CYTOLOGY smear is a method of microscopic examination of the cervical epithelium for the purpose of PREVENTION AND EARLY DIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL CANCER.
A cytology smear primarily performed to detect atypical cells , which allows early diagnosis of dysplasia (CIN, LSIL, HSIL) or cervical cancer. It is an inexpensive and convenient method for reaching large numbers of women with preventative care. Of course, the sensitivity of a single study is low, but annual mass screening in developed countries has significantly reduced the mortality rate of women from cervical cancer.
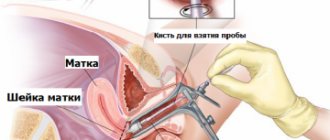
Due to the fact that atypical cells can be located in a relatively small area of the mucosa, it is very important that the material is obtained from the entire surface of the cervix, especially from the cervical canal ! For this purpose, special brushes have been created that make it possible to obtain material from areas inaccessible to inspection.
Particular attention is paid to the transformation zone, the cells of which most often undergo tumor degeneration. It is in the transformation zone that up to 80-90% of cervical cancer develops, the remaining 10-20% occur in the cervical canal.
When to take a smear for cytology? A smear for cytology should be taken starting from the 5th day of the menstrual cycle and 5 days before the expected start of menstruation. The analysis cannot be carried out within two days after sexual intercourse or insertion of suppositories into the vagina. Failure to follow these rules may lead to erroneous interpretation of the results. Also, the presence of a pronounced inflammatory process in the cervix and vagina seriously complicates diagnosis.
It should be noted that collecting material is a rather unpleasant procedure. The gynecologist must scrape the epithelium from the surface of the cervix and enter the cervical canal. The more epithelium from different zones gets in, the better the diagnosis. Sometimes bruising may remain after cytology, this is considered normal.
Thus, the main significance of a cytology smear is to determine qualitative changes in cells. To determine the infectious agent that caused the inflammation, it is better to use a smear on the flora or bacteriological culture . However, during a cytological examination, the doctor may note the presence of any microorganisms. Normal microflora includes rods (lactobacillus), single cocci, and in small quantities there may be opportunistic flora. The presence of specific infectious agents (Trichomonas, amoebas, fungi, gonococci, gardnerella, leptothrix, chlamydia, an abundance of cocci) is considered a pathology that needs to be treated.
Processing of smears. Cytology deadlines
After collecting the material, the sample is transferred to a glass slide, fixed and stained. When directly transferring a smear from a brush, partial loss of material and cell deformation are possible, which leads to a decrease in the sensitivity of the method and a large number of false results. The classical method was replaced by liquid cytology, which significantly increased the accuracy and quality of the study.
Liquid cytology is a new technology for processing smears, which involves placing samples in a container with a special stabilizing solution. In this case, the entire resulting epithelium enters the solution, which is then centrifuged and cleared of unwanted impurities (mucus, etc.). Today, liquid-based cytology is becoming the “gold standard” for examining smears from the cervical mucosa. But even in this case, the sensitivity of a single study does not exceed 60-70%. During reproductive age, false negative results are common, and in menopausal women, false positive results are common. Only triple cytological examination allows one to approach 100%.
There are various methods for staining preparations: according to Papanicolau (Pap test), according to Romanovsky, according to Wright-Diemsa, according to Gram. All methods are aimed at staining certain cellular structures, which makes it possible to differentiate different types of epithelium and distinguish between cells with keratinization and tumor transformation. The Pap test is widely accepted and is now used as the main standardized test.
How long does the test take? Depending on the organization of the process, the result can be obtained within 2-3 days.
Cytogram without features - what does this mean?
Cytological findings vary widely. As a variant of the norm, the following conclusions can be used: “ cytogram without features ”, “ cytogram within normal limits ”, “ cytogram without intraepithelial lesions ”, “ cytogram corresponds to age - atrophic type of smear ”, “ NILM - Negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy”, " proliferative type of smear ." All this is NORMAL!
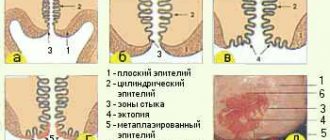
The cervical mucosa is normally smooth, shiny, and moist. The squamous epithelium is pale pink, the glandular epithelium is bright red. The cellular composition that can be found in normal cytology is presented in the table.
| Exocervix | Well-preserved cells of squamous epithelium, mainly of the superficial, intermediate layers. |
| Endocervix | Cells of glandular (cylindrical) epithelium. |
| Transformation zone | Squamous epithelial cells, single cells or small clusters of metaplastic squamous epithelium, small clusters of glandular epithelium. |
Atrophic type of smear - what does it mean?
