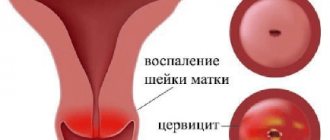
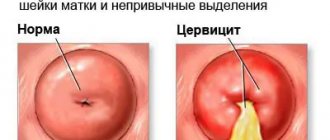
Cervicitis is a disease of the female reproductive system.
It is accompanied by an inflammatory process localized in the cervix.
The disease is considered quite common.
And no woman can be insured against it, regardless of her age.
Representatives of the fair sex are interested in what types doctors distinguish, and how the approach to treatment changes depending on the type of disease.
Is the pathological process dangerous for pregnant women, and is it possible to cope with the disease without leaving home?
Causes of cervical inflammation
The reasons for which the inflammatory process of the cervix develops are very extensive.
Cervicitis can be caused by opportunistic bacteria. Every person has them. Bacteria live on the mucous membrane and skin. The most common types: Escherichia coli, staphylococci, streptococci, Klebsiella, etc. The disease is also caused by sexually transmitted infections. This could be chlamydia, trichomonas, ureaplasma.
There are a number of other reasons for the inflammatory process of the cervix:
- Various mechanical injuries and damage can be caused as a result of abortion, hysteroscopy, installation of intrauterine contraceptives;
- A weakened immune system cannot cope with opportunistic bacteria, resulting in an inflammatory process;
- Other gynecological diseases are a good environment for the occurrence of cervicitis;
- Hormonal disbalance;
- Douching at home with solutions of iodine, citric acid, etc.;
- Promiscuity and more.
Causes of cercivitis
The occurrence of cervicitis is possible against the background of changes in pathogenic microflora: Escherichia coli, streptococcus, staphylococcus, fungi. In addition to opportunistic microflora, specific infections can provoke cervicitis: gonococcus, chlamydia, syphilis, trichomonas, mycoplasma, viruses.
The emergence of specific genital tract viruses is caused by infection during sexual intercourse; opportunistic vaginal microflora is formed due to the penetration of microbes from the rectum, blood, and lymph inflammation.
The appearance of cervical cervicitis is preceded by factors such as:
- cervical injuries during childbirth;
- diagnostic curettage;
- surgical termination of pregnancy;
- use of an IUD;
- benign neoplasms of the uterus;
- cicatricial deformities of the genital organs.
Cervicitis, what it is, is mainly diagnosed by women of reproductive age. Rarely, symptoms appear in patients during menopause. Cervicitis is characterized by spontaneous abortion and chronic miscarriage; in case of gestation - premature birth. The disease provokes the occurrence of erosion and polyps of the cervix, inflammation of the upper segments of the genital organs.
Types of inflammation and their treatment
Doctors distinguish several types of cervicitis. Inflammation of the cervix and treatment completely depend on the course of the disease and the pathogens that caused it.
Acute inflammation of the cervix
It can be caused by chlamydia, streptococci and, more often, gonococci. In the acute course of gonorrheal cervicitis, the infection begins from the cervical canal, affecting the superficial layers of the cervical mucosa. If acute cervicitis is provoked by streptococci or staphylococci, then tissue damage occurs much deeper and, penetrating the lymph, the infection spreads to nearby organs and tissues.
When treating acute cervicitis, antibiotics are prescribed, to which the strain that caused the development of the disease is sensitive. Treatment of the cervix with this course of the disease is not recommended. Tampons and other processing tools can serve as conduits for the spread of infection. Physiotherapy and UHF can be used, but after the exacerbation is relieved. For the entire period of treatment, the patient must maintain sexual rest.
Since acute cervicitis most often occurs against the background of sexually transmitted diseases, examination of the partner and further treatment are required.
Important! Condoms should be used during the partner's examination to avoid re-infection.
Chronic inflammation of the cervix
In the absence of proper treatment for acute cervicitis, the disease develops into chronic disease, the vivid symptoms go away and the disease penetrates into the deeper layers of the cervix.
