An important sign indicating problems in the female body is an unpleasant odor after menstruation. As a rule, it is accompanied by vaginal discharge. The reasons for this phenomenon are varied, from hormonal disorders to infectious and inflammatory diseases. If a woman detects the presence of an unpleasant odor during or after menstruation, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist to determine the presence of pathology in the body.
During the menstrual cycle, a woman's hormonal levels change. Minor changes in the consistency and smell of the discharge may be recorded. Menstrual blood itself has a specific smell, but within the physiological norm, without causing disgust. Why does there be an unpleasant odor from the vagina?
Candidiasis
Thrush is caused by yeast-like fungi. When they multiply, unpleasant symptoms appear in the form of vaginal itching and cheesy discharge. Microorganisms love a sweet environment, but during menstruation an acidic environment forms in the vagina, and the fungal population decreases. With chronic candidiasis, after the end of menstruation, favorable conditions are again created for thrush. To cure the disease, it is necessary to use antifungal agents externally and in tablets. You should also strengthen your immune system and reduce your consumption of confectionery products.
Causes of postmenstrual discharge odor
The content of the article:
The secretion from the female body, which is rejected during menstruation, consists of small clots of dark-colored blood, as well as natural mucus, endometrial particles that have already been “worked out”. All this is natural, therefore it does not cause a very disgusting odor, much less an unpleasant one, except that it may have a slight “aroma” of iron.
If there is a strong smell of rot or rotten meat after “these days,” then this indicates that there is inflammation, and already in a difficult phase. Most likely, its occurrence is directly related to the fact that bacteria have entered the vagina and caused an infection.
It is important to understand that the reasons for the appearance of a particularly unpleasant odor after the onset of menstruation may lie in the occurrence of far from simple diseases, or perhaps in the most banal failure to comply with hygiene rules.
Bacterial vaginosis
Changes in vaginal microflora. Occurs due to the death of lactobacilli, which normally constitute the majority of microorganisms on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. Their place is taken by opportunistic bacteria. As a result, patients develop white or gray foamy discharge with a fishy odor. Itching and pain are most often absent. The disease often goes away on its own. But treatment helps speed up recovery and avoid concomitant infections. Therapy consists of antiseptic treatment of the external genitalia, the use of vaginal prebiotics and antimicrobials.
Opinion of gynecologists
Gynecologists have repeatedly given advice on how to carry out prevention in order to avoid problems with unpleasant odor. In fact, there is nothing complicated, you just need to follow the rules, which should become a life credo once and for all.
- Personal hygiene should be a way of life without missing a single session. Perform water procedures in the intimate area every day.
- Be responsible and selective when choosing a partner, thereby protecting yourself from contracting infections. Use contraception (condoms) if you do not know your partner too well. However, it is better to follow this rule with loved ones too.
- Consult a gynecologist regularly, ask the doctor all the questions that interest you.
- Do not take too strong antibacterial drugs.
- Use special substances for intimate hygiene that are sold in pharmacies, for example, preparations containing lactic acid.
See also: Weakness during menstruation
Endometritis
If you have an unpleasant odor after your period, it may be due to inflammation of the endometrium. Most often, pathology occurs when there are foci of infection in the pelvic area. The disease can be triggered by childbirth, miscarriages, gynecological operations and manipulations. Patients complain of pain in the lower abdomen, fever, unusual discharge, and painful urination. Treatment consists of taking antibiotics, injections to relieve intoxication, and strengthening the immune system. Physiotherapeutic procedures are often prescribed.
When to see a doctor
If following the rules of hygiene and refusing to use scented tampons and pads does not help get rid of the unpleasant odor, then you need to consult a gynecologist. The doctor will take a smear and, based on its results and visual examination data, will be able to determine the cause of the problem and prescribe treatment.
Depending on the reasons that caused the stench, the doctor selects treatment tactics. Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antifungal drugs, and oral contraceptives may be prescribed.
Immediate consultation with a gynecologist is necessary for women who complain that the discharge before menstruation smells, it has become yellow-green or brown. A doctor's examination is required if the discharge is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen.
Venereal diseases
The risk of contracting a sexually transmitted infection increases sharply with unprotected sexual intercourse during menstruation. The fact is that during this period immunity is reduced, and the inner layer of the uterus is an extensive wound surface. The first symptoms, as a rule, appear after the end of menstruation and consist of an unpleasant odor from the vagina. Then purulent, serous or foamy discharge appears. The mucous membrane becomes red and swollen, and a rash appears on the labia. There may be fever and difficulty urinating. The infection is eliminated by antiseptic treatment of the genitals and taking antibacterial drugs.
