Pregnancy is a very difficult period in the life of every woman. Even if pregnancy proceeds without complications, there are many factors that can contribute to the deterioration of a woman’s physical condition. During this period, dramatic changes occur throughout the body, and you need to be prepared for this, which is why a woman should know the nuances of pregnancy and prenatal preparation. Today we’ll talk about how to soften the cervix before childbirth and why it’s needed.
Cervical ripening before childbirth
Quite complex changes occur in a woman’s body during pregnancy, this also applies to the cervix, which, in turn, changes in all its characteristics and parameters. Throughout the entire period of bearing a child, the normal state of the uterus is closed, and only the onset of labor will change its condition.
- Closure of the uterus during pregnancy is a normal process, because its premature opening can lead to termination of pregnancy, which is why, when the time of birth approaches, doctors are required to conduct frequent examinations to determine the maturity of the cervix and its condition.
- If the pregnancy proceeds without complications, the cervix softens and smoothes out to some extent before childbirth. This condition is normal in the last stages of gestation and means that there is very little time left to wait, and labor is about to begin.
- As soon as labor begins, the pressure in the uterus begins to increase, which provokes its opening.
- Dilation of the cervix before childbirth is characterized by cramping pain in a woman giving birth. The pain is concentrated in the lumbar area and abdomen.
How is the cervix dilated?
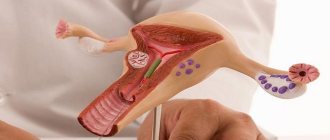
A woman's uterus is a hollow organ consisting of muscle tissue. Around the pharynx there is a ring of muscles - the cervix. It is closed throughout pregnancy. The entrance to it is protected by a mucous plug, which is a barrier to the penetration of infections. The cervix is quite dense, looks like a cylinder 3 cm wide and about the same length. The cervical canal runs in the center. After 32-34 weeks of pregnancy, the cervix gradually opens and softens.
During an internal examination, the uterine os allows the tip of the finger to pass through. The fetus begins to descend into the pelvis, thereby creating a certain pressure on the neck, which contributes to its further opening. By 36-38 weeks, the cervix is already completely smoothed out. The expansion begins with the internal pharynx, which in primiparas has the shape of a funnel with the base facing upward. Gradually moving forward, the fetus stretches the external pharynx. In multiparous women, the cervix dilates more easily, and the internal and external os expand almost simultaneously.
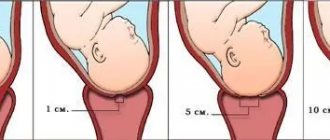
With each contraction, under the influence of hormones, the cervix first dilates to one finger, then two. At the time of birth, full dilation is 10 centimeters in diameter. With this degree of dilation, the baby’s head and torso will be able to pass through the birth canal.
In total, there are three phases in the first stage of labor:
- The latent phase begins with regular contractions with a frequency of one or two per ten minutes. At this time, the cervix shortens and smoothes. The duration of this phase is on average 4-6 hours. Contractions during this period are usually not painful;
- The active phase is characterized by increased labor activity. The intensity of contractions increases, becoming more frequent, stronger and painful. The dilation of the cervix from 2 fingers increases to approximately 8 centimeters. The duration of this period is from 4 to 6 hours;
- The transition phase begins when the cervix is almost completely dilated and the intensity of contractions is more than once every seven minutes. After this, some weakening of labor occurs. The duration of the phase ranges from 20 minutes to 1-2 hours; in multiparous women it may be absent.
Also, during the active phase, rupture of amniotic fluid usually occurs due to increased intrauterine pressure. The volume of liquid is approximately 150-200 ml. Normally, amniotic fluid should be clear and light. If, when the cervix is dilated by 6-8 centimeters, the waters do not break spontaneously, then the obstetrician usually performs an amniotomy - opening the amniotic sac.
Cervical length before birth
There are three components of the condition of the uterus, which determine how easy the birth will be and whether there will be any complications:
- location of the uterus
- how much the uterus is softened and smoothed
- How much has the length of the cervix decreased?