In women in perimenopause and menopause, due to a decrease in the overall level of estrogen, many metabolic processes slow down, which results in atrophy of the squamous epithelium. These changes can be seen in the cytogram. The atrophic type of smear refers to a variant of the normal cytogram. You can often find in the conclusion the phrase “ cytogram corresponds to age ” or “ age-related changes nilm ”. All these are variants of the norm!
You need to understand that in menopausal women, false-positive cytogram results are very common - this is the case when it is difficult for a cytologist to distinguish atrophic squamous epithelium from dysplasia. This needs to be understood because subsequent cervical biopsies usually do not find any pathology. In addition, older women may have a tendency to keratinize the epithelium with the formation of hyperkeratosis (leukoplakia).
| Exocervix | Well-preserved squamous epithelial cells, mainly of the parabasal and basal layers. More often there are smears of the atrophic type, but they can also be of proliferative or mixed types. |
| Endocervix | The absence of columnar (glandular) epithelial cells is not an indicator of poor quality of the smear, since during this period the transformation zone moves deep into the canal and to obtain glandular epithelium the brush must be inserted to a depth of more than 2-2.5 cm. |
| Transformation zone | Cells of squamous, metaplastic epithelium. |
The mucous membrane of the cervix in menopause is thinned, easily injured and damaged, which is a consequence of a decrease in estrogen.
Decoding the cytogram
Terminology
Cytology smear is normal
Dyskaryosis and dyskaryocytes are abnormal cells with hyperchromatic (dense and dark) nuclei and irregular nuclear chromatin. Dyskaryosis will be followed by the development of a malignant neoplasm. Used as a synonym for dysplasia, but as a more general term.
Atypia is any difference in cell structure from the norm. The meaning often depends on the context. But more often it is used to describe pre-tumor and tumor changes.
Inflammatory atypia is a combination of degenerative, reactive, proliferative changes in cells during inflammation. These changes can cause a false-positive diagnosis of dysplasia or cancer.
Dysplasia is a process of impaired maturation of squamous epithelium. It is a true pre-tumor process. Has 3 degrees. The first usually includes a viral lesion, the second and third - a lesion with tumor potential.
Severe epithelial dysplasia
ASCUS are atypical cells that are difficult to differentiate from reactive atypia and the pretumor process itself. Atypia of unknown significance.
Dyskeratosis is a disorder of keratinization of individual squamous epithelial cells. Is a sign of HPV.
What is an atrophic type of smear in gynecology?
A cytology smear is one of the most important gynecological examinations. For a gynecologist, this is the easiest and most reliable way to find out what condition the cervix is in.
The atrophic type of smear is a good and reliable way to find out the quantitative ratio of standard and parabasal cells. This analysis makes it possible to get a clear picture of the condition of the cervix, as well as find out the amount of hormones in the ovaries.
Presence of atrophy in the smear
The most popular question about the atrophic type of smear is “what does it mean”? An atrophic smear occurs with certain disorders of the vaginal and uterine mucosa.
Atrophy is a change in the mucosa, which is caused by a decrease in estrogen levels.
Often the prerequisite for the pathology, which results in an atrophic smear, is menopause or artificial menopause.
Video:
Atrophy can manifest itself in dryness of the vaginal mucosa, decreased secretion of vaginal lubrication, and increased acidity of the organ environment.
This type of smear is often accompanied by a violation of the microflora of the genital organs. The number of lactobacilli decreases, and the percentage of pathogenic flora increases.
Patients may complain of burning sensations and itching. A specific sign accompanying an atrophic smear may be loss of pubic hair.
An atrophic smear may indicate a gynecological disease such as vaginitis.
This disorder is not a temporary failure, but a morphological change in the structure of the cells of the uterus and vagina. Therefore, various types of research are used to diagnose the disease.
Some signs of atrophy can be revealed by a simple gynecological examination. The doctor will make preliminary conclusions by visually observing the cervix using a speculum.
If necessary, an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs may be prescribed.
A smear for microflora, a study of the acidic environment of the vaginal contents, and, in particular, a smear for cytology are informative.
Atrophy can occur both for natural reasons (for example, menopause) and in the case of malignant cell changes.
Therefore, if an atrophic type of smear is detected, the doctor should prescribe the patient a comprehensive examination of the uterus.
