The intrauterine device is one of the most common means of protection against unwanted pregnancy. The popularity of the contraceptive is due to its high efficiency, ease of use and long service life. Doctors recommend installing the IUD for no more than 5 years. Modern models can be worn for up to 8 years. But in any case, you should regularly undergo examination by a gynecologist to monitor the position of the spiral.
Penetration of the contraceptive into the muscle wall is one of the possible complications. If you use the IUD longer than expected, it will grow into the uterus. The situation may arise if the IUD installation technique is violated. In such cases, it is necessary to remove the ingrown helix.
You can understand that the spiral has grown into the muscle wall by the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen,
- pallor of the skin,
- frequent dizziness,
- heart rhythm disturbance,
- internal bleeding,
- increased weakness,
- deterioration of general condition.
PROCEDURE FOR REMOVAL OF THE INTRAUTERINE DEVICE
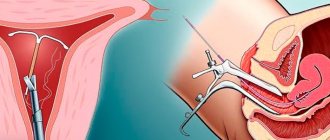
- This manipulation, which takes only a few minutes, is performed on an outpatient basis. In most cases, IUD removal occurs without anesthesia, but if necessary, the doctor can use an anesthetic to relieve discomfort.
- To gain access to the cervix, the doctor inserts a dilator into the vagina - this manipulation allows you to find the “antennae” (threads) of the IUD. After this, the patient takes a slow, deep breath and relaxes, and the doctor, using forceps or other instruments, grabs the threads and carefully pulls out the spiral. If necessary, a new one is installed in place of the old contraceptive
- If difficulties arise during the removal of the IUD, a hysteroscope can be used - a thin, long tube with a built-in camera and medical instruments. This instrument, which is inserted into the vagina and uterus, allows you to quickly locate and remove the intrauterine device.
The effectiveness of this contraceptive depends on the type of IUD, as well as the correct installation.
The average duration of the contraceptive function of the IUD lasts 5 years. There are modern types of IUDs that effectively prevent conception for 10 and even 15 years. The spiral is removed after its expiration date or at any time at the woman’s request. The removal procedure is carried out during menstruation and consists of the following steps:
- the woman sits on the gynecological chair;
- all natural secretions are removed from the vagina;
- After the examination, the doctor removes the contraceptive by simply pulling the special antennae.
After removal of the IUD, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs is required.
If the patient did not have any inflammatory diseases while wearing the intrauterine contraceptive, then its removal is completely painless. To avoid possible pain, it is recommended to perform the procedure using anesthesia.
If the spiral cannot be removed in the usual way, because some of its parts have grown into the wall of the uterus (this, alas, sometimes happens), it is removed using a diagnostic curettage procedure. At ON CLINIC, such manipulation, due to its increased traumatic nature, is necessarily performed under the visual control of a hysteroscope. This approach allows the operation to be performed as carefully as possible and to avoid possible complications.
The main indications are:
- expiration date;
- bias;
- severe side effects (severe pain in the lower abdomen, uterine bleeding);
- infectious and inflammatory processes of the uterus and appendages;
- pregnancy;
- growing fibroids;
- pregnancy planning.
Under no circumstances try to remove the intrauterine contraceptive device yourself!
The choice of method for removing a spiral that has grown into the wall of the uterus depends on the location of the foreign object. It is quite dangerous if the spiral grows close to vital organs or blood vessels. For example, near the ureter or bladder, the removal process will not be an easy process and quite dangerous. This is due to the fact that the organ can be damaged. The fact that there is a clear need for surgical intervention by surgeons is undeniable.
In order to perform the operation efficiently, special laparoscopic forceps are used. This device is the only surgical option in this case. If it is observed using ultrasound that most of the IUD is located in the thickness of the uterus, then it’s time to think about removing it. Laparotomy will help in eliminating the IUD. If the spiral is not deeply embedded in the organ, then hysteroscopic forceps are used.
Advantages of using forceps:
- Tissues are little damaged;
- Bleeding is not as profuse as during surgery.
Doctors advise women to install an IUD for a period of no more than 5 years. With modern spirals you can walk for up to 8 or even 15 years. To prevent complications, it is necessary to periodically visit a gynecologist to monitor the position of the spiral.