Treatment of the disease causing the odor
To eliminate the atypical “aroma” it is not recommended to overuse douches and folk remedies. In this case, these methods are ineffective and unsafe. You can't deal with the problem without a doctor. The first thing a specialist does is to identify the cause of the smell. After this, a treatment plan is drawn up and the necessary appointments are made.
The treatment tactics for gynecological pathologies are approximately the same. The difference lies in the use of drugs. The most effective method of eliminating the unpleasant odor of discharge after menstruation is drug therapy, which includes antimicrobial, antibacterial and antiseptic agents:
- When diagnosing any disease of the reproductive system, it is very important to strengthen and support the immune system. For this purpose, the drugs Polyoxidonium, Immunal, Derinat, Ribomunil are prescribed.
- Fluomizin, Clindacin, Gynoflor, Lactobacterin and Bifidumbacterin help tidy up the composition of the microflora.
- Sexually transmitted diseases are treated with antibiotics Unidox Solutab, Neo-Penotran Forte, Doxycycline, Ciprofloxacin.
To cure the disease and forget about the unpleasant odor, you must follow the recommendations of a specialist. This applies not only to taking medications. Stop smoking and alcohol, maintain a drinking regime, good personal hygiene, and regularly visit your gynecologist.
Even if after menstruation bad-smelling discharge occurs irregularly and does not cause any particular discomfort, you should seek help from a doctor. Don't save time at the expense of your health.
Uterine cancer
A rotten smell after menstruation can be a sign of cancer. The tumor can affect the endometrium or cervix. The clinical picture includes pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, impaired defecation and urination, prolonged menstruation and intermenstrual bleeding. The discharge may have impurities in the form of leucorrhoea and pus or take on the appearance of meat slop. The choice of treatment depends on the stage of the pathology. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal treatment and surgery are used.
An unpleasant odor after menstruation should not be a cause for concern if it lasts for a couple of days and is not accompanied by accompanying symptoms. In other cases, it is necessary to take microflora tests and be examined by a gynecologist.
Symptoms that may bother a woman
Menstrual blood has its own specific smell, but in a healthy woman it has a mild character and does not cause disgust. In atypical (pathological) conditions, discharge after menstruation may smell differently. It depends on the type of bacteria growing in the vagina.
During thrush, there is a discharge that smells sour; in case of hormonal disorders, it smells like vinegar. If bacterial vaginosis is diagnosed, a woman experiences an obsessive fishy odor from the discharge.
Putrid, rotten stench is a symptom of infectious diseases. The smell of acetone after menstruation indicates diabetes mellitus, disorders of the endocrine and genitourinary systems.
You should not evaluate your condition based solely on the smell of discharge after menstruation. In rare cases, it is an independent symptom. More often than not, this is one of the signs of the presence of pathology. In addition to the fetid odor in the intimate area, there is general weakness, pain in the abdomen and lower back, burning and itching in the vagina, and irritability. Along with the deterioration of the condition, the abundance, consistency and color of menstrual flow change. The more typical symptoms and the more expressive the smell in the intimate area after menstruation, the more dangerous the disease progressing in the body.
Gynecological pathologies have many similar signs. It is impossible for a person far from medicine to identify the cause of the phenomena occurring. You can learn about the diagnosis and treatment methods only after visiting a doctor and passing the necessary tests.
Particular attention should be paid to discharge with the smell of ammonia, since in almost all cases it is considered pathological. Read more information in a separate article on our website.
After menstruation, purulent discharge and unpleasant odor
The intensity, abundance, shade and smell of the discharge rejected by the uterus during menstruation is an important indicator of the health of both the organs of the reproductive system and the entire body. The slightest changes associated with a violation of the cyclicity or nature of the released substances should serve as a reason to contact a specialist. Many girls notice discharge with an unpleasant odor after menstruation. What might this phenomenon indicate? Is such a process physiological or are mucous substances with a pungent, nauseating odor a sign of pathological changes in the genitals?
Female discharge rejected by the genitals during menstruation consists of blood clots, natural mucus covering the walls of the reproductive organs and “waste” particles of the endometrium. Such a “cocktail” cannot smell unpleasant. The naturalness of the process is evidenced by the light aroma of iron present on the days of the most abundant discharge. A pungent odor reminiscent of rotten meat indicates inflammatory processes in the acute phase, resulting from the penetration of various infections into the genitals.
It is worth noting that the appearance of a characteristic unpleasant aroma that accompanies postmenstrual discharge may be associated with neglect of personal hygiene rules. According to gynecologists, laxity in caring for the intimate area during menstruation is fraught with the appearance of a rotten smell, which will be felt not only by the woman, but also by the people around her. Many representatives of the fair sex prefer to use pads with maximum absorption during regulation. This choice is justified not by an urgent need caused by the abundance of discharge, but by the desire to reduce the number of “changes” of intimate hygiene products. Experts say that this practice entails the occurrence of various skin diseases that affect the external genitalia. The characteristic putrid aroma is caused by decomposition processes activated by the “greenhouse” effect during the long stay of a pad filled with blood clots in the groin area.
