Causes of uterine bleeding
Repeated surgical interventions are considered the main cause of the disease. The risk of endometriosis increases with each abortion; operations and childbirth with complications can also cause uterine bleeding later. With weak immunity, this becomes an impetus for the development of endometrial cells, and monthly bleeding distributes fragments of pathogenic tissue inside the fallopian tubes, to the ovaries. They, in turn, can become attached to the cervix, vagina, external genitalia, etc.
If you experience nagging pain during menstruation in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back and sacral area, you should consult a gynecologist. Endometriosis of the vagina and cervix can be detected by visual examination using gynecological speculum. Laparoscopy and ultrasound will show the presence of pathogenic tissues during a deeper examination.
Mid-cycle bleeding: treatment
Most often, prolonged and painful bleeding in the middle of the cycle is explained by the presence of sexually transmitted infections. Treatment is prescribed after examining the patient and conducting tests. Therapy consists of taking antibacterial drugs and topical agents.
If the tests do not reveal sexually transmitted diseases, then non-infectious causes of bleeding are diagnosed. For this purpose, a hormonal analysis is often prescribed. If a hormonal imbalance is detected, the doctor prescribes therapy to correct it.
Extensive uterine bleeding is a possible symptom of the following diseases:
- cervical erosion;
- endometriosis;
- myoma;
- chorionepithelioma;
- cervical cancer.
To treat these diseases, as a rule, surgical intervention is necessary.
Contact the Ameda family clinic - our specialists will help you establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe the most appropriate treatment for intermenstrual bleeding.
The nature of bleeding in various forms of endometriosis
Bloody discharge with different types of endometriosis has a different character:
- With internal genital bleeding, heavy menstrual bleeding continues much longer than usual. The discharge may be copious throughout, or may be scanty and painful. Discharge may appear during the intermenstrual period. Blood that is released abundantly and constantly can provoke anemia with iron deficiency. It is difficult to treat. Causes a feeling of constant fatigue and weakness.
- External genital endometriosis is characterized by prolonged discharge, but has some peculiarities: with endometriosis of the vagina and cervix, the discharge is spotting and begins 2 days before menstruation. There may be a few more days after the bleeding is over. During sexual intercourse and medical procedures, blood may also be released with painful sensations.
- Extragenital endometriosis can manifest itself in different organs. Bleeding is not uterine. Discharge can be from the intestines or from the lungs when coughing.
Read more about internal endometriosis in the article Adenomyosis of the uterus: what is it and how to treat
Bloody discharge in the middle of the cycle: an alarming symptom or physiological manifestation
Menstrual bleeding in a healthy woman occurs according to a clear schedule. Its volume is strictly determined so that the body does not experience severe consequences of blood loss. But sometimes there is discharge in the middle of the cycle. What diseases are they associated with, and can this be considered a normal variant?
During the month, a woman of reproductive age, in addition to menstruation, may experience physiological leucorrhoea, the volume of which does not exceed 20 ml per day. They consist of the mucous secretion of the cervix, a small amount of lactic acid, hydrogen peroxide produced by normal microflora, and dead cells and bacteria. Almost colorless, more like mucus, sometimes with a white tint. The smell may be a little sour, but not pronounced.
Ways to stop bleeding
Uterine bleeding with endometriosis looks like very heavy menstruation, accompanied by pain. Taking hemostatic drugs is not recommended, since the accumulation of blood in any organ can cause additional inflammatory processes. Since bleeding can be stopped only after hormonal therapy or through surgery. Treatment with other drugs and medications relieves symptoms and reduces pain, but cannot solve the problem.
To relieve pain and reduce the amount of discharge during the next heavy bleeding, you can use an ice compress. Apply to the lower abdomen or lower back for no more than 20 minutes. After 3 hours, you can repeat the procedure if the abundance has not decreased.
Drug elimination
If uterine bleeding occurs with endometriosis, drug treatment is possible. Hormonal drugs are used that are designed to increase progesterone levels. The concentration of estrogen decreases proportionally, which helps to normalize the condition. It is preferable to use a combination course of treatment that simultaneously controls estrogen levels without reducing its minimum amount, since this can also adversely affect the functioning of other internal organs:
- Monophasic oral contraceptive drugs: Janine, Regulon, Non-ovlon and others. The treatment regimen for hormonal medications is prescribed by the attending physician. It can be recommended as a hemostatic agent for nulliparous women predisposed to tumor diseases, also after surgical cleansing, if pathological endometrial changes are not detected during examination.
