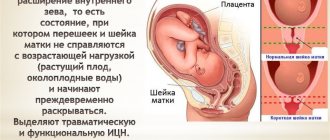
The process of natural childbirth is a complex mechanism, the launch of which includes changes in the functioning of several fundamental systems of the female body: fetoplacental, hypothalamic-pituitary and uterine homeostasis itself. A pregnant woman’s cervix is not always ready for childbirth, despite the timing of the baby’s birth.
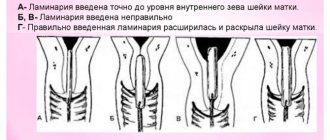
The cervix is an anatomical structure of the female genital area that serves as a barrier to the uterine cavity. During the first stage of labor, the process of expulsion of the fetus is completely determined by the degree of cervical dilatation. During the last months of gestation, the pregnant woman’s body undergoes the process of preparing the reproductive organs for childbirth, which ultimately, at 38–42 weeks, triggers a cascade of hormonal reactions leading to full uterine contractions and dilatation. But this doesn't always happen. The cervix may not be ready for labor, which may lead to the need for a caesarean section.
Before childbirth, the cervix softens, shortens, and as the internal os opens, it takes a central position. The listed factors play a serious clinical role for doctors; specialists use them to determine the method of labor management. Starting from the 38th week, routine examinations of the cervix occur to check its softening. When she is ready to give birth, it speaks of her maturity. But only a gynecologist can determine this during a routine examination.
During the first routine examination, the cervix may not yet be fully mature; this is not a reason to worry, because changes can begin within a few days.
Sometimes softening occurs quite quickly just before birth. When there is no required dynamics, the gynecologist can advise the patient on what to do to speed up the process.
Timely softening of the cervix will avoid obstetric trauma. When the cervix is immature, the risk of rupture increases. The most popular and frequently used drugs for softening the cervix are gels. They make it possible to soften it quickly and painlessly.
Important
Currently, a gel for softening the cervix is considered the simplest method of stimulating labor. A gel inserted into the vagina provides an artificial prenatal hormonal balance. Such softening gels contain prostaglandins - substances that in the body of a pregnant woman begin to trigger the process of childbirth. They contribute to the smoothing and opening of the cervix. After using the product, labor can begin within four hours. The specific time of the onset of labor corresponds to the individual characteristics of the pregnant woman’s body.
For normal childbirth, dilation should reach 10 cm. Prostaglandins have been used in obstetric practice for 20 years. They have proven themselves to be highly effective drugs that imitate natural labor.
For normal birth, dilation should reach 10 cm.
Prostaglandins have been used in obstetric practice for 20 years. They have proven themselves to be highly effective drugs that imitate natural labor.
Why is the gel used, what is its effectiveness?
The gel accelerates the natural processes of childbirth by stimulating uterine contractions. In the absence of pathologies during pregnancy, such a remedy will help prepare the cervix and give birth to a healthy baby, eliminating the risk of carrying it without causing harm to the mother’s health.
The gel contains prostaglandins - these are biologically active substances that are produced in our body. These are natural substances, they are found in different quantities in all types of tissues of a healthy person, but the largest amount is concentrated in the amniotic fluid.
As a rule, the closer the birth is, the higher the concentration of prostaglandins in the woman’s body. When this amount reaches its peak, the cervix becomes softer, in addition, this substance stimulates the contraction of smooth muscles.
If a woman has hormonal imbalances or malfunctions of the endocrine system, the natural amount of prostaglandins is not enough to start the labor process in a timely manner. The gel introduced into the cervical cavity replenishes the supply of prostaglandins, and the problem with the absence of contractions is stopped.
A gel may also be prescribed if the fetus is too large. In this case, this remedy greatly facilitates the process for the mother in labor and will shorten the time of labor.
Cases in which administration of the gel is recommended:
- the birth process began, but there was a malfunction, which caused the birth to be delayed;
- pregnancy for a period of 42 weeks, without the presence of precursors of labor;
- pregnancy up to 40 weeks in the presence of oligohydramnios, an aged placenta or a poor biochemical blood test;
- the cervix is not dilated (or not fully dilated);
- when the amniotic fluid has receded and there are no contractions;
- irregular weak contractions;
- the presence of gestosis (late toxicosis of pregnancy, in which complications may arise in the form of disorders of the child’s systems and organs);
- sudden cessation of contractions;
- high blood pressure;
- dangerous kidney disease in a pregnant woman.