To prevent this phenomenon, it is necessary to promptly change the pad or tampon. It is necessary to wash intimate parts during menstrual periods during each change of hygiene items. Experts recommend carrying out hygiene procedures using chamomile or calendula decoctions.
It is worth noting that the specific pungent aroma emitted by mucous secretions is an accompanying symptom indicating the presence of a problem. To identify the cause of smelly vaginal secretion, a comprehensive diagnosis is required with a detailed study of all changes in the functioning of the reproductive system.
Gynecologists identify several diseases that can provoke the appearance of discharge with a specific unpleasant odor in women after menstruation:
- Vaginal dysbiosis (bacterial vaginosis).
- Nonspecific colpitis.
- Sexually transmitted diseases.
- Hormonal imbalances caused by dysfunction of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands.
- Functional lesions affecting the functioning of the entire body (diabetes mellitus, lesions of the central nervous system, eating disorders, etc.).
Let us consider in more detail the reasons given in the article for the occurrence of an unnatural odor in the discharge rejected after the end of menstruation.
Based on the latest medical statistics, the most common reason for the appearance of discharge with an unpleasant odor after menstruation is a sharp change in the vaginal microflora. This disease is called dysbiosis or dysbacteriosis.
From a physiological point of view, the problem lies in the disruption of the “equilibrium” in the environment of bacteria that ensures the normal functioning of the reproductive organ. The dominance of lacto and bifido microorganisms is being replaced by a quantitative advantage of candida, gardnerella, and enterococci. These bacteria, in small quantities, are part of the microflora that ensures health in the vaginal environment. But an excess of saprophytes is fraught with the development of dysbacteriosis in the intimate area.
The presence of a specific odor is far from the only symptom of the disease. Women experiencing the disease note:
- copious vaginal discharge;
- severe itching in the groin area;
- burning during urination;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
If you notice such symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist. Lack of timely treatment of vaginal dysbiosis can provoke the occurrence of gardnerellosis. This disease is manifested by copious creamy gray discharge. Their rejection is accompanied by a characteristic smell of rotten fish.
In gynecology, colpitis is called inflammation of the mucous membranes covering the vagina. This disease acquires nonspecific status when a pathogen containing pathogenic flora is diagnosed:
- Staphylococcus.
- Escherichia coli.
- Proteus.
- Streptococcus.
The diseases have pronounced symptoms. This includes:
- the presence of a strong unpleasant, in most cases, sour odor of discharge;
- discomfort in the groin area;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- sharp cutting pain during urination.
The disease, which has passed into the chronic stage, may be accompanied by spotting and spotting.
Nonspecific colpitis requires immediate treatment. Prolonged ignorance of the problem contributes to the spread of pathogenic flora in the cervical canal of the cervix, especially during menstruation. It is during critical days that this area is susceptible to infection due to the lack of a protective barrier - the mucus plug.
Violations of this nature have a direct negative impact on the general condition of the body. Pathological processes affecting the functioning of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands can provoke the rejection of a secretion that is unusual for a woman, has a pronounced color, and has an unpleasant aroma.
Doctors include factors that negatively affect hormonal levels:
- eating disorder;
- starting to take hormonal contraception;
- a sharp increase in loads;
- stress;
- a sharp fluctuation in the content of the female hormone estrogen in the blood.
These factors cause strong fluctuations in the cycle and the appearance of liquid discharge during the intermenstrual period, which has a specific fishy aroma.
Sexually transmitted diseases, in most cases, are provoked by pathogenic bacteria transmitted from partner to partner during coitus. According to doctors, along with inflammation caused by fungi, several of the most common STD pathogens can be identified:
Depending on the pathogen, the smell and color of the rejected liquid will vary:
Gonorrhea: Thick white-yellow discharge with a characteristic “rotten” odor.
Trichomoniasis: The discharge is scanty, rather spotting, and has a foamy structure. Sometimes they are light pink or brown in color. The smell of this secretion is similar to the rejected fluid from gonorrhea.
Candidiasis: The main symptom of this disease is curdled discharge after menstruation in women, which has a strong sour aroma.
It is worth noting that such symptoms are far from normal and the slightest suspicion of an STD requires immediate consultation with a doctor!
Experts say that the more advanced the disease, the stronger the “stink” of the rejected secretion. The transition of pathology to the chronic stage threatens female infertility and peritonitis.