It is quite simple to find out whether the birth canal is prepared for childbirth; it is necessary to determine the softness of the cervix. If she misses two fingers, it means she is fully prepared for childbirth. If the uterus opens, the mucus plug comes out - these are interconnected processes.
Just before childbirth, shortening of the cervix can be observed, and the results of an ultrasound examination can confirm this. The length of the uterus in this case is only one centimeter.
About the mature cervix
Before childbirth, the location of the cervix in the pelvis, as well as its length and softness, are of great importance. The last indicator when ready for childbirth should be such as to let 1-2 fingers inside. With this softening, the woman notices that the mucous plug is coming off. This sign of approaching contractions appears the earlier the earlier the cervix begins to dilate before childbirth.
And it also shortens at this time. Transvaginal ultrasound shows that its length before birth is about 1 cm.
As labor approaches, the cervix occupies a position in the center of the small pelvis. For comparison, a month before it was rejected back.
That is, these 3 parameters (softness, length and location) are indicators of the maturity of the cervix. They are rated on a 2-point scale. The neck is considered mature if the total indicators are 5 points.
Softening the cervix before childbirth
Childbirth will take place without any complications and injuries for mother and child if the uterus is properly softened and smoothed. Hormonal changes control this natural process.
The fetal head presses on the muscle tissue, thereby relaxing them and increasing in size. This process makes it clear that the uterus is fully mature and ready for labor. If the softening of the tissues provoked the removal of the plug, then labor should begin very soon.
It happens that the uterus does not soften or smooth out until childbirth. This behavior of the body is abnormal and indicates that it is not ready for the onset of labor. In this case, if the birth process does start, there is a high risk that when the baby’s head begins to move forward, muscle tissue will rupture.
How is the readiness of the cervix for the upcoming birth determined?
When pregnancy approaches 38–39 weeks, the gynecologist monitoring the pregnant woman is required to evaluate the cervix during a routine examination. The conclusion about her maturity is made on the basis of the scores given by the doctor for four parameters. The Bishop scale is used, giving 0–2 points. If the total result reaches 5, then the cervix is considered ready for childbirth.
The four parameters assessed by the gynecologist include:
- Consistency. The soft neck gets the maximum score. If it is softened, but has compactions, then it will be given a score of 1; a hard cervix is not ready for childbirth, it will be given a score of 0.
- Length. Up to 1 cm is considered the most optimal. For a length of 1–2 cm they give one, more - 0.
- Location. The middle position gets the maximum score. Deviation forward – 1, posterior – 0.
- Patency of the cervical canal. Closed external mouth – 0, closed internal mouth with open external one – 1, both open – 2.
Methods for softening the cervix before childbirth
If there is very little time left before childbirth, and examination of the cervix before childbirth reveals its immaturity, doctors prescribe common methods of preparing the uterus for labor. Such manipulations include the use of:
- non-medicinal drugs
- gel for the cervix before childbirth
- antispasmodics
- massage
- kelp, etc.
Pregnancy is a period in a woman’s life when independent decision-making about her condition is contraindicated. You shouldn’t think that you know better what to do during pregnancy, because no one but you can feel all the sensations.
You must understand that self-medication during this period can result in spontaneous abortion and even death for the mother.
Remember, you can take antispasmodics immediately before giving birth only if your doctor has prescribed such treatment for you. Among other things, the doctor may also prescribe the following medications:
- pills for the cervix before childbirth
- suppositories for softening the cervix before childbirth
- use of oxytocin
- special gels
The most common method to prepare the uterus for childbirth is to inject a hormone called Oxytocin. If the pregnancy proceeds without complications and the pregnant woman’s health is normal, this hormone is produced in the required quantity naturally. The process of its active development begins before and during labor.
