The labor period for pregnant women does not always proceed as desired. Providing assistance to a woman in labor is almost always urgent . Sufficiently early and correctly selected specialist tactics can preserve the health of the expectant mother and reduce perinatal mortality many times over. One of these methods of surgical delivery is vacuum extraction of the fetus. The frequency of use of this method in Russia is only 0.7% .
Childbirth with a vacuum or vacuum extraction is an artificial surgical extraction of the fetus by its head during labor using a special apparatus ( vacuum extractor ), carried out by creating negative pressure between the fetal head and the inner surface of the vacuum extractor cup. This procedure is performed after pudendal anesthesia , which is used to block the pudendal nerve (anesthesia of the perineal area).
It should be noted that to work with this device, the participation of the woman in , since when the pushing period is completely turned off, it is possible to use only obstetric forceps. Therefore, childbirth with a vacuum is a rather rare surgical intervention, despite its fairly simple use.
Conditions for this procedure:
- Live fruit.
- Full dilatation of the cervix (10 cm).
- The ability of a woman in labor to participate in the second stage of labor (in pushing).
- Absence of an anatomically or clinically narrow pelvis in the diagnosis.
- The fetal head should be in the pelvic cavity.
- Opened amniotic sac.
- Empty bladder.
Indications:
- Secondary weakness of labor, not amenable to drug therapy.
- Progressive acute hypoxia (lack of oxygen) of the fetus.
As a result of an error in the technique or untimely application of a vacuum extractor to the fetal head, there is a possibility of developing unforeseen consequences and complications .
What a woman needs to know about vacuum birth
Vacuum birth is a complex procedure, the essence of which is to remove the baby from the birth canal of the woman in labor using a certain apparatus. Such manipulation is associated with certain risks for the health of the expectant mother and her baby. It is also technically complex and requires certain training and dexterity of the doctor. But, when performed correctly, it is vacuum extraction that is more modern and relevant compared to the same obstetric forceps.
Patient reviews
Most women who have undergone the use of a vacuum during childbirth claim that there were no serious consequences for the child. But the presence of hematomas, including cephalohematomas, occurs in almost every baby. For most, they resolve on their own over time and do not require treatment. Serious intracranial hemorrhage is reported infrequently.
The procedure itself, according to women, is not too painful; for many, it was used against the background of a previously performed epidural anesthesia. The use of vacuum during childbirth usually does not affect the length of stay in the maternity hospital, and the mother and baby are discharged in the absence of complications at the same time, that is, on the 3rd or 5th day.
For more information about the indications and consequences of using a vacuum during childbirth, see the following video.
Vacuum extraction of the fetus: when indicated
Like any third-party manipulation performed on the human body, especially on a pregnant woman and her baby, vacuum birth requires the presence of some reason for the intervention. These include:
- Weakness of labor, for which drug therapy is not effective.
- Development of fetal distress.
- Low transverse condition of the swept seam.
- Developed acute hypoxia in a child in the womb, which is actively progressing.
- Some pathologies of gestation, of various etiologies.
- The presence of an infectious-septic process in the reproductive system of the expectant mother, accompanied by a significant deterioration in health and fever.
Indications for use
All issues related to the use of vacuum extraction during labor are outlined in the recommendation letter of the Russian Ministry of Health No. 15-4/10/2-748 dated July 19, 2012.
The document names the following conditions as direct indications for the use of vacuum:
- fetal hypoxia and other signs of extreme distress of the child during childbirth, negative symptoms increase;
- a state of acute hypoxia of the baby at the moment when his head is already at the exit from the pelvis;
- the pushing period of labor lasts too long (2 hours for those giving birth for the first time and an hour for those giving birth again);
- pre-planned shortening of the second stage of labor, if a woman is contraindicated in pushing when refusing a cesarean section;
- assistance in removing the head from the incision during caesarean section.
Only doctors who have similar experience in obstetrics perform the procedure. The woman must give her written consent to such manipulation.