In the absence of symptoms, the disease is difficult to suspect. However, when examined with mirrors, the cervix will be swollen and eroded. Chronic inflammation can lead to the development of dysplasia. Therefore, it is recommended to take a biopsy of the “changed” cervical areas.
In addition to antibiotics, which are prescribed from the first day of the cycle, for greater effectiveness, treatment will necessarily consist of physiotherapeutic methods. These include:
- EHF;
- Electrophoresis;
- Ultrasound therapy.
In sanatorium-resort conditions, mud therapy, bathing in radon springs and treatment with hydrogen sulfide mineral water can be used.
In addition, suppositories with Longidase have a good anti-inflammatory effect; they should be used rectally.
Chronic cervicitis is difficult to treat. In the absence of improvement from drug therapy, surgical methods may be used:
- cryotherapy;
- laser therapy;
- diathermocoagulation.
During the entire course of treatment, it is very important to use drugs that restore the natural microflora of the vagina.
Atrophic inflammation of the cervix
The cause of this type of cervicitis is genitourinary infections, human papillomavirus (HPV) and other diseases of viral etiology. Also, atrophic inflammation of the uterus is preceded by mechanical damage due to abortion, hysteroscopy, trauma to the cervix during childbirth, etc. During the menopausal period, the concentration of estrogen in the blood serum decreases. As a result, the mucous membrane of the cervix becomes thinner, becomes traumatic and turns into an ideal environment for pathogenic flora. In this regard, atrophic cervicitis develops.
Treatment will include antiviral drugs, for example Allokin alpha, various immunomodulatory agents, and multivitamin complexes. The basis of treatment for atrophic cervicitis will be hormonal preparations containing estrogen. They will normalize the structure of the cells of the mucous epithelium of the cervix and help restore the flora and acidity of the vagina.
Purulent inflammation of the cervix
The causative agents of purulent cervicitis are most often sexually transmitted diseases, for example, urethritis or gonorrhea. If purulent cervicitis is viral in nature, then it may be caused by a herpes virus or Trichomonas virus. Before the appearance of purulent discharge, ectopia (pseudo-erosion) of the cervix may be observed. In this case, there will be bleeding after sexual intercourse. In addition to antibiotics, vaginal suppositories with metronidazole, tetracycline preparations, antiviral therapy and immunomodulators will be prescribed.
Important! The lack of drug therapy for purulent cervicitis can lead to severe complications.
Candida inflammation of the cervix
This form of the disease is caused by a fungal infection. During its treatment, antifungal drugs will be prescribed, for example, Diflucan, Pimafucin, etc. Treatment of candidal cervicitis is a lengthy process; therapy is also required for the sexual partner.
Pregnancy and cervical inflammation
During pregnancy, cervicitis poses a great danger to the fetus. Pathogenic bacteria pass through the cervical canal and enter the uterus. In this case, intrauterine infection of the fetus (purulent lesions of the skin and internal organs), premature onset of labor, and miscarriage are possible.
In the early stages of pregnancy, cervicitis can cause placental insufficiency, negatively affecting the development of the child. This can lead to fetal freezing.
Treatment of the inflammatory process of the cervix during pregnancy is carried out with the prescription of antibiotics, predominantly from the macrolide group. Depending on the pathogen, tetracycline preparations, antiviral therapy and multivitamin complexes can be used.
Treatment of the disease
Cervicitis is a common disease that is often diagnosed by gynecologists.
It is not surprising that a large number of methods have been developed to combat this pathology.
