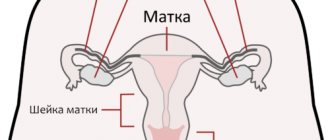
The uterus is an unpaired muscular organ that is necessary for bearing a fetus. Normally, the uterus is located in the pelvis, between the bladder and intestines, and on both sides of the uterus there are its appendages: the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Uterine displacement is a situation in which an organ changes its location. As a result, the normal distance between the pelvic organs changes.
It is worth noting that normally the uterus constantly moves left and right, forward and backward, for example, when the bladder fills. Also, the uterus changes location as a woman ages, which is also a physiological norm. In a girl, the uterus is located higher than in a woman of reproductive age. But in some cases the displacement is too strong, which is a pathology.
Definition
What it is? Retroposition is a type of displacement of an organ relative to the horizontal plane. In this case, the organ moves relative to the midline. The fundamental difference from bending in this case is that the entire organ is displaced relatively evenly, whereas when bending, only the body of the organ is displaced predominantly, as a result of which an acute angle is formed between it and the neck. Therefore, in general, this situation is much less favorable than the retroposition being discussed.
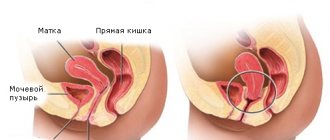
Retroposition always refers to only posterior displacement. That is, a position where relative to the midline the organ is displaced towards the back and spine. And if normally the body of the uterus practically lies on the bladder, then with such an anomaly it is much closer to the rectum than normal.
Displacements in other directions have different names. For example, anteposition is a displacement anteriorly, lateroposition is a displacement to the side, to the right or left.
A woman can develop such a deviation at any age. Both teenagers and women of reproductive age and after menopause are not immune from it. The only ones who are “protected” from this phenomenon are girls under the age of approximately 10 years. Until this age, the uterus has not yet descended to its normal physiological place - in the wide lower part of the small pelvis. Once it moves there, there is a potential risk of developing retroposition. In addition, such an anomaly is completely
Depending on the reasons that caused this condition, it can occur in two forms. In its pathological state, the uterus can be fixed, or it can be mobile. It becomes fixed when it is attracted by adhesions, pressed down by tumors, etc. It remains mobile when ligaments and fascia weaken; in this case, the organ can move slightly depending on the posture, type of physical activity and other characteristics.
Moreover, with a fixed position, this feature causes much more inconvenience and pain, since the adhesions stretch with load, change in body position, etc. Whereas with a mobile version, retroposition of the uterus can go unnoticed for many years.
Retroposition options
Displacement of the uterus - left, right
More often, displacement of the uterus is one of the individual variations of the normal location and does not cause problems.
In the absence of gynecological diseases, this displacement does not affect the woman’s health. Are you having any problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease. The site provides reference information.
Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious doctor. Any medications have contraindications.
Consultation with a specialist is required, as well as detailed study of the instructions! Here you can make an appointment with a doctor.
Normal position of the uterus
The uterus is located between the bladder and rectum, in the center of the pelvis. The normal position of the uterus is tilted forward, towards the pubic joint.
An open angle of 70 to 100 degrees is formed between the cervix and the body of the uterus.
The uterus is in this position due to the muscles, vaginal walls, and ligaments that attach it to the pelvis on all sides. When the intestines and bladder are filled, the uterus can freely move towards the direction of least resistance. This allows you to avoid discomfort and a feeling of fullness when these organs are overfilled.
Ligaments and muscles can weaken, as a result, the uterus can shift in either direction - towards the right or left ovary. The elasticity of the supporting structures of the small pelvis ensures the mobility of the woman’s internal genital organs.
The following may be subject to displacement:
- Uterus,
- Ovaries,
- The fallopian tubes,
- Bladder.
Only 2 positions of the displaced uterus have pronounced consequences, moving backward, or regression, and moving down, or prolapse.
Uterine displacement - different options
With age, the tissues of the internal genital organs and ligamentous apparatus undergo atrophic changes. In older women, the internal genital organs - the uterus along with the appendages - are located lower, i.e. Set deep in the pelvic floor. The angle between the cervix and the body of the uterus increases, it seems to lean back.
There are 4 offset options:
- Left,
- Right,
- Forward,
- Back.
