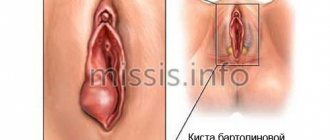
A Bartholin gland cyst is a pathological cavity with rounded shapes, its own wall and purulent contents inside. The appearance of such a formation in the large glands of the vaginal vestibule is associated with infection and raises many questions among women who are faced with the problem for the first time.
For example, gynecologists often have to answer questions of the following nature:
- Is it worth removing a Bartholin gland cyst?
- can a Bartholin gland cyst resolve on its own?
- what to do when a Bartholin gland cyst ruptures;
- Are there options in which the cyst in the Bartholin gland does not need to be removed?
Services table
| Service name | Price |
| Initial consultation with a gynecologist | 2,300 rub. |
| Ultrasound gynecological expert | RUB 3,080 |
| Insertion of an intrauterine contraceptive device | 4,500 rub. |
| Hysteroscopy | RUB 22,550 |
| Repeated consultation with a gynecologist | 1,900 rub. |
| Taking a smear (scraping) for cytological examination | 500 rub. |
| Laparoscopy (difficulty category 1) | 61,000 rub. |
| Program "Women's Health after 40" | RUB 31,770 |
| Treatment of the cervix (medication) in 1 procedure | 800 rub. |
| Diagnostic curettage | 12,000 rub. |
The answers to them are collected in the article.
GET A FREE CONSULTATION
By clicking on the button, you consent to the processing of your personal data
Causes
Let's start with a brief anatomical excursion.
Bartholin's glands are located in the vestibule of the vagina. Their main function is to produce a secretion that is secreted during sexual intercourse for lubrication and to create a special microflora that protects against certain types of bacteria. The glands are named after the Danish anatomist Caspar Bartholin, who first described this paired organ in the 17th century. Inflammation of the glands creates ideal conditions for the unhindered penetration of microbes into the vagina. The woman begins to feel dryness, turning into itching. Convulsive scratching injures the delicate skin of the genitals, which only worsens the situation, contributing to the progression of the inflammatory process.
Possible causes of bartholinitis (or disruption of the Bartholin glands):
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- insufficient genital hygiene;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- wearing tight or synthetic underwear;
- sexual intercourse during menstruation;
- surgeries on the genitourinary organs, incl. abortions;
- local microtraumas (scratches, cracks, tears).
Indirect or enhancing factors that increase the risk of developing bartholinitis include: hypothermia, stress, weakened immunity due to chronic or acute diseases.
Currently, the exact causes of the formation of Bartholin gland cysts in women are unknown, but the risk factors are similar to those for sexually transmitted infections. Some of the risk factors include:
- a history of cysts;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- presence of sexually transmitted infections;
- episiotomy during childbirth or other trauma to the vaginal vestibule;
- low parity of births (less than 2 births);
- insufficient toilet of the external genitalia;
- inaccurate depilation, leading to damage to the skin in the area of the vaginal vestibule and labia minora;
- wearing tight, uncomfortable underwear;
- excessive sexual intercourse.
Also, factors such as congenital narrowing of the gland ducts and changes in the consistency and viscosity of secreted secretions cannot be excluded as causes for the formation of Bartholin cysts. The latter can happen due to various conditions associated with metabolic disorders in the body.
Treatment after surgery for Bartholin gland cysts, its features and nuances
After enucleation of the Bartholin gland cyst, the postoperative period involves a course of antibacterial treatment. The general treatment regimen includes the following points:
- taking antibiotics (they kill the infection that led to inflammation of the Bartholin gland duct and the formation of a cystic capsule);
- a course of anti-inflammatory drugs;
- applying gauze bandages with anti-inflammatory and wound-healing ointment (Levomekol) to the surgical wound;
- applying cold (ice in a bag wrapped in cloth) during the first hours or days after surgery (this method helps relieve pain and reduce swelling at the wound site);
- treatment of postoperative sutures with antiseptic solutions 2-4 times a day (brilliant green, iodine, chlorhexidine are used for this purpose);
- 1-2 weeks after surgery, the woman should undergo a course of physiotherapeutic procedures (they are prescribed by a gynecologist).