Gynecologists say that more often than other representatives of the fair sex, women who prefer to frequently change sexual partners and neglect the use of condoms are susceptible to developing diseases.
To summarize, it should be noted that the presence of an uncharacteristic, bad odor in the secreted secretion is the first sign of the development of pathological processes in the organs of the reproductive system.
A sour smell indicates the development of thrush after menstruation. In the first months of the disease, a specific aroma is perhaps one of the most obvious symptoms.
The smell of rot, noticed by many women, can go hand in hand with a discharge that visually resembles pus. The symptom indicates inflammatory processes caused by an infection transmitted through unprotected sexual contact.
Discharge with a fishy odor is a frequent “companion” of bacterial vaginosis and other non-venereal diseases.
Only after establishing the cause of the appearance of discharge with an odor after menstruation can treatment begin. Gynecologists prefer to begin collecting anamnesis with an examination in a gynecological chair. Women who experience a similar symptom undergo a number of examinations prescribed by specialists:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Gynecological scraping: microscopic and bacteriological.
- Hormone analysis.
- Detection of sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Colposcopy.
The results of these examinations will serve as the basis for specialists to draw up an effective course of treatment. Among the many offers on the pharmacological market, certain drugs stand out, the symbiosis of which becomes a real panacea for women faced with the unpleasant odor that accompanies postmenstrual discharge. These include:
- Antibiotics.
- Antimicrobial and antifungal agents.
- Immunomodulators (including those of plant origin).
- Local antiseptics.
- Probiotics.
Please note that only a practicing specialist can create the most accurate course of treatment, tailored to the individual needs of the patient. You should not self-medicate on such a sensitive issue!
source
During the intermenstrual period, vaginal discharge is also normally present, but attention should be paid to the nature of the latter. If a woman notices a change in odor or color of the leucorrhoea after her next period, this often indicates the presence of a disease. In such a situation, consultation with a gynecologist is necessary. After all, critical days make a woman vulnerable to infectious agents, and blood is a breeding ground for microorganisms. The above factors, combined with violation of basic rules of personal hygiene, lead to the development of vaginitis and vaginosis, requiring specialized treatment.
Every woman should have vaginal discharge every day. They are transparent or whitish in nature, odorless or with a slight sour-milk aroma, their volume is no more than one teaspoon per day. A change in the smell of leucorrhoea is a clear sign of a violation of the optimal vaginal microbiocenosis. The normal flora consists of lactobacilli - Doderlein bacilli; They maintain vaginal health and perform the following functions:
- provide resistance to pathogenic pathogens by acidifying the environment (pH 4.5);
- do not let through and have a detrimental effect on the male secretion, thus only the most mobile and healthy sperm can penetrate and fertilize the egg;
- form active radicals and hydrogen peroxide, which stimulate local immunity.
The normal and permanent biotope of the vagina is lactobacilli acidophilus. A healthy woman also has a conditionally pathogenic flora. In small quantities it does not cause harm, but under the influence of provoking factors it begins to actively multiply, causing the development of the disease and the appearance of clinical symptoms.
Often the cause of violations is failure to comply with basic rules of personal hygiene:
- infrequent washing;
- Using pads and tampons that are too large and changing them rarely.
The introduction of tampons during menstruation causes recurrence of candidiasis and bacterial vaginosis, so many gynecologists do not recommend using them. But if a woman is unable to refuse these hygiene products, then she should at least use varieties without aromatic fragrances and small sizes - with frequent changes.
Microflora disturbances often occur after a period of menstrual flow. The fact is that during menstruation, the protective mechanisms in the genitals are suppressed, the vagina and uterus become vulnerable to infection. Bloody discharge is a favorable environment for the development of microorganisms. The most common are bacterial vaginosis, thrush, and aerobic vaginitis, that is, those diseases whose etiological agent is constantly present in the vagina, but in small quantities.
Their manifestation (activation) occurs if, before menstruation, a woman was influenced by some trigger (provoking) factor:
- hypothermia;
- the appearance of a new sexual partner;
- stress;
- emotional shock.
Doderlein's rods die in such a situation, since they are unstable to changes in the microenvironment and cannot fight off other types of pathogenic bacteria.
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) develops when the following microbes become active:
- 1. Gardnerella vaginalis.
- 2. Mobiluncus mulieris.
- 3. Atopobium vaginae.
- 4. Leptotrichia.
- 5. Veilonella.
BV develops as a biofilm infection. Biofilm is a polymicrobial community where bacteria are interconnected, attached to epithelial cells and surrounded by a special matrix that protects microorganisms from drugs, which is the reason for the frequent recurrence of the disease. In addition, pathogens have developed resistance to the main drug against BV, metronidazole.