A problematic pathology is organ torsion around a vertical axis and prolapse, i.e. Excessive downward displacement.
Variants of displacement occur with a sharp loss of body weight or after traumatic injuries to the ligamentous apparatus of the pelvis.
Reasons for displacement
With age, changes in the anatomical position of the organ occur due to characteristics, as a result of various diseases or injuries. The causes are inflammatory processes of the appendages. Factors provoking its displacement:
- Severe bruises in the sacrum or tailbone;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Adhesive process of the small pelvis,
- Operations;
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- Weakening of the pelvic ligaments after pregnancy and childbirth;
- Lifting, carrying heavy objects before or during menstruation, too soon after childbirth;
- Weak pelvic muscles;
- Chronic spasm of the muscles of the lower back, sacrum.
At risk are women who are underweight and, conversely, those who are overweight.
In the first category, weakness of the perineal muscles and ligaments is observed. In obese women, displacement occurs due to increased pressure in the abdominal cavity and pelvis.
https://www..com/watch?v=dDkHE_8rySw
Symptoms of changes in organ position
Symptoms of displacement depend on which direction and how many degrees the uterus deviates. There are general signs of changes in the position of the uterus and individual ones inherent in each option.
General signs:
- Pain in the lower back before and during menstruation, when the uterus increases in volume;
- Painful or irregular periods;
- Dark brown discharge at the beginning and end of menstruation;
- Recurrent vaginal infections;
- Painful sexual intercourse.
When displaced towards the rectum, constant pressure occurs on this organ.
With pronounced deviation of the uterus backwards, the following is observed:
- Periodic back pain
- Chronic constipation,
- Varicose veins on the legs,
- Fatigue and numbness in the legs.
If the uterus moves forward, there is constant pressure on the bladder. Women are concerned about:
- Urinary incontinence;
- Frequent urination;
- Urinary infections.
When the organ is displaced to the right or left, periodic nagging pain on the side of the deviation is added to the general symptoms.
This is due to tension in the ligamentous apparatus and irritation of nerve endings. Deviation from the normal location of the organ provokes chronic venous and lymphatic stagnation. This adversely affects tissue nutrition and can disrupt the normal functioning of the organ.
Possible complications of pathology
The pressure of the displaced uterus on neighboring organs (bladder, rectum) gradually causes dysfunction of these organs. The displacement of the organ to the right or left is provoked by inflammatory processes in the ovaries or tubes. It is attracted to the side where inflammation occurs.
Since the main reasons for displacement to the right or left are inflammatory changes in the appendages, a change in position in their direction causes the formation of adhesions, connective tissue cords that fix the organ to each other.
The process of organ adhesion is fraught with some loss of mobility, then with natural movement during bowel movements or urination, the patient may experience discomfort or pain on the affected side.
If the uterus has moved down or prolapsed, dysfunction of the bladder and intestines occurs. Weakened ligaments are unable to hold organs in a fixed position. Gradual sagging of the ligaments provokes urinary or fecal incontinence. Options for displacement are subject to surgical treatment.
Exercises and surgical treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on how much the displaced position of the organs causes disruption of their function. Since changes in the position of the uterus are caused by various pathologies, they are treated with medication and physiotherapy.
In the initial stage, when the patient has not yet begun to be bothered by severe pain or urinary incontinence, they are limited to local procedures and gymnastics:
- Douching with a decoction of oak bark;
- Kegel exercises;
- Exercises according to Yunusov.
With small degrees of deviation from the norm, these methods help return the uterus to its original position.
In case of pronounced downward displacement or prolapse, when other pelvic organs are displaced after the uterus, surgical treatment is indicated.
Plastic surgeries are performed aimed at restoring the ligamentous apparatus. In case of complete organ prolapse, the uterus is removed followed by pelvic floor plastic surgery.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
Several methods are used to diagnose this pathology:
- Examination by a gynecologist. This is the very first stage, which allows you to notice that the uterus is displaced. The patient lies down on a gynecological chair, and the gynecologist, by palpating the abdomen and inside the vagina, can determine the displacement of the organ. If the fingers rest against the body in the posterior fornix of the vagina, this means that the uterus has moved back. When palpation is carried out above the womb, you can notice a forward displacement of the organ. The diagnostic method is also effective for other locations of the uterus.