Additional introduction of the hormone in question into the woman’s body is needed so that the uterus softens, opens and childbirth takes place without complications and difficulties, as well as injuries to the mother and child. In medical practice, for the purposes under consideration, special gels are also used by introducing them into the cervical canal.
- To keep the muscle muscles relaxed and the cervix to open at the right time, using a gel is an excellent and effective method.
- Tablets, as well as suppositories, are also often used in cases where the uterus is not softened, and labor should begin very soon. To prepare for childbirth in this way, the pregnant woman must undergo hospital treatment, because this type of treatment is contraindicated at home. Doctors can prescribe such drugs as early as 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- The most effective way to speed up the opening of the uterus and influence its softness is the use of kelp. Seaweed contains a large amount of polysaccharides. The main ability of such algae is to quickly absorb liquid, while increasing in size.
The effectiveness of such dried sticks is observed within four hours after their introduction into the cervical canal.
The main advantages of this method are:
- affordable price
- no side effects
- high efficiency of application
Preparation
Medical preparation of the cervix begins with insufficient maturity or complete immaturity by 39-40 weeks. Medicines and mechanical methods help to relax the cervix and make it more elastic. The latter include a Foley catheter for dilating the cervical canal and kelp sticks. The first is tablets, suppositories, hormonal gel, which is applied directly to the cervix itself.
The doctor may recommend taking antispasmodics (“No-shpa”, “Papaverine” in suppositories, “Buscopan”). These products have a moderate relaxing effect on the muscles, and the smoothing process is somewhat accelerated. A woman can easily use such remedies at home along with gymnastics, recommendations to move more and drink tea with raspberry leaves. Other preparation measures are carried out exclusively in a hospital setting.
- A Foley catheter is a thin latex-silica tube with a small balloon. It is inserted into the cervical canal by a doctor, and the balloon at the outer end is filled with saline solution. Mechanical pressure accelerates ripening and opening. The effectiveness of the method is no more than 50%, which means that in half of the cases the catheter does not give the desired result.
- Laminaria are sticks of dried kelp seaweed that are inserted into the cervical canal. Gradually the channel expands due to the swelling of the algae. After a day, the sticks are changed or removed completely, if there is a result. The efficiency is higher than that of a catheter, but not by much.
- Medicines are mainly prostaglandins and estrogens. The efficiency is high, but again, not one hundred percent.
If, even after preparation, the cervix stubbornly does not open, labor is not stimulated - the thick and long cervix is not ready to open. If indicated, a caesarean section may be performed.
Traditional medicine methods
The use of any of the following methods should only be done after consulting with your doctor:
- raspberry leaf decoction
- primrose oil
- cinnamon powder decoction
These methods should be used no earlier than 36 weeks of pregnancy.
Under no circumstances should the following methods be used, because they are dangerous to the health of the pregnant woman and her baby:
- Enema
- taking hot water treatments
- sex
- excessive stress on the body, including physical
All this stimulates the dilatation of the cervix, but the consequences of what is happening can be far from positive. It is worth noting that regular visits to the doctor during pregnancy will reduce the risk of problems during this period to a minimum.
What are the consequences of insufficient readiness of the organ?
A prepared, fully mature cervix before childbirth plays an important role in the favorable course of labor. If the organ is not mature by the time the baby is born, this can cause the following complications:
- internal and external breaks;
- fetal injury;
- premature discharge of amniotic fluid;
- protracted labor.
Long neck
One of the parameters by which one can judge whether the cervix is not ready for childbirth is its size. The normal length during pregnancy is 3–4 cm. As labor approaches, the cervix changes. Due to the pressure that the child puts on the base of the organ, it rises and shortens. An organ whose size during contractions exceeds 2 centimeters is considered long. An elongated cervix is unable to deliver the fetus, as it is dense and narrow, which will prevent the baby from passing through the birth canal on its own.
Complications of a long organ can include:
- weak labor activity;
- prolonged labor;
- injuries, ruptures;
- fetal hypoxia;
- untimely removal of the plug.