Vaginal candidiasis occurs while taking systemic antibacterial agents and immunosuppressants. Thrush is caused by the growth of fungi:
- 1. Cand>2. C. tropicalis.
- 3. C. parapsilosis.
- 4. C.glabrata.
- 5. C. crusei.
The most common cause is C. albicans, which is sensitive to many antifungals. The last two options are resistant to all medications except Itraconazole. They constantly recur; conventional therapy only slightly suppresses their growth.
Aerobic vaginitis (AV) develops against the background of bacterial activation:
- 1. Streptococcus spp.
- 2. Enterococcus spp.
- 3. Staphylococcus aureus.
- 4. Escherichia coli.
It occurs in girls or postmenopausal women, since the reproductive period is the prerogative of bacterial vaginosis. Unlike BV, this pathology is accompanied by an inflammatory reaction of varying severity.
Normally, menstrual flow has little or no iron aroma. But sometimes women note that during menstruation their discharge acquires an unpleasant odor and smells strongly of rot and mustiness. The reason for this is a simple lack of compliance with hygiene rules.
Stagnant blood is an ideal environment for the proliferation of bacteria, including opportunistic ones, and the manifestation of their harmful qualities. After critical days, vaginal dysbiosis persists, affecting changes in the nature of vaginal secretions. This situation requires medical intervention and sanitation of the genital organs, depending on the clinical form of the infection.
Bacterial vaginosis is in first place for detection after menstruation. With this pathology, vaginal discharge smells like rotten meat, fish, eggs, it is abundant and liquid, foamy, and the color is gray-white. This is actually the only symptom, since itching, burning, dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse) are not typical for this pathology.
If there is a strong aroma from the vagina, reeking of sour milk, the consistency of the leucorrhoea is curdled, and they come out in large quantities, then these are most likely symptoms of developed thrush. It is characterized by a variety of subjective characteristics:
- itching;
- burning;
- discomfort during sexual activity;
- dysuria (impaired urination);
- peeling in an intimate place.
Aerobic vaginitis is indicated by a sweetish aroma and a small amount of yellowish thick vaginal secretion. Vivid clinical manifestations are not typical for infection.
Treatment for unpleasant vaginal discharge after menstruation should be prescribed only after a personal consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist and appropriate additional examination to determine the probable cause of the pathology. A smear on the flora helps to figure this out. The material is collected during a vaginal examination, and the result is usually ready in 4-5 days. But it is better to conduct a more thorough diagnosis, with an accurate picture of the biotope, where each microorganism is taken into account. These methods include:
- 1. Femoflor screen.
- 2. Femoflor 8.
- 3. Femoflor 16.
- 4. Florocenosis.
They are performed in paid commercial laboratories. Knowing the exact bacterium that caused the disease, it is possible to select treatment as accurately as possible and avoid recurrence.
Both local and systemic antibacterial medications are used, and their combination is possible. Additionally, general strengthening and immunomodulating medications are taken. After a course of etiotropic therapy, it is necessary to restore normal microflora: seed the vagina with natural microorganisms. After 1-2 months, the examination should be repeated to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
Previously, it was believed that the main drug for this nosology was metronidazole, but scientists have now found that most pathogens are resistant to it. If the patient has symptoms of BV, and Gardnerella was identified as the main cause at the diagnostic stage, then metronidazole will indeed be beneficial. It is used orally: Trichopolum 250 mg 4 times a day for 5 days.
It is optimal to use topically in the form of suppositories: Rumizol, Neo-Penotran (Forte), Limenda, Ginocaps, Klion-D - a combination of metronidazole with miconazole. Suppositories are applied 2 times a day for 1-2 weeks, depending on the severity of the infectious process.
The complex drug Terzhinan (contains ternidazole, prednisolone, nystatin, neomycin sulfate) is more powerful, effective in this situation and helps get rid of the pathology.
If Mobiluncus and Atopobium are detected in the smear, therapy with clindamycin alone will bring results (it destroys biofilms and cellular associations of bacteria). It is dangerous to take this antibiotic internally; it may lead to the development of a dangerous complication - pseudomembranous colitis.
But local use has virtually no side effects and prevents repeated attacks of BV. Clindabiox, Dalatsin S contain 100 mg of clindamycin in each suppository, taken once a day for 3 days, treatment can be prolonged up to 6 days. The growth of fungi during antibiotic therapy will help to avoid Clindacin B - the drug includes butoconazole.
In pregnant women, all of the above remedies are contraindicated in the 1st and 2nd trimester, but it is extremely necessary for them to restore vaginal normal flora, since gestational complications may develop: premature birth, fetal malnutrition, chorioamnionitis. The optimal solution in this situation is the use of Betadine, Ruvidon, Hexosept, Hexicon, Fluomizin - local antiseptics of general action.