- Gestogens: Norethisterone, Linestrenol, Dydrogesterone. The effect is slow, therefore, if anemia is detected, their use is not recommended.
In case of heavy bleeding, it is possible to prescribe hemostatic drugs:
- Aminocaproic acid. Increases blood clotting.
- Dicynone. Activates platelets and increases their number.
- Tranexam. Has a versatile effect, in addition to hemostatic (anti-allergenic, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor)
- Ascorutin.
- Oxytocin. Causes contractions of the uterus, constricts blood vessels. It has a number of contraindications and is used strictly as prescribed by a doctor.
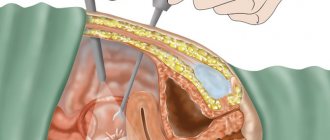
Surgical
If drug treatment does not produce positive results, the bleeding is stopped with surgery. The operation is prescribed in critical situations when heavy discharge can lead to a sharp deterioration in health.
There are several types of surgical treatment of bleeding:
- Cleaning. The overgrown layer of the endometrium is removed. The operation is performed under general anesthesia for 15 minutes.
- Cryodisruption. Liquid nitrogen is used to destroy the outer layer of the endometrium through special devices.
- Ablation. Laser removal of the pathological layer.
- Uterus removal.
It is impossible to stop uterine bleeding using folk remedies alone. Medicinal plants in the form of decoctions and compresses can be used as an addition to drug treatment. In folk medicine, the following plants have hemostatic properties:
- Stinging nettle. Strengthens blood vessels, increases blood clotting, and tones the uterus.
- Viburnum bark. Antiseptic, analgesic and vasoconstrictor.
- Horsetail. Wound healing, hemostatic, antiseptic.
- Highlander. Increases the rate of blood clotting, strengthens blood vessels, anti-inflammatory.
- Yarrow. Preventive and restorative agent.
- Shepherd's purse. To increase the tone of the uterus during bleeding.
In what cases is surgery required?
If the doctor does not know how to stop bleeding due to endometrial hyperplasia with drug treatment, or rather, this method of intervention does not give the desired effect, the doctor may prescribe a surgical method of treatment. To do this, the patient is given anesthesia, and then the surface layer of the endometrium is removed using a curette.
Sometimes the “freezing” method is used, when damaged areas of the endometrium die under the influence of cold, and then the cells are removed.
Some doctors recommend cauterization with a laser or special instruments heated to a high temperature. Subsequently, the damaged cells leave the uterus naturally, and the mucous membrane is restored.
Can a complete hysterectomy be prescribed? This method of intervention is provided, but only for very complex, atypical forms. Most often, this method of treatment is prescribed to patients during menopause, since the likelihood of developing a cancer tumor significantly increases. If there are no changes in the ovaries, then they are left in place.
Uterine bleeding with endometriosis
The causes of endometriosis are varied. Uncontrolled growth of endometrioid tissue can be provoked by dyshormonal disorders, previous surgical interventions, childbirth and abortion. The impetus for the formation of this pathology can be a sharp decrease in the body’s defenses.
The danger of endometriosis is that this pathological condition over time leads to loss of reproductive function, as well as to the development of bleeding of varying degrees of intensity.
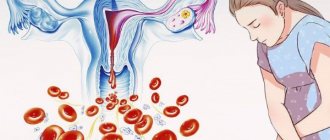
The nature and volume of bleeding in endometriosis directly depends on the location of the pathological foci, the area they occupy, as well as on the state of the blood coagulation system in the female body. Knowing how to stop uterine bleeding with endometriosis, a woman will be able to provide herself with pre-medical assistance in a timely manner.
Bloody discharge from the genital tract that occurs with endometriosis may have the following characteristic signs:
- In the extragenital form of endometriosis, the location of the bleeding site is not the uterus. The release of bloody contents occurs from the organ on which the growth of endometrioid-type tissue has occurred.
- With external genital endometriosis, prolonged bleeding from the genital tract occurs. If the disease affects the cervix and vagina, the discharge is spotting and occurs a couple of days before the start of menstruation. With external genital endometriosis, there is an increase in the volume of bloody discharge during intimacy.
- Internal genital endometriosis is characterized by heavy menstrual bleeding that lasts longer than usual. In addition to heavy menstruation, a woman with the internal form of genital endometriosis complains of spotting during the menstrual period. This complication often provokes the development of iron deficiency anemia, accompanied by signs of general malaise, dizziness, nausea, sleep disturbance and other clinical signs.