For therapy to be successful, a woman is recommended to follow a number of simple principles, including:
- refusal for the duration of therapy from sexual contact, both protected and unprotected (even with protection, the genitals will still be exposed to irritation, which will negatively affect the recovery processes, and with sex without protection, all treatment may be completely useless due to re-infection );
- careful adherence to medical recommendations regarding treatment (this especially applies to the duration of taking antibiotics or antiviral drugs, which many representatives of the fair sex tend to neglect);
- complete refusal to try to self-medicate cervicitis without prior consultation with a medical professional (in order to begin proper therapy for cervicitis, you need to clearly know what the cause of its development is, otherwise you can start taking the wrong medications, thereby only aggravating the situation as a whole);
undergoing treatment not only by the woman, but also by her sexual partner (in most cases, cervicitis is a consequence of an infectious disease sexually transmitted, which means the woman most likely became infected from a man who either does not know about his disease or does not suffer from it so much to be treated);
- compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene (if a woman neglects intimate hygiene during therapy, the inflammatory process may migrate higher through the genitals, which will only worsen the general condition).
Treatment in each case must be selected strictly individually.
It is necessary for the doctor to take into account the general condition of the patient, her personal characteristics, and the severity of symptoms.
If a woman is diagnosed with cervicitis, treatment should begin as early as possible.
Drugs for treatment
Many women are concerned about what medications are used for treatment and how to choose them correctly.
It is important to understand that only a doctor can prescribe treatment for a disease, based on the characteristics of the disease.
The following drugs may be used during therapy:
- Antibiotics
Antibiotics are drugs used against bacterial pathogens.
The choice of drugs is made individually.
Before prescribing drugs, it is recommended to carry out bacteriological culture followed by sensitivity testing.
For example, Erythromycin or Doxycycline are suitable for treating the chlamydial form.
They are prescribed in a course for 7-10 days.
- Antiviral agents
If it is determined that the infection is caused by a viral pathogen, the patient is selected for antiviral therapy.
For herpes, it is recommended to use Acyclovir for 10-14 days.
When human papillomavirus is detected, interferons and drugs from the group of cytostatics are used.
- Antifungal agents
If a patient has a fungal infection, it is useless to treat it with antiviral or antibacterial agents.
It is worth giving preference to antimycotics such as Fluconazole.
- Drugs for local therapy
After active inflammation has subsided to a minimum, treatment is recommended for women.
Local agents are applied to the lesions, which will enhance regeneration and prevent re-infection.
Silver nitrate, Chlorophyllipt and other agents can be used.
- Immunostimulants
If a decrease in immunity is determined, the woman is recommended additional therapy aimed at correcting the immune status.
For example, Galavit and vitamin complexes can be used.
If therapy using conservative methods was useless?
Or is the woman forced to deal with a chronic form of the disease?
Then she is recommended to undergo surgical interventions.
I use cryotherapy, laser therapy, diathermocoagulation. The optimal method is chosen at the discretion of the doctor.
How to cure cervicitis at home
Treatment with folk remedies is also possible if a doctor's approval is first obtained.
When used correctly, folk recipes can speed up regeneration in the female body.
And even fight some infections.
The following decoctions can be used for douching:
- you can mix flaxseed, coltsfoot leaves, white willow bark, stinging nettle, birch leaves, caraway berries, juniper roots and bird cherry leaves in equal proportions and, pour half a liter of boiling water over everything, hold on fire for 10 minutes and then cool;
a combination of equal proportions of knotweed, leaves of cuff and three-leaf watch, agrimony, elecampane roots, fennel fruits, and shepherd's purse is suitable, after which the decoction is prepared according to similar instructions and cooled to an acceptable temperature before use.
In addition to decoctions, ointments are suitable.
You can make an ointment by mixing clover and calendula flowers, Icelandic moss, flaxseed, and juniper pine.
You can use plantain leaves, sea buckthorn fruits, chamomile flowers and horsetail.
50 g of the resulting collection is crushed, filled with half a liter of water and kept in a water bath until half the volume is lost.
Then add 15-20 g of butter and cook the mixture for another 15 minutes.
Glycerin is added to the almost finished ointment and cooled, after which it can be used.