The patient should remember that an excised Bartholin gland cyst (photo) may recur after surgery. This happens due to non-compliance with medical requirements during rehabilitation. If relapses occur constantly, the gynecologist decides to remove the gland completely. This option is undesirable for young girls, as it subsequently leads to difficulties in their sex life.
Marsupialization does not require any special procedures or medications. The woman will only need to refuse intimate contacts so that the installation does not fall out. It is also recommended to protect your body from colds to prevent re-inflammation of the Bartholin gland.
After extirpation for bartholinitis, treatment will be required for the recovery period. It involves a course of antibiotics and other medications aimed at preventing inflammation in the near future of rehabilitation. The woman is also prescribed applications with medicinal ointments and physiotherapeutic sessions (UHF, magnets). This will help soothe pain and tugging in the vaginal area and prevent the wound from becoming infected.
Intimate life after surgery to remove purulent bartholinitis is allowed no earlier than a month later. Some patients have to increase the period of abstinence due to problems with wound healing.
Symptoms
Symptoms of bartholinitis can be divided into general and specific (local). General signs include all signs of intoxication: high fever, chills, headache, lack of appetite. Blood tests show an increase in the number of leukocytes and the ESR parameter.
Spicy
Fever is an indicator that bartholinitis is developing in an acute form. It is not difficult to confuse the disease with ARVI or any infection, because there are also local symptoms. This is a swelling in the labia majora area. A cyst with bartholinitis has a rich red color and is painful when pressed.
Chronic
The acute form of bartholinitis can sometimes be treated conservatively (with antibiotics in the form of tablets and injections). If you miss the moment, the disease will become chronic and will often recur. Chronic bartholinitis is treated only with surgery.
Women suffering from chronic bartholinitis experience pain and burning during almost every sexual intercourse. And each time the immunity decreases, the disease manifests itself more clearly, causing symptoms of general intoxication and increased swelling. And it is unknown when a relapse can become critical: sometimes a cyst with bartholinitis becomes inflamed and swells so much that it becomes difficult and painful for a woman to urinate.
Canaliculitis
There is another type of bartholinitis - canaliculitis. Although, rather, this is one of the forms of the disease, meaning the very first stage.
Canaliculitis is suppuration of the excretory ducts of the Bartholin glands, which are located between the entrance to the vagina and the labia minora.
The inflammation looks like a pimple through which pus is initially released. Then the duct is completely clogged, and purulent masses accumulate in the gland. This is how a swelling forms, which partially blocks the entrance to the vagina.
Depending on whether inflammation is present in the cyst, the clinical picture of the pathology and its possible consequences develop.
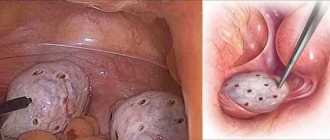
If the cyst is small and not infected, practically nothing bothers the woman. She may discover it by accident. The cyst can be felt at the base of the labia majora as a round, soft formation, mobile, painless.
If the cyst is large, the external genitalia are deformed on its side, and the genital slit has an irregular shape. A “mound” appears – a raised formation above the unchanged skin. As the tumor increases in size, it interferes with normal sex life and even walking.
In the "acute" period
When inflammation occurs, the symptoms of a Bartholin gland cyst become more pronounced. The following is noted:
- sharp or even throbbing pain in the area of the cyst;
- a painful ridge is visible under the skin;
- the labia may swell;
- the fireplace is hot to the touch;
- Fever, chills, weakness, and lethargy appear.
As inflammation progresses, a false abscess of the Bartholin gland may form. In this case, the contents of the cyst are filled with pus. A high temperature rises, the woman notices throbbing pain in the labia area, and it is impossible to walk due to swelling and pain.
Often the false abscess opens on its own, after which the woman feels noticeably better. It can also develop into a true one, in which case the gland tissue itself is exposed to active inflammation.
As a rule, Bartholin cysts do not cause discomfort and are asymptomatic. In such cases, only an obstetrician-gynecologist can detect a cyst during a routine annual gynecological examination. However, the condition may worsen when the cysts become large. The main complaints made by women with a Bartholin gland cyst include the following:
- discomfort and “strange” sensations in the perineum while walking or sitting;
- unpleasant or even painful sensations during sexual intercourse;
- a feeling of fullness in the perineum, labia minora on the affected side;
- redness and a feeling of pulsation in the area above the cyst;
- asymmetry of the vulva;
- fluctuation on palpation;
- increased sensitivity when palpating the cyst area.