The gel is strictly contraindicated for:
- health problems of the mother in labor;
- non-standard position of the baby in the uterus;
- when the size of the mother’s pelvis does not correspond to the child’s head (if the fetus is large);
- if a child has a pathology.
Gels based on prostaglandins
Modern obstetrics prefers to use prostaglandin-based gels to soften the cervix. They exactly repeat the structure of active substances that are produced in the mother’s body before and during childbirth. In addition to the main effect of the gel on stimulation, it helps to quickly soften the cervix, thereby promoting the development of softer contractions without spastic components. Unlike oxytocin, prostaglandins do not disrupt uteroplacental blood flow.
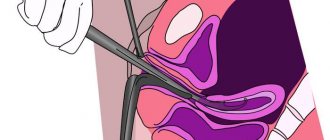
Softening gels are a sterile product with a volume of 2.5 mg. For insertion, the woman lies on her back and the gel is injected into the posterior vaginal fornix. The doctor constantly monitors the management process using gynecological mirrors.
It is prohibited to introduce the gel into the cervical canal - this will provoke hyperstimulation of labor. To prevent the product from leaking out, the patient should remain in a lying position for half an hour.
After administration of the gel, the patient's condition is assessed every 6 hours. If positive dynamics in the dilatation of the cervix are not evident, then the gel is injected again. The cervix should dilate by at least 3 cm within 4 hours. The maximum dosage is 3 mg.
The decision on re-introduction is made only by the attending physician after assessing the current situation.
The dose of the gel determines the desired result:
- 1 mg is administered for weak labor.
- 2 mg are administered in the complete absence of labor after a single injection.
The third time the gel is not used, and against the background of the first two applications, the patient’s well-being, contractile activity of the uterus and the condition of the child are constantly assessed.
How to administer the gel correctly?
Delivery of prostaglandins is carried out by introducing a gel into the cervical canal of the cervix. Usually the drug is available in disposable syringes filled with gel to a volume of 2.5 ml. The procedure for introducing the gel takes place on a gynecological chair, the contents of the syringe are poured into the posterior vaginal fornix, since insertion directly into the cervix is strictly not recommended.
After the procedure, the pregnant woman lies without changing position for 30 minutes to prevent the drug from leaking out. From the moment the active substances begin to act and until contractions appear, it takes from 40 minutes to 4 hours (it all depends on the individual characteristics of the mother’s body).
After 6 hours, the cervix softens and opens by approximately 3 cm. The readiness of the cervix for childbirth is determined if it is completely softened and shortened to 1-2 centimeters, and the cervical canal allows one finger or more to pass through (dilated to 10 cm). The immature cervix is firm or slightly softened, tilted back, may be closed or barely allow part of a finger through. In this case, the procedure is carried out again.
Important! The introduction of cervical gel should be carried out exclusively in a hospital setting. In case of complications, qualified assistance can only be provided by a specialist using special equipment.
From the very beginning of the procedure, the woman in labor and the fetus must be under the careful supervision of a doctor, who will monitor the process, focusing on the health status of the participants in the birth process.
With a correctly calculated dose, absence of contraindications and correct assessment of data, the possibility of complications is reduced to zero.
Indications and contraindications
Do not forget that any artificial stimulation of labor has risks, so doctors use this and other methods in extreme cases in accordance with indications.
With the correct dose and professional administration of the gel, it does not cause side effects compared to other medications and methods (oxytocin, Foley catheter).
Contraindications include:
- discrepancy between the size of the child’s head and the volume of the woman’s pelvis;
- deterioration of fetal CTG parameters confirmed on a cardiac monitor;
- breech and other types of pathological presentation of the fetus in the womb;
- contraindications to natural labor;
- presence of placental abruption;
- placenta previa - its close location to the internal os;
- location of the umbilical cord vessels below the baby’s head;
- the presence of a thinned scar on the uterus;
- large fruit;
Independent use of the gel is strictly prohibited, because in some cases it still causes side effects, namely:
- a strong increase in uterine tone, up to tetanus, when placental abruption occurs and the death of the child;
- sometimes when administering the gel there is a risk of intrauterine fetal hypoxia, and regular cardiac monitoring will be required for timely detection of such a complication;
- the gel can have a systemic effect on the body, that is, provoke an exacerbation of bronchospasm if a woman has bronchial asthma or a chronic form of obstructive bronchitis.