Endometriosis blood in the middle of the cycle
- Vozdukhoflotsky Avenue, 51
- Obolonskaya embankment, 1 building 3
- Zlatoustovskaya street, 16
- Citadelnaya Street, 7
- Sofievskaya Borshchagovka, st. Yuzhnaya, 7
- Sofievskaya Borshchagovka, st. Petrovskaya, 1 (Residential complex Barcelona)
Vozdukhoflotsky Avenue, 51 Obolonskaya embankment, 1 building 3 Zlatoustovskaya Street, 16 Tsitadelnaya Street, 7 Sofievskaya Borshchagovka, st. Yuzhnaya, 7 Sofievskaya Borshchagovka, st. Petrovskaya, 1 (Residential complex Barcelona)
Clinic opening hours: Mon-Sat: 8:00 – 20:00 Sun: 9:00 – 18:00
Intermenstrual bleeding is something that occurs completely spontaneously, in the middle of the cycle. This is a fairly common phenomenon, which is both a variant of the norm and a sign of dangerous diseases. Why does spotting occur in the middle of the cycle , and is there any reason for concern?
Prevention
Bleeding caused by uncontrolled proliferation of endometrioid tissue is easier to prevent than to combat its severe consequences. To minimize the risk of bleeding due to endometriosis, the following recommendations will help:
- Regular intake of multivitamin complexes;
- Prevention of psycho-emotional and physical overload;
- Refusal to lift heavy objects;
- Regular visits to the antenatal clinic at least once every 3 months.
Regardless of the location of endometriosis and the amount of bleeding that occurs, this condition requires qualified medical intervention and comprehensive treatment.
Diagnostics
During the survey, the date of the last menstruation, duration of bleeding, and cycle are determined. The factors that could provoke bleeding are clarified. Determine the symptoms of anemia: pale, dry skin, rapid pulse, low blood pressure. Next they move on to a gynecological examination: examination of the external genitalia, vestibule of the vagina, examination using gynecological speculum. If necessary, perform a rectal examination. Laboratory diagnostics:
- general blood test to determine the level of leukocytes, hemoglobin, red blood cells;
- coagulogram to determine blood coagulation function;
- determination of the level of hormones: follicle-stimulating, luteinizing, thyroid, as well as estrogens, progesterone, prolactin, cortisone, thyroxine and other hormones according to indications.
The main instrumental research method is ultrasound of the pelvic cavity. This is a standard study to identify formations in the uterine cavity, ovaries, retrouterine space, and bladder. With its help, the condition and volume of the uterine membranes are determined. According to indications, hysteroscopy is performed - a minimally invasive procedure to examine the uterine cavity, which can be combined with diagnostic curettage to take material for a biopsy. During the procedure, the upper (superficial) layer of the uterine lining is removed for histological examination.
To determine the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, the following studies may be prescribed:
- X-ray of the brain with recording of the sella turcica;
- Electroencephalography to determine the functioning of brain structures.
- Magnetic resonance imaging to obtain layer-by-layer images of certain areas of the brain.
- Computed tomography for a detailed study of the required areas.
- Echoencephalography to determine the state of blood flow, vascular walls, and brain structures.
If there is a suspicion of dysfunction of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands, an ultrasound of these organs is indicated.
Important!
In case of juvenile bleeding, cysts in the mammary gland are often detected, so an additional consultation with a mammologist is prescribed.
What causes bleeding associated with endometriosis?
Endometriosis is the growth of tissue lining the uterus beyond the hollow organ. The disease can begin with endometrial hyperplasia and end with adenomyosis. At the same time, very often women suffering from one of the above diseases develop other gynecological problems, such as:
- Myoma;
- Polyps;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- Fibrosis.
It is necessary to understand that the mechanism for the development of bleeding due to problems with the endometrium is in no way related to any mechanical damage to the uterus. In most cases, bleeding is very similar to normal menstruation and is hormonal in nature.
For example, with adenomyosis, when tiny masses of endometriotic cells grow directly in the thickness of the uterus, bleeding develops during normal menstruation. But the blood does not come out, but accumulates in the surrounding muscles.
When to see a doctor
To stop the development of the disease and prevent the occurrence of infertility, you need to contact a gynecologist who will conduct a series of studies and determine at what stage the endometriosis is. You should make an appointment with your doctor if you experience heavy bleeding that is not related to your period. Periodic intermenstrual discharge, which is not typical for the cycle of a healthy woman, should also be alarming.
Pelvic pain of unknown etiology is a reason to visit a gynecologist. Dysmenorrhea that occurs suddenly should alert you, as it may be a sign of endometriosis. An irregular menstrual cycle with heavy discharge and an unpleasant odor is a reason to consult a specialist.