All of the above symptoms are characteristic of uncomplicated, that is, non-inflamed Bartholin gland cysts. If for some reason the cyst becomes infected and an inflammatory process develops, then the symptoms of this condition will be much more severe and can even significantly reduce the woman’s quality of life. Symptoms of an inflamed Bartholin cyst include:
- increased body temperature;
- chills;
- drowsiness, decreased performance;
- acute pain in the perineum;
- pain on palpation of the external genitalia;
- redness of the mucous membrane over the cyst;
- purulent discharge from the mouth of the excretory canal
- swelling of the outer labia;
- enlarged inguinal lymph nodes.
If you experience the above symptoms, then you urgently need to seek help from an obstetrician-gynecologist, since the Bartholin gland cyst does not go away on its own and requires mandatory comprehensive treatment.
A Bartholin gland cyst does not bother a woman in the first stages of its development, and has practically no external manifestations. At the same time, with the increasing size of the Bartholin gland cyst, the symptoms (in the photo) are visible to the naked eye:
- the area of skin near the outlet of the gland turns red and becomes denser;
- purulent masses are released when pressing on the ball under the skin;
- if the Bartholin gland is completely clogged, the symptoms are complemented by the release of a large amount of pus;
- pain appears in the area of the external genitalia;
- the patient is overcome by malaise and increased weakness;
- performance decreases sharply;
- the temperature rises (in some women with bartholinitis its levels reach 40 °C).
A false abscess occurs due to incomplete closure of the Bartholin gland duct and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- inflammatory process in the excretory duct;
- redness, pain, swelling of the Bartholin gland;
- mobility of the skin over the developed abscess;
- the Bartholin gland can protrude greatly due to a cyst and block the entrance to the vagina;
- When walking and active body movements, severe pain appears.
An exacerbation of a false abscess occurs in the case of a staphylococcal or gonococcal infection or E. coli entering the external genitalia. Against this background, the size of the Bartholin glands increases and the first abscesses form.
If an infectious agent enters the tissue of the Bartholin gland, a real abscess (abscess) develops. As a result of pathological processes, the parenchyma tissue in the gland is transformed, and the skin over the site of inflammation becomes immobile.
Bartholinitis with the addition of true suppuration is accompanied by the following external manifestations:
- severe swelling of the labia;
- incessant sharp pain in the perineum (usually one-sided);
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin;
- high temperature (up to 40 °C);
- the formation of an extensive abscess inside the Bartholin gland (it can be easily felt by palpating the inflamed area).
An abscess with a real abscess of the Bartholin gland can spontaneously open, but this does not lead to complete emptying of its capsule. After a short period of time, it again fills with pus.
Doctors recommend opening a true abscess with bartholinitis in a hospital setting. Spontaneous rupture of the abscess leads to the outflow of pus. This process, in turn, is accompanied by the appearance of pathological discharge from the vagina, infection in the genitals and the development of inflammation (vaginitis, vulvitis).
Symptoms of a Bartholin gland cyst are similar to the primary signs of cancer of this organ. In order not to trigger a more dangerous disease, you need to know what Bartholin gland cancer is, the symptoms and characteristic signs of this malignant oncological formation in the glandular ducts.
With cancer, as with benign cysts of the Bartholin glands, the following general symptoms occur:
- constant fatigue, physical weakness even with a minimal amount of exercise or immediately after a night’s sleep;
- a slight increase in body temperature that persists for a long period of time;
- rapid weight loss (up to 10% of initial values).
There are also local symptoms that can be used to judge the nature of the tumor (malignant or benign). Thus, the following manifestations are characteristic of Bartholin gland cancer:
- itching in the perineum;
- psychological problems due to which the patient refuses to engage in sexual relations;
- bleeding from the vagina, which is a consequence of hormonal imbalance and is practically resistant to the action of hemostatic drugs;
- thick vaginal discharge, emitting a putrid odor (it comes from the decay products of tumor tissue);
- pain syndrome that occurs already at stages 1-2 of cancer and is accompanied by severe unpleasant sensations due to mechanical impact on the inflamed area.
get a free consultation
Timely diagnosis of Bartholin gland cysts will help eliminate the possibility of developing a malignant tumor.