The cause of an atrophic smear may be insufficient blood flow to the pelvic organs. The risk of atrophy increases with smoking.
In older women, vaginitis and atrophy can develop against the background of natural hormonal changes.
In many cases, the changes are not associated with any pathologies, but they need to be monitored and the dynamics of the disease progressed.
In some cases, due to a decrease or complete deficiency of estrogen, the disappearance of lactobacilli in the genitals may be observed.
Due to structural changes in the vagina caused by old age, conventional diagnostic methods can be very difficult.
In some cases, it is necessary to perform anesthesia for examination and taking a smear.
READ Throat swab analysis and interpretation
Why is this smear used in gynecology?
The atrophic type of smear (you can read what this means in this article) is considered the most reliable method of passing gynecological cytology tests. This method is considered very simple and accessible to all segments of the female population. With its help, you can determine the condition of the cervix and take subsequent therapeutic or preventive actions.
The atrophic type of cytology smear has the main goal of identifying unnatural and foreign cells found in the female body. Usually, in a normal, healthy woman, such cells are absent. Very often, it is these foreign cells that are the beginning of the appearance of malignant tumors.
If the gynecologist informs you that the test result is unsatisfactory, do not delay treatment under any circumstances. If there are deviations of any type, immediately undergo additional medical tests that will help establish the whole picture. Most often, such examinations help detect cancer in the early stages. The sooner you start treatment, the more likely it is to be successful.
Procedure and preparation for the study
For an informative and accurate result, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations for preparing for the analysis. The timing of the study is of great importance.
The doctor chooses a specific day for taking a smear depending on the schedule of menstruation and ovulation.
There is an opinion that it is best to do the analysis a few days after your period. However, the acceptable time frame for sample collection may be longer.
It is best to choose a specific day for a smear together with a gynecologist, in accordance with the menstrual schedule of a particular woman.
To accurately navigate the date of menstruation and the timing of ovulation, it is useful to use special calendars, which can often be obtained from a antenatal clinic.
In addition, it is possible to use special computer programs and mobile applications that allow you to record not only the dates of menstruation, but also track the symptoms and complaints of a woman on each specific day of the cycle, and mark the dates of sexual intercourse. In this case, you can set the optimal time for a smear.
Video:
A smear is performed during an examination in a gynecological chair. To take a sample, which is taken from a specific area of the uterus, the doctor uses a sterile phytobrush.
The doctor must obtain cervical cells located under the first layer of the epithelium, since the cells of such a layer do not allow for an informative study.
This type of smear is not performed during inflammation, as it can lead to the spread of infection and complication of the disease.
In the case of itching and unusual vaginal discharge, the nature of which is unknown, such research will have to be abandoned until the cause of the unpleasant symptoms is clarified.
A few days before the analysis, the patient should refrain from any sexual intercourse, the use of vaginal suppositories, creams and gels.
A week before the test, you should not douche. Before the analysis, at least two hours must pass from the last urination.
This type of smear procedure is virtually painless and takes only a few seconds. In some cases, slight bleeding may appear after the examination.
Therefore, women are advised to carry panty liners with them. Preservation of spotting is acceptable for 1-2 days after the smear.
In case of heavy or prolonged bleeding that is not associated with menstruation, you should seek help and report that it was caused by scraping.
READ Why and how do they take a smear from men for infections?
Analysis results are prepared within 24 hours. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe a repeat examination for the patient.
What is atrophy
Before dealing with the disease itself, you should understand what atrophy is. In gynecology, this concept refers to the predominance of parabasal cells in the body. At the same time, the number of ordinary cells decreases significantly. Most often, a large number of leukocytes will be found in the smear, and the volume of Dederlein bacilli is as low as possible.
In some women, ideally, the same number of these cells can be observed only during menopause. This condition lasts no more than five years. At this time, the amount of estrogen in the female body decreases significantly, but this does not affect the microflora, and it can be in ideal condition.
The atrophic type of cervical smear begins to develop due to a deficiency of the female hormones estrogen. It is worth paying attention to the fact that there are several types of cells contained in the cervix:
- upper stratum corneum.
In this case, each cell belongs to its own layer of tissue. For example, superficial keratinizing cells are considered the outermost layer of the vaginal epithelium. In front of them are several intermediate layers of epithelial cells.
The lowest layer of epithelial tissue consists of basal cells, which over time begin to transform into other cells located in the intermediate layers.
