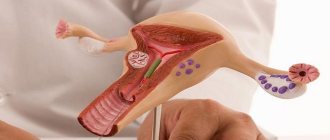
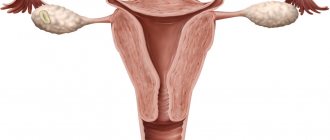
Inflammation of the cervical canal (endocervicitis) is a pathology that occurs more often in women. This is explained by the anatomical structure and topography of the cervical canal. It connects the vagina to the uterine cavity. Typically, inflammation occurs in the vagina, then moves to the cervix - colpitis develops.
Therefore, if the diagnosis is not made in time and treated immediately, the disease will turn into a latent, sluggish form. This, in turn, is fraught with serious complications. Their treatment will take a lot of time and it is not at all a fact that the treatment will be successful.
In case of timely diagnosis and treatment, unpleasant complications will not occur.
Why might the cervix bleed?
Normally, spotting in women of childbearing age appears once a month for several days (menstruation). If spotting appears between cycles, this indicates some kind of problem.
The causes of cervical bleeding may be:
- trauma to the mucous membrane during sexual intercourse
- after an abortion
- curettage
- after installation of the intrauterine device.
- Or for inflammatory/infectious diseases. Such as staphylococcus, streptococcus, chlamydia, etc.
Doctors identify several diseases that can cause cervical bleeding.
Cervical erosion
The most common disease. Cervical erosion often bleeds when examined by an obstetrician-gynecologist.
This happens due to the fact that there are ulcers on the neck, which, with any intervention, begin to bleed. However, there are cases when erosion bleeds even with the simple secretion of mucus. Erosion appears and spreads with frequent inflammation, infections, and hormonal imbalance.
After cauterization of erosion, bleeding is also possible.
- Licking the scab. A scab is a film formed after cauterization that protects the wound from infections. This film can thicken and collapse, and after the blood clots break down, the cervix may begin to curve.
- Damage to the scab. The scoop may come off due to heavy lifting or sexual intercourse.
Therefore, after the procedure for 2 months, it is necessary to protect yourself from lifting heavy things and refuse sexual intercourse.
Cervicitis
This is an inflammation of the cervix caused by injuries to the genital organ, pathogenic bacteria and fungi.
Polyps
Those. benign formations. A polyp leads to bleeding when it is large, since wounds and ulcers appear on it, which tear and bleed.
Cervical rupture
This is a postpartum injury caused by rapid childbirth, unqualified medical care, during late first births, and also rupture occurs during abortion (when tissue elasticity is lost).
The most terrible disease, for many people, it sounds like a death sentence. Often, advanced erosions, polyps, and inflammatory processes lead to malignant tumors of the cervix.
After a cervical biopsy, i.e. After plucking off living material, discharge is the norm. However, you need to carefully monitor your condition. Depending on the method of tissue collection, the cervix may bleed for three to five days. If this period is longer, you need to see a doctor. In this case, it is likely that there is a blood clotting disorder, as a result of which the vessels located in the cervical cavity bleed.
There is such a procedure as conization. The procedure is an operation in which part of the cervix in the form of a cone is removed (the operation is performed as a means of diagnosing cancer, as well as in the treatment of certain female diseases). After conization, bloody discharge along with mucus will be observed for four months. But bleeding should not be normal.
Many women have a question about whether the cervix can bleed when taking a smear for examination (cytology, flora, etc.). With such a simple and practically painless procedure, the cervix should not bleed. And if there is such a phenomenon, then this may be a sign of diseases, for example, erosion, polyp, endocervicitis, ureaplasma. Even a doctor can’t say for sure. We need an examination. A smear test will tell.
What should the cervix look like before menstruation?
Signs of approaching menstruation in women are approximately the same. This is pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, malaise, irritability, and digestive system disorders. Their severity depends on the characteristics of the organism.
However, there is another interesting symptom that not every woman knows about. Today we will talk about what the cervix should be like before menstruation - its density, position and other indicators.
General information about the cervix and its examination
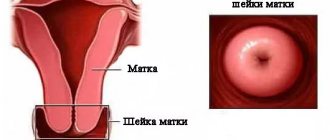
The cervix is a part of the reproductive organ, which is a hollow body measuring 2.5 x 3 cm. It can be called the connecting link between the vagina and the uterus.
A woman can independently feel this area at home by completely immersing her middle finger into the genital tract. As soon as the fingertip touches the bulge, there is no need to move further - the desired element has been found.
By doing such diagnostics every day for several cycles, a woman will learn to determine the position of the cervix before menstruation, calculate ovulation and select days favorable for conception. Or vice versa, he will understand on which days it is necessary to strengthen contraceptive measures.
The doctor examines the patient's genital tract on a chair using a special mirror. At home, it will be convenient for a woman to examine the cervix in several positions:
- Sitting on the toilet.
- Squatting.
- Standing, but one leg placed high.
The study is not carried out during menstruation. On “clean” days, the organ is felt once a day before bed at the same time. If a gynecological disease of an infectious-inflammatory nature is suspected or with the onset of bleeding, the diagnosis is canceled.
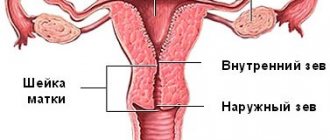
The speed of its detection helps determine whether the cervix is high or low on a particular day. If the location is high, the area is difficult to palpate; if it is low, it can be detected immediately. The amount of openness is judged by the recess. If a small gap is felt, the uterus is closed. If the hole is round and deep, then the organ is open.
Despite the simplicity of this method, doctors do not recommend examining internal organs yourself. The ban is justified for the following reasons:
- When the hole is open, there is a risk of damage to the uterus by pathogenic bacteria. Because of them, the ovaries become inflamed and obstruction of the fallopian tubes develops. In advanced cases, the disease can result in infertility.