It is important to remember that traditional recipes can provoke allergies!
And also that they cannot cope with all diseases.
To avoid the transition of the acute form to the chronic form due to incorrect treatment, it is recommended to obtain the approval of the attending physician.
Symptoms of cervical inflammation
It is important that the clinical picture of cervicitis will depend on what bacteria and microorganisms provoked it. Cervicitis occurs together with endocervicitis (inflammation of the cervical canal), since it is there that pathogenic organisms are initially localized, subsequently affecting other tissues and organs.
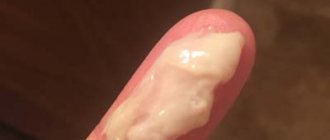
Very often, cervicitis is asymptomatic, especially if there are no other gynecological diseases. With chronic, low-grade inflammation of the cervix, the only symptom may be slight vaginal discharge. In the acute course of the disease, the patient will be bothered by pain in the pelvic area and lumbar region, vaginal itching and burning, as well as discharge, which can be mucous and, in some cases, purulent. If cervicitis has developed as a result of trichomoniasis, foamy vaginal discharge is characteristic, and if the inflammation is caused by gonococci, the discharge becomes yellowish.
During sexual intercourse, pain often occurs. And after that, there may be slight bleeding or pale pink discharge.
What antibiotics are prescribed for treatment in gynecology?
It is most correct and rational to prescribe antibiotics for cervicitis, taking into account the sensitivity of the microflora cultured from the vagina. To do this you need:
- undergo testing for STIs not only by PCR, but also by culture - for ureaplasma, mycoplasma;
- take a smear to culture the entire vaginal microflora - determines the entire microbial landscape, especially relevant in the absence of an absolute pathogen.
The results indicate which microbes in the vaginal flora exceed acceptable levels and which antibiotics they are sensitive to. This will help avoid treatment with ineffective drugs, reduce the cost and duration of therapy.
If necessary, two antibiotics can be combined in the treatment regimen, for example, short-acting and long-acting. In case of mixed infections (detection of several harmful microbes at once), such combinations give a more reliable effect.
Macrolides
This is one of the popular groups of drugs for several reasons:
- courses of taking them are often short - for example, for Azithromycin you need to take only one tablet;
- wide spectrum of action - they act both on their own opportunistic flora and on absolute pathogens - chlamydia, myco- and ureaplasmas;
- well tolerated - usually the severity of side effects is minimal;
- many are allowed during pregnancy - Azithromycin, Josamycin, Rovamycin.
The course of treatment (scheme, dose, duration) is determined by the doctor individually. Standard assignments include the following:
| A drug | Application diagram |
| Azithromycin | 1 g once or 500 mg orally for 5-7 days; |
| Josamycin (Vilprafen) | 500-750 mg twice a day for 10-14 days; |
| Midekamecin (Macropen) | 400 mg three times a day orally for 10-14 days; |
| Clarithromycin (Klacid) | 250-500 mg twice daily orally for 10-14 days; |
| Rovamycin (spiramycin) | 3 million units three times a day for 10-14 days. |
Tetracyclines
A typical and most popular representative of the group is Doxycycline (Unidox and other analogues).
Recently, this antibiotic has been used frequently, since pathogens are highly sensitive to it and, in rare cases, resistance is observed. Dosage regimens usually include 100 mg twice daily for 10-14 days.
The drug is effective not only against nonspecific pathogens of inflammation, but is also detrimental to chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma and some other specific microbes.
Doxycycline is often well tolerated, but in some cases it causes side effects - nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain.
Another representative of tetracyclines is the drug of the same name - Tetracycline. However, the high frequency of allergic reactions to it, as well as the inconvenient dosage regimen (up to 4 times a day) have led to the rare use of the drug.