Bartholin gland abscess
If treatment for inflammation of the Bartholin gland is not started in time, the disease will develop and worsen. Until one day pus begins to accumulate in the gland itself - an abscess of the gland will occur. It develops quickly - in less than a week the abscess can grow up to 8-10 cm.
- False. When it occurs, the exit channel is blocked, the liquid is not able to be removed. It is caused by the accumulation of fungi, various coccal microorganisms, and anaerobic microbes in the organ.
- True. With this form of the disease, purulent degeneration of the tissues of the gland itself begins. Sometimes caused by gonococci, most often occurs with gonorrhea. It can also be caused by other pyogenic microbes. It can also develop with untreated false abscess.
Symptoms
The disease begins suddenly and acutely. Severe and cutting pain can even wake you up at night.
- The patient's temperature rises sharply and quickly - up to 39 degrees, she feels weakness and chills.
- Pain occurs in the pelvic area and labia majora.
- Painful sensations intensify while walking, visiting the toilet, and difficulty sitting.
- The pain intensifies when lying on the side on the side of the inflamed gland.
- Sexual intercourse becomes almost impossible due to swelling, which often closes the entrance to the vagina. When palpated, the labia majora is hot and hard, with pronounced hyperemia. Skin mobility is still maintained.
If urgent measures are not taken, the false abscess will develop into a true one. Its symptoms are deeper than those of a false one. Its onset can be determined by the characteristic symptom of sudden softening of the swelling.
- The woman's condition worsens even more - the temperature rises to 40 - 40.5 degrees, she exhibits signs of intoxication, severe chills, and headaches.
- Pain in the pelvis intensifies, becomes constant, sharp and throbbing, swelling increases even more
- The skin is motionless, scarlet, very painful on palpation
- The lymph nodes in the groin are enlarged.
Treatment
Treatment of an abscess is more complex and lengthy than for simple inflammation. At the very beginning, things may be limited to conservative methods using antibiotics and general hygiene procedures.
In complicated forms, when the abscess is already large, an operation to drain it is necessary. An abscess of the gland is rarely single-chamber; more often there are many foci. And during manipulation it is necessary to drain each one, otherwise the disease will relapse.
This method of treatment is not very effective, since after a while the abscess occurs again. This happens due to the fact that the edges of the opened passage stick together - a layer of epithelium does not have time to form on them. To prevent this from happening, a special catheter is installed while the epithelial layer is forming.
Drainage is carried out if an abscess is formed. There is no point in doing this before.
It happens that all manifestations of inflammation of the Bartholin gland occur in a hidden, mild and blurred form, without an increase in temperature and all the symptoms of the disease. This is how subacute bartholinitis manifests itself. It still needs to be treated, otherwise the phenomena of general intoxication and poisoning of the body will accumulate and intensify. Such long-term untreated inflammation carries a serious threat of degenerating into a malignant formation.
Recommendations for women after surgery to remove a Bartholin gland or a cyst in it
After proper examination in the clinic and the patient is allowed to undergo surgery, surgical intervention is prescribed. Currently this can be done in several ways. It all depends on what results the examination by the doctor showed. Based on them, he prescribes the required method, each of which has a different execution technique. Among the main ones are:
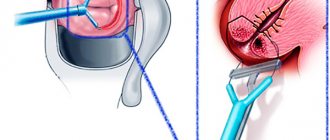
- Marsupialization is the most common method of cyst removal. It is done using a scalpel, with which the surgeon opens the tumor, clears the node of secretions, disinfects and suturing it. The operation is carried out using painkillers.
- Vaporization - in this case, the procedure is performed using a laser. This is a relatively new treatment method, which is based on the evaporation of secretions from the node under the influence of thermal energy. After this, sclerosis is carried out, that is, tissue compaction in the place where the swelling was. The method is also painful and therefore requires local anesthesia.
- A puncture is not a treatment, but rather the removal of the secretion itself. It is pumped out with a special device, but the cause of the tumor is not eliminated. That is, in this case there is a high risk that the problem will reappear in the patient.