The listed deviations indicate that the drug can be administered only in hospital settings. A pregnant woman and child require constant dynamic medical supervision.
Possible side effects
Only the doctor decides on the use of the gel. In women giving birth, the drug may cause side effects:
- hypertonicity of the uterus;
- nausea, vomiting;
- uterine rupture;
- rise in temperature;
- allergic reactions.
Adverse reactions can also develop in the fetus:
- abnormal heart rate;
- deterioration in the assessment of the child’s condition immediately after birth on the Apgar scale;
- manifestation of distress syndrome;
- in rare cases, stillbirth.
Over a long period of use of the gel to soften the cervix, it has proven itself positively due to its ease of use, a small list of contraindications and good results. The gel activates and normalizes labor and the production of endogenous oxytocin.
What gels are used?
The most popular gels for softening the cervix and stimulating the labor process are Prepidil and Prostin E2.
"Prostin E2"
This drug is available in two forms: tablets and gel. The active substance is prostaglandin E2 (or dinoprostone) - an artificially synthesized prostaglandin similar to natural one.
The initial dose of intracervical gel is 1 milligram. It is inserted into the posterior vaginal fornix. If there is no effect, the dose is repeated after 6 hours, in the amount of the initial or double dose.
For endocervical administration, the dose is 0.5 milligrams and is injected into the cervical canal using a catheter. The localization of the injection is below the internal pharynx. The waiting time in the gynecological chair is about 15 minutes.
The effect of the drug is to contract the smooth muscles of the uterus and cervix, induced softening, smoothing of the cervix and its opening, increasing its blood supply.
Side effects may include hypertonicity of the myometrium, tetanic contractions of the uterus, compression of the baby, decreased fetal Apgar status, nausea, diarrhea or vomiting.
The drug is contraindicated for patients with hypersensitivity, early surgical interventions on the uterus, more than six pregnancies, fetal distress, discrepancy between the volume of the mother's pelvis and the child's head, genital tract infections, bloody discharge, and ruptured membranes.
"Prepidil"
This drug also contains dinoprostone. Gel for endocervical administration is available in syringes; the kit includes a catheter.
The gel helps stimulate labor, improves blood supply to the uterus, increases the contractile activity of the myometrium, reduces the resistance of the cervix, promotes the opening and softening of the cervix.
Achieving the maximum concentration of prostaglandins is achieved after a period of 30-40 minutes after activation of the active substance, then their level declines.
Contraindications for use include: a history of cesarean section, surgical interventions on the uterus, or its previous mechanical damage, the presence of infection of the lower tract of the reproductive system.
Contraindications may be due to adverse effects on the gastrointestinal tract, effects on the fetus (acceleration of the child’s heart rate, fetal distress is observed). The method of application is similar to “Prostin-E2”.
Important! Information about the drug is given for general information; the use of the above gels can only take place as prescribed by a doctor and in full compliance with the instructions.
Gel for the cervix during childbirth is an effective means of stimulating the process. When used correctly, the occurrence of complications is minimal, and the drug itself has a very gentle effect and does not affect the health of the mother and baby.
Video: Induction of labor at 38-42 weeks - Dr. Elena Berezovskaya
Video: oxytocin during childbirth
Prepidil mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of the gel is that it stimulates the softening and ripening of the cervix.
The active substance contained in the drug is an unsaturated fatty acid. Such substances are synthesized under physiological conditions.
The specificity of Prepidil gel is to increase blood supply to the cervix, which significantly accelerates its ripening - it softens, smoothes and opens. All these indicators characterize normal labor; they reduce the degree of cervical resistance, enhance the contractile capabilities of the myometrium and lead to successful natural delivery.
Do not be afraid of the gel intended to soften the cervix. The doctor necessarily studies the history of pregnancy and, in accordance with the individual characteristics of the woman, chooses labor management tactics. It is important to completely trust the specialists - then both stimulation and childbirth will be successful.