If you are treating endometriosis and there is no result, you should also make another appointment with a gynecologist, who will help you choose a different drug. It is especially important to consult a doctor if spotting occurs several months after cauterization of cervical erosion, since endometriosis is a common complication of electrocoagulation. This is typical for errors during the procedure.
An irregular menstrual cycle accompanied by pelvic pain is a reason to consult a gynecologist.
It is important to differentiate endometrioid cysts from malignant tumors. Only a doctor can do this during a colposcopy. The inability to get pregnant for a long time is a reason not to postpone a visit to a specialist.
How to stop bleeding associated with endometriosis on your own?
In fact, bleeding with endometriosis for most women is similar to a very heavy and painful period. Therefore, doctors recommend not stopping the bleeding, but trying to reduce the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms.
Retention of rejected blood in the body, on the contrary, will lead to negative consequences. Since abnormal uterine bleeding can be stopped only after surgery or a course of hormonal therapy, all home methods should be considered only “symptomatic” treatment, in no way related to solving the root of the problem .
So, if the next menstruation is accompanied by severe pain and the release of an abnormally large amount of blood, then you can apply a heating pad with cold water to the lumbar area, or to the lower abdomen.
The sudden cooling will cause the blood vessels to constrict, which will help stop the bleeding. Cooling compresses can be left on the skin for no more than 20 minutes. Then you need to take a break for three to four hours and repeat the procedure only if the discharge of an abnormally large amount of blood resumes.
Important! If there is heavy uterine bleeding, it is prohibited to use hot heating pads. Despite the fact that heat will help relieve spasms and eliminate painful sensations, the intensity of bleeding (due to relaxation of the walls of blood vessels) will only increase. Ultimately, such “self-help” can result in anemia.
Since cold heating pads do not relieve spasmodic pain well, it is additionally recommended to take a loading dose of vitamin B. B vitamins will not only reduce estrogen levels, but also promote the synthesis of prostaglandins (compounds that prevent the formation of clots in the blood).
If there are no synthetic vitamins in the house, then you can eat green beans and black bread. After the bleeding has stopped, you need to take iron supplements, which will prevent the development of anemia.
The appearance of painful sensations
Critical days are characterized by the presence of pain of varying intensity. Women have long been accustomed to this. However, with pathology, things are somewhat different. Pain during menstruation with endometriosis is usually accompanied by the following symptoms.
- Increased weakness.
- Difficulty urinating if endometrial growth occurs in the genitourinary system.
- Nausea with vomiting.
- Problematic stool if the pathology has spread to the intestines. In this case, it is even possible that blood may appear from the anus during bowel movements.
This pathology is characterized by severe pain. It can be aching, cramping or shooting pain. They can appear quickly and disappear just as quickly or last throughout menstruation. In this regard, there is no such category as “typical pain.”
Since the endometrium can grow in different tissues and create many foci, the sensations are constantly changing. The stage of the pathology also affects the pain. It’s one thing if we are talking about a simple superficial lesion, and a completely different matter if organ fusion occurs and many lesions appear.
As the disease progresses, the pain becomes constant, and at the initial stage it occurs periodically.
Painful sensations can continue not only during menstruation, but also after their end. This is due to the abundant flow of blood into the uterus due to illness.
Answering the question about what kind of periods are with endometriosis, we can definitely say – painful. The more advanced the pathology, the more noticeable the pain will be.
Tablets for uterine bleeding in endometrial diseases
If uterine bleeding is very profuse and is accompanied by convulsions, fever and even temporary clouding of consciousness, then it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance.
While waiting for the doctor, you are allowed to drink non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs based on paracetamol, as well as take hemostatic agents ( Tranexam, Vikasol ). The tablets will help eliminate pain in the pelvic area, relieve muscle cramps and temporarily stop bleeding.
But if heavy uterine bleeding occurs again and again over several months, then the above methods may not work. It is best to consult a doctor to select medications.
Official medicine believes that the problem can only be solved through surgery. But if a woman for any reason does not want to see a surgeon, then hormonal drugs are prescribed. You need to know that such therapy does not always help eliminate the root of the problem.
Most often prescribed:
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (Buserelin, Leuprorelin).
These drugs reduce estrogen levels, reduce pain and prevent the development of heavy uterine bleeding. Without first consulting a doctor, taking drugs of this type is quite dangerous, because there is a risk of triggering artificial menopause.
Side effects such as vaginal dryness, unexplained fatigue, bone loss, and even hot flashes may also occur.
Oral contraceptives (Zhanine, Diane-35).