The indication for removal is the end of the contraceptive's useful life. There are several types of IUDs: copper (duration of use from 3 to 5 years), silver with hormones (suitable for 5 to 7 years), gold (worn for 10 to 15 years in the absence of contraindications).
Other indications for removal: the onset of menopause (a year after the last menstruation, the device is removed from the internal organ due to uselessness), pregnancy (while using a contraceptive in women, in rare cases, ectopic conception of the baby may occur), displacement of the device or its partial loss (removed old and a new one is installed).
The IUD is also removed at the request of the patient if she wants to conceive a child or this method of contraception is not suitable for her. Medical indications for removing the IUD: pain in the lower abdomen, bleeding, the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the uterine cavity and ovaries, the development or growth of tumors and neoplasms.
Contraceptive penetration (ingrowth of the IUD into the muscular wall of the uterus) is a complication that is an indication for removing the IUD. When an IUD is used longer than necessary, it begins to grow into the organ tissue. This can also occur due to improper installation of the contraceptive.
Symptoms indicating the ingrowth of a spiral: deterioration in a woman’s well-being, constant fatigue, internal bleeding, heart rhythm disturbances, dizziness and fainting, pale skin, pain in the lower abdomen.
The operation is most often performed during menstruation, since during this period the external os of the cervix of the internal organ is slightly open and removal of the IUD will be more painless and gentle. The most favorable days for the procedure are the first or last day of menstruation, when there is a minimal amount of bleeding.
If the patient is bothered by discomfort or discomfort due to the contraceptive, it can be removed any day. Some experts recommend removing the IUD on days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle.
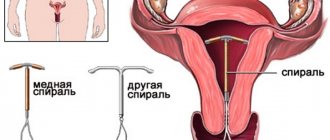
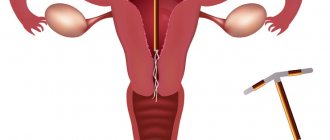
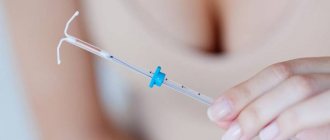
The IUD is a reliable means of contraception. It looks like a T-shaped tube with strings (antennae) at one end. It is placed in the uterine cavity so that the strings remain in the vagina for easy removal. The installation procedure is performed by a gynecologist. The most commonly used devices are made of plastic with the addition of metals (copper, silver). An IUD in the uterine cavity prevents the egg from implanting and developing.
There are hormonal intrauterine devices. Their action is aimed at preventing the onset of unplanned pregnancy and regulating the menstrual cycle. In addition, when using hormonal IUDs, pain during menstruation and the volume of discharge are reduced. Hormones change the fluid in the cervical canal, making it thicker.
Methods for removing an ingrown helix
Using hyteroscopy, a gynecologist can see the overall picture of the patient’s condition. The diagnostic method is the most reliable. Further treatment tactics depend on how deeply the contraceptive is immersed in the wall of the uterus and the location of its location. Women wonder when removing an IUD: what to do when the IUD has grown into the uterus?
The choice of method for removing a spiral that has grown into the wall of the uterus depends on the location of the foreign object. It is quite dangerous if the spiral grows close to vital organs or blood vessels. For example, near the ureter or bladder, the removal process will not be an easy process and quite dangerous. This is due to the fact that the organ can be damaged. The fact that there is a clear need for surgical intervention by surgeons is undeniable.
In order to perform the operation efficiently, special laparoscopic forceps are used. This device is the only surgical option in this case. If it is observed using ultrasound that most of the IUD is located in the thickness of the uterus, then it’s time to think about removing it. Laparotomy will help in eliminating the IUD. If the spiral is not deeply embedded in the organ, then hysteroscopic forceps are used.
Advantages of using forceps:
- Tissues are little damaged;
- Bleeding is not as profuse as during surgery.
This is a special device that will allow you to get rid of a foreign object without using laparotomy.
WHEN SHOULD IT BE REMOVED?