- Hysterosalpingography. Such a study is aimed at determining the patency of the fallopian tubes, their condition, the position of the uterus, and the presence of problem areas in the pelvic area. With the help of a contrast agent that is injected orally, which moves through the fallopian tubes, any abnormalities can be detected using x-rays or ultrasound.
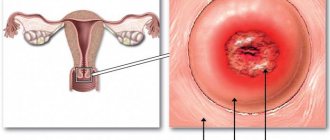
- Colposcopy. Such a study may show a downward shift of the uterus. To carry out this procedure, no anesthetic is used; everything is done using a special device - a colposcope. In addition to displacement, it can also show other diseases of the uterus, for example, neoplasms or dysplasia.
The presence of such a pathology is detected using traditional diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the pelvis and vagina;
- A blood test that helps identify any inflammatory processes;
- Taking a smear to determine the presence of any infections or viruses;
- X-ray, which can be used to see the displacement of an organ.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the help of a gynecologist and other specialists is required: proctologist, urologist. This is necessary to notice any changes that accompany the displacement.
Help from folk remedies
Traditional methods help with displacement of the uterus, but before carrying out the procedures you should consult with a specialist so as not to aggravate the condition of the disease.
Douching with medicinal infusions is effective for this pathology:
- To prepare, mix sweet clover, marshmallow leaves and chamomile in equal quantities. Pour one spoon of the resulting mixture into a glass of boiling water and leave covered for half an hour. Strain, syringe twice a day, a quarter cup.
- Douching with an infusion of St. John's wort and cinquefoil effectively helps with displacement. To prepare, pour 2 liters of water into a container, put it on the fire, when it boils, add 4 tablespoons of chopped St. John's wort, cook for half an hour. Then add a spoonful of bloodroot and boil for another 5 minutes. Strain and use twice a day.
- Pour a glass of water into a container, add a spoonful of crushed oak bark. Boil over low heat for 5-10 minutes. After straining, dilute a little with cold water. Use half a glass every day for 2 weeks.
- Mix 2 servings of St. John's wort, one each of horsetail and chamomile. Pour a spoonful of the mixture into a glass of water and place on low heat. After 15-20 minutes of boiling, turn off and let sit for half an hour. Strain, take a quarter glass three times a day.
- Dilute a teaspoon of tannin in 200 ml of warm boiled water and take half a glass twice a day.
Often, displacement of the uterus is associated with inflammatory processes.
To get rid of unpleasant symptoms you can use the following recipes:
- Mix chamomile, peppermint, and valerian root one spoon at a time. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over one spoon of the resulting mixture and let it brew for 1-2 hours. Drink before meals three times a day.
- Pour 4 tablespoons of chamomile into a glass of boiling water, let it brew for half an hour, strain, drink half a glass twice a day. You can wash yourself with this infusion, it gives a good result.
- Make an infusion of plantain leaves, it will help relieve inflammation and pain. pour a spoonful of crushed, dried herbs into two glasses of boiling water, leave for 20-30 minutes, strain, drink a teaspoon three times a day.
- If spasms occur in the pelvic area, an infusion of prickly plum flowers will help. Pour 2 tablespoons into a glass of boiled cold water and leave overnight. Afterwards, strain, take half a glass three times a day.
- A decoction of acacia flowers effectively relieves pain. Pour boiling water over a spoonful of flowers, leave for 30 minutes and drink before eating.
With the help of such herbal preparations you can douche or take a bath. They effectively fight inflammation and help relieve pain.
Features of dietary nutrition
With this pathology, you do not need to adhere to special diets. You need proper and balanced nutrition, which will help the body restore its functionality, increase the level of the immune system in order to prevent the ingestion of dangerous viruses that can aggravate the condition.
You need to eat as many fruits and vegetables as possible, preferably fresh or steamed. Drink plenty of liquids and freshly squeezed juices.
Do not consume in large quantities:
- Fatty and fried foods;
- Spicy dishes;
- Alcohol.
To prevent displacement, consume as many vitamins and microelements as possible. A huge amount of which is found in sea fish, seaweed, and cereals.
No need to neglect dairy products. They saturate the body with necessary substances that increase immunity. It is healthy and important to eat a lot of nuts and dried fruits, especially prunes. It cleanses the body of toxins and prevents frequent constipation.