After just a month of use, they reduce menstrual pain and prevent the development of sudden uterine bleeding. Common side effects include bloating and slight weight gain.
Steroid drugs (Danazol, Danatrol).
These steroid drugs are sold only by prescription and help not only completely get rid of abnormal bleeding, but also stop the proliferation of endometriotic tissue. Long-term use may cause side effects such as hirsutism, acne and voice changes.
Every woman suffering from endometriosis should know how to stop uterine bleeding. But you shouldn’t refuse treatment, because there is a risk of getting cancer. It is better to undergo an individually selected course of therapy and not be afraid of recurrent bleeding.
How to prevent the development of complications
Uterine bleeding is a natural outcome of progressive endometriosis. To avoid complications, you need to:
- Diagnose the disease in a timely manner. Consult a doctor if the first symptoms of endometriosis appear - pain in the lower abdomen, menstrual irregularities, infertility;
- Undergo treatment taking into account the severity and extent of the process. During surgery, the lesions can be removed and the risk of bleeding can be reduced. Hormonal therapy suppresses the growth of heterotopias and prevents the progression of the disease;
- Monitor the course of the disease. Do an ultrasound every year and be examined by a gynecologist, even if there are no complaints.
This tactic prevents uterine bleeding - one of the most dangerous complications of endometriosis.
source
Bleeding with endometriosis. Drugs to stop uterine bleeding in endometriosis
In this article we will look at the reasons why bleeding may occur with endometriosis.
Every woman of reproductive age may face a problem such as endometriosis. Quite often, signs of a pathological process are bleeding and spotting. Against the background of endometriosis, there is a disturbance in the cyclicity of menstruation and associated pain in the lower abdomen. Many people are interested in the dangers of uterine endometriosis.
In the absence of appropriate treatment, the disease can cause serious and life-threatening consequences for the patient’s health. For this reason, you should consult a specialist at the first signs of pathology. The gynecologist will prescribe a comprehensive examination, after which he will select an effective therapeutic regimen, the purpose of which will be to eliminate both the symptoms and the causes of its development.
Let's figure out why bleeding occurs with endometriosis.
Intermenstrual bleeding: when there is cause for concern
Light spotting after menstruation that occurs during ovulation and stops quickly should generally not be a cause for concern. However, in this case, you should still visit a gynecologist to make sure there are no serious diseases.
If spotting in the middle of the cycle intensifies, is accompanied by pain, or does not go away after 2-3 days, you should immediately seek medical help. The specialist will be able to determine why intermenstrual bleeding occurred and prescribe appropriate treatment.
If the bleeding becomes severe and the woman’s condition worsens, an ambulance should be called immediately. These symptoms indicate serious problems, many of which require emergency surgery.
Causes of bleeding
An egg that has not been fertilized during menstruation causes the layer of the uterine wall on the inner surface, which is called the endometrium, to be rejected. Subsequently, the rejected tissue is removed from the uterine cavity naturally. If this process goes wrong, menstrual blood can enter the peritoneal cavity through the uterus. There the process of proliferation or hyperplasia of endometrial cells occurs. The consequence of hyperplasia can be endometriosis of the genital type of external nature. If endometrial cells grow into the muscles of the uterus, then we are talking about internal endometriosis of the genital type.
Endometriosis of any type occurs against the background of bloody discharge from the uterine cavity. There are a number of reasons that can trigger bleeding with endometriosis, including the following:
1. Reduced production of progesterone and other hormones produced by the pituitary gland.
2. Complete absence of ovulatory processes.
3. Increased levels of female sex hormones in the blood.
4. Pregnancy that occurs outside the uterus.
5. Hyperplasia and prolonged rejection of endometrial cells.
Bleeding with endometriosis is prolonged, and its severity and intensity may vary.
As a rule, the initial stage of development of endometriosis occurs without pronounced symptoms, that is, in a latent form. Subsequently, foci of the pathological process grow not only in the uterine cavity, but also in other organs of the woman’s reproductive system. In especially advanced cases, endometrial cells can spread throughout the body, affecting the liver, kidneys, lungs, etc. all this leads to cysts, adhesions and bleeding.
The main signs of endometriosis are:
1. Pain in the lower abdomen of an aching nature.
2. Menstrual irregularities.
3. Spotting outside the cycle.
4. Breakthrough bleeding.
5. Menstruation, characterized as painful and heavy.
6. Feeling of discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Consequence of pathology
Vaginal discharge may take on more than just a brown tint. Sometimes it all starts with the appearance of atypical leucorrhoea: it is accompanied by itching, becomes cheesy, thick, and the sour smell intensifies. Most likely, this is a sign of thrush. If left untreated, the inflamed mucous membrane will begin to bleed a little and pink impurities will appear.