- Husking is a serious operation, since the entire node with the secretion is cut out at once, capturing part of the healthy tissue. The procedure is not easy, so it is performed under anesthesia. The rehabilitation period is much longer than for others, and there is a risk of complications.
- Trimming the gland - this method is used only if others have failed. Then the paired Bartholin organ is removed and the place where it was is simply sutured.
These tumor removal techniques are effective and are still used today. The required method of operation is prescribed by the doctor who examined the patient. They are different in cost, but the price does not differ much. For example, if you take clinics in Moscow, then on average they will charge about 10,000 rubles for such an operation.
Moreover, about 30% of this amount goes to pay for infiltration anesthesia, which is much better than conventional painkillers. After it there are practically no side effects. Accordingly, if you refuse such a service, it will be cheaper, but the recovery period will last a little longer.
To minimize the risk of relapse after removal of a cystic formation in the Bartholin gland, the patient should carefully monitor her health and adhere to the following tips:
- at night, insert gauze swabs soaked in Miramistin or Chlorhexidine into the vagina;
- wash the wound daily with antiseptic solutions (for example, Betadine);
- use ointments with a healing effect only after all the pus has come out of the opened cystic cavity (otherwise the thick gel will clog the outlet and a purulent abscess will form again);
- carry out disease prevention, take measures to prevent relapses (wash yourself thoroughly and correctly, performing the procedure in such a way that the flow of water from the shower is directed from the external genitalia to the anus, and not vice versa);
- for preventive purposes, wash with antibacterial decoctions of medicinal herbs, use condoms during sexual intercourse, wear loose underwear;
- contact a doctor immediately after the onset of inflammation (this will help to identify the pathology at an early stage and treat it without surgery).
Complete excision of an organ leads to certain problems for a woman during sexual intercourse and severe bleeding during surgical procedures. Sex after removal of the Bartholin gland becomes painful, and intercourse causes discomfort. This happens due to the lack of lubrication that the removed gland previously produced. To eliminate this inconvenience, a woman has to use artificial lubricants throughout her life before intimacy with her partner.
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland
This gland disease is observed most often. According to statistics, 2% of women have one form or another. In some of them, the disease occurs in such a smoothed and asymptomatic form that the woman does not even realize that she has a source of infection and learns about it only when examined by a doctor.
Types of inflammation
The disease manifests itself and proceeds in different ways, it all depends on the nature of the inflammation and the place where it arose.
Acute
Usually unilateral, when one of the glands becomes inflamed. When both become inflamed, the doctor has reason to suspect the patient has sexually transmitted diseases.
At first, the disease is asymptomatic, but all signs of the disease appear very quickly. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, a false and then a true abscess may develop.
Subacute
It is characterized by all the same manifestations as in acute inflammation, but occurring in a mild, blurred form.
With these two types of bartholinitis, complete recovery is possible. But more often it becomes chronic.
Chronic type
There are periods when this inflammation does not manifest itself in any way, but the process continues anyway, and an exacerbation occurs. It can be triggered by anything - hypothermia, stress, flu, and so on. During exacerbations, all the manifestations of acute bartholinitis are present.
Most often it ends in the formation of a cyst. This disease cannot be cured conservatively; surgery is necessary.
Recurrent (recurrent) bartholinitis
Its course is a bit like chronic. With the difference that sometimes the disease subsides, there are no foci of inflammation in the body. But under certain circumstances (hypothermia, stress, and so on), it appears again and relapses. The disease is in acute form. Such relapses can be repeated many times.
The disease is difficult to treat conservatively, most often ends in an abscess, and surgery to remove the Bartholin gland may be necessary.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on examination and history taking of the woman. Additionally, vaginal material is collected for a smear, as well as for subsequent bacteriological examination in order to prescribe adequate antibacterial therapy. How to distinguish bartholinitis from other conditions is described in the table.