Prevention of organ displacement
To prevent displacement it is necessary to take preventive measures. It is most effective to start doing this from early childhood, so as not to give such a pathology a single chance.
The most well-known and effective methods of preventing such pathology are:
- Do not lift or carry weights exceeding 10 kilograms.
- During pregnancy, you should carefully monitor its correct course.
- Protecting the genitals from germs, bacteria or damage.
- Avoiding frequent constipation and following a diet aimed at preventing it.
- Regular exercise to maintain a healthy body. Regular exercise helps strengthen all muscles and prevent uterine displacement.
- Taking hormonal therapy, which helps restore blood circulation and strengthen the ligaments of the organs in the pelvic area. You should only take medications after consulting a specialist.
- Walk outdoors more often.
- Avoid prolonged colds.
Doctor: Olga Shishkina ✓ Article checked by doctor
Source: https://FeedMed.ru/bolezni/reproduktivnoy-sistemi/smeshchenie-matki.html
Causes
There is the concept of physiological retroposition of an organ. This is a condition in which the uterus temporarily deviates for normal reasons, such as a full bladder. But in this case, it returns to its normal position when it is empty. But if the uterus is in this position constantly, then this occurs as a result of pathological processes. For what reasons does such a condition arise?
- With the development of an inflammatory process in the pelvic organs, adhesions from connective tissue can form. Such adhesions can “tie” the uterus to the tissues of other organs, holding it in a physiologically incorrect position;
- Also, adhesions can develop after surgical interventions performed with poor sanitation of the surgical pit, retention of a certain amount of blood in the cavity, etc.;
- Abortions and other interventions can theoretically lead to the formation of adhesions;
- Weakening of the fascia and muscles can occur when lifting heavy objects and during certain types of physical activity. As a result, they can no longer properly support the uterus, and it sags, in one direction or another, sometimes towards the colon;
- In some cases, this condition is a congenital abnormality. That is, it is normal for the patient to have just such a deviated position of the uterus. Most often, the condition is accompanied by some other features and anomalies - underdevelopment of the endometrium, etc.;
- The condition can develop as a result of pressure on an organ from a tumor, such as a bladder tumor.
The most common causes are adhesions or tumors. They account for about 70% of all cases where such a diagnosis is made. However, other reasons cannot be discounted.
Pregnant woman's tone
Increased uterine tone during pregnancy is the main cause of miscarriages and premature births. It is caused by various reasons, the most common of which are:
- hormonal deficiency. The lack of progesterone, which is responsible for muscle relaxation, leads to the fact that the uterus, being a muscle, does not relax during pregnancy. She perceives the attached embryo as a foreign body and pushes it out, causing muscle contractions. To preserve the fetus, the woman is prescribed special hormonal medications;
- stressful situations. During stress, adrenal hormones release adrenaline, which puts the body on alert. Blood flow increases, heart rate increases, muscle tone increases, including uterine tone. Adrenaline blocks the production of progesterone, which is responsible for relaxation. During pregnancy there is a risk of miscarriage. This is why a pregnant woman needs peace and only positive emotions;
- structural changes. Multiple uterine fibroids, detected in an advanced state, make the structure of the walls heterogeneous, causing involuntary contractions. With small node sizes, pregnancy proceeds safely;
- polyhydramnios and multiple pregnancies. After 20 weeks, the uterus increases in size only due to stretching of the wall. Despite the fact that muscle fibers can stretch several dozen times, they have a limited resource. Excessive load provokes overstrain of the uterus;
- past infections and viruses. During illness, the body works at an increased rate, body temperature increases, which leads to muscle spasms. Blood clotting increases, and blood supply to the uterus becomes difficult. All this leads to hypertonicity;
- After an abortion, a scar remains on the uterus , which does not completely dissolve. It causes uterine contractions, causing miscarriage;
Symptoms
How does this condition manifest itself and is it possible to suspect it in a timely manner based on its symptoms? This phenomenon is very often completely asymptomatic, especially when it is congenital. In this state of affairs, it is discovered by chance during the first gynecological examination. But in some cases, this condition can still form a characteristic clinical picture:
- Pain during bowel movements, as well as constipation, which develops because the organ puts pressure on the colon;
- Pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- Painful ovulation;
- Increased pain during menstrual syndrome;
- Pain in the lower abdomen, which may occur with certain types of physical activity or while in a certain position;
- Difficulty getting pregnant can also sometimes be present;
- Frequent miscarriages and spontaneous terminations of pregnancy.