The Ministry of Health fully permits childbirth using a vacuum without anesthesia, but quite often the use of epidural anesthesia is allowed.
Methodology and devices used
The principle of performing vacuum childbirth from the technology side is quite similar.
The sequence of the main stages is not affected by the selected device. This is due to the fact that both existing devices have the same operating principle, which is to form negative pressure between the inside of the device and the baby’s head. The technique consists of a number of actions:
- Installation of the device through the vagina of the woman in labor onto the fetal head.
- Creation of pressure below atmospheric – vacuum.
- Direct extraction of the baby.
- Removing the device from the child's head.
And the devices themselves, which are used in maternity hospitals, are divided into two types:
- Maelstrom apparatus.
- Device of Chachaev and Vashakidze.
Maelstrom apparatus
The device developed by Maelström is a set of metal cups. The diameter of the cups ranges from 15 to 80 mm. This device was the first to be created for vacuum childbirth, therefore it is currently considered an outdated technology and is rarely used, in most cases, only when there is no other device in the hospital.
Chachaeva and Vashakidze
The device made by Chachaev and Vashakidze is considered to be a more modern device, the use of which is considered preferable. It looks like a rubber cap that is used to grip the baby's head.
Consequences for the child
- A lump ( swelling ) at the site where the vacuum extractor cup was applied. Occurs at the site where the device is applied. It usually resolves on its own on the 3rd day after the baby is born.
- Formation of cephalohematoma (collection of blood under the skin). Often in the frontal, facial or occipital region. As a rule, it disappears after 3 weeks.
- The risk of intracranial hemorrhages in the subperiosteal space . If the hemorrhage is localized in the occipital region, then there is a high risk of developing central nervous system depression syndrome (decreased muscle tone, weakened sucking, swallowing and motor reflexes, strabismus, facial asymmetry). If the hemorrhage is localized in the right parietal region, then there is a risk of developing a syndrome of increased excitability of the central nervous system (constant shuddering, tremors, tearfulness, restless sleep).
- Damage to the skin.
- Facial disfigurement (deformity).
- Pathology of the central nervous system : cerebral palsy (motor disorders), epileptic seizures.
- Lack of advancement of the fetal head.
- Changing the head configuration.
- The appearance of a bruise or bruise on the child’s head.
- jaundice or hyperbilirubinemia.
- Anemia of any severity. It may be associated with a large accumulation of blood in the area of the cephalohematoma. Clinical manifestations: pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, increased heart rate, hypovolemia.
- Attachment of infection , suppuration of the hematoma, its abscess formation. Possible symptoms of sepsis, septic shock: pallor, increased body temperature, tachycardia, gradually giving way to bradycardia, depression of consciousness.
- Destruction of the underlying skull bone.
- Difficult birth of the shoulders ( dystocia ), their injury (clavicle fracture, dislocation of the shoulder joint).
- Hemorrhages in the organs of vision . Blood accumulates behind the eyeball. This occurs during difficult and protracted labor.
- In the future, there is a possibility of delayed psychomotor, physical and speech development, and learning problems are possible.
- Functional disorders of the digestive and urinary systems.
- Lateral type rectal paralysis . Often temporary.
- Subependymal cystic formations ( pseudocysts ).
- Periventricular ischemia (insufficient blood supply to the brain).
- Periventricular and diffuse cerebral edema.
- Hydrocephalus with subsequent increased intracranial pressure.
- Comatose (unconscious) state.
Preparing for surgery
For a vacuum birth, the expectant mother assumes a reclining position on her back, with her legs apart and bent at the knee joints.
Before starting the procedure, the woman must undergo bladder catheterization using an elastic catheter.
Just before the start of the operation, the doctor performs a vaginal examination to determine the obstetric situation.
On the part of the medical staff, preparation for the manipulation includes calling into the room: an assistant, an anesthesiologist and a neonatologist who is capable of performing resuscitation measures for the newborn.