- Since the cervix drops slightly before menstruation, inept palpation can injure it and provoke the development of erosion. The pathological focus is susceptible to infection and is dangerous in terms of oncological degeneration.
- The woman does not see the true state of the uterus. The gynecologist evaluates the real picture visually using a mirror.
The shape of the cervix before menstruation should resemble a pupil. Deviation indicates estrogen deficiency and improper functioning of the corpus luteum.
:
Position of the cervix in different phases of the cycle
The entrance to the uterine cavity changes in different periods of the cycle. The cyclic work of the ovaries goes through the ovulatory, follicular and luteal phases. Uterine functions change from secretory to menstrual and proliferative.
The composition of the fluid in the cervical canal also changes. It can be studied in detail in laboratory conditions. At home, a woman can analyze the consistency.
The cervix feels like this:
- Soft.
- Elastic.
- Dense.
- Loose.
- Solid.
Its position is either high or low.
Secretory stage
The tone of the uterus in the 2nd half of the cycle decreases and after ovulation, closer to menstruation, the cervix becomes soft. The external pharynx opens to such an extent that the tip of the finger penetrates inside.
The high position of the cervix helps sperm reach the fallopian tube faster. The glandular part of the cervical canal intensively produces transparent whitish mucus. The alkaline index of the secretion reaches 8 units. The mucus doesn't stretch.
In the absence of a fertilized egg, the body begins to prepare for endometrial rejection. A plug forms in the canal, the neck hardens and falls. The pharynx closes, the cervical canal narrows. In case of pregnancy, the cervix does not change its position. It will be difficult to feel the pharynx manually at home.
Experts know exactly what the cervix looks like on the eve of menstruation, and characterize it as follows:
- Located below.
- It has a loose soft surface.
- The external pharynx is open, the canal is expanded.
- Little cervical mucus is produced.
- The secretion has a sticky, thick consistency.
- pH
Thus, before the start of menstruation, the cervix becomes completely ready to reject bloody discharge. Along with internal changes, symptoms of PMS appear - nagging pain in the lower abdomen and deterioration in general well-being.
Proliferative stage
At the proliferation stage, the endometrium is restored in the uterus. It forms its own connective substances and blood network. The proliferative stage lasts until ovulation occurs. It begins in the 2nd half of the follicular phase.
After menstruation, the cervix undergoes changes again:
- Descends into the vagina.
- The external pharynx narrows greatly.
- The endocervix becomes denser.
- The amount of cervical fluid increases.
- The pH level gradually increases to 7.3 units.
The endocervix is the mucous part of the canal. Its epithelium produces cervical fluid. Its role is to protect the uterine cavity from microbial invasion. When the egg is released, the mucus thins and makes it easier for the male seed to penetrate the uterus.
Menstrual stage
Critical days are a difficult stage for the body. You are not feeling well and your genitals are at risk of infection. For this reason, it is not recommended to examine the uterus manually, and it is not recommended to constantly use hygienic tampons.
During the menstrual period, the cervix has other characteristics:
- She's hanging low.
- He is in low tone.
- The acidity level is approaching 7 units.
- The vaginal epithelium is slightly flaky.
- Cervical fluid is secreted in moderate volumes.
- The external pharynx is slightly open, the opening is directed towards the vaginal vault.
Menstruation occurs during the first segment of the follicular phase of the ovaries. Next, the reproductive system begins to prepare for the next ovulation.
The value of cervical palpation as a diagnostic method
Daily palpation of the cervix, including before menstruation, helps to track cyclic changes. In order not to injure or infect a delicate organ, it is necessary to cut off the nail on the desired finger and polish the edge of the plate.
For greater safety, it is better to perform the procedure with sterile gloves or a fingertip. It is recommended to record all data collected before the onset of bleeding in a notebook.
The purpose of diagnosis is to assess the position of the cervix before menstruation and during other phases of the cycle, as well as during pregnancy, if it has occurred. It is also important to know the density of the organ at the proliferative and secretory stages of MC.
The information collected over several months will help the woman with family planning and will signal the need to see a doctor if there are any abnormalities.
Source: https://MenCikl.ru/sostoyanie-shejki-matki-pered-mesyachnymi.html
What do we have to do?
First of all, if a woman’s cervix begins to bleed, she needs to see a doctor to identify the causes and make a diagnosis. Depending on this, the doctor recommends/prescribes one or another treatment. The erosion needs to be cauterized. However, this is not recommended for those who have not given birth. For this, there are less radical traditional medicines:
- Sea buckthorn oil tampons.
- Aloe juice tampons.
- Spinning with herbs.
- Candles.
Polyps must be removed. Treat inflammation. The main thing is not to start the problem. Timely diagnosis means good health in the future.
Principles of treatment
Only after identifying the cause of bleeding and making a diagnosis, appropriate treatment is prescribed
To stop bleeding, drugs that stop bleeding are prescribed:
- If the cervix bleeds due to infectious cervicitis, then antibiotics are used for treatment. Depending on the type of infection, the doctor prescribes the necessary antibacterial drug. The most commonly used antibiotics are: Ceftriaxone, Azithromycin, Erythromycin, Ofloxacin, etc.
- For inflammation of the cervix, vaginal suppositories may be prescribed, which have antifungal, antiviral and antimicrobial effects. The following are used in the treatment of cervicitis: Metronidazole, Doxycycline, Diflucan, Terzhinan, etc.
- If the cause of bleeding is cervical erosion, then various innovative methods are used: cryodestruction, laser coagulation, radio wave treatment, etc. For erosion, the drugs Hexicon, Depantol, Suporon are also used. They have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. Only a doctor should prescribe medications, as there are contraindications to their use.
- For cervical polyps and associated bleeding, surgical removal is resorted to. In case of an inflammatory process in the cervix, antibacterial therapy is carried out, only after this the polyp is removed. The operation is usually performed after menstruation.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional methods can be used as an addition to conservative therapy
When using alternative methods of treatment, you should consult your doctor.
