Indications for the procedure
Thanks to puncture, excess fluid is removed from the peritoneum, which facilitates further diagnosis. After the procedure, it is easier for the doctor to feel the internal organs and detect pathological neoplasms. But this does not make a puncture through the posterior vaginal fornix or abdomen a safe intervention, since intestinal loops can be damaged. Among the indications for puncture are:
- presence of internal bleeding;
- perforation of a stomach ulcer;
- suspicion of perforation of the intestinal walls;
- closed abdominal injuries;
- accumulation of fluid inside the cavity due to diseases of the liver, heart - ascites;
- injury due to puncture by knife or firearm;
- suspicion of the development of pancreatitis;
- symptoms of ectopic pregnancy;
- suspicion of the development of purulent processes;
- combination of open and closed abdominal injuries.
There are diseases and clinical cases in which puncture is not prescribed.
What can a puncture show?
This manipulation is carried out to determine the composition of the biological fluid in the pelvis in order to establish a diagnosis of certain surgical and gynecological diseases. Puncture for ectopic pregnancy is one of the main diagnostic procedures. Also, puncture is often used for therapeutic purposes, that is, for introducing medications into the rectal-uterine space.
Indications for puncture are many gynecological pathologies:
- uterine hemorrhages of unknown etiology;
- female factor infertility;
- diagnosis of hyperplastic processes in the endometrium;
- diagnosis of benign neoplasms;
- cycle disorders;
- taking tissue to monitor the effectiveness of hormone therapy;
- exclusion of oncological formations;
- in rare cases, to diagnose abnormalities in the structure of the uterus.
If performed correctly, the puncture is not accompanied by complications. Sometimes a violation of the surgical technique leads to minor injuries to the intestines or uterus, but these injuries do not require treatment and go away on their own.
Contraindications for puncture
It is impossible to pump out excess fluid from the abdominal cavity:
- in the presence of adhesions;
- with severe bloating;
- if there is suspected injury to the peritoneal walls;
- in the presence of a ventral hernia, which often forms as a result of surgical interventions;
- during pregnancy;
- against the background of inflammatory and purulent processes in the body;
- with low blood clotting;
- with tumor formations and hemorrhagic diathesis.
Repeated indications for laparocentesis may be considered once the condition that has limited physicians' options has been resolved.
Ignoring serious contraindications and interfering with the patient’s body can cause a deterioration in his well-being, as well as dangerous conditions: intestinal puncture, infection.
Features of preparation for surgery
Since puncture of the peritoneum is, first of all, an operation, it can only be performed after special preparation. The patient must pass general laboratory tests, undergo a coagulogram and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, and also take an x-ray.
In some cases, during the examination and removal of excess fluid, doctors immediately move on to laparoscopic procedures, which allow solving a particular problem when identifying surgical pathologies. If laparoscopy is possible, the patient needs to undergo blood clotting tests. Right before the procedure:
- you need to empty the intestines and bladder - the second is cleaned using a catheter, if the person cannot do this on their own, and the gastric contents are removed using a probe;
- sometimes patients are prescribed an enema 2-3 hours before surgery;
- In case of shock, doctors connect the patient to a ventilator.
A puncture through the posterior vaginal fornix is most often performed under local anesthesia. Often the fluid obtained through a puncture in this area consists not only of exudate, but also blood and pus.
Method of manipulation during surgery
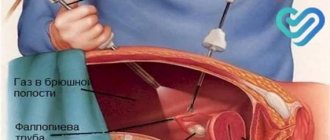
Without grasping with forceps, the cervix is exposed and retracted with a lift to the pubic symphysis.
This allows the back of the vaginal vault to stretch between the speculum and the lift. Before the puncture, the puncture site is numbed with lidocaine solution. Some time after the anesthesia has taken effect, a long injection needle, with a light but decisive push, strictly along the midline, pierces the back of the vaginal vault and sucks out the liquid present in the rectal uterine cavity. The needle is inserted to a depth of up to two centimeters.