Penicillins
Amoxicillin, Ampicillin, Azlocillin are used most often. However, their sensitivity spectrum does not extend to specific pathogens, for example, chlamydia and mycoplasmas. They are used for nonspecific inflammation associated with the activation of opportunistic own flora.
Usually this group of drugs is well tolerated. Forms are produced with “protection” from bacteria acquiring resistance - clavulanic acid is added to the preparations. The dosage regimen is usually as follows:
- Ampicillin - 250 mg four times a day for 7-14 days;
- Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid - 0.5 g three times a day for 10-14 days.
Cephalosporins
They have five generations of drugs. They are used for the treatment of nonspecific cervicitis, since they do not have an effect against pathogens such as chlamydia, urea and mycoplasma. Active against Escherichia coli, almost all types of staphylococci and streptococci, enterobacter, gonococcus.
Most drugs are used intramuscularly. Only a few exist for oral administration. Representatives - Cefazolin, Cefexime, Cefepime, Cefuroxime and others. Most often used in hospitals.
Fluoroquinolones
These are reserve drugs - they are used for resistance to other main drugs, as well as for mixed infections and relapses. Antibiotics of this group are active against nonspecific pathogens, as well as chlamydia. However, in relation to the latter, their efficiency is somewhat lower.
Examples of drugs:
- Ciprofloxacin - 500-750 mg twice a day for 14 days;
- Norfloxacin - 400 mg twice a day for 10-14 days;
- Ofloxacin 200 mg twice a day or 400 mg once a day for 9 days.
Diagnosis of cervical inflammation
In the absence of specificity of the symptoms of cervicitis, diagnosis of the disease can be difficult. Comorbidities are also a barrier to detection. This may cause the transformation of cervicitis into a chronic form.
During a gynecological examination with mirrors, you can see swelling of the cervical mucosa, the blood vessels will be filled with blood (hyperemia). Hemorrhages are possible. Around the external pharynx there may be erosive areas with signs of ulceration. Discharge from the cervical canal, depending on the course of the disease, can range from scanty to profusely purulent with mucus.
Next, it is recommended to conduct a detailed examination of the cervix - colposcopy and ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
In order to identify the cause of cervicitis and prescribe adequate treatment, it is necessary to establish which pathogen provoked the pathogenic process. To do this, laboratory diagnostics are performed. It includes:
- Polymerase chain reaction;
- Enzyme immunoassay;
- Flora smear and vaginal culture.
Possible complications after
All antibacterial drugs are metabolized in the liver and excreted along with bile acids through the intestines and urine through the kidneys. Accordingly, the load on these organs is maximum. Failure to comply with the indications and contraindications may result in serious disruption of the functioning of these organs.
Also, caution should be exercised when prescribing drugs to women with a tendency to allergic reactions. If necessary, you can first check individual sensitivity to the drug.
Common adverse reactions include the following:
- dyspeptic disorders - nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, etc.;
- candidiasis of the intestines and vaginal mucosa - for this purpose, it is necessary to start taking antifungal agents while taking antibiotics.
The list of adverse reactions for any drug is wide. If a woman notices a deterioration in her general health, she should seek medical help to resolve the issue of replacing the drug.
We recommend reading about the causes and treatment of chronic cervicitis. From the article you will learn about the types of chronic cervicitis, symptoms of pathology, methods of diagnosis and therapy.
And here is more information about when you can use folk remedies in the treatment of cervicitis.
Antibiotics are widely used to treat cervicitis in gynecology. Only a doctor can select the most suitable drug, taking into account a comprehensive examination. For the most effective treatment, you should take tests for culture and sensitivity of the microflora of the cervical canal and vagina. If necessary, treatment of the sexual partner is carried out.
Inflammation in the cervical canal
The inflammatory process in the cervical canal is called endocervicitis. Usually occurs simultaneously with cervicitis. The disease is dangerous because it instantly turns from an acute form into a chronic one, as a result of which inflammation spreads to the cervix, etc. The main symptoms of endocervicitis will be light mucous discharge and mild pain in the lower abdomen. In the acute form of the disease, the discharge will contain impurities of pus and have an unpleasant odor.
