharp. Body temperature rises. |
| Malignant and benign neoplasms | In the initial stages, rare spasms occur in one part of the intestine. As the tumor grows, its frequency, strength and duration increases. In the later stages, the pain is dull and aching. There may be intestinal bleeding (stool turns black), fever (up to 37-37.5 degrees), cachexia (weight loss). |
| Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum | Pain may occur in the stomach area 30-90 minutes after eating food. If absorption processes are disrupted, intestinal motility changes - pain in any part of the abdomen. |
| Nephroptosis, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis | Spasms can be in the right and left parts of the abdomen, as well as in the lumbar region. Less often - all over the abdomen or encircling. If infected, there is a rise in body temperature, symptoms of intoxication (weakness, headache). After the attack, the spasms stop |
| Miscarriage, uterine bleeding, heavy menstruation | Against the background of incoordination of contractions of different parts of the uterus, painful sensations arise that can spread to the entire abdomen. |
| Dysbacteriosis | Against the background of constant diffuse dull pain of low intensity, sharp and strong spasms occur in the lower abdomen, which stop after a few minutes. May experience: diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, heartburn. |
| Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction | Abdominal pain in the right hypochondrium occurs periodically. Accompanied by bitterness in the mouth, nausea and vomiting. |
| Gastroesophageal reflux | After eating, gastric contents are thrown into the esophagus. Against the background of irritation, its walls contract. Spasms are localized behind the sternum, in the epigastrium and in the navel area. |
| Psychogenic disorders (stress, depression, psychasthenia) | In addition to mental disorders, there may be short-term spasms and pain in any part of the abdomen, followed by constipation or diarrhea. |
Causes of pain after ovulation
To understand why the lower abdomen feels tight after ovulation, you need to understand the process itself and its effect on the female body.
Every month, vesicles called follicles form in the ovaries. At a certain moment, one of them accelerates in development, while the rest gradually fade away and disappear. An egg matures in a large follicle. The duration of its development until full maturity is different for each. On average 11-17 days. When it is ready, the follicle “explodes” and the cell descends into the fallopian tube. Here, upon meeting the sperm, it is fertilized and continues on its way to the uterus. Attaching to its wall indicates a successful conception.
A mature egg ruptures the follicle. Because of this, during ovulation the lower abdomen pulls
At this time, on the wound of the ovary, from where the cell emerged, the corpus luteum begins to mature. Its function is to produce a hormone that allows the fertilized cell to develop properly. In addition, the hormone contributes to the entire process of pregnancy and is produced throughout the entire period.
If no sexual intercourse took place at the time of ovulation, the cell dies within a day or two. The ovary is gradually healing and preparing for a new cycle. This stage is the same for everyone – 14 days. Very rarely it can have a shorter duration - up to 11-12 days.
Thus, when the lower abdomen feels tight after ovulation, the reasons are quite obvious. A rupture of the ovarian wall occurs, which is accompanied by unpleasant sensations. But it’s worth noting that some people don’t feel it or don’t pay attention. This pain is not always obvious. This depends on the pain threshold of the woman herself and on some internal processes.
For others, on the contrary, after ovulation, the lower abdomen and lower back pull quite strongly. There's no need to worry. This phenomenon occurs and is explained by the girl’s greater sensitivity to pain. The side on which the pain is felt indicates the ovary that produced the cell. They are known to work in turns. But sometimes, one of them may miss the line due to a failure caused by stress or infection. Climate change could have a similar impact. All these reasons affect, by the way, the speed of ovulation. They are quite capable of moving this moment, even with a usually rhythmic cycle.
Pulling in the lower abdomen after ovulation - what could be the reasons?
Diagnostics
The first auxiliary sign indicating the affected organ is the localization of pain. Then the doctor begins palpation (the affected organs are painful) and auscultation (listening to the sounds of mass movement through the intestines). To accurately determine the causes of pain, additional research methods are prescribed:
- General blood analysis. With inflammation, ESR and leukocyte levels increase. An increase in the number of neutrophils will indicate a bacterial etiology, and an increase in the number of lymphocytes will indicate a viral etiology. In the presence of bleeding, the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin decreases.
- General urine analysis. An increase in leukocytes, red blood cells, and casts in the urine is a sign of an inflammatory process in the urinary system.
- Fecal occult blood test. The test is aimed at detecting minor bleeding.
- Blood chemistry. The contents of amylase and lipase (increase with damage to the pancreas), AST and ALT (indicators of liver destruction), bilirubin (concentration changes with pathology of the gallbladder and biliary tract) are assessed.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Using ultrasound, the condition of parenchymal organs (kidneys, liver, spleen, pancreas) is assessed.
- Survey radiography of the abdominal organs. The method detects gas accumulation (in case of perforation of an ulcer), intestinal obstruction (for example, in case of tumors), and the presence of fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity (in case of bleeding or heart failure).
- FGDS. A flexible endoscope with a camera inserted into the stomach allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
- Colonoscopy. The procedure is similar to FGD, but the probe is inserted through the anus and the rectum and colon are visualized.
- CT and MRI are the most informative methods. Allows you to assess the nature of the lesion with millimeter accuracy.
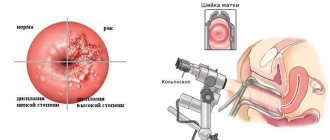
Colorectal cancer detected by colonoscopy
Drugs: method of use and mechanism of action
The main drugs used for spastic pain are:
| Name of the medicine | Indications | Mechanism of action | Mode of application |
| Atropine, Platifilin | Acute inflammatory diseases of the upper intestines, pancreas and biliary tract, renal colic. | They block M-cholinergic receptors, preventing the conduction of impulses. | To eliminate an attack - 1 ml intramuscularly. |
| Mebeverine | Inflammatory bowel disease, functional dyspepsia. | Blocks smooth muscle sodium channels, causing membrane depolarization and impaired contraction | Take 1 tablet orally in the morning and evening. |
| Otilonium bromide | Motor disorders of the gastrointestinal tract due to peptic ulcer disease, tumors. | Disturbs the passage of calcium ions from the intercellular space into myocytes, as a result the cells do not contract | Orally 1 tablet 1 time per day |
| Drotaverine, Papaverine, No-Shpa. | Urolithiasis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, dyskinesia of the gallbladder. | Suppresses the activity of the enzyme - phosphidediesterase, which is involved in the contraction of smooth muscle cells | 1 tablet 3 times a day |
| Phenobarbital | Severe spastic pain of any location and etiology. | Affects the autonomic centers of the brain, causing a general anticonvulsant effect (relaxation of all muscles). | 1 tablet (100 mg) up to 3 times a day |