When any pathological vaginal discharge appears, it is necessary to determine the reasons that caused the change in the nature of secretion. The development of the disease can be indicated by a change in color, the appearance of blood during the intermenstrual period, an increase in the volume of discharge, as well as additional symptoms - pain, cycle failure.
With any change in secretion, a diagnosis of women's health is necessary, since getting rid of secretions does not mean eliminating the main cause of their appearance.
Definition of the norm and deviations from it
The norm in gynecology is mucous discharge in women, which is a natural protection and lubricant for the vagina. They consist of lactobacilli, the main task of which is considered to be the destruction of infections coming from outside.
Abnormal leucorrhoea differs from normal discharge:
- unpleasant odor;
- yellow or green tint, inclusion of blood streaks;
- large volume.
Vaginal discharge is normal:
- are distinguished by a light cream, white or yellowish color, which varies depending on the period of the cycle;
- do not have a pungent or fetid odor, may be characterized by a slight lactic acid aroma or be completely without it;
- have a slightly viscous or liquid consistency;
- the amount of leucorrhoea per day should not exceed 1 teaspoon;
- The volume of mucus can normally increase after sex, before the onset of menstruation, and during pregnancy.
In the first period of the cycle and immediately after the end of menstruation, there should be a lot of leucorrhoea. They have a uniform consistency, may include small white flakes, the color varies from whitish to yellowish, and there is a sourish odor.
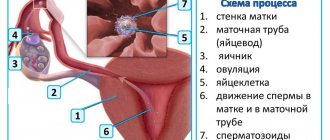
In the middle of the cycle at the time of ovulation, a slight inclusion of blood streaks or a change in shade to pink may be observed. This process reflects the maturation of the egg and is called ovulatory bleeding. The structure becomes more viscous.
Towards the end of the cycle, from the 16th day after menstruation, the volume of secretion decreases, and immediately before the onset of menstruation, thick brownish discharge with a mushy consistency appears.
Treatment of discharge in women is necessary only if it accompanies any disease - bacterial, infectious, sexually transmitted, as well as the development of erosion and polyps.
Cervicitis
Cervicitis is a disease characterized by inflammation of the cervix. This inflammatory process is characterized by gray cloudy discharge (possibly purulent), urination problems, pain in the lower abdomen, and painful sexual intercourse. Advanced cervicitis can lead to the development of cervical erosion. Occurs when opportunistic microflora enters the cervix: staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, fungi, trichomonas, chlamydia, gonococci, parasitic infections. Sexual transmission is also possible.
Cervicitis often develops together with other diseases of the genital organs, such as vaginitis, entropion, vulvitis, pseudo-erosion of the cervix, etc. It is quite rare in women during menopause; this disease is mainly typical for women of reproductive age. To diagnose cervicitis it is necessary:
- conducting a gynecological examination;
- laboratory examination of smear and bacterial culture;
- performing colcoscopy.
Treatment of cystitis depends on the causative agent of the disease. They mainly use antibacterial and antiviral agents, douching with a solution of dimethyl sulfoxide, chlorophyllipt, and silver nitrate. In some cases, it is necessary to use vitamins, immunostimulants, interferons, and cytostatics. The sexual partner should also undergo treatment. In complex stages of cervicitis, surgical intervention is used: cryotherapy, diathermocoagulation, laser therapy.
The main causes of pathological leucorrhoea
Before treating discharge, it is necessary to establish the cause of its occurrence. The main factors for changes in secretions in women are considered to be the development of polyps, fibroids, hyperplasia, hormonal imbalance, cancer, as well as various infectious pathologies of the reproductive or genitourinary systems.
In this case, the discharge becomes intensely colored, increases in volume, may have an unpleasant odor and cause burning and itching of the skin of the genital organs. In accordance with the symptoms, treatment should be aimed at eliminating the causative agent of the disease.
Bacterial vaginosis
Vaginal dysbiosis leads to the appearance of leucorrhoea, which causes discomfort, causes burning and itching, and has an unpleasant odor reminiscent of rotten fish.
Pathology occurs with a sharp decrease in immune strength, against the background of an inflammatory disease, hormonal imbalance, with improper or too long-term use of IUDs and antibacterial drugs.
The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- intense unpleasant odor in women;
- the appearance of spotting or copious white or yellow discharge;
- discomfort during examination or sexual intercourse, burning, itching.
The pathology is often asymptomatic, the only manifestation being an increase in the volume of secretion and the appearance of an unpleasant odor. The disease does not pose a threat to a woman’s health, but during pregnancy it can cause spontaneous miscarriages, infection of the fetus or membranes, and premature birth.