But the reason may also be a sexually transmitted infection. If the discharge is watery, copious, and there is pain in the abdomen, then this is an inflammatory process. A yellow tint usually indicates a nonspecific process, and a greenish tint usually indicates Trichomonas.
Pathological bleeding can be suspected if the following symptoms appear:
- copious discharge;
- the appearance of blood clots;
- sharp pain in the abdomen;
- nausea;
- temperature increase;
- unpleasant odor;
- prolonged metrorrhagia;
- scanty menstruation.
Endometriosis and endometrial hyperplasia
Pathological growth of the endometrium in atypical places leads to hormonal imbalance. This tissue has its own hormonal activity and can change the general background. In turn, excessively high levels of estrogen lead to endometrial hyperplasia. It can be diffuse and local, in the form of a pedunculated polyp. The thickened endometrium is capable of shedding, which leads to the appearance of metrorrhagia. In this case, for a woman of reproductive age, curettage simultaneously becomes a therapeutic and diagnostic procedure.
Sometimes endometrioid lesions in the uterine cavity are emptied, which can grow deep into the muscles. They empty themselves without a clear connection with the menstrual cycle, and the blood is almost black.
The proliferation of muscle and fibrous tissue leads to the appearance of lesions, which, if large in size or located under the mucous membrane, can disrupt endometrial rejection. This happens regardless of the day of the cycle. It also manifests itself in the form of prolonged menstruation, which at first subsided and then intensified.
Pathology of the cervix
The discharge of blood from the cervix during erosion is often of a contact nature. It appears after sexual intercourse or a doctor's examination. Sometimes brown discharge is a consequence of cauterization of erosion: ten days after the procedure, the scab begins to come off.
Bleeding in itself is not dangerous. But you need to undergo examination and treat erosion. Signs of cellular atypia indicate the risk of pathology developing into cancer.
Oncological diseases are increasingly common at a young age, and in premenopausal and menopausal women they are one of the most common causes of bleeding. The tumor can be located on the cervix, in the uterine cavity. Sometimes the discharge takes on an extremely unpleasant odor (of decaying flesh). Only timely diagnosis and radical treatment will help get rid of the disease in time and increase the chances of survival.
Ectopic pregnancy
Nagging pain in the lower abdomen and bleeding in the middle of the cycle can be a consequence of an interrupted ectopic pregnancy. This condition is accompanied by internal bleeding, and the blood that spills out is only a small part. The severity of the condition will gradually increase, blood pressure will drop, tachycardia and signs of vascular collapse will appear. This situation requires an immediate response.
When the fertilized egg attaches to the cervix, bleeding also occurs - first at the time of implantation, and then in a new cycle as the embryo grows. This is dangerous for a woman's life.
Types of bleeding
In addition to genital endometriosis of internal and external types, there is also an extragenital type of pathology. In this case, it is not the organs of the woman’s reproductive system that are affected, but other structures, for example, the gastrointestinal tract.
If the disease is characterized as internal, bleeding occurs over a long period of time. Along with this, the discharge can be either very abundant or insignificant. Blood loss is often observed, accompanied by pain outside of menstruation.
The external type of endometriosis is characterized by spotting of blood several days before the onset of menstrual bleeding. Also, scanty discharge may accompany the end of menstruation. Spotting and spotting is typical during sexual intercourse and gynecological examination.
Extragenital endometriosis, depending on its location, may be accompanied by coughing up blood during menstruation, as well as the appearance of bloody spots in the stool.
What kind of discharge can there be?
Discharge in the presence of endometriosis differs from normal. Throughout the cycle, their consistency changes. If a bacterial infection occurs, they become thicker and may have an unpleasant fishy smell. This aggravates the course of the disease and contributes to its progression. Discharges can be:
Menstrual
In the presence of pathological changes in the cervix, foci or hormonally dependent cysts appear. At the end of the cycle, spotting black discharge often occurs. They gradually turn into bleeding.
With the progression of endometriosis, menstruation is always heavy, and strong cramps in the lower abdomen often occur.
Menstruation can last from 5 days to a week. At the beginning of menstruation, the discharge of blood is insignificant and intensifies on the 2nd day. It is accompanied by pain, which often radiates to the hip and lower back. Towards the end of menstruation, a dark-colored daub appears, which may remain present for some time.
Menstruation is accompanied by blood clots that have a brown tint. Painful sensations become less intense towards the end of menstruation.