The female hormones estrogens are responsible for the process of cell transformation. If there are not enough of these hormones in a woman’s body, then the process of cell transformation begins to be disrupted, which is why the main problems appear.
Most often, the atrophic type of cytology smear occurs in more mature women as a result of decreased hormonal levels. These processes occur as a consequence of decreased performance of the female genital organs. It is no exception that in adulthood this smear may even be considered absolutely normal. At a younger age, problems arise due to improper functioning of the genitourinary system and problems with hormonal levels.
What is an estrogen smear?
Among gynecologists there is a stable expression estrogen smear. Is it good or bad when a woman has just such a smear?
Not all representatives of the fair sex have an estrogen smear during menopause. The essence of such a smear is that the number of cells of the surface epithelium, which performs the main protective function of the vagina, practically does not change. This means that the level of estrogen in a woman’s body is so high that it allows this type of smear to appear.
The reason for the estrogenic type of smear is the body’s ability to compensate for the lack of sex hormones and primarily estrogen. Also, an estrogen smear may appear when a woman receives treatment aimed at maintaining hormonal balance. Hormone replacement therapy helps to maintain normal vital parameters, so the smear will be “like a young person.”
However, such indicators do not always please doctors, who, based on objective indicators, see that the woman is approaching menopause.
In some cases, maintaining high estrogen, and therefore ensuring an estrogen smear, can be a consequence of malignant processes localized in the uterus or ovaries.
Atrophic type of smear: parakeratosis
Only a gynecologist can diagnose this disease after examination. To effectively treat this disease, it is recommended to restore hormonal levels. The specialist will select the medications based on your tests. In this case, the hormone estrogen can enter the female body with the help of tablets, suppositories, patches or ointments. It is also recommended to take vitamins and improve vaginal tone through special exercises.
Parakeratosis is a disease of the cervix, namely the keratinization of its mucous layer. This phenomenon is most often associated with traumatic factors. This may include medical intervention, as well as the formation of infections. Human papillomavirus is also possible.
To treat this disease, the mucous membrane of the cervix is scraped and further studied to determine the presence of foreign cells. Laser cauterization of damaged areas is very often used. Under no circumstances should this disease be treated with traditional methods.
What does a smear look like?
Looking at a smear with the naked eye, it is impossible to understand that there is something wrong with it. After all, outwardly it will be no different from a smear of a young healthy woman. Therefore, cytological examination (atrophic type of smear) can only be carried out using a modern microscope. Women should pay attention to the fact that they need to do this every six months to maintain their health and longevity.
The atrophic type of smear (what this means can be read in this article) has the appearance of parabasal cells, which make up the bulk of the total cell mass. Estrogen deficiency leads to the fact that the epithelial tissue in the vagina does not pass into other types of tissue, and this is the main problem.
Scientists also noticed that the more progressive the atrophy, the more the nucleus of the parabasal cells increases. The deepest atrophic stages allow us to notice that the nucleus becomes so large that it can displace all other vital elements of the cell. Despite the fact that the nucleus increases significantly, the cell itself remains the same size.
Products containing estrogens
Estrogens are female hormones responsible for the correct and coordinated functioning of the female genitourinary system. If the body does not have enough of these elements, then not only medications, but also food can come to the rescue.
Estrogens are very important for women's health in general. They are responsible for the beauty and general condition of a woman. Therefore, if your hormones are not enough, you should take phytoestrogens into account.
Scientists have proven that the largest amount of them is found in beer. But you definitely shouldn’t abuse this product. In addition, other foods of plant origin also contain a large amount of estrogens, which are worth paying attention to first.
A very large amount of the much-needed female hormone is found in legumes. Especially in soy. But peas, red beans and other beans are also not inferior to it.
Pay attention to flax seeds, which in addition to hormones also contain large amounts of other beneficial substances. In modern medicine, it is the extract from them that is used as a substitute for natural female hormones.
There are a lot of estrogens in grain crops. Especially in wheat. For a woman, the most optimal breakfast would be porridge, especially with bran.
Don't ignore dairy products. Since the cow that produces milk eats a lot of grass rich in estrogen, the milk will contain a large amount of female hormones.
However, do not forget that moderation is needed in everything. Before starting to take herbal hormones, be sure to consult your doctor. After all, their excess can lead to many diseases, one of which is breast cancer.
Cytology smear
In order to determine the condition of the genitourinary system in gynecology, it is customary to do a cytology smear. This procedure allows you to find out about the condition of the mucous membrane of the cervix, as well as pay attention to the presence of various pathologies. A cytology smear allows you to carefully examine the epithelial cells. This method is the most accurate and reliable for determining the composition of the epithelium, because even the slightest changes will be noticeable under a microscope.