Treatment consists of normalizing the ratio of lactobacilli in the vagina and restoring acidity. Systemic or local antibiotic therapy, drugs with an anaerobic effect, and immunomodulators are also prescribed.
Candidiasis
Thrush is one of the most common and most unpleasant diseases in women. This pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
- copious discharge with a smell and the inclusion of curdled flakes;
- severe itching, burning, feeling of fullness;
- pain when going to the toilet;
- swelling of tissues.
The cause of the pathology is infection with the fungus Candida albicans, which normally forms part of the vaginal microflora, but with changes in health status, decreased immunity, taking antibacterial drugs and against the background of other factors, shows intensive growth.
The presence of Candida fungi in itself does not lead to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. Thrush develops against the background of their intensive growth. Primary candida constitutes the intestinal microflora; secondary dysbiosis of the vagina, oral cavity and other areas can develop.
It is necessary to treat white discharge in women with candidiasis with antifungal agents - tablets, suppositories for thrush. For men, antimycotics are available in the form of tablets, creams, and ointments, mainly based on clotrimazole.
How can you change the color of your labia?
Creams, gels, and solutions are produced to whiten the skin of the genitals. There are also special laser procedures. However, they are effective only for the labia majora, which are covered with skin. An attempt to whiten the labia minora using chemicals can cause severe inflammation, accompanied by pain, swelling, redness, and the appearance of ulcers on the mucous membrane.
The darker edges of the labia minora can be removed using labiaplasty. In this case, the genitals will not only look lighter, but will also become more neat. This is precisely the intimate zone of the beauties who pose in erotic photographs and serve as a guide for me only for men, but also for women. Modern medicine makes it possible to resemble them not only in color, but also in the shape of the intimate area.
Share link:
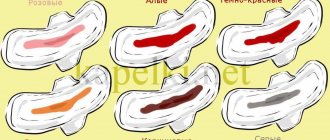
Types of discharge: what are they?
Almost all diseases of the female sphere are accompanied by changes in the structure and color of leucorrhoea. As pathology develops, you can almost immediately notice the appearance of an unpleasant odor or a change in the color of the discharge.
Bloody, bloody and brown discharge streaked with blood
Secretion of a brownish tint indicates that drops of blood enter normal physiological leucorrhoea. They come out of damaged vessels, which can be observed for several reasons.
Normally, the appearance of blood streaks or a change in color to reddish can occur in the following cases:
- Implantation bleeding. Indicates the readiness of the egg to be fertilized; it occurs in approximately 30% of women of reproductive age.
- Premenopause With the onset of menopause, more often in the first phase, which lasts about a year, periodic intermenstrual discharge of mucus with blood streaks may be observed. This condition indicates a decline in reproductive capabilities and a change in the hormonal balance in the body.
- Before menstruation and a few more days after its end, the inclusion of blood in normal secretions is also considered normal.
Brownish leucorrhoea, which occurs for a number of reasons, is considered a deviation from the norm:
- Pathology of pregnancy. Brown secretion may indicate placental abruption, incipient spontaneous abortion or abnormal fetal development, as well as ectopic pregnancy.
- Mechanical impact. After an examination by a gynecologist, sexual intercourse, douching or using tampons, leucorrhoea with drops of blood or streaks may occur. The causes may be erosion, polyps, fibroids.
- Hormonal disbalance. Occurs with improper use of contraceptives or long-term treatment with hormonal drugs. As a result, a brown secretion appears.
- Stress and physical activity, climate change, colds and infectious diseases. Against the background of a general weakening of the body, long-term treatment, diet or poor poor nutrition, the nature of secretion also changes.
Such discharge poses the greatest danger during pregnancy, especially at the beginning of the first trimester. It is necessary to establish the exact cause, which potentially threatens the development and even the life of the fetus, since getting rid of brown discharge with the help of drugs is not enough.
Yellow and green discharge
Bacteria give the greenish, beige or yellow tint to the secretion. Main diseases:
- trichomoniasis;
- bacterial vaginosis;
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea;
- gardnerellosis;
- nonspecific bacterial inflammation.
The hue of ordinary physiological leucorrhoea is given by a large number of white blood cells. In medicine, discharge with this tint is called leukorrhea. They occur when bacterial residues enter the secretion from the vaginal mucosa.
Often the greenish secretion has an unpleasant odor and causes discomfort and burning of the external genitalia. During pregnancy, if there is no odor, it may be normal and indicate fluctuations in hormonal status.