Removal of the intrauterine device is carried out in the following cases:
- displacement or expulsion (spontaneous prolapse) of the IUD. If after replacing the contraceptive the problem recurs, then the woman should think about changing the method of protection against pregnancy
- the end of the IUD service life specified by the manufacturer. Most often, spirals are designed for 3-5 (rarely 10) years. If the annotation of the intrauterine device does not indicate the period of use, then by default it is equal to 5 years
- pregnancy. The effectiveness of the IUD is 98%, however, unfortunately, in very rare cases, pregnancy can occur (including ectopic)
- woman's desire to have a child
- development of uterine fibroids. A small fibroid, which is not accompanied by deformation of the uterus, does not prevent the installation of an IUD (it is advisable to opt for a product with a gestagen). If, after the introduction of a contraceptive, the fibroid begins to grow or a new one appears, then the product must be removed immediately
- the occurrence of diseases of the pelvic organs. In this case, removal of the IUD is accompanied by antibacterial therapy
Diagnostics
The diagnosis can be made after a hysteroscopy has been performed. After this procedure, specialists determine the condition of the spiral and determine the severity of the problem.
The intervention of microsurgery will allow you to choose the right tactics for eliminating the IUD and performing the operation as a whole. The risk is borne by the operation that is associated with touching internal organs. If the coil grows into the vessels, this can lead to major bleeding during the operation.
Contraindications:
- Infectious diseases and inflammatory processes;
- Bleeding due to problems with the uterus;
- Uterine cancer;
- Liver or kidney failure;
- Cervical stenosis;
- Vascular diseases;
- Heart problems.
Popular articles
- When can you do an ultrasound to determine pregnancy?
- How much does an ultrasound cost in Astana?
- Treatment of complications of STIs
- Treatment of complications of STIs in women
A specialist can diagnose an ingrown helix after performing a hysteroscopy. The study helps determine the condition of the contraceptive and the degree of its growth into the walls of the uterus. Microsurgical intervention allows you to choose the tactics for removing the IUD and determine its location. If the spiral is located near other internal organs and large vessels, surgical intervention will be risky. The patient is warned about all possible risks before the procedure.
Contraindications to hysteroscopy include: inflammatory and infectious diseases of the genitourinary system, uterine bleeding, pregnancy, cervical cancer or stenosis, vascular and heart diseases, renal and liver failure.
Main indications
Symptoms indicating the ingrowth of the spiral and are indications for its removal:
- severe bleeding;
- pallor;
- blood pressure problems;
- tachycardia;
- severe malaise;
- pain of various types in the lower abdomen.
But strongly expressed signs rarely appear, and it is not recommended to let things happen until they occur.
There are no special contraindications to the procedure - when the first symptoms appear, it is necessary to urgently remove it. If you have severe pain, your doctor may prescribe painkillers.
Features of removing an ingrown helix
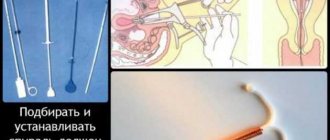
You cannot remove the IUD yourself; to do this, you should contact a qualified gynecologist. Before the procedure, the specialist will examine the patient in a gynecological chair and refer her for tests. Laboratory tests that a woman must undergo before manipulation:
- Analysis of urine;
- blood analysis;
- microflora smear;
- bacterial culture.
An ultrasound examination of the uterus and colposcopy should also be performed. After the doctor is confident that the IUD has grown into the patient’s organ, the doctor sets the time and day of the operation.
Extraction is carried out in stages using local anesthesia. Intimate organs are sanitized: the woman’s genitals are treated with antiseptic medications. Dilators are installed in the cervix to facilitate access to the uterine cavity. Next, a hysteroscope is inserted through the cervix, with which the gynecologist can examine the muscle walls in detail.
After the specialist detects the IUD, it is removed with sterile forceps or a curette. In cases where most of the contraceptive grows into the abdominal cavity, laparoscopy is prescribed.
If the coil is located near the bladder, urinary tract and large vessels, laparotomy is indicated. At the end of the procedure, the doctor scrapes out the overgrown mucous layer. The duration of the operation varies from 15 to 30 minutes.