Most often, cytological studies are carried out in order to study all kinds of changes in the cervix, as well as in the vaginal mucosa. During this test, several types of smears may be noticed:
- regressive or atrophic type of smear (you now know how to treat the pathologies that cause it);
Each of these types of smears has its own essential characteristics, which are expressed in the predominance of some cells over others. If we talk about an atrophic type smear, then in this case the epithelium is largely dominated by parabasal cells. They will have very large kernels. At the same time, the size of the cell itself remains insignificant.
Types of strokes
Depending on the level of hormones and epithelial cells, cytological analysis can show several types of smears, in particular:
- Estrogenic. This smear consists of flat surface cells that have degenerative changes in the cytoplasm (vacuolization) and basal folding of cell membranes. Individual nuclei and cell fragments are observed in the material.
- Progesterone. It shows an increased number of intermediate layer elements that are prone to clumping.
- Proliferative is characteristic of the first five years of menopause. It is characterized by a separate position of surface epithelial cells and a low concentration of leukocytes. Such smears are detected when progesterone production decreases, but estrogen is still synthesized in sufficient quantities.
- The mixed type combines an approximately equal proportion of cells from the intermediate and superficial layers. Often this type of smear occurs in the initial period of menopause.
- Atrophic (regressive). It is characterized by a predominance of parabasal epithelial cells over elements from other layers of the epithelium. Very often this type occurs in postmenopause.
- Androgenic. It is determined when a collection of intermediate, parabasal and basal cells correlates with a small number of superficial ones. Such a smear may indicate the development of tumors of the ovaries and adrenal glands.
- Inflammatory. This type of smear indicates the presence of fungi, trichomonas, cocci, and leukocytes. At the same time, the number of epithelial cells in the smear is sharply reduced.
Determining the condition of the cervix
The female genitourinary system can work perfectly only if the ovaries produce a sufficient amount of hormones - estrogens. In case of their deficiency, the condition of the cervix may not change for the better. Along with this, changes occur in the vaginal ecosystem. Dysbiotic processes begin to actively progress, and alkalization of the mucous membranes also occurs. At the same time, the content of bacteria and infections in the female genital organs increases significantly.
The upper layer of the cervix is epithelial tissue, under which there are subepithelial stroma. They can easily begin to bleed even with the slightest damage.
If during the examination a woman is found to have an atrophic type of smear, then the patient urgently needs to undergo other types of examinations. The sooner this is done, the faster and easier the treatment process will be.
Features of treatment
If, as a result of the test, an atrophic type of smear is observed, then you definitely shouldn’t despair in advance. This does not provide a 100% guarantee that you are susceptible to cancer. Most often, such a smear is done for general monitoring of the female genitourinary system. Therefore, even if you heard that you have an atrophic type of smear, this is not the main indicator of oncology.
Quite often, women are susceptible to a disease such as atrophic colpitis. It is not very dangerous for women's health, but nevertheless requires immediate treatment.
Most often, this disease is successfully treated with hormonal therapy. For this, special suppositories or ointments are used, which are inserted into the vagina for two weeks. In addition, tablets or patches are used. For best results, this therapy is practiced for six to seven years. Many doctors recommend eating foods rich in phytoestrogens.
The atrophic type of smear, in which the cervix is in a damaged state, can only be cured if complex methods are used. This may include medications prescribed by your doctor, as well as the use of special products.
The atrophic type of smear, the treatment of which should be started immediately, most often manifests itself as atrophic vaginitis. This disease is associated with an incorrect hormonal background of a woman and with an insufficient amount of the hormone estrogen secreted. Very often, vaginitis can be caused by menopause, which can be either natural or artificial.
During natural menopause, the amount of hormones is a normal response of the female body to age. In cases of artificial menopause, an insufficient amount of hormones is a consequence of a disruption in their production by the ovaries. This problem can be solved quite simply using special methods.
What the atrophic type of smear means can only be determined by your attending physician. If your diagnosis is “atrophic vaginitis,” then you definitely shouldn’t be upset. It is treated with very simple and accessible methods. By the way, the harbinger of such a disease are the following symptoms:
Atrophic type of smear - what does it mean?
If you have had a smear for oncocytology, the atrophic type of smear may be indicated in the conclusion.
Let's talk about what this means.