Inflammation in the cervical canal can be caused by various mechanical damages during intrauterine interventions: abortion, diagnostic hysteroscopy, etc. A prolapsed uterus puts the uterus at risk for infections. And, of course, pathogenic bacteria such as streptococci, staphylococci and others.
When diagnosing endocervicitis, standard research methods are used:
- Ultrasound;
- Colposcopy;
- PCR diagnostics;
- Bacteriological culture;
- Smear on the flora of the cervical canal;
- Blood test (including for HIV and RW).
When treating endocervicitis, the basis will be the use of etiotropic therapy (antibiotic treatment), depending on the pathogen that provoked the infection. Next, antiviral and antifungal drugs can be used, as well as immunomodulators, various vitamin complexes and lactobacilli.
Cervicitis in women
Since cervicitis is diagnosed quite often, it is necessary to clearly know what the symptoms of the disease are and the characteristics of the course.
The disease can be asymptomatic or with severe symptoms.
If objectively a representative of the fair sex does not have any complaints, this does not mean that she does not have a pathology.
If there are no other complaints, the patient’s story about mucous discharge from the vagina should alert the doctor.
If the clinical picture is severe, the woman will complain of:
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen, which, although defined as uncomfortable, are not very strong;
- unpleasant sensations that sexual contact brings;
- episodic bleeding, which may contain an admixture of pus;
- the appearance of unpleasant mucus from the vagina, the release of which is not associated with menstruation;
- pain during menstruation.
Any of these symptoms should be a reason for a woman to see a gynecologist.
Cervicitis during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the disease occurs with approximately the same frequency as in non-pregnant women.
Moreover, when carrying a child, the disease can pose quite a serious danger.
The reasons for the development of inflammation are basically the same.
It is important to keep in mind that cervicitis becomes chronic much faster during pregnancy than outside of it.
This is explained by the fact that a woman’s body becomes more susceptible to infections.
After all, not only active hormonal changes occur in it, but immunity also drops significantly.
Cervicitis is dangerous for the fetus.
Firstly, with an infectious form, the likelihood of infection of the fetus increases.
Either during childbirth or through the placenta, since it is not able to protect against all pathogens.
Secondly, the risk of premature birth or miscarriage increases.
Because the inflammatory process in the reproductive organs never contributes to the normal development of a small organism.
It is also important to remember that any inflammation can complicate the process of conception.
When planning pregnancy, women are advised to first get rid of the disease.
Treatment of cervical inflammation with folk remedies
There are many traditional medicine recipes for treating cervical inflammation. Many plants actually have anti-inflammatory properties. It must be remembered that without traditional medicine it is impossible to cope with the disease. Herbal treatment can be used for preventive purposes, but use it with caution, since douching and tampons soaked in herbal infusion can disrupt the natural microflora of the vagina. It is strictly forbidden to use tampons and douches during an exacerbation.
The misconception that folk remedies cope well with cervicitis is due to the fact that the acute form (very often) becomes chronic after 2-3 weeks, and pronounced symptoms stop on their own.
Possible complications and prevention of cervical inflammation
When moving from acute, the inflammatory process can take on a chronic form, which is extremely difficult to treat. In addition, the infection begins to rise upward, affecting the body of the uterus, and can spread to nearby organs, appendages, bladder, and peritoneal organs. Chronic inflammatory processes lead to the formation of adhesions, which can cause infertility.
By following simple preventive measures, you can easily protect yourself from cervical inflammation or detect the process in the early stages, which will be the key to successful treatment.
Regular visits to the gynecologist are necessary, at least once every six months. Choose adequate contraception to avoid abortion. Do not neglect the use of condoms in the absence of a regular sexual partner. It is important to maintain your immunity and maintain good hygiene.