- Fresh nettle juice will help with erosion. Take a few sprigs of nettle, rinse, chop and squeeze out the juice. Soak a tampon with the resulting juice and insert it into the vagina.
- Flaxseed oil also has a positive effect. Regular tampons are soaked in oil and inserted into the vagina overnight. You can use eucalyptus oil instead.
- If cervical polyps bleed, it is recommended to follow the following procedure: take a little fresh cottage cheese, add aloe juice and a small spoon of honey. Stir the mixture well, prepare a tampon, and then insert it into the vagina.
- To eliminate the inflammatory process and restore the cervical mucosa, it is recommended to take a decoction of St. John's wort. Pour a tablespoon of water into a glass of water and boil. Take 100 ml every morning before meals.
- It is effective to douche with a solution of copper sulfate. Pour a tablespoon of vitriol into a liter of water, first grind it into powder. Next, boil for 5 minutes, let cool and strain. As a result, the water should turn blue. The solution should be stored in a dark container in the refrigerator. Dilute the resulting solution in a liter of boiled water and perform douching. The procedure should be carried out within 10 days.
Possible complications
If you do not take measures to eliminate bloody discharge from the cervix and do not treat the diseases that provoke the development of this pathology, then there is a possibility of developing serious complications.
Possible consequences that may occur against the background of bloody spotting:
- Infertility.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Miscarriage.
- Premature birth.
- Cervical cancer.
conclusions
And so, this article examined almost all the reasons for which the cervix bleeds. They are very diverse and require different treatments. And some do not need treatment; after a certain time everything will pass.
The consequences of diseases are different. Advanced inflammation, erosion, polyps can lead to malignant formations or infertility. Bloody discharge after surgery may indicate the presence of an infection, which must be dealt with. If a woman feels any abnormalities in the discharge of mucus interspersed with blood, or sees brown spots on her underwear, she should not hesitate and consult an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Treatment of cervical bleeding
Therapy is entirely determined by the reasons that caused bleeding from the cervix.
But we can highlight the key principles of treatment:
- Stopping bleeding: with the help of drugs (hormones and medications that stop bleeding), surgical treatment;
- Taking medications that will relieve bacterial or fungal infections; (if they were discovered during surveys);
- General strengthening therapy (taking medications containing iron and vitamins);
- Physiotherapy.
Erosion and ectopia
The main cause of background diseases of the cervical uterus is sexually transmitted infections, less often - traumatic (physical) and chemical factors. The result of infection with various STI pathogens is true erosion, which lasts approximately 10-14 days. Erosion is considered a reaction of the cervical epithelium in the form of the formation of a wound that bleeds. The most common causes are chlamydia, genital herpes, myco and ureaplasmosis, gardnerellosis and other opportunistic flora.
Destruction of a section of multilayered squamous epithelium under the influence of bacteria and viruses leads to its necrotic changes and desquamation - desquamation. A bleeding surface is formed.
One of the reasons why a wound appears on the cervix and it begins to bleed is considered to be injury, burn, or disruption of tissue trophism. The decrease in estrogen levels during menopause leads to vaginal dryness, which is a cause of injury. In addition, injuries also occur during rough sexual intercourse and rape. The cause of cervical burns and bleeding is considered to be attempts at self-medication and douching, which destroy the mucous membrane. During the destruction of various pathological formations with the help of liquid nitrogen, radio waves, lasers, and current, a burn scab is formed - this is one of the reasons why it can bleed. Increased bleeding occurs when the burn scab passes away.
As the ulcer heals, ectopia or pseudo-erosion forms. This means that the wound is healed not by flat epithelium, characteristic of the vaginal part of the cervix, but by cylindrical epithelium, which forms the cervical canal. The result of improper healing is ectopia.
In addition, the addition of infectious inflammation to ectopia leads not only to contact discharge containing blood, but also to the formation of purulent discharge from the genital tract. Erosion and ectopia can be asymptomatic.
One of the reasons why the cervix may bleed is ectropion. Often after a difficult birth, as well as with significant interventions, a deformation process - ectropion - can form. The pathology is an inversion of the cervical canal. Being in an unnatural environment, the columnar epithelium is attacked by the acidic environment of the vagina, which leads to tissue destruction and scarring. When contacting the lesion, the cervix bleeds.
After sexual intercourse or gynecological manipulations, the pathological lesion bleeds. Fresh blood is found in small quantities on underwear. The next day, the spotting turns brown and disappears.
The cervix is bleeding: what does it mean, spotting during examination
Menstrual bleeding is a natural monthly occurrence in the life of every woman of childbearing age. The appearance of other discharge containing streaks of blood indicates the development of dangerous pathologies, therefore such a symptom should be given due attention.
Most often, the cause of bleeding is the impact of physical factors: mechanical damage during rough sexual intercourse or when taking a smear from a gynecologist. The unreasonable appearance of discharge is a reason to consult a doctor, because only after diagnosis can the risk of developing dangerous pathologies be eliminated.
Find out more about the reasons that can provoke bleeding not related to menstrual bleeding.
What factors can provoke bleeding?
The intensity of cervical bleeding may depend on the nature of the ongoing gynecological disease. The cause of the symptom is often injuries to the cervix, which are obtained in this way:
- having sex with a sexual partner;
- self-examination of the cervix;
- performing ultrasound transvaginally;
- gynecological examination in speculum or bimanual examination.
It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that bleeding from the cervix, which appears as a result of a gynecological examination or having sex, is not the norm. If a small drop appears once, we can talk about accidental damage, but if this is typical for each examination, the patient needs a comprehensive examination.
The intensity of bleeding of the cervix may vary depending on the degree of its damage or the nature of the progress of gynecological pathology.