If an ingrown intrauterine contraceptive cannot be pulled out through the cervical canal (due to occlusion or atresia), then a specialist removes it through the abdominal cavity. In this case, extraction occurs using laparoscopic methods under general anesthesia. After surgery, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and the doctor gives a referral for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
Indications for removal of the intrauterine device
There are a number of symptoms that may occur in women who have inserted the IUD. Thanks to them, even before examination using an ultrasound or gynecological examination, it is possible to determine that the spiral has grown into the wall of the uterus. These may be the following indications:
- pain of varying strength in the lower abdomen, lumbar region, pelvis and bladder;
- severe weakness;
- pallor;
- tachycardia;
- bleeding.
Serious signs such as bleeding and severe pain are extremely rare in women. Therefore, to prevent these symptoms, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist in time.
Procedure for removing an ingrown IUD
How the operation to remove an ingrown IUD into the wall of the uterus will be performed largely depends on its location. If the contraceptive is located close enough to internal organs or the walls of large vessels, then removal will be quite difficult and time-consuming.
The operation takes place in several stages:
- A hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity.
- Using laparoscopic forceps, the doctor removes the spiral, making his way to it from the abdominal cavity.
- If most of the spiral is located in the thickness of the walls of the uterus, then the doctor is forced to perform a laparotomy.
- Hysteroscopic forceps can be used to remove an ingrown intrauterine device if only a small part of it has entered the uterus.
Rehabilitation period
There is no need to follow any special regimen after the procedure to remove a contraceptive that has grown into the uterus. A few hours after the operation, the patient can go home. She must comply with the following recommendations:
- carefully monitor personal hygiene;
- limit physical activity.
About complications of an ingrown IUD
Removing an IUD is a routine, simple procedure that in the vast majority of cases does not cause any complications. However, there are cases when, after examining the vagina, the gynecologist does not detect the spiral thread. This is often caused by a thread that is too short being pulled into the cervical canal.
It is very rare for an IUD thread to enter the uterus directly. In this situation, a sonogram or ultrasound is used to confirm the presence of the spiral in the uterus. If the contraceptive is still in the uterus, and the end of the thread is still not detected, the intrauterine device is removed directly from the uterus using special instruments
An even rarer case is the impossibility of removing the IUD due to the tight attachment of its ends to the walls of the uterus. To confirm this situation, special studies are carried out - hysteroscopy, hysterography or ultrasound. When removing the intrauterine device in this case, the doctor pushes the walls of the cervix apart with a special device and removes the contraceptive with surgical forceps. Often this intervention is performed under local anesthesia.
Most patients do not experience any consequences after removing the IUD. This is a common, frequently performed procedure in gynecology, so if the technique is followed and there are no complications, it is quick and painless.
Normally, after the procedure, a small amount of blood is released from the vagina, the lower abdomen may hurt, and sometimes spastic contractions of the smooth muscles of the uterus are felt. These symptoms disappear after two or three days and do not require seeking medical help.
After removing the IUD, women notice disruptions in their menstrual cycle. Usually after a few months everything returns to normal. How quickly this happens depends on the patient’s health and age, the presence of concomitant pathologies, and the type of spiral.
The nature of menstrual flow also changes. As a rule, after installing the device, periods become abundant. After the procedure for removing the intrauterine contraceptive device, the volume of discharge decreases, this is normal. The IUD inhibits the endometrium and the functioning of the ovaries; they need time to recover and begin to function fully.
An increase in the amount of blood during menstruation after removal of the IUD is uncharacteristic and indicates a pathological process (damage to the uterine walls or inflammation of the endometrium).
If the cycle does not return within three or four months, this indicates a hormonal imbalance. It is recommended to undergo an examination of the reproductive organs or endocrine glands.
You should not delay removing the IUD longer than the time specified by the gynecologist during installation. If pregnancy is still undesirable and there are no contraindications, then removal of the IUD is combined with the installation of a new intrauterine contraceptive device. Both manipulations can be done at once, visiting the doctor just once.
IUD removal is done in all gynecological clinics, the cost of the procedure is 1400-2500 rubles.
The IUD is a long-term contraceptive. For several years, a woman does not think about pregnancy and gets used to a foreign object in the uterine cavity. Some representatives of the fair sex forget about the wearing period and do not remove the spiral on time. This may lead to:
- ingrowth of the spiral into the uterus;
- inflammatory processes;
- contracting an infection;
- infertility.