Table - Diseases similar to bartholinitis
StageDisease or conditionDistinctive features
| During the "cold" period | Varicose veins | - Appear in the labia area; - more common during pregnancy in the 2nd and 3rd trimester; - pronounced cyanosis, tortuosity; - no clear boundaries and no “ball” feeling |
| Gland cancer | — Formation of irregular shape and any size is determined; - it is “fused” with the skin and surrounding tissues | |
| In the "acute" period | Acute bartholinitis and abscess of the Bartholin gland | — It is necessary to take into account the woman’s medical history, in which she has not noted cysts before; — the clinical picture is almost identical to cyst inflammation |
| Furuncle or carbuncle | — Symptoms of intoxication are not so pronounced; - can be located anywhere on the labia, most often in the area of hair growth; - no significant tissue swelling |
Diagnosis of Bartholin gland cysts usually does not cause difficulties for an obstetrician-gynecologist. If you suspect you have this condition and complain to your doctor, he will take the following steps to confirm the diagnosis:
- will ask in more detail about your complaints and feelings;
- will examine the external genitalia;
- perform a speculum examination of the cervix and vagina;
- take smears for flora and atypical cells;
- will conduct a two-hand study.
If there is a suspicion of an infectious lesion of the cyst, it may be necessary to additionally undergo a clinical blood test, a urine test, and a culture of the secretion discharged from the gland.
Usually this volume of diagnostic procedures is enough to make a diagnosis, but it is worth carrying out a differential diagnosis of a benign disease with other pathological conditions of the vulva. Typically, the doctor has to exclude diagnoses such as glandular cyst of the vaginal vestibule, papillary hidradenoma, lipoma, fibroma, angiokeratoma and cancer.
Diagnosis of a Bartholin gland cyst involves a complex of medical procedures.
- Examination by a gynecologist.
- General blood test (during acute purulent processes, red blood cells settle in the blood at a higher rate, a shift of rod neutrophils to the left is observed).
- General urine test (with inflammation in the body, the number of leukocytes in the urine increases).
Correct separation of cysts from conditions with similar symptoms is of particular importance in diagnosis. Ordinary papillomas, which arise as a result of the proliferation of gland tissue on both sides, can be confused with a cyst. Swelling due to a pimple on the labia minora or clitoris also has nothing to do with a Bartholin cyst.
A thorough study of the structure and characteristics of the Bartholin gland cyst helps to identify concomitant pathologies and differentiate benign formations. The following activities are being carried out in this direction:
- bacteriological analysis of genital smears for sensitivity to antibiotics and to identify the pathogen;
- general blood analysis;
- carrying out enzyme immunoassay and PCR to detect sexually transmitted infections;
- Ultrasound of the Bartholin gland (an additional research method that is used to classify a neoplasm, allows you to check the extent of the purulent process, diagnose a false or true abscess);
- blood test for biochemistry.
To diagnose a Bartholin gland cyst, doctors examine smears taken from the lining of the vagina. A bacterioscopy is performed to determine the type of infection, the microbial composition of the biomaterial, and to exclude the possibility of symptoms similar to sexually transmitted infections. The diagnostic results help the gynecologist develop the correct treatment regimen for the patient.
How does an abscess open?
A true abscess of the Bartholin gland is a direct indication for an autopsy procedure.
Such manipulation is well processed today, so you should not be afraid of it.
Such an intervention is carried out even for pregnant women, which once again indicates its complete safety for the body. How is the procedure done? Doctors make careful cuts (usually no more than three), opening the cavity with pus. After which the accumulated liquid is released. The gland is washed with a solution of hydrogen peroxide (3%). Often a special tube (drainage) is inserted into the cavity; this is necessary to remove the remaining pus, which will accumulate for some time before the final recovery. The corresponding tube is removed after five to six days.
Simultaneously with these measures, hypertonic saline solution can be used. It’s quite easy to make at home; add 3 level tablespoons of salt to 1 liter of warm purified water. Mix the mixture thoroughly until completely dissolved, then moisten a clean gauze swab and then apply it to the injured area. Antibiotics (other means necessary to combat the pathogen) work quite well; in addition to them, applications with ointments are used.
The treatment process usually takes place in a hospital setting. Here the patient can be provided with bed rest and the absence of disturbing factors, in addition to sexual rest. You should also avoid any stress. If there are other medical recommendations, it is also reasonable to adhere to them.