The discharge can be almost transparent, containing streaks of blood, and thick (brown or almost black). Women call them “daubs.” If there is an open, fresh wound on the surface of the cervix, the blood will be a rich scarlet color.
The appearance of such a discharge really indicates bleeding resulting from an injury.
In general, bleeding from the cervix in women occurs in the following cases:
- a few days before or after menstruation;
- in the middle of the menstrual cycle;
- during the healing period after surgery;
- after a gynecological examination or sexual intercourse.
Attention! The most dangerous occurrence of bleeding is before menstruation and in the middle of the cycle; such a violation indicates the possible development of endometriosis and other diseases.
The list of main reasons that can provoke bleeding includes:
- taking hormone-containing drugs to prevent unwanted pregnancy;
- intrauterine device;
- hormonal disbalance;
- erosion;
- dysplasia;
- cervical endometriosis;
- myoma;
- papillomas on the cervix;
- adenomyosis;
- polyps of the cervical canal;
- endocervicitis;
- erythroplakia;
- leukoplakia;
- cervical cancer.
Bleeding that occurs during pregnancy indicates a threat of miscarriage or placental abruption. In the early stages, the appearance of non-standard discharge may indicate an ectopic localization of the fertilized egg.
It is impossible to determine the cause of blood discharge from the genital tract on your own.
Since such a change is one of the symptoms of dangerous female diseases, the girl should seek medical help as an emergency.
After conducting an examination and receiving the results of the required studies, the doctor can give an opinion and answer the question of why you are worried about bleeding that is not related to menstrual bleeding.
| Background and precancerous diseases that can provoke cervical bleeding | |
| Background | Precancerous |
| Ectopia; Polyps; Papillomas; Endometriosis; Ectropion; Fistulas; Erosive lesion (true and false); Cervicitis. | Dysplasia; Leukoplakia; Erythroplakia; Adenomatosis; Cancer polyps; Condylomas. |
The reason for the bleeding is that the violation leads to the destruction of the mucous layer lining the cervix, while the vessels are located close to the surface.
Attention! Bleeding is rarely observed in background diseases; more often it accompanies precancerous conditions.
Features of the course of erosion and ectopia of the cervix
The reason for the appearance of erosion and ectopia of the cervix is infectious or traumatic, chemical damage to its mucous membranes. The causative agents of diseases are various sexually transmitted infections. By definition, erosion is a wound on the surface of the cervix that has a tendency to bleed.
The list of main pathogens includes:
- chlamydia;
- herpes;
- mycoplasmosis;
- ureaplasmosis;
- gardnerelez.
When multilayered squamous epithelium is destroyed as a result of increased activity of pathogenic microflora, necrosis of certain foci appears, desquamation occurs, and a bleeding surface forms at the site of the lesion - erosion.
Ectropion
Ectropion is a process of tissue deformation that can form after severe surgery and childbirth. The concept refers to inversion of the cervical canal.
It can evert out due to internal ruptures of the cervix.
When exposed to an unnatural environment, the columnar epithelium is attacked by the acidic environment of the vagina, which provokes cell destruction and leads to scarring.
In this case, after sexual intercourse or a gynecological examination, a woman discovers a few drops of fresh scarlet blood on her underwear. The next day, the discharge becomes spotty and disappears completely within 24 hours.
Papillomas and polyps
Polyps and papillomas can form on the surface of the cervix and cervical canal. There is no clear clinical picture for such changes.
The only characteristic feature is the appearance of intermenstrual bleeding in a woman. During the entire cycle, ichor is released from the vagina; after examination in the speculum, bleeding becomes profuse.
The reason lies in hormonal disorders, namely in the active production of female sex hormones.
Against the background of excess estrogen, proliferation and active growth of abnormal tissues is ensured, hyperplasia develops and polyps form. Genital warts are formed as a result of the activity of the human papillomavirus. With these neoplasms, the discharge is of a contact nature.
Attention! When identifying genital papillomas, you cannot hesitate; HPV activity is the most common cause of cervical cancer in women of different ages.
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a disease of the female reproductive system, which is characterized by excessive growth of uterine tissue, accompanied by menstrual irregularities. With a long and uncontrolled course, the disease is dangerous not only with bleeding, but also with infertility. It is often detected untimely due to a blurred clinical picture.
The peculiarity is heavy menstrual flow, the duration of bleeding is more than 7 days, and symptoms of anemia can be observed. Extramenstrual bleeding, similar to ichor, is small and brown in color. Premenstrual syndrome manifests itself intensively, the stomach hurts before and during bleeding.
The main reason for the development of the disease is trauma to the cervix, which creates favorable conditions for the growth of endometriotic tissue. The risk of developing cancer against the background of adenomyosis is minimal; a particular danger lies in the development of infertility.
Endocervicitis
Endocervicitis is a pathology that causes bleeding that is not associated with menstruation. The disease affects the cervical canal and external os. The reason for the development is the addition of pathogenic microflora; progress can be traced against the background of the activity of bacteria and viruses.
Discharge appears upon contact with irritants, the cervix not only bleeds when touched, purulent inflammation is also observed. The blood turns a dirty brown color.
During menstruation, bleeding is heavy and clots may be present. To determine the diagnosis, an examination is required; the woman must take a smear for flora.
Based on the results of the analysis, depending on the pathogen, a treatment regimen is determined.
Precancerous conditions
In this case, bleeding occurs due to significant damage and complete destruction of the capillaries.
Attention! Cervical cancer is the most common oncological disease with a latent course. The danger is that the woman does not feel acute pain and does not experience other bothersome symptoms. The lesion can only be detected by vaginal examination.
Grade 1 dysplasia is not accompanied by bleeding. Symptoms appear with damage of 2 and 3 degrees. With cervical cancer, bleeding is quite abundant, this is due to a change in the structure of the mucous membranes and an increase in their permeability. Bleeding does not only appear on palpation; it can open suddenly when large vessels are damaged.