The most common complications of an ingrown IUD are: inflammation, bleeding, chronic endometritis. Normal and acceptable symptoms after surgery are:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- bleeding in small quantities;
- discomfort in the pelvic area;
- muscle spasms in the abdomen.
If symptoms do not go away after 5-7 days, you should seek medical help from your doctor.
After conducting a series of studies and diagnostics, the specialist will be able to determine the reason for the deterioration in the woman’s well-being and prescribe a course of therapy.
Removing an ingrown intrauterine device
One of the complications of long-term wearing of an IUD is its rotation into the wall of the uterus. Typically, this situation occurs when the recommended time of use of the device is exceeded or when the technique of its insertion is violated. Suspect such a phenomenon based on the following signs:
- pain of varying intensity and character, localized in the lower abdomen, sometimes radiating to the lumbar region;
- general weakness, dizziness, pallor of the skin, tachycardia indicate internal bleeding;
- Sometimes such a condition does not have pronounced symptoms, but is discovered by chance during an ultrasound.
Diagnosis of the pathological condition occurs during hysteroscopy, which makes it possible to accurately determine the degree of immersion of the structure into the uterine wall. The method of removal and anesthesia is determined depending on the location of the lesion. Typically, extraction is performed using a hysteroscope using laparoscopic forceps. In difficult cases, when a significant part is immersed in tissue, a laparotomy is required - abdominal surgery. If the ingrown parts are located close to blood vessels and internal organs, all manipulations may take a long time and require significant effort from the doctor. After surgery, special attention must be paid to personal hygiene, as well as limiting physical activity for some time.
Perhaps one of the most common methods of birth control in Russia is used by every fourth woman.
Intrauterine device
(IUD) is a small device that is inserted into the uterine cavity.
Spirals differ from each other in size, shape, and the material from which they are made.
The simplest device is a polyethylene IUD that looks like a double letter S (called a Lips loop).
There are spirals of a more complex design - they look like the letter T or the number 7 and contain a ton of copper wire (as an antiseptic).
In addition, there are IUDs and vaginal rings containing the hormone.
The contraceptive effect of the spiral is achieved by preventing the attachment of a fertilized egg to the uterine mucosa. The IUD is an abortifacient contraceptive, because , but the development of pregnancy is not possible, since the embryo cannot attach in the womb.
A natural question arises: why do so many women use this contraceptive?
Most likely, most women simply do not know about the abortifacient mechanism of action, and doctors in antenatal clinics usually do not talk about it. So what does the spiral hide behind it, and is it as harmless as it seems at first glance?
RECOVERY PERIOD
After removal of the IUD, no specific rehabilitation measures are required, but the woman should follow some recommendations. To prevent possible consequences within a week after the procedure, you must:
- refuse vaginal sexual intercourse;
- carry out thorough intimate hygiene;
- do not be exposed to physical activity, do not play sports;
- refuse to visit the pool, steam room;
- do not use hygienic vaginal tampons;
- do not douche.
Removal of the IUD may be accompanied by dull aching pain in the abdomen and scanty bleeding, which spontaneously disappears after a few days. If after this time the patient’s temperature rises, vaginal discharge becomes profuse and is accompanied by an unpleasant odor, and abdominal pain intensifies, then it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor.
Within 4-5 days after performing this manipulation, it is prohibited:
- use vaginal tampons
- have sex
- do douching
- take a bath, visit a bathhouse or sauna
- play sports, lift weights
- take medications containing acetylsalicylic acid
After the IUD is removed, the next menstruation may come on time or be delayed for several days. When using a hormonal IUD, periods can be restored after a longer period.
The intrauterine device is removed quite simply and quickly, but in no case should this manipulation be carried out independently. One awkward movement is enough and the contraceptive can injure the cervix, leading to erosion or bleeding. Incorrect removal can also result in parts of the IUD being torn off and retained in the cervix.
After removing the device, the woman should adhere to the following recommendations:
- abstain from sexual intercourse for 5-6 days;
- do not use tampons and vaginal suppositories;
- do not take hot baths, do not visit baths and saunas;
- limit physical activity.
Removing the IUD may affect your menstrual cycle. Your next period may be delayed. A woman sometimes feels discomfort in the lower abdomen and spotting appears.