But, often, this condition occurs without the formation of a clinical picture. This is due to the fact that necrosis and tissue nutritional disturbances do not occur, as, for example, when bending.
Diagnostics
Unfortunately, retroposition can be the main cause of spontaneous abortion in the early stages. This is due to a disruption in the flow of blood to the uterus due to its backward bending. The organ itself changes its location and can even extend beyond the pelvis, which provokes a miscarriage.
A doctor can diagnose retroposition during a simple examination. To do this, he inserts two fingers of one hand into the vaginal area, and with the second he probes the lower abdomen. With the help of such palpation, the correct position of the uterus can be determined. If the doctor diagnoses retroposition, that is, a posterior deviation, then an additional ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs will be required, thanks to which it is possible to accurately determine how much the body and its neck have deviated from the normal position.
In this case, the doctor may detect a slight displacement of the uterus towards the rectum due to inflammatory processes in the appendages or the fixation of a fertilized egg outside the body of the uterus. In such a situation, it is necessary to treat the root cause of the organ deviation.
Consequences
What complications can such a process lead to in the absence of complete and timely treatment?
- Chronic constipation;
- Chronic pain symptoms that significantly impair the quality of life;
- Frequent miscarriages, infertility;
- The development of an inflammatory process or tumor and the consequences associated with it;
- Gradual deterioration of the condition as the pathological process develops.
However, if this condition is congenital, there may not be any negative consequences.
Prevention
Prevention of uterine displacement involves preventing various gynecological pathologies. To do this, you must follow the following recommendations:
- lead an active lifestyle, play sports and do exercises;
- eat right, avoid obesity and exhaustion;
- do not drink alcohol or smoke;
- have sex regularly, use proper protection, avoid promiscuity;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- avoid overwork and stress;
- dress according to the weather. do not overcool;
- undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist.
A healthy lifestyle and regular preventive examinations will help prevent the development of pathology, and if it occurs, quickly identify and treat it.
Treatment
Treatment for this condition is specific and differs from other approaches used for displacements and kinks. First of all, it is important to eliminate the cause that caused the pathological process, that is, remove the tumor, remove inflammation or cut adhesions. Before any surgical intervention, a course of treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs such as Ibuprofen and Nurofen is carried out for 5-10 days. This is due to the fact that no manipulations, even massage, can be performed against the background of potential inflammation.
If the presence of an infectious or inflammatory process is confirmed during the study, then broad-spectrum antibiotics such as Ceftriaxone may be prescribed. They are also accepted within five to ten days. Once the inflammation is completely defeated, you can proceed to surgery.
Tumors are removed in different ways, depending on the position of the tumor, its nature, and the effect it has on neighboring organs. Adhesions are most often dissected laparoscopically and with relatively little trauma. After eliminating adhesions or tumors, the uterus almost immediately returns to its physiologically correct position.
If this does not happen, then a special gynecological massage may be prescribed, which is performed at least 10 times for 10 minutes. During it, the organ returns to its usual place gradually. Sometimes this method can be used without cutting the adhesions, since as a result of the massage they will stretch enough.
If it is decided to avoid surgical intervention, then, as mentioned above, a massage is prescribed to stretch the adhesions. UHF procedures are also prescribed, which contribute to the gradual resorption of adhesions and the removal of inflammation. Additionally, physical therapy may be prescribed.
Conclusion
During pregnancy, a woman's uterus enlarges and rises over the weeks. Based on the size and location of the organ, the obstetrician-gynecologist understands how far along the expectant mother is and whether everything is okay with the baby. A low position of the uterus is a sign that a woman has a short period of pregnancy. If the enlargement and elevation of the organ does not occur, then doctors suggest fetal fading or developmental delay. To confirm the diagnosis, additional diagnostic measures are prescribed. Sometimes additional symptoms help to understand that the pregnancy process is complicated. To ensure that everything is in order and that the unexpected does not happen, doctors conduct serious monitoring throughout the entire 9 months. It is important to register in a timely manner and pass all the necessary tests.