Hormonal imbalance
Dysfunctional vaginal bleeding in women can be caused by hormonal imbalance.
With intense production of estrogen and a decrease in the concentration of progesterone in the body, ovulation is absent. Minor discharge may be present continuously for several months or years.
The most common cause of changes in hormonal levels is the use of COCs.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, the cervix bleeds when there is a threat of unintentional abortion. There may be copious discharge of fresh blood or the appearance of a brown smear. Such changes are often accompanied by acute girdle pain in the lower abdomen. In the early stages, ectopic pregnancy must be excluded. If discharge appears, a woman needs to consult a gynecologist as an emergency.
Treatment
The treatment regimen can be determined after receiving the results of basic examinations:
- gynecological examination in speculum and bimanual examination;
- determination of the concentration of female sex hormones in the blood;
- general blood analysis;
- ultrasound examination.
Basic rules of therapeutic intervention:
- If the disease has an infectious basis, the treatment regimen necessarily includes antibiotics. The required medication and its dose are determined by the attending physician after an accurate determination of the pathogen. To increase efficiency, you need to take immunostimulants.
- For the development of non-infectious diseases, vaginal suppositories and capsules are used.
- If the cause is erosive damage to the cervix, the woman needs surgery. Treatment is provided by laser therapy, cryodestruction and radio wave treatment.
- Polyps and papillomas are removed surgically. After surgery, the use of antibacterial agents is indicated.
If the bleeding is contact and appears after sexual intercourse, ultrasound or gynecological examination, there is no need to worry. There is probably some minor damage to the mucous membranes. If blood from the vagina begins to flow heavily, its volume is commensurate with menstrual blood loss, you need to visit a gynecologist. It is not always possible to stop bleeding on your own.
A disease that causes blood loss must be treated comprehensively. The course of therapy may include traditional methods, when properly combined with drug therapy. Douching or other procedures can only be done as prescribed by a doctor.
Prevention
Bleeding most often occurs against the background of the development of serious diseases of the female reproductive system; in order to prevent it, you need to follow simple rules:
- Visit a gynecologist and undergo an ultrasound examination once a year.
- Eliminate the risk of mechanical injuries, warn your sexual partner about the required caution.
- Follow the rules of intimate hygiene.
- Avoid unprotected sex due to the risk of contracting STIs.
- Keep a mandatory menstruation calendar; it is better to use a special program that can be installed on a smartphone.
The appearance of periodic bleeding cannot be ignored; with the systematic progression of the disease, serious complications can arise. The list of main consequences resulting from prolonged bleeding includes the following conditions:
- infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- miscarriage;
- premature birth;
- precancer and cervical cancer.
If bleeding is heavy, anemia is likely to develop.
A woman should understand that bleeding not associated with menstrual bleeding most often indicates the development of pathology in the body. There is no reason to panic only in the case when the symptom appears one-time and is the result of an injury.
When you first suspect the development of the disease, you should contact a gynecologist; after an examination, ultrasound and obtaining cytology results, the doctor can prescribe competent treatment to ensure the prevention of consequences and complications.
Source: https://sheika-matka.ru/zabolevaniya/shejka-matki-krovit-vozmozhnye-patologii-ih-lechenie-i-profilaktika/
Polyps and papillomas
The surface of the cervical uterus and cervical canal may be covered with polyps and papillomas.
One of the reasons why the cervix may bleed is a polyp.
Women note bloody discharge, and after sex or examination in the mirror, the cervix bleeds. The cause of the polyp is considered to be hormonal disorders, in particular, increased production of estrogen. Hormones stimulate the growth and proliferation of cervical tissue, which leads to hyperplasia - pathological growth and formation of a polyp. Damage to the vascular component leads to bleeding and spotting not associated with the menstrual cycle. Polyps often accompany endometrial hyperplasia.
Among the reasons why bleeding from the cervix occurs is papillomatosis. Genital condylomas are formed as a result of infection with human papilloma viruses. With such formations, contact discharge occurs.
Papillomas and polyps can develop into cancer.
Reasons for the development of pathology
If the cervix is bleeding, this is an alarming sign that may indicate a dangerous disease.
There should be no bleeding from the cervix. However, there are times when a woman notices a slight discharge of blood outside of menstruation.
The mucous membrane can be injured due to:
- Gynecological examination.
- After sexual intercourse.
- Transvaginal ultrasound examination.
- Installation of the spiral or after its removal.
If the bleeding after the procedures goes away on its own, then there is no need to worry. Blood discharge can be observed during abortion, curettage, or during hysterography.
The cervix may bleed due to the development of certain gynecological diseases, namely:
- Cervicitis. Cervicitis is commonly understood as inflammation of the cervical mucosa. The disease can occur when a fungal or bacterial infection occurs.
- Polyps of the cervical canal. Polyps are classified as benign formations; their development can be asymptomatic and can only be detected during a gynecological examination. In appearance, it is a wart on a stalk. The tumor must be treated, as it may increase in size, resulting in increased bleeding. Polyps can appear due to hormonal imbalance, prolonged stressful situations, and age-related changes. The formation of polyps may be associated with infectious diseases.
- Erosion. With erosion, the mucous epithelium of the cervix changes due to mechanical stress or infectious and inflammatory STDs.
Characteristic signs
Vaginal flora smear is an effective diagnosis of gynecological diseases
Bloody discharge from the cervix appears outside of menstruation. They are usually spotty and brown in color. Discharges are observed periodically. In addition, the following symptoms may be observed:
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen.
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Discharge of serous, purulent leucorrhoea.
- Heavy periods.
Pain in the lower abdomen can be of different types: sharp, dull, cutting, pulling. These unpleasant sensations usually appear after sexual intercourse.
If you experience pain in the lower abdomen and spotting from the vagina between periods, then this is a serious reason to contact a gynecologist and undergo an examination.