What to expect after IUD removal
After the procedure, aching pain in the lower abdomen may occur for several days (as during menstruation). Scanty bleeding may appear. Such manifestations are normal and disappear after a couple of days. It is recommended to maintain sexual rest for 4-5 days after removal of the IUD. You should also avoid taking a bath, visiting the sauna and bathhouse, using tampons and douching.
The next period may come on time or be delayed by several days. If a hormonal type of IUD was used, restoration of a normal cycle may take a little longer. You can plan a pregnancy already in the first cycle after removal.
Women's health is a fragile thing, so every representative of the fair sex should have a good gynecologist. Make the right choice - contact ON CLINIC.
Trust your health to professionals! ON CLINIC
The contraceptive method does not affect the subsequent conception of a child. After a recovery period (2-3 months), a woman may think about becoming a mother. During this time, the mucous membrane (mucosal layer) will be completely restored and the microflora will be normalized.
If the patient experiences complications, such as endometritis, due to wearing a contraceptive, she should refrain from conceiving until the disease is cured. After a successful course of therapy, you can get pregnant safely. If a woman feels well and does not have any contraindications, pregnancy can occur immediately after removal of the IUD.
After removing the ingrown IUD, the woman must follow simple rules; complete sexual rest is recommended for 3-4 days. You cannot play sports or lift weights for 1-2 weeks; you must follow the rules of intimate hygiene.
In addition, you should avoid visiting baths, saunas, solariums and swimming pools for 1-2 months. The use of tampons is prohibited, and douching cannot be used as a method of treating diseases of the genital organs. The recovery period can take from 3 to 14 days.
The presence of a foreign body in an internal organ and wearing it for a long time can have a negative impact on a woman’s body. These are not only possible complications, such as the growth of a contraceptive into the wall of the uterus, but also inflammatory and infectious diseases and even rupture of the cervix.
The female body can react to an IUD in different ways, so at the first feeling of discomfort and pain, you should visit a gynecologist and undergo an examination.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
Preparing the patient
Preparation begins with a consultation with a gynecologist. You can ask the doctor any questions you have about the procedure. If conception is undesirable, the method of contraception that the woman will use in the future is determined. Doctors advise starting to take some contraceptives well in advance, some time before the IUD is removed.
In cases where a woman does not plan to become pregnant after removing the IUD, unprotected sexual intercourse is excluded 3-4 days before the procedure. You should have sex using barrier contraception to prevent sperm from entering the cervical canal. This is due to the fact that male reproductive cells remain viable for some time. If ovulation occurs immediately after the procedure, conception is likely.
How to prepare for the procedure
If an ingrown helix is suspected, an ultrasound examination and examination by a gynecologist are first performed. For a more accurate diagnosis and drawing up a complete clinical picture, they resort to hysteroscopy. This procedure also helps the doctor decide on further actions. There are various methods for removing a spiral, the choice of which depends on the degree and location of its ingrowth.
Before the procedure, the medical staff tells the patient how the removal will be performed and what complications may arise. A woman needs to calm down and relax.
A week before the procedure, you should stop taking medications that affect blood clotting. It is strictly not recommended to remove the coil yourself at home.
Intrauterine device: what is the contraceptive method, how long is the IUD placed?
It is categorically unacceptable to remove the intrauterine device on your own; this procedure is performed only by a gynecologist in a medical institution.
It is preferable to prescribe the procedure on days 3-4 of the cycle, while menstrual bleeding continues. At this time, the cervix is soft and elastic, which makes it easier to remove the device. The secretions ensure easy sliding of the spiral. However, according to indications, the procedure is performed at any time, regardless of the cycle.
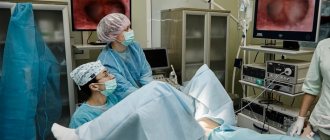
The patient is placed in a gynecological chair. The doctor examines the patient, palpates the uterus to determine the location of the spiral. Then you need to detect the tendrils of the IUD located outside the uterine cavity. After this, the organ is stabilized using an expander, and the manipulation area is treated with an antiseptic solution.
If the spiral threads cannot be found, hysteroscopy may be required - examination of the uterine cavity using a special optical system.
Standard IUD removal only takes a few minutes and no painkillers are needed. The issue of anesthesia is discussed in advance; its need is determined by the patient’s individual pain threshold.