During the puncture, the needle should be directed horizontally or slightly upward so as not to damage the rectum. The reverse movement of the piston, simultaneously with the slow withdrawal of the needle, removes the liquid, then conducts its bacteriological and cytological examination.
To confirm the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy
defibrinated blood is sucked out. But this does not always work out, since this blood quickly clots and the needle is thrombosed by a blood clot. This clot is pushed out with a syringe onto a gauze pad and tested in the same way as with blood, since this is enough to confirm an ectopic pregnancy. If the blood that gets into the syringe is thick and dark with clots, this is also an indicator of an ectopic pregnancy.
Blood is also detected when the spleen ruptures, ovarian apoplexy, and also after curettage of the uterus.
Puncture of the posterior vaginal vault is also used if an abscess of the uterine appendages is suspected. In this case, when the pus is sucked out, antibiotics are injected into the cavity of the purulent tumor.
Procedure technology
The technique of puncture of the abdominal cavity through the posterior vaginal fornix includes the following manipulations:
- The doctor thoroughly disinfects the external genitalia.
- Using a speculum and a dilating instrument, the area is expanded to the cervix.
- Using gynecological forceps, bends the posterior lip of the uterus.
- A puncture is made in the place where the peritoneum passes close to the walls of the vagina. This area is located below the cervix in the area of the divergent uterosacral ligaments.
- The puncture needle - long and relatively thin - enters strictly between the ligaments, deepens it by 2 cm.
- After reaching the required depth, the doctor removes biological material.
Just by the appearance of the fluid, the gynecologist can make an assumption about what process is developing inside the abdominal cavity. If the fluid is dark in color, this may indicate a termination of an ectopic pregnancy.
Strict adherence to the technique of performing the procedure is the key to a successful operation. To avoid complications, the patient should not only take care of her well-being and rehabilitation, but also initially choose a good clinic with responsible doctors.
Purpose of puncture
This procedure is carried out to determine the structure and composition of the existing fluid in the pelvis, to diagnose certain gynecological diseases, such as: rupture of an ovarian cyst, uterine rupture, ovarian apoplexy, tumors of the uterus and ovaries, inflammatory diseases. This procedure is also irreplaceable if you suspect an ectopic pregnancy. Puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix
can be used for medicinal purposes, namely for the administration of drugs into the pelvic organs.
Preparing for surgery
As with any other gynecological procedure, a woman needs to prepare. This will reduce the risk of various complications, as well as significantly shorten the recovery process. Recommendations before puncture of the posterior vaginal vault will be as follows:
2-3 days before the puncture, it is forbidden to be sexually active;
Refuse to use vaginal ointments and sprays, as well as hygiene products for intimate hygiene;It is necessary to shave hair from the pubis and genitals;
Avoid eating and drinking 10 hours before the procedure;
Before the puncture, the woman must empty her bladder and rectum.
Carrying out the procedure
After the necessary preparation, the woman comes to the hospital. The patient undresses, puts on sterile clothing and sits in the gynecological chair. The cervix and external genitalia are treated with antiseptic agents. The required dose of anesthesia is administered and after the woman falls asleep, the puncture begins. Speculums are inserted into the vagina to expose the vagina and cervix. Next, by retracting the posterior lip of the uterus, the doctor opens the posterior vaginal fornix. Using a needle and syringe, the doctor pierces the posterior fornix and collects the fluid present in it by suction. An experienced doctor will insert the needle slowly to avoid puncturing nearby internal organs. After collecting the required amount of fluid, the doctor carefully removes the needle from the vagina and treats it and the external genital organs with antiseptic agents.
The resulting material is placed in a special container, on which detailed information about the patient will be written, and sent for histological analysis. Having obtained material from the posterior vaginal fornix, the doctor can visually assess the structure of the fluid. If, during a puncture, blood is detected in the syringe, this indicates a serious pathological development. In this case, a decision may be made to undergo urgent surgery. Our medical center specializes in pathological diseases of the female pelvic organs. Qualified doctors will conduct high-quality diagnostics and prescribe a further treatment plan. If necessary, our specialists will perform a puncture of the posterior vaginal vault. Having our own laboratory, the test results will be ready in the shortest possible time, and the most correct and effective treatment will be selected.