Intermenstrual
Bloody discharge in the presence of endometriosis can occur on days 10-14 of the cycle. At first they may be pink, then they acquire a brown tint. Spotting may also appear after slight straining during bowel movements. Mucus and yellow discharge are more often present in the second phase of the cycle. As the disease progresses, they become purulent, which also indicates damage to the ovaries.
The presence of an inflammatory process is characterized by a white tint of vaginal discharge. Brown discharge often occurs immediately after sexual intercourse or a gynecological examination. This is associated with contact with the endometriotic lesion. There may be no pain in this case.
If the lesion grows into the thickness of the rectum, then spotting also occurs during the act of defecation, not only from the vagina, but also from the anus. Watery discharge may indicate the presence of bacterial flora, which often accompanies endometriosis.
What to do if there is heavy bleeding?
There are certain rules for combating open uterine bleeding with endometriosis. Before you begin to relieve hemorrhagic syndrome, it is necessary to assess its intensity and duration. The greatest danger with endometriosis is heavy and prolonged bleeding. In this case, it is important to understand what measures can be taken and which are strictly prohibited. If there is heavy bleeding due to endometriosis, you must remember the following:
1. Immediately seek qualified medical help.
2. You cannot take hemostatic drugs without consulting a specialist.
3. Avoid any warming procedures, visiting saunas and baths. This can provoke an increase in the intensity of blood loss.
4. Stop taking medications that can thin the blood, including acetylsalicylic acid.
5. Against the background of bleeding, it is prohibited to introduce any drugs into the vagina, as well as douching.
6. Rest, or better yet bed rest, is required.
7. Applying cold to the stomach is allowed.
When visiting a doctor, you should describe in detail all existing symptoms, paying special attention to the duration and intensity of bleeding. Hemorrhagic syndrome against the background of endometriosis may indicate the presence of concomitant pathological processes.
Side effects that occur when using Duphaston
Since Duphaston is a potent hormonal drug, its use sometimes causes a number of side effects in patients, such as:
If these symptoms occur, it is necessary to replace the drug used with a drug of similar effect. To choose a medicine that is right for you, you must visit a doctor.
Drug treatment
Based on the patient’s collected medical history, gynecological examination and examination data, the specialist makes a conclusion about the method of stopping the bleeding. Conservative methods of treating hemorrhagic syndrome due to endometriosis involve long-term use of hormonal drugs, as well as hemostatic pills for uterine bleeding. Such therapy is aimed at normalizing the functions of the ovaries, preventing the development of new pathological foci and bleeding.
If blood loss is heavy and prolonged, the woman is prescribed drugs from the hemostatic group. The most popular hemostatic drugs used in gynecological practice are “Diferelin” and “Vikasol” in tablets. The instructions for use are very detailed.
"Vikasol" effectively stops uterine bleeding and reduces the amount of discharge during menstruation. The drug is taken exclusively according to the indications of a doctor, who conducts diagnostics and takes into account the individual characteristics of the body. "Vikasol" is a publicly available drug that every woman can buy. It is available without a prescription and is sold at any pharmacy.
The instructions for use of Vikasol tablets must be strictly followed.
It is not recommended for use by women who have been diagnosed with increased blood clotting, thrombosis, thromboembolism and hypercoagulation. Side effects occur in patients who have kidney failure and menstruation problems. If a woman is breastfeeding during menstruation, it is necessary to consult with your doctor before taking it.
According to the instructions for use, Diferelin is used to treat severe pathological diseases of the reproductive system in both women and men, as well as for premature puberty in adolescents.
It is produced in the form of a so-called lyophilisate - a powder intended to create a solution.
For endometriosis, the drug is administered at a dose of 3.75 mg once every 4 weeks. The injection is carried out in the first 5 days of the menstrual cycle. The duration of treatment is no more than 6 months. The instructions for use for Diferelin confirm this.
Other effective drugs for stopping bleeding and reducing its intensity are Oxytocin, Secometrin, Panergal, etc. To strengthen the capillary walls and reduce the fragility of the veins, medications such as “Profilaktin S”, “Ascorutin”, etc. are prescribed.
Drugs to stop uterine bleeding with endometriosis should be selected by a doctor.
The basis of therapy is the use of hormonal drugs, the main of which are:
1. Combined-action drugs based on estrogen and gestagen.
2. Progestogens and progestogens.
4. GnRH agonists.
Hormonal drugs such as Diane-35 and Janine help normalize the menstrual cycle, as well as reduce the amount of bleeding. The duration of hormonal therapy is determined individually.