The vacuum method of childbirth requires the abandonment of inhalation or intravenous anesthesia, since the woman must push during the process. Instead, bilateral novocaine blockade of the pudendal nerves can be used as anesthesia, especially if the expectant mother is a first-time mother.
Pregnancy after cleansing. Video
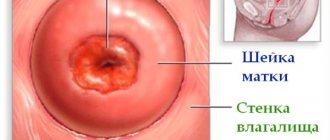
Vacuum aspiration is a mini-operation during which the contents of the uterine cavity are extracted (suctioned) using a special vacuum suction. During vacuum aspiration, only the superficial ball of the endometrium of the uterus is removed; its cervix and walls are practically not damaged.
Vacuum aspiration in gynecology - the essence and goals of the procedure
For most women, the concept of “vacuum aspiration” is associated with an unwanted pregnancy, or more precisely with a certain method of terminating it. Indeed, in gynecology this method is most often used to terminate pregnancy, but other purposes of its use are also possible, in particular:
- Postpartum vacuum “cleaning”. Vacuum aspiration after delivery is necessary in case of poor uterine contractility to remove blood clots and placental tissue.
- Vacuum “cleaning” after a frozen pregnancy or spontaneous miscarriage. It is carried out with the aim of extracting the fertilized egg (in case of 3D) or its remains (in case of incomplete miscarriage).
- Therapeutic vacuum aspiration for inflammatory diseases of the uterine cavity.
- Diagnostic vacuum aspiration of pathologically altered endometrium followed by histological examination.
Vacuum aspiration is performed on an outpatient basis, the procedure lasts no more than 10 minutes, after which the woman must be supervised in a hospital setting for 1 hour.
Is it painful to do vacuum aspiration? No. The procedure is practically painless, as it is done under local anesthesia. A woman may feel a slight aching pain in the lower abdomen.
Termination of pregnancy using vacuum aspiration
Vacuum aspiration () of the contents of the uterine cavity is perhaps the safest and least traumatic method of abortion of all those existing in our time. But such mini-abortions are effective only in the early stages of pregnancy (up to 5 weeks).
The most common question that gynecologists hear from their patients concerns the nature and duration of discharge after the vacuum aspiration procedure. It is not possible to give a clear answer to this, since the abundance and duration of discharge directly depends on the duration of pregnancy and other factors. But there are some “average” data.
Thus, scanty spotting bloody discharge can be observed for several days after vacuum aspiration, then it becomes serous or mucous in nature. In some women, after a short break (2-5 days), heavier menstrual-like bleeding resumes, the presence of which may be normal or may indicate post-abortion complications. Massive bleeding, yellowish discharge with a putrid odor is a reason to immediately seek medical help.
The first periods after vacuum aspiration usually begin after 30-35 days, a delay of 7 days is allowed. The menstrual cycle improves within a few months.
Rehabilitation and possible complications after vacuum aspiration
The technique of vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterine cavity is relatively safe. In most cases, no serious physical complications are observed, and long-term rehabilitation is usually not required. The most common complication is endometritis - inflammation of the walls of the uterus, and in case of termination of pregnancy - incomplete extraction of the fertilized egg. In some cases, there are more serious consequences: massive bleeding, pneumoembolism, infertility.
Recovery of the female body after vacuum aspiration occurs within one to two weeks. If the purpose of vacuum aspiration was to terminate the pregnancy, then as rehabilitation, the doctor will prescribe the use of COCs (Regulon, Novinet and others) for several menstrual cycles. If necessary, antibiotics may be prescribed.
A prolonged absence of menstruation after the vacuum aspiration procedure may indicate both a hormonal imbalance and a new conception (it is important to remember that a new pregnancy after vacuum aspiration can occur before the start of the first menstruation). Content
Content
Vacuum cleaning of the uterine cavity is one of the gentle methods for removing the endometrial layer and organ contents. There are many indications for the procedure, but most often the method is used to terminate an early pregnancy. Vacuum aspiration (cleaning) is performed after childbirth, spontaneous miscarriages, and if a woman wishes to terminate the pregnancy.