Polyoxidonium is prescribed for general strengthening purposes. The drug has an immunomodulatory, antioxidant effect, increases the concentration of drugs in the blood, making the treatment more effective.
Afterwards, it is necessary to inoculate the vaginal environment with lactoflora. Lactriol, Acylact, Gynoflor are used - 1 suppository 2 times a day, 5-10 days.
In rare cases of candidiasis, local antimycotics can be used. Sertazol, Zalain (1 suppository is administered once), Mikozol, Ginezol (course - a week) are used. Fluconazole, Diflucan - 150 mg orally (1 tablet), then after 3 days another one. Natamycin and Pimafucin are allowed for pregnant women (at least 3 days).
For recurrent forms, the use of Lomexin in the form of vaginal capsules or cream is effective. The latter helps to treat the sexual partner at the same time.
Candida glabrata and crusei lead to a protracted course of thrush, due to resistance to many antimycotics. In this case, a drug based on itraconazole is used (Mikotrox 2 capsules 2 times a day - 1 day).
Polygynax is a combination drug that includes nystatin, polymyxin B, neomycin. It is not active against its own lactobacilli. During therapy, 1 vaginal capsule is placed at night, for a course of 6 to 12 days. It is worth noting that Polygynax is used in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy. It is actually not effective against BV, so it should not be prescribed in this case.
Therapy is supplemented with antiseptics (Ruvidon, Hexosept, Fluomizin), Polyoxidonium, Lactritol.
source
An important sign indicating problems in the female body is an unpleasant odor after menstruation. As a rule, it is accompanied by vaginal discharge. The reasons for this phenomenon are varied, from hormonal disorders to infectious and inflammatory diseases. If a woman detects the presence of an unpleasant odor during or after menstruation, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist to determine the presence of pathology in the body.
During the menstrual cycle, a woman's hormonal levels change. Minor changes in the consistency and smell of the discharge may be recorded. Menstrual blood itself has a specific smell, but within the physiological norm, without causing disgust. Why does there be an unpleasant odor from the vagina?
Diseases of the female reproductive system are the most common cause of pathological odor. Let's consider the conditions under which an unpleasant odor may appear.
- Candidiasis. Fungal infection of the vaginal mucosa or vaginal candidiasis is accompanied by a sharp sour odor. This is due to a change in the quantitative composition of normal microflora and intensive proliferation of fungi. In this case, the woman experiences severe itching and discomfort, and abundant cheesy, unpleasant-smelling discharge appears.
The development of candidiasis is due to the fact that before menstruation, immunity decreases, so by the end of menstruation, microbes are actively parasitizing the vagina. - Gardnerellosis. Sometimes women complain about the rotten smell of fish in the intimate area. This indicates the presence of bacterial vaginosis or gardnerellosis - an infectious disease in which the immune system does not produce a response. As a result, inflammation develops against the background of a decrease in the quantitative composition of the physiological microflora of the vagina. The absence of leukocytes promotes the proliferation of polymicrobial associations of bacteria. The infection manifests itself as a thick, foamy gray or white discharge that smells like fish. Symptoms that worry patients: itching and burning in the intimate area, frequent urination, pain during and after sexual intercourse. The infection often recurs.
- STDs (sexually transmitted diseases). These diseases are asymptomatic in most cases. But during periods of exacerbation, their signs appear - discharge, painful sensations. At the same time, the woman’s smell of menstruation intensifies. Menstrual blood is a source of iron and other nutrients for pathogenic flora. In such an environment, bacteria and protozoa, especially Trichomonas, actively multiply, causing trichomoniasis.
Yellow, gray discharge with a rotten odor appears. Signs: itching and swelling of the labia, inflammation of the walls of the vagina and cervix, sometimes discharge with pus. With chlamydia, mycoplasma and ureaplasma, during the period of exacerbation, women experience a persistent and unpleasant odor. A yellowish discharge appears from the vagina and urethra. The act of urination is painful, itching and pain intensify at the end of emptying the bladder. Symptoms of urethritis appear: burning and pain when urine passes through the urethra, mucopurulent discharge, redness of the entrance to the urethra. - Cervicitis. Menstruation with an unpleasant odor occurs with cervicitis - inflammation of the cervix. Early signs of the disease are vaginal discharge immediately after menstruation. They may not stink at first. There are often streaks of blood in the mucus. How to recognize cervicitis: burning in the perineum, pain during sexual intercourse, spotting, sometimes moderate bleeding.