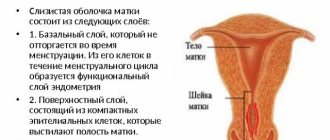
The mucous membrane of the genital tract consists of various cells.
They all have different degrees of maturity.
That is, one type of cell gradually turns into another.
All cells are divided into four types:
- superficial - large in size, with a small core, separately located, detected in large quantities in the middle of the menstrual cycle;
- intermediate - slightly smaller in size, have a large round core, located mainly in layers;
- parabasal - small round cells with a large nucleus, normally found only during menstruation, and even then in small quantities (an increase in their number indicates atrophy);
- basal - even smaller than parabasal, the nucleus occupies a third of the cytoplasm, appear only after menopause, as well as after childbirth.
Superficial ones are located at the very top, while basal ones are located deep in the mucous membrane.
Superficial ones have the highest degree of maturity, and basal ones have the least.
Thus, if a large number of mature cells enter the smear, this means that they develop normally and tissue trophism is preserved.
If there are many immature cells present in the smear, this indicates atrophic processes.
Atrophy is a relative concept, not an absolute one.
That is, it does not belong to those processes that either exist or do not exist.
There is no clear boundary between normal and intermediate type of smear, intermediate and atrophic.
These changes occur gradually.
There are more and more immature cells, and fewer and fewer mature cells.
The more pronounced the atrophy, the more parabasal cells are contained in the cervical epithelium.
As atrophy develops, the size of their nuclei also increases.
Causes of the atrophic type of cervical smear
If you have an atrophic type of cytology smear, the reasons for this may be different.
The main ones:
- age-related decline of reproductive function;
- an atrophic type of smear is often observed after childbirth;
- estrogen deficiency at a young age;
- long-term chronic inflammatory processes (colpitis).
Women of reproductive age may also experience an atrophic type of smear.
This happens when:
- dysfunction of the ovaries;
- dysregulation of ovarian function with a decrease in estrogen production (this is caused by pathology of other endocrine glands, for example, the hypothalamic-pituitary system).
An atrophic type of smear is possible after removal of the uterus and appendages, for example, in the case of malignant neoplasms.
The ovaries can also be damaged by radiation therapy.
Young women sometimes develop ovarian failure syndrome, characterized by anovulation and hypoestrogenemia.
Resistant ovarian syndrome is possible due to disruption of their receptor apparatus.
In this case, their full work is impossible due to the fact that the ovaries do not perceive “signals” coming from other endocrine glands.
That is, they do not respond to changes in the level of other hormones that should stimulate the formation of estrogen.
Types of Estrogen Response
Such a smear allows you to assess the condition of the uterus and ovaries according to four characteristic types of estrogenic reaction:
- with the first type of reaction, there is a clear lack of estrogen and an increased number of leukocytes and atrophic cells;
- the second is characterized by a moderate estrogen deficiency, as well as the presence of leukocytes and atrophic cells, but their concentration is less than in the case of the first type;
- the third is characterized by an equal ratio of all types of epithelial cells;
- with the fourth type, the estrogen content is excessive.
During the premenopausal period, a smear with a slight increase in estrogen content can be considered a variant of the norm, since the reproductive system has not yet lost its reproductive function and the amount of estrogen is synthesized by the ovaries in sufficient quantities, in addition, the influence of changes in the general hormonal background is added. In this matter, it is the quantitative characteristics of the indicators that mean a lot.
As menopausal changes progress, the estrogen type of smear reveals an increased content of dying cells. In this case, there is a significant decrease in the amount of progesterone.
By the time of entry into postmenopause, leukocytes and cells that make up the basal layer are not detected in the smear. This period is characterized by a change in the structure of the cytoplasm (the internal environment of the cell) - its granularity and heterogeneity are observed. This may be a symptom of trouble, for example, indicating the development of inflammation.
The estrogenic type of smear in menopause is more common in women with increased body weight, which is probably explained by the fact that adipose tissue cells are also capable of synthesizing estrogens along with the adrenal glands.
To determine the quantitative ratio of epithelial cells, the karyopyknotic index (KPI) is used, which is calculated by the ratio of the number of surface cells with a pyknotic nucleus (that is, a wrinkled nucleus that has been exposed to a pathological factor) to the total number of all epithelial elements. It is the indicator of the quantitative ratio of elements that helps determine the estrogen saturation of the body. For the menopausal period, the level of the CPI should not be higher than 25%; during postmenopause, its indicators should be within 10-20%.