Progestogens such as Ingesta, Duphaston, Visanne, etc. help reduce estrogen levels, as well as the proliferation of endometrial cells, which helps reduce blood loss.
Antiprogestins, for example Danazol, stop blood loss. Such drugs are rarely prescribed, as they have many adverse reactions.
Agonists such as Zoladex and Buserelin are often used to control bleeding associated with endometriosis. Most women notice improvement after just a few months of using these medications.
It is important to find out in advance if you have this disease how to stop bleeding with endometriosis.
Symptoms of endometriosis
The main symptoms indicating the presence of endometriosis are the occurrence of dysmenorrhea of varying degrees, as well as spotting on different days of the menstrual cycle (long before or immediately after scheduled menstruation). In addition, characteristic signs of endometriosis are:
To treat mild forms of the disease, modern doctors actively use Duphaston, a drug that suppresses the effect of estrogens and has a beneficial effect on stabilizing the overall hormonal levels.
Cryodestruction
During cryodestruction, the affected areas are exposed to liquid nitrogen. The advantages of this procedure are the absence of pain and scars, the absence of blood during the procedure and the minimal likelihood of complications. Nevertheless, experts warn patients about the risk of damage to the uterine walls, as well as incomplete elimination of tissue affected by the disease.
Ablation involves removing overgrown cells using a minimally invasive method. Surgery cannot be performed if endometrial cancer or uterine tumor is detected. Resection is a last resort and is performed only if the patient is older than middle age and has already given birth to children.
During ablation through the cervical canal of the cervix, overgrown endometrial cells are removed using modern minimally invasive techniques. This procedure is prohibited if endometrial cancer or uterine cancer is detected.
Why does fibroid bleed?
Myoma (fibromyoma, leiomyoma) is a tumor consisting of smooth muscle and connective tissue cells. The formation grows in the thickness of the myometrium and can extend into the uterine cavity or beyond the genital organ. The location of fibroids directly affects the likelihood of bleeding. Mostly submucosal nodes located in the organ cavity bleed. Bleeding also occurs with interstitial formations located in the wall of the uterus. Subserous tumors almost never cause such complications.
Other factors that influence the likelihood of bleeding:
- Leiomyoma size. Tumors up to 2.5 cm in diameter are usually asymptomatic and do not cause bleeding. The exception is submucosal formations on the stalk, which give the clinic even in small sizes;
- Presence of concomitant pathology. When fibroids are combined with endometriosis, endometrial hyperplastic process or polyps, the risk of bleeding increases;
- General condition of the woman. Pathology of the blood coagulation system can cause bleeding.
With pathological uterine bleeding, a woman is forced to change pads almost hourly.
The immediate causes of increased bleeding with fibroids include the following conditions:
- An increase in the size of the uterus and the area of the endometrium - the inner layer that is shed monthly;
- Concomitant hyperplastic changes in the uterine mucosa;
- Impaired contractility of the muscle layer.
- Increase in the number of vessels (venous plexuses);
- Decreased tone and elasticity of blood vessels.
All these phenomena provoke changes in the structure of the organ and lead to disruption of its function with the development of uterine bleeding.
Traditional methods
In folk medicine, there are many effective recipes that help stop bleeding from endometriosis. Popular herbs in the treatment of endometriosis are red brush and other herbal preparations. For treatment, various medicinal plants that have a hemostatic effect are used:
- Viburnum bark. For treatment, a decoction is made from tree bark. It improves blood circulation, relieves pain symptoms and stops bleeding. To prepare the decoction, take 100 g of bark and pour two liters of boiling water, simmer in a water bath for half an hour, filter and drink half a glass in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Borovaya uterus. One of the most effective herbs for the treatment of gynecological pathologies. Restores the normal menstrual cycle, improves blood flow in the endometrium, reduces the risk of developing uterine cancer. To prepare the decoction, take 60 g of herb and pour a liter of boiling water. The broth simmers over low heat for about 10 minutes. Then strain and drink half a glass 2-3 times a day.
- Nettle. Helps quickly stop bleeding, strengthens blood vessels, increases blood clotting. Pour two tablespoons of dry herb into a liter of boiling water, leave for about 20 minutes and drink half a glass 3 times a day.
- Beet. When bleeding due to endometriosis, it is very helpful to regularly drink freshly squeezed beet juice. It helps to quickly restore the damaged endometrium, increases hemoglobin after heavy blood loss.
Treatment of bleeding with endometriosis is a long and complex process, so you need to be patient and follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Complex therapy eliminates clinical symptoms and preserves a woman’s reproductive functions.