When contacting a gynecologist with these symptoms, the doctor will conduct an examination using special mirrors. During the examination, the size and shape of the cervix, the presence of deformation, ruptures, etc. are determined. The gynecologist will also take smears for flora and infections.
If necessary, colposcopy is performed. This procedure allows you to study the mucous membrane of the cervix in more detail and collect material for research. The gynecologist may also refer you for an ultrasound examination to exclude or identify tumors, cysts and other formations.
Adenomyosis and fibroids
One of the common reasons why the cervix bleeds is adenomyosis. This pathology is considered a type of endometriosis - pathological growth of the endometrium in places unusual for it. The inner layer of the uterine cavity begins to grow into the muscles and cervix - this is internal endometriosis or adenomyosis. A woman is worried about heavy bleeding during menstruation, and her cervix also bleeds before and after menstruation. In this case, the blood discharge has a brown, chocolate color. In addition to bleeding, pain occurs. The stomach hurts before, during and after menstruation.
Why does the cervix bleed during examination and what to do when erosion bleeds
The uterus is one of the main female reproductive organs in which the fetus is born. It is located in the pelvis. If the cervix bleeds, the cause may lie in both inflammatory diseases and more dangerous pathologies (polyps, tumors, erosion). This symptom requires immediate consultation with a doctor and a complete gynecological examination.
Inflammatory process
One of the reasons why the cervix may bleed is endocervicitis. This pathology is an inflammation of the cervical canal and external pharynx. The cause is bacteria and viruses. Most often, the inflammatory process is initiated by chlamydia, herpes, myco and ureaplasma, trichomonas, gonococci, gardnerella, and candida.
With endocervicitis, contact discharge occurs. Inflammation itself does not cause bloody discharge. In addition to the fact that the cervix is bleeding, there is mucopurulent discharge from the genital tract and periodic aching pain in the lower abdomen.
Among the reasons why there may be bleeding from the genital tract is endometritis - an infectious inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus. The discharge is brown and patchy, and menstrual blood becomes dark or dirty brown.
Precancerous conditions and cancer
The causes of bleeding caused by precancerous changes are associated with the destruction and damage of capillaries. Dysplasia develops as a result of the pathogenic action of HPV with a high risk of carcinogenesis.
At levels 2 and 3 of dysplasia, contact bleeding occurs.
One of the few reasons why the cervix bleeds is a malignant tumor. Cervical cancer is accompanied by the destruction of blood vessels by a growing tumor, and not by a change in their structure and permeability, so bleeding develops not only upon contact, but also spontaneously. When a large vessel is destroyed, bleeding can be profuse.
Causes of bleeding
Normally, women should not have bloody vaginal discharge. If the cervix hurts and bleeds, this indicates the presence of diseases of the female reproductive system.
This situation may arise due to the presence in the body of inflammation of the mucous membrane of this organ. This disease is called cervicitis.
Cervicitis as one of the causes of cervical bleeding
It appears due to a fungal or bacterial infection entering a woman’s body.
The cervix may bleed due to polyps. These are formations that resemble warts in appearance.
The most common cause of vaginal bleeding is cervical erosion.
This is damage to the mucous epithelium of the organ. This disease cannot be ignored, because it can develop into cancer.
If the cervix bleeds upon examination, this is a consequence of minor damage to the mucous membrane of the organ.
This happens quite often due to overly thin capillaries and vessels. After a gynecological examination, the spotting should go away.
Other reasons why the cervix bleeds:
- Carrying out sexual intercourse.
- Installation of a contraceptive device.
- Carrying out hysterography.
- Cauterization.
Often, spotting appears after a transvaginal ultrasound examination.
Cervical bleeding due to the installation of a contraceptive device
A similar situation may arise in the first days of an abortion.
Pregnant women also face this problem. Small discharge appears due to a slight abruption of the placenta or a damaged cervix due to infection. In the latter case, a pregnant girl should undergo a course of treatment.
Diagnosis of the causes of bleeding
It is impossible to diagnose the cause of bloody discharge at home.
A woman should contact a gynecologist if symptoms such as:
- Lower abdominal pain.
- Disturbed menstrual cycle.
- Menstruation streaked with blood.
The main reason to visit a doctor is the appearance of pain after sexual intercourse.
Pain in the lower abdomen as one of the symptoms of cervical bleeding
Diagnosis of the cause of bloody discharge is as follows:
- Interview of a patient by a gynecologist.
- Examination by a doctor using a mirror.
- Taking tests.
- Undergoing an ultrasound examination.
A woman will need to undergo smears for flora, sexually transmitted infections and cancer cells.
A blood test for hormones is also taken for diagnosis.
If the doctor suspects that the cause is dysplasia (the initial form of cancer), then an examination is carried out using a colposcope.
Treatment
Treatment for this problem is prescribed based on the causes of bleeding.
To eliminate the disease, both medications and traditional medicine are used.
Drug treatment
Antibiotics are used to treat inflammatory processes in the appendages. Remember, self-medication is dangerous to health, so all drugs and dosage are prescribed by a qualified doctor.
Cefazolin for the treatment of cervicitis
List of cephalosporin antibiotics used to treat cervicitis:
If test results confirm the presence of fungal and bacterial infections, then topical medications are used for treatment.
To treat erosion, suppositories and douching are used. If the lesions of the cervix have reached a large size, the doctor recommends cauterizing the wounds to avoid the development of oncology. Cauterization is done with liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction), current (diathermocoagulation) or laser (laser vaporization).
Important! If this procedure does not help, then it is worth removing part of the organ.
Depanthol for the treatment of erosion
Medicines for the treatment of erosion:
If the discharge appears due to damage by cancer cells, then local treatment will not help. Cervical cancer is treated only in oncology clinics using surgery, radiation and gamma therapy.