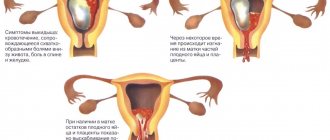
- Endometriosis. This is the proliferation of cells in the inner lining of the uterine wall (endometrium). Throughout the menstrual cycle, the overgrown layer comes under the influence of hormones and undergoes structural changes. As the disease develops, the patient develops profuse purulent discharge with mucus and a rotten smell. The nature of menstruation changes.
The secreted blood is thick, dark red, sometimes with a black tint. When the growths spread to the muscle layer and lymphatic vessels, abundant liquid discharge appears, which has an unpleasant pungent odor. During this period, a woman may notice blood clots that come out of the vagina. - Cancer of the uterus and its appendages. With a malignant tumor, dirty pink discharge appears against the background of menstrual irregularities. At first they are watery and do not smell sharp. Their cause is damage and destruction of lymphatic vessels. Discharge can be constant or periodic, with varying degrees of intensity. Signs of endometrial cancer: pain in the lower abdomen, hormonal imbalances, bleeding after exercise or sexual intercourse.
Important! As the tumor progresses, a strong, persistent odor appears after menstruation. In the last stages, the pain is intense and continuous. When metastasis occurs in the bladder, discharge from the urethra appears with the smell of rot.
The causes of smelly discharge during ovarian cancer before and after menstruation are tumor disintegration and destruction of lymph nodes. The mucus coming out of the vagina is watery with ichor. The intensity of the odor depends on the presence of genital infection.
A simple reason for the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the vagina after menstruation is neglect of personal hygiene rules. During menstruation, more careful care of the intimate area is necessary to avoid the development of an infectious process - candidiasis, vaginitis, colpitis.
The released blood smells intensely, and the smell can be felt not only by the woman, but also by the people around her. If the gaskets are not changed in a timely manner, a persistent and unpleasant stench appears. The process increases the heating of the blood to body temperature, which contributes to the rapid spread of the stench.
If a woman maintains personal hygiene, but her periods smell sharp, she should consult a gynecologist for advice. There may be several reasons for this:
- hormonal imbalance in the female reproductive system;
- vaginal dysbiosis;
- age-related changes in the pelvic organs;
- avitaminosis;
- decreased general and local immunity;
- stress and depression;
- bad habits - smoking, alcoholism.
If a woman has a specific odor before or after menstruation and does not go away, a study is carried out, which includes several stages.
They find out the complaints, symptoms that bother the woman, the regularity of the menstrual cycle, its nature, the intensity of bleeding, the number of births and abortions, the presence of PMS.
Next, an external and internal gynecological examination is performed. Externally, the condition of the labia majora and minora, the condition of the urethra, and the vestibule of the vagina are assessed. At this stage, discharge is noticeable, which normally should not be there. A woman may smell bad.
Then the vagina is examined using gynecological speculum and a colposcope (optical device) to examine the vagina and cervix.
Important! During the interview, a woman may be asked questions on abstract topics that do not relate to her complaints. This is how the connection between pathology and a woman’s mental health is determined and her emotional state is clarified. To help your doctor make the right treatment decisions, you need to answer questions honestly and truthfully.
It is mandatory to take a flora smear for laboratory testing. This method allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane, identify rancid, purulent, mucous discharge.
A smear is taken from a woman to determine bacterial, fungal infection, and lactoflora.
Unpleasant odor during and after menstruation can be eliminated with the help of medication and traditional medicine. To determine a way to combat fetidity, it is necessary to take into account the reasons that caused it.
If a woman has an infection, general and local treatment with pharmacological drugs is prescribed. For STDs, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. If Trichomonas is detected in a woman, medications based on metronidazole (an antimicrobial agent) are prescribed - Trichopolum, Klion, Flagyl. Complex therapy for infections includes three areas - antibacterial, antimicrobial, antiseptic.
Recommendations for maintaining personal hygiene to eliminate unpleasant odors:
- change personal hygiene products in a timely manner;
- take a shower and bidet more often;
- select pads and tampons according to the required parameters;
- wear underwear made from natural fabrics;
- avoid frequent douching.
To prevent blood from thickening and odor appearing during menstruation, a woman should drink enough fluid. Water dilutes blood sugar and removes it from the body, preventing the creation of a favorable environment for the growth and reproduction of bacteria. Citrus juices rich in vitamin C are beneficial.
To maintain physiological lactoflora, it is recommended to eat fermented milk yoghurts without additives, flavors and taste enhancers. It is important for any pathology of the female genital area, regardless of where the inflammatory focus is localized, to strengthen and maintain the immune system. Preparations:
- Polyoxidonium;
- Immunal;
- Derinat;
- Dr. Tice's Tincture;
- Ribomunil;
- Imudon;
- suppositories - Viferon, Kipferon, Galavit.
To restore the beneficial microflora of the vagina - Lactobacterin, Bifidobacterin.