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes serious changes that allow her to bear and give birth to a baby. Based on such changes, doctors determine how well the pregnancy is proceeding and the fetus is developing. One of the main indicators of the condition of a woman and child is the height of the uterine fundus during pregnancy. Determining the height of the uterine fundus by week of pregnancy is of great diagnostic importance. Let's consider what the term “fundus of the uterus during pregnancy” means, why it is defined, and what its normal meanings are.
Pregnancy
There is no clear prohibition on pregnancy in this condition. For example, if it is congenital, then as the fetus grows and the size of the uterus increases, it itself will return to its normal place from a physiological point of view by the fourth month of gestation. On the other hand, if it is secured with adhesions, then its movement will be accompanied by severe pain, and maintaining a pregnancy in such conditions will be very difficult. In addition, the inflammatory process that caused the formation of adhesions can have an extremely negative impact on the fetus.
On the other hand, pregnancy itself can be difficult for several reasons. Firstly, the penetration of sperm into the uterus is complicated, and secondly, it is difficult for the fetus to attach to the walls of the altered organ. Therefore, miscarriages are likely at very early stages.
Features of the structure of the uterus and description of the main parameters
In a woman who has never given birth, the weight of the reproductive organ is approximately 30-50 grams, the length is up to 8 cm, while the width is about 5 cm. If there was a previous birth, then the weight of this organ reaches up to 100 grams.
During pregnancy, a woman’s reproductive organ can stretch due to the elasticity of the walls. Its height can increase up to 32 cm, and its width up to 20 cm. Strong uterine ligaments help support the fetus, whose weight can reach up to 5 kg. The anatomy of this organ allows for the possibility of extensibility to the required size.
During menopause, the size of the uterus becomes smaller, which happens due to atrophy of its epithelial layer. This feature is also affected by sclerotic changes in blood vessels.
Pathogenesis
The typical position is conventionally considered to be the position of the genital organs in a healthy, sexually mature, non-pregnant and non-lactating woman, who is in an upright position with the bladder and rectum emptied. In this case, the uterus occupies a mid-position in the small pelvis, the fundus of the uterus does not protrude above the plane of the entrance to the small pelvis, the vaginal part of the cervix is at the level of the plane passing through the ischial spines. The fundus of the uterus is directed upward and anteriorly, the vaginal part of the cervix is directed downward and posteriorly. The entire axis of the uterus is slightly inclined anteriorly (anieversio). A curve forms between the body and the cervix. The resulting angle is obtuse and open anteriorly (anteflexio).
The proper tone of the genital organs depends on the proper functioning of all body systems. A decrease in tone may be associated with a decrease in the level of sex hormones, disruption of the functional state of the nervous system, and age-related changes.
The relationships between the internal organs (intestines, omentum, parenchymal and genital organs) form a single complex due to their direct contact with each other. In this case, capillary cohesion is formed, which, together with the gaseous contents of the intestine, helps to balance the heaviness of the internal organs and limits their pressure on the genitals.
The suspensory apparatus consists of the round and broad ligaments of the uterus, the proper and suspensory ligaments of the ovary.
The anchoring apparatus includes the uterosacral, cardinal, uterovesical and vesico-pubic ligaments.
The supporting apparatus is represented by the pelvic floor muscles, the vesico-vaginal septum, the rectovaginal septum and dense connective tissue located at the lateral walls of the vagina.
[26], [27], [28], [29], [30], [31], [32], [33]
Forms
Displacement of the uterus can occur along a vertical plane (up and down), around the longitudinal axis and along a horizontal plane.
Displacement of the uterus along the vertical plane includes elevation of the uterus, prolapse, prolapse and inversion of the uterus. When lifted, the uterus moves upward, its bottom is located above the plane of the entrance to the pelvis, and the vaginal part of the cervix is above the spinal plane. Pathological elevation of the uterus occurs when menstrual blood accumulates in the vagina due to atresia of the hymen or lower part of the vagina, with voluminous tumors of the vagina and rectum, with encysted inflammatory effusions in the pouch of Douglas. Lifting (elevation) of the uterus can also occur when it is fused with the anterior abdominal wall after laparotomy (caesarean section, ventrofixation).