If the cause of bloody discharge is polyps, then surgical intervention is required to remove them.
Menstrual irregularities and pregnancy
Among the many reasons why the cervix bleeds, there is a hormonal imbalance. Menstrual cycles without ovulation, occurring against the background of increased estrogen production and low progesterone levels, lead to dysfunctional bleeding. It may bleed for several months, and profuse bleeding is also typical. This is due to constant estrogen stimulation of the endometrium. Spotting is observed when taking COCs and intrauterine devices.
The cervix may bleed if there is a threat of miscarriage. In this case, both the separation of fresh blood and brown daub are observed. In such situations, it is important not to miss an ectopic pregnancy, in which the same symptoms are observed, as well as severe pain.
After childbirth and surgical interventions, bleeding from the genital tract due to injury. Normally, bleeding gradually weakens and turns into bloody discharge. If bleeding resumes, consult a doctor immediately.
To find the cause of bleeding, ultrasound, extended colposcopy, PCR diagnosis of infections, smear cytology, and blood tests for sex hormones are performed.
You have questions? Feel free to ask any questions! And our staff specialist will help you. Go>>
Inflammation of the cervical canal may cause unpleasant symptoms that cause discomfort and worsen a woman’s quality of life. This disease is common, but curable if therapy is started in a timely manner and carried out correctly. Otherwise, serious consequences are possible.
Cervix bleeds before menstruation
What is the cervix like before menstruation? This is of interest to women who are trying to independently determine whether pregnancy has occurred or not. But you need to know not only what the uterus looks like before menstruation, but also what the uterus looks like after menstruation, as well as in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
Only knowledge of the different states of the female reproductive organ at different periods of the cycle will allow us to draw correct conclusions about whether the cervix is located before menstruation or after conception with an embryo. It is not difficult to find out all this on your own, for which you will have to check your own vagina by touch.
If this option does not suit you, you should not despair, because no one has canceled a trip to the gynecologist. A doctor is able to give a much more accurate assessment of a woman's condition.
Physiology of the female body
In the human body, the work of all systems is interconnected. And the female body is completely coded to carry out a strictly defined program: to conceive, bear and give birth to offspring. Every month, the woman’s condition returns to its original state, reaching the ovulation phase. And after this, there are two ways for the female body:
- fertilization of the egg;
- setting the body to repeat all the familiar phases of the menstrual cycle.
Menstruation is understood as a completely natural process in the physiology of the female body, which gets rid of an unclaimed egg in such an intricate way and strives to start a new cycle.
And every representative of the fair half of humanity is simply obliged to study her anatomy and know all its subtleties, especially those related to the reproductive system, menstruation and ovulation.
And even more so, every woman should know what the cervix looks like before menstruation: its density and size before and after menstruation, at the time of ovulation, what is the standard position of the cervix before and during menstruation.
Few people know how to properly examine the vagina. Those interested can familiarize themselves with this in more detail.
ARVE Error: id and provider shortcodes attributes are mandatory for old shortcodes. It is recommended to switch to new shortcodes that need only url
What to consider during inspection
The cervix is a hollow body (2.5 by 3 cm), forming a kind of “bridge” between the vagina and the uterus. Any woman can feel the cervix on her own. The examination is performed by inserting the entire length of the middle finger into the vagina. When a finger touches a certain bulge or tubercle, we can say that the cervix has been detected.
By conducting regular (over several months) self-diagnosis in different phases of the menstrual cycle, a woman can learn to identify different assessments of the condition and position of the cervix.
And such an examination will serve her as a true help in determining such a moment as the onset of pregnancy or its absence.
This kind of self-study will allow you to calculate the most suitable (or unfavorable) phases for conception.
The most convenient positions for examining the vagina are the following:
- in a squatting position;
- sitting on the toilet;
- from a standing position, with one leg placed on an elevated platform (stool, edge of the toilet, bathtub).
To ensure the reliability of the home examination results, it must be performed in the same position each time.
It is better to explore your genital tract after your period ends. This should be done no more than once a day and always at the same time. The procedure is not recommended if there is a suspicion of an inflammatory process or infection in the genital organ and if bleeding has begun.
ARVE Error: id and provider shortcodes attributes are mandatory for old shortcodes. It is recommended to switch to new shortcodes that need only url
You can determine whether the cervix is high or not by how quickly it is felt with the center of the fingertip. When it is raised high, it is difficult to feel; when it is low, the opposite is true. The amount of openness is studied as follows: when the uterus closes, the notch in the middle looks like a small gap, and when it opens, this hole becomes deeper and more rounded.
Cervical canal before ovulation
A woman can guess that ovulation is imminent based on several signs. The approach of the ovulatory process is indicated by:
- raising the cervix upward;
- the channel opens slightly and softens;
- the presence of sticky secretions.
On peak days for conception, the position of the cervix also reaches its maximum point, while its consistency becomes very loose, and the canal opens to the maximum possible width to ensure better passage for sperm.
Source: https://karma-laws.ru/krovit-shejka-pered-menstruaciej/
Description of the disease
In medicine, inflammation localized in the cervical canal is called cervicitis or exocervicitis. It is included in the list of the most common diseases, which is determined by the anatomical features of the structure of the female genital organs. The cervical canal connects the vagina to the cervix, and inflammation often spreads upward, coming from the outside and coming directly from the vagina.
Video from a specialist!
In the absence of timely relief of inflammatory processes, they take a chronic form, change the normal structure of tissues and spread to the cervix, causing endocervicitis and then erosion.