In folk medicine, the plant Emblica officinalis from the Euphorbiaceae family is widely used to treat unpleasant odor after menstruation. Other names: Indian gooseberry, amla. The fruits are used for medicinal purposes. They contain large amounts of vitamin C.
Beneficial properties of the medicinal plant:
- Removal of toxins and decay products of pathogenic microorganisms. Emblica eliminates purulent and other discharges and eliminates foul odor.
- Increasing immunity at the general and local level. Biologically active substances in the fruit strengthen the protective functions of the vaginal mucosa.
- Sanitation of the genital tract.
Tea tree oil, chamomile, plantain, and St. John's wort eliminate unpleasant odors. Decoctions for douching are prepared from herbs.
To normalize the nervous system and psycho-emotional state, women are recommended to drink teas with the addition of mint or lemon balm.
source
Purulent discharge in women is a sure sign of trouble. Very often they are accompanied by symptoms such as pain, irritation, redness and swelling of the reproductive organs. At the same time, general health often worsens. In any case, the appearance of pus always indicates that the inflammatory process is progressing in the body.
Let's look at what are the most common causes of purulent discharge in women, and the treatment that is most likely to be used in one case or another.
Pus is an unnatural secretion product of the gonads, which contains a large number of bacteria and dead leukocytes (neutrophils).
Purulent discharge is quite easy to recognize. Most often it is a mass of yellow-green color, which has a repulsive specific odor and is characterized by abundance.
Non-infectious causes
A foul odor that intensifies after menstruation does not always indicate the development of viral or infectious diseases. Sometimes the reason lies in poor genital hygiene. If a suspicious symptom is detected, a woman needs to pay attention to the nature of the smell. If associations with acetone occur, then you need to check your glucose level. Possible development of diabetes mellitus. The smell of semen occurring the day after intimacy is considered normal.
Disturbance of vaginal microflora
If a woman is healthy, then in her vagina, namely in the internal cavity, there is its own microflora and its various representatives. They live there all the time, but do not have a negative impact. They help the body cleanse itself.
For example, lactobacilli produce lactic acid. It prevents pathogens from entering the cervical canal of the uterus.
If their number decreases, then pathogenic microbes that live on the mucous membrane may increase their number. And this will already provoke an infectious disease. Such pathologies include candidiasis.
When the population of pathogenic microflora increases, very often a specific smell is noticed from the vagina after menstruation. It becomes stronger not only during menstruation, but also after it.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7IbrrSkAj2k
There are many sexually transmitted diseases that cause the discharge to have an unpleasant odor. The most common of them are:
- ureaplasmosis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- chlamydia.
Blood in the vagina
Sometimes menstrual bleeding continues for a long time and ends with spotting brown discharge. The process can continue for a week or more.
In this case, menstrual blood may stagnate in the leathery folds of the vagina. It is an excellent nutrient medium and promotes the proliferation of permanent microflora, some of which again acquire pathogenic properties.
The result will be an imbalance, which causes an unpleasant odor. It is felt especially strongly during menstruation.
Failure to comply with hygiene rules
It is very important for a woman to keep her own genitals clean. However, not everyone treats this responsibly. Cleanliness of the genitals is especially important during menstruation, because otherwise the unpleasant odor will be felt by others.
Regardless of the intensity or volume of discharge, a woman must adhere to hygiene every day. You cannot buy and use large tampons or pads only for the purpose of changing them less often. It is in such cases that the discharge stinks, since mucus and blood accumulate on the lining materials. They heat up and as a result begin to decompose. It does not matter in what quantity these secretions are.
It happens that the discharge lingers in the vagina itself. This is possible when menstruation is light, but long (last days). If a woman regularly neglects cleanliness during her period, this can cause big troubles. Major problems appear with the internal reproductive organs, mucous membranes, and skin.
Preventive measures
An unpleasant odor and atypical discharge not only bring discomfort, but are also a signal from the body about possible violations. No one is immune from the occurrence of diseases accompanied by these symptoms.
But a woman can reduce the risk of pathologies by following basic prevention rules. These include the following:
- Protected sexual contact will reduce the risk of infectious diseases. The best option for protection is the use of condoms.
- To prevent inflammatory processes, overheating and hypothermia of the reproductive organs should be avoided . Particular care must be taken during the cold season.
- Proper nutrition reduces the likelihood of thrush. Its development is provoked by baked goods and sweets. It is advisable to avoid using them.
- It is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist. The doctor may suspect the presence of gynecological diseases based on visual signs.
- Hygienic procedures should be carried out 1-2 times a day, and during menstruation at least 3 times a day.
- The body's resistance to harmful bacteria depends on the strength of the immune system, so you need to monitor the state of its defenses.