In some cases, the IUD does not come out of the uterus, then the doctor has to expand the cervical canal. Sometimes the threads break, but an experienced gynecologist will be able to remove the device using a hook inserted into the cervix. In such cases, the use of local anesthetics is required.
Methods and methods for removing an IUD
Most often, IUD removal is performed on an outpatient basis in the middle of the menstrual cycle. The standard IUD removal procedure does not require pain relief. Removal of the IUD is carried out by pulling with a forceps (a special surgical instrument) or tweezers by the antennae, which normally should hang from the cervical canal. This method of removing the intrauterine device is the simplest, safest and least expensive.
If the IUD antennae are missing, the intrauterine contraceptive can be removed instrumentally during hysteroscopy or using an extractor.
Instrumental removal of the IUD is carried out under local or intravenous anesthesia. After mechanical expansion of the cervical canal, a hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity. If the intrauterine device lies freely in the uterine cavity, it is grabbed with special forceps and then pulled out. In severe cases, the instrumental method of removing the IUD may be accompanied by damage to the walls of the canal, uterus and bleeding. If the reason for the removal of the intrauterine contraceptive is the presence of inflammatory, infectious or tumor processes in the uterine cavity, after removal of the IUD, smears in the form of fingerprints are taken from it for further histological examination.
Often, during a preliminary gynecological examination, the doctor can identify an IUD that has grown into the uterine walls. In such a case, removal of the intrauterine contraceptive is performed by curettage of the uterine cavity, followed by histological diagnosis of the resulting biomaterial. If part of the IUD is located near large vessels, the ureter and bladder, or has grown into the abdominal cavity, removal of the spiral is carried out through laparotomy or laparoscopy.
In any case, removal of the IUD should only be performed by a qualified gynecologist. Removing the intrauterine device yourself at home is contraindicated. Such actions can cause mechanical damage to the mucous membranes of the genital organs and their infection. When removing an IUD, the doctor can determine the possible consequences of using the IUD and, if necessary, develop an individual course of therapeutic action.
What could be the consequences of installing a spiral?
When removing the intrauterine device, sometimes more serious difficulties arise. In some cases, the spiral antennae are not detected. Then it is necessary to determine the location of the device and determine whether it is there at all. For this purpose, visual examination methods (ultrasound or radiography) are used. If during the study it turns out that the spiral has perforated the wall of the uterus and is located outside its cavity, emergency surgery is required.
There are situations when the antennae of the spiral are in place, but the gynecologist is unable to remove it. In such cases, an ultrasound or x-ray is needed to determine the cause of the immobility of the spiral. It happens that the device fits too tightly to the walls of the uterus.
Much more dangerous is the situation when a foreign body grows into living tissue. Most often, this consequence occurs if the spiral is not removed in due time, that is, the validity period of the medical device has been exceeded. In such cases, invasive surgery is necessary to remove the coil.
Cost of services
| Name of service | price, rub. |
| Primary, outpatient appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist (complaints, history taking, examination, drawing up an examination plan) | 2100 |
| Repeated appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, outpatient | 2100 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences | 2400 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, head of department | 2600 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences, head of department | 2800 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of medical sciences, professor | 3000 |
| Consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, chief physician of the clinic | 3300 |
| Removal of an intrauterine device (IUD) | 2000 |
| Removal of an intrauterine device (IUD) in the operating room | 9000 |
Dear patients! You can find a full list of services and price list at the reception or by phone. The administration tries to promptly update the price list posted on the website, but in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to check the cost of services on the day of contact at the reception or call center by phone. The posted price list does not constitute an offer.
| Make an appointment | Make an appointment by phone or by filling out the online form |
The administrator will contact you to confirm your appointment. IMC "ON CLINIC" guarantees complete confidentiality of your request.
Advantages of ON CLINIC
The Center for Obstetrics and Gynecology ON CLINIC provides services for the introduction and removal of intrauterine contraceptives. Our doctors have extensive experience in performing such procedures. Highly qualified specialists allow the procedure to be performed quickly, painlessly with minimal discomfort for the patient.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kV5CI8T9m3E
We use only safe drugs for anesthesia. They are quickly eliminated from the body without causing harm to it.