Such discharge characterizes acute inflammatory processes, for example adnexitis, salpingoophoritis.
Purulent
When purulent leucorrhoea appears, the following are often diagnosed:
- vaginitis;
- trichomoniasis;
- inflammation of the cervix and fallopian tubes.
An inflammatory focus on the vaginal epithelium (vaginitis) or the mucous membrane of the external genitalia (vulvovaginitis) occurs due to infection. They are not an independent disease, but accompany more serious pathologies - trichomoniasis, gonorrhea.
In addition to the appearance of purulent, unpleasant-smelling discharge, pain occurs during urination, sexual intercourse, itching and burning, and the volume of leucorrhoea increases.
Damage to the tubes, cervix and ovaries is also accompanied by purulent secretion and nagging pain, cycle disruption and signs of general intoxication.
White discharge
When cheesy discharge appears, suspicion falls on candidiasis, but there are other reasons for such secretion:
- symptoms of premenopause;
- some days of the cycle;
- climate change;
- starting to take oral contraceptives;
- excessive passion for gels, suppositories and creams;
- pregnancy, lactation;
- weight fluctuations;
- taking hormonal medications;
- insertion or misuse of an IUD.
Copious white discharge may appear as an allergic response of the body.
White secretion indicates an imbalance of microflora, which can also be observed with excessive washing and douching.
Copious white discharge can appear against the background of cervicitis, endometritis, adnexitis, aerobic vaginitis, erosion, and inflammation of the fallopian tubes.
You can get rid of white discharge by identifying the cause of its appearance. Depending on the diagnostic results, antifungal, antibacterial or anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
What is pathology?
In the case when gray vaginal discharge is accompanied by an unpleasant odor, this indicates a pathological process. In particular, the appearance of an extraneous “aroma” is characteristic of bacterial infections such as vaginosis and candidiasis.
During vaginosis, a white-grayish secretion with a stale fishy odor is present in the genitals. This type of disease is not sexually transmitted; bacteria that infect the genital tract are opportunistic microorganisms.
Candidiasis involves the appearance of white cheesy discharge with a characteristic sour odor. It is caused by a fungus called candida, which lives in the human body. Under the influence of certain factors (stress, colds, change of environment), the fungus begins to multiply intensively, as a result of which the vaginal environment is disrupted.
Vaginosis and candidiasis begin with the appearance of the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- temperature increase;
- general deterioration of health;
- loss of appetite;
- vaginal dryness;
- sudden weight loss;
- secretion of a dark gray secretion during gestation;
- discomfort in the reproductive system (dryness, itching);
- a feeling of pain when emptying the bladder with little urine output;
- abundant white curdled secretion.
If the above symptoms are not treated, the diseases become chronic, and getting rid of them will no longer be so easy. In the early stages of development, the disease is treated quickly and successfully.
Diagnosis and drug treatment
Before treating discharge in women, a diagnosis is carried out:
- examination by a gynecologist;
- smear;
- blood and urine tests;
- PCR analysis;
- Ultrasound (abdominal and/or transvaginal).
After testing, treatment of discharge with medications is used if the cause of changes in secretion is bacterial or inflammatory processes. For most sexually transmitted infections, antibiotics are used in the form of tablets, intravenous solutions, or suppositories.
If the secretion has changed during pregnancy, other medications are used - hemostatics, vitamin complexes, as well as drugs aimed at preserving the fetus.
Duplication of the uterus and vagina in incomplete form
A fairly common malformation of the uterus is its duplication with incomplete vaginal duplication. The second vagina is isolated from the external environment and its blood circulation has inferior functionality, as a result of which an inflammatory process develops in the double organ . Purulent discharge accumulates in the organ cavity, which after some time breaks into the normally formed vagina through the fistulous tract.
This pathology must be treated without fail. The treatment method for this pathology is surgical. The surgeon removes the paired organ that has festered without damaging the reproductive function.
Treatment at home
You can use folk remedies only after agreeing on treatment tactics with your doctor. The following methods are used:
- washing with Furacilin, chamomile infusion, soda solution;
- the use of decoctions of oak bark, eucalyptus, St. John's wort, meadowsweet, plum roots, and calendula. You can douche with them at home;
- use of immunomodulators, vitamin complexes. Helps strengthen the body's defenses;
- normalization of nutrition and lifestyle.
The advantages of traditional methods of treatment are that they can be combined with taking medications prescribed by a doctor. For example, a douching solution can be used in the morning after using medicinal suppositories at night.
It is also necessary to carry out preventive measures - use baby or other neutral soap or special intimate hygiene products for washing.