Vaginal puncture, or culdocentesis, is performed to diagnose various pathological conditions. At its core, this is a minimally invasive examination technique that uses a special needle. Vaginal puncture allows you to accurately diagnose:
ectopic pregnancy;
Ovarian apoplexy;Uterine rupture;
Peritonitis;
Malignant neoplasms;
Inflammation of the pelvic organs.
Rehabilitation period
Puncture of the abdominal cavity through the posterior vaginal fornix is normally tolerated by women, but discomfort may persist for several days after it is performed. At the same time, trauma remains minimal.
Bed rest is prescribed only in cases where it is required by the treatment of the underlying disease. The patient for several weeks or months - according to the doctor's indications - must follow a salt-free diet with minimal fluid intake. This speeds up recovery and prevents excess water from accumulating again.
Most women who have undergone laparocentesis can drink up to 1 liter of water per day. The diet should contain lean proteins in the form of white meat, eggs, and dairy products. Fatty, spicy and pickled foods should be limited, as well as refined sweets.
During the course of treatment after puncture, you should avoid physical activity. If a catheter is installed, the position of the body must be changed every 2 hours so that the fluid comes out better.
Possible complications
After laparocentesis, complications occur only in 10% of cases and less often. They are due to the fact that the doctor does not disinfect the puncture area well. As a result, infection occurs. Another common complication that occurs during the procedure is bleeding, which causes low blood pressure and fainting. Other complications are very rare:
- If a malignant tumor was not detected and a puncture was performed, rapid metastasis may begin.
- The doctor can cut the vessels, which will lead to hematomas, external and internal bleeding.
- A loop of intestine is punctured, which causes peritonitis due to the release of feces into the peritoneum.
- If the procedure is performed with intense ascites, prolonged, almost uncontrollable fluid secretion may begin.
Modern equipment and medical experience have made it possible to reduce the manifestation of dangerous consequences to isolated, very rare cases. Laparocentesis is an almost 100% safe procedure.
The puncture necessary to obtain and analyze fluid from the abdominal cavity is performed only by specialists. A correctly performed mini-operation will protect the patient from complications. However, a woman must remember that after the procedure she must adhere to certain rules so that the puncture heals quickly and does not fester.
Vacuum aspiration tip
The vacuum aspiration handpiece (Uterine handpiece) consists of an aspiration tube, a restrictor and an aspirate removal tube connected in series.
Vacuum aspiration is a simple and effective method of obtaining the contents of the uterine cavity using a special apparatus consisting of a set of aspiration tips and a vacuum pump that creates negative pressure in the uterine cavity, allowing its contents to be aspirated.
Manufacturer: Russia
| vendor code | Name | Price |
| NV-1 | Vacuum aspiration tip No. 6 straight, 236 mm | RUB 1,328.00 |
| NV-2 | Vacuum aspiration tip No. 7 straight, 236 mm | |
| NV-3 | Vacuum aspiration tip No. 8 straight, 236 mm | RUB 1,358.00 |
| NV-4 | Vacuum aspiration tip No. 6 curved, 236 mm | RUB 1,328.00 |
| NV-5 | Vacuum aspiration tip No. 7 curved, 236 mm | |
| NV-6 | Vacuum aspiration tip No. 8 curved, 236 mm | RUB 1,518.00 |
| NV-7 | Vacuum aspiration tip No. 9 curved, 236 mm | |
| NV-11 | Vacuum aspiration tip No. 9 straight, 236 mm | |
| NV-8 | Vacuum aspiration tip No. 10 curved, 236 mm | |
| NV-9 | Vacuum aspiration tip No. 11 curved, 236 mm |
DETAILS: Peony tincture: harm and benefits, properties, reviews. The use of peony tincture in gynecology