When is the use of vacuum contraindicated?
The use of an extractor is not allowed in a number of cases:
- Dead fetus.
- The uterine os has not fully opened.
- The baby has hydro- or anencephaly.
- The woman in labor has an anatomically (at least 2-3 degrees of narrowing) or clinically narrow pelvis.
- The fetus has an extensor presentation, and the sagittal suture is in a straight, high position.
- Gestation less than 36 weeks.
- The child's body weight is less than 2500 g.
- It is necessary to stop pushing in a woman due to any somatic pathologies or obstetric complications.
The specialist also takes into account the presence of certain conditions that are necessary for permission to carry out vacuum extraction:
- The pharynx should be completely open.
- There should be no amniotic sac.
- The parameters of the baby's pelvis and head must match.
- The baby should be in an occipital presentation.
- The baby is alive.
- The head is completely fixed by its large segment at the entrance to the small pelvis, in it or in the plane of exit from it.
- The mother's bladder should be empty.
Only if the absence of all contraindications is taken into account, the necessary conditions are present and the woman signs consent to the intervention, the doctor will begin vacuum extraction of the fetus.
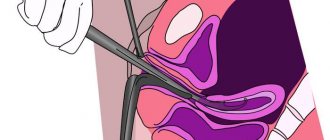
How is the cleaning done?
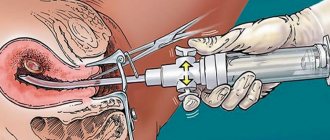
To carry out the procedure, the woman sits on a gynecological chair. If the uterus is cleaned after childbirth, then the manipulation is carried out directly on the birth table.
Local or general anesthesia is required for vacuum aspiration, which involves forced dilation of the cervix, as this is the most painful part of the procedure. Postpartum cleansing in most cases is performed without anesthesia, since the cervix during this period has a sufficient degree of dilation.
Sequence:
- The vaginal walls and cervix are fixed using dilators;
- The genitals are treated with an aseptic solution;
- Anesthetic injections are performed into the cervix and periuterine tissue; for general anesthesia, preference is given to intravenous anesthetic drugs;
- The doctor inserts a speculum into the vagina to monitor the progress of the operation, opens and dilates the cervix, if necessary;
- The gynecologist uses a special probe to measure the distance from the entrance to the cervix to its fundus in order to calculate how far the aspirator catheter can be immersed;
- An aspiration tube is inserted into the uterus and a vacuum is created in it;
- The gynecologist fixes the aspirator tip in one position or rotates it to collect the desired material.
After a period of time determined by the doctor, the woman needs an ultrasound examination of the uterine cavity to monitor the condition of this organ. If the study shows that there is no blood, placenta or fertilized egg inside the organ, then the cleansing was successful.
Features of vacuum aspiration in various conditions:
Vacuum cleaning of the uterine cavity after childbirth.
If there are placenta particles, blood clots, and other atypical tissues in the uterus, it will not be able to fully contract after childbirth. After an ultrasound confirming the atypical condition of this organ, medications that contract the uterus or manual cleaning may be prescribed.
If these methods are ineffective, the woman in labor is prescribed vacuum cleaning. After aspiration, she takes antibiotics to prevent inflammation, and the woman undergoes antiseptic treatment of her reproductive organs. Breastfeeding will have to be stopped for the period of treatment, saving milk by expressing.
Vacuum cleaning of the uterine cavity during a frozen pregnancy or hydatidiform mole.
Fetal death may result in spontaneous abortion. If it remains in the uterus, sooner or later its decomposition begins, which leads to intoxication of the female body, to sepsis. Vacuum aspiration allows you to get rid of particles of the fertilized egg and placenta that were not exfoliated when the dead embryo was released.
With a hydatidiform mole, the contents of the uterus cannot be expelled spontaneously. Bubbles with liquid remain inside the organ and cause the development of a malignant tumor.
If a woman experiences hyperthermia after the procedure, careful examination is required to ensure complete removal of the foreign tissue. After cleaning, the woman must be prescribed a course of treatment with antibacterial drugs.