Causes of inflammation
The risk of inflammation of the cervical canal increases the influence of the following factors:
- inflammatory gynecological diseases (vulvitis, vaginitis, colpitis, endometritis);
- sexually transmitted infections (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis);
- diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, urethritis);
- non-compliance with personal hygiene rules (irregular washing, rare changes of sanitary tampons or pads during menstrual periods, improper wiping after visiting the toilet);
- constant or frequent use of aggressive solutions for douching or washing;
- use of spermicidal suppositories;
- hormonal disruptions and changes during periods of menopause or menopause, pregnancy, puberty, as well as after taking hormonal drugs, medical termination of pregnancy;
- invasive manipulations performed that violated the integrity of the tissues of the cervical canal (installation of an intrauterine device, curettage or abortion);
- promiscuity without the use of barrier contraceptives;
- rough sexual acts;
- human papillomavirus (HPV);
- decreased general immunity;
- severe stress, sudden climate change.
As you have already understood, inflammation localized in the cervical canal can penetrate into it in different ways: from the outside through the external genitalia, from neighboring organs, as well as through the blood or lymph flow. As a result, changes occur in the vagina: pathogenic microorganisms begin to predominate in the microflora, and the environment changes and becomes favorable for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. One way or another, a healthy and strong female body is able to independently suppress inflammatory processes, but if it is weakened, the situation gets worse.
Symptoms
Symptoms of inflammation of the cervical canal depend on the causes of the pathological condition. The picture may be blurry and unexpressed, but with an acute course and the addition of infections, the signs intensify and become obvious.
Cervicitis can cause discomfort during sexual intercourse or examination of the cervix.
Let's consider possible symptoms characteristic of inflammation of the cervical canal:
- Changes in the nature of vaginal discharge. The consistency, shade, quantity, and smell may vary. The discharge often becomes thick, viscous or foamy, turns yellow, greenish, grey, brown or pink, and smells unpleasant and strong (sour or rotten fish).
- Discomfort localized in the vagina: itching, sensation of the presence of a foreign body, burning.
- Swelling of the mucous membranes of the vagina, hypertrophy of its tissues. The external female genitalia appears swollen and becomes very red or burgundy.
- Nagging or aching pain localized in the groin area, lower abdomen, and sometimes in the lower back.
- Unpleasant sensations that occur during sexual intercourse: discomfort, pain, unbearable itching.
- Increased frequency of urination, pain, burning or itching when emptying the bladder.
- In acute inflammation, an increase in body temperature and general malaise are possible.
Obvious and pronounced symptoms usually appear in the first few days after the introduction of infectious agents into tissues or after mechanical stress. Further, the signs smooth out and practically disappear, appearing occasionally and almost without bothering the woman. This is taken as an independent cure, but in fact the process becomes chronic, resulting in periodic relapses. Exacerbations are caused by the influence of unfavorable or irritating factors: menstruation, hypothermia, sexual intercourse.
Diagnostic measures
To make a diagnosis, the gynecologist first of all conducts an examination on a gynecological chair with dilators. If inflammation of the cervical canal is suspected, flora smears are prescribed to identify possible infectious agents, as well as cytology to determine the risks of degeneration of healthy cells.
The doctor may prescribe a general blood test: an increase in the level of leukocytes will confirm the presence of an inflammatory process, and with an increase in ESR we are talking about a chronic form. Additionally, colposcopy may be performed. When an infection is detected, tests are prescribed to determine the sensitivity of pathogens to different groups of antibiotics.
Therapy
Treatment of inflammation of the cervical canal will depend on the causes of the disease. Therapy may include the following areas:
- Antibacterial therapy is prescribed when infections are detected. Drugs are selected individually after identifying pathogenic microorganisms and determining their sensitivity to certain substances.
- When HPV is detected, cytostatics are recommended to stop the processes of pathological cell division. These are Busulfan, Nimustine, Cytarabine, Buserelin.
- To help the body suppress the activity of viruses (including HPV) and bacteria, as well as to increase immunity, immunomodulators and adaptogens are prescribed: Wobenzym, Isoprinosine, interferons.
- When vaginal candidiasis (thrush) occurs, antifungal drugs are prescribed for topical use in the form of suppositories and creams or broad-spectrum capsules and tablets.
- In case of hormonal imbalances, hormonal therapy is carried out. Drugs and dosages are selected strictly individually.
- In case of severe pain, NSAIDs are prescribed - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including local ones in the form of suppositories.
- To normalize the vaginal flora, suppositories with beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli are prescribed.
- In case of severe erosion of the cervix or multiple papillomas in the cervical canal or the cervix itself, tumors or the outer layer of the canal are removed. The following techniques are used: UHF therapy, laser, cryodestruction, radio wave exposure, classical surgical method (excision with a scalpel).
- To accelerate the healing of damaged tissues, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out, for example, electrophoresis, UHF therapy, iontophoresis and others.
- Folk remedies can relieve symptoms and enhance the effect of the main therapy. Thus, douching is carried out with sea buckthorn oil and decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula, string, coltsfoot).
Treatment of cervicitis. Video from an experienced gynecologist.
Any medications are prescribed exclusively by a doctor after an examination. Self-medication is ineffective and sometimes dangerous.
Inflammation of the cervical canal and pregnancy
The onset of pregnancy against the background of inflammation of the cervical canal is possible, but is complicated by discomfort during sexual intercourse, changes in the acidity of the vagina (in an unfavorable environment, sperm can die) and narrowing of the canal due to tissue hypertrophy (this creates obstacles to the passage of male germ cells into the uterine cavity) .
If inflammation is detected during pregnancy, it should be stopped as soon as possible. Firstly, pathogens are able to penetrate the placenta to the fetus. Secondly, when the cervix becomes inflamed, it can become loose and open prematurely, causing premature birth or miscarriage.
Prevention
Let's consider preventive measures:
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Refusal of promiscuity, use of barrier methods of contraception.
- Regular visits to the gynecologist - twice a year.
- If possible, avoid mechanical influences: abortions, installation of spirals.
- Strengthening the immune system.
Inflammation of the cervical canal is a common but solvable problem. Timely effective treatment will allow you to get rid of the disease and avoid consequences.