Vacuum cleaning of the uterine cavity after miscarriage.
The manipulation is carried out to remove placental particles after the loss of an embryo older than 13 weeks, or during a miscarriage between 6 and 12 weeks, when there is a possibility that blood clots and particles of the fertilized egg remain in the uterus.
Here, a wait-and-see approach is more often used, and cleaning is prescribed for severe bleeding and signs of acute infection.
Mini abortion.
Early termination of pregnancy is performed by aspiration of the contents of the uterus along with the embryo. The procedure greatly reduces the trauma and negative consequences for women’s health inherent in the traditional method.
What is more dangerous – vacuum extraction or forceps?
Given the option of using a vacuum extractor or obstetric forceps, most expectant mothers begin to worry about the risks associated with these instruments.
In fact, the degree of danger to the fetus from both methods is almost the same, because tissue damage or the development of hematomas is likely with either device. But from the side of the mother’s body there is a difference. Thus, the use of extractors requires less pain relief; when used, the risk of ruptures of the soft tissues of the birth canal is significantly reduced and further rehabilitation is much easier. And in terms of their effectiveness, both options are equivalent.
If there is a need to use an extractor or forceps, the main task of future parents is to choose an obstetrician-gynecologist who is highly qualified and familiar with the operation of such devices.
Vacuum birth is one of the modern methods of helping expectant mothers in the birth of their babies. They assume the presence of a number of indications and contraindications, as well as certain conditions that the doctor must take into account when choosing this type of procedure. It is also associated with a number of risks, both for the baby and for the woman in labor. But with the correct technical performance and high professionalism of the obstetrician-gynecologist, as a result of vacuum birth a healthy newborn will be born, and his mother will tolerate the birth process well.
What you need to know if the cleaning was during a frozen pregnancy:
If you are feeling normal, you will be ready for discharge within a few days. The doctor prescribes the necessary medications and sends the patient home. Strict adherence to bed rest and no physical activity, so as not to cause bleeding and other discharge. For pain in the lower abdomen (which can be prolonged), it is recommended to take painkillers. It cannot be tolerated under any circumstances. Bloody discharge is normal after using the vacuum method. Their duration can be up to two weeks. You can use gaskets
It is important to note that tampons are strictly prohibited in this case. Using them to stop discharge can cause inflammatory diseases. After the procedure, you should refrain from intimate relationships for at least the first 2 weeks.
Interesting video:
Practice shows that the method of vacuum aspiration of the uterus is the most effective and safe. Many people tolerate it well and do not suffer any consequences. But still, it is worth noting the situations when you urgently need to see a doctor:
- A sharp increase in temperature to 38 degrees or more. Inability to knock it down for a long time;
- Increased bleeding to the extent that you have to change the pad more often than every 2 hours;
- The pain syndrome does not subside even after taking strong painkillers or it increases;
- The bloody discharge does not stop for more than two weeks and has an unpleasant odor.
Do not forget that manipulation using the vacuum method is used for different purposes. It helps well in treatment and is indispensable in diagnosing various diseases of the uterus. Of course, besides this method there are others. But vacuum cleaning has the most gentle effect on a woman’s body. And in our time it has been so improved that it has almost no negative consequences.
But there are cases when the aspiration procedure is contraindicated:
- during pregnancy more than 5 weeks;
- the presence of defects in the development of the uterus (bifurcation of the reproductive organ, the presence of a complete or incomplete septum, etc.);
- disease of the reproductive organs (this may be indicated by discharge with an unpleasant odor);
- malignant and benign tumors in the uterine cavity (for example, fibroids);
- ectopic pregnancy;
- if six months have not passed since the last abortion.
In fact, vacuum aspiration of the uterus is a very effective and gentle method today. It is used both for treatment and for the purpose of identifying a particular disease. To avoid complications, you need to carefully monitor your body after such a procedure and consult a doctor if there is the slightest deviation.