List of restrictions for Bartholin gland cyst after surgery
Removal of a Bartholin gland cyst in the postoperative period involves some prohibitions for the patient. These include:
- sexual contacts (sexual activity after removal of a Bartholin gland or cystic tumor is prohibited for 4 weeks);
- taking hot baths, visiting a bathhouse, sauna or solarium;
- wearing tight underwear that interferes with the blood supply to the external genitalia;
- alcohol consumption;
- uncontrolled use of medications, self-medication without prior consultation with a gynecologist;
- playing sports, lifting weights, strenuous exercise.
A woman should temporarily exclude all of the above factors from her life. The main limitation for the patient is more careful control over her own lifestyle. You have to go on a diet, take medications, attend physiotherapeutic procedures, and perform dressings. After the completion of the rehabilitation period, many prohibitions are lifted, but doctors recommend that a woman prevent the appearance of new cysts in the Bartholin gland.
It is necessary to strengthen the immune system, take care of intimate hygiene and adhere to a healthy diet. Of great importance in the prevention of inflammatory diseases and the formation of cystic tumors in the Bartholin glands is the timely treatment of concomitant pathologies (thrush, gonococcal and streptococcal infections).
What's happened
Near the entrance to the vagina there are sebaceous and sweat glands, necessary for the production of secretions that moisturize the mucous membrane of the genital organs and protect the vulva from the effects of pathogenic microbes and microorganisms.
The largest is considered to be the Bartholin gland, which is a paired organ reaching about 1-2 centimeters in size. During normal functioning, it cannot be felt, and it does not cause any discomfort.
This neoplasm has a number of features. Only unilateral formation of a cystic tumor is noted. Bilateral lesions are diagnosed in extremely rare cases.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Differences between cytology and colposcopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2021
In addition, the tumor can grow to a size of 10 centimeters in diameter.
Also, the peculiarity of such a cyst is that during its development there is no hormonal imbalance.
The neoplasm has a tendency to recur.
Complications of the cyst
Despite the fact that the Bartholin gland is a fairly small structure, complications arising from the presence of cyst complications can have significant consequences for a woman’s fertility and can even be a factor in the occurrence of infertility. This happens because a woman with such a pathology cannot engage in sexual intercourse due to painful and unpleasant sensations, and without this, conception is impossible.
You can get a free consultation on the website, where experienced doctors with extensive experience will tell you whether you are at risk of developing fertility problems due to Bartholin gland pathology.
Complications of Bartholin gland cysts include the following pathologies:
- Chronization of the process. If the patient does not seek medical help in a timely manner, then this pathology becomes chronic and then it will be possible to cure it only by radical removal of the gland, which, as we found out earlier, is painful and traumatic.
- Formation of fistula tracts. Pus from an inflamed cyst can form passages and break out, thereby forming fistulas from which the purulent contents of the cyst will constantly drain. The location of the fistula tracts is unpredictable; they can open on the skin, as well as inside the pelvic organs (bladder, vagina). Such conditions require additional surgical intervention.
- Spread of the inflammatory process to other pelvic organs. Along the ascending path, infection from the vulva can move higher and cause colpitis, endometritis and adnexitis. Since the opening of the urethra is located in close proximity to the cyst, the infection can spread to the organs of the urinary system, causing inflammatory diseases such as cystitis, urethritis and pyelonephritis.
Long-term persistence of infection and inflammation in the organs of the genitourinary system leads to irreversible changes and disruption of their function. Women develop persistent, intractable chronic pelvic pain syndrome and fertility problems. Chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs are the number one cause of infertility in women.
- Cancerous transformation of Bartholin gland cyst. Although cystic transformation of the gland is considered a benign process, under the influence of a number of factors and circumstances, the epithelium of the gland can undergo cancerous degeneration. Bartholin's gland, which is affected by the oncological process, quite often cannot be treated due to late detection, when time has already been lost. In such cases, most often there are already metastases.
Complications that can result from a Bartholin gland cyst deprive a woman of the opportunity to have sex. The reproductive functions of the body are at risk; a patient with bartholinitis cannot conceive and give birth to a child. In this regard, it is important to know what consequences a Bartholin gland cyst has if it is not treated at all or it is too late to tell the doctor about the problem.
Possible complications of bartholinitis are as follows.
- Transition of a disease from an acute state to a chronic phase. If a woman does not turn to doctors for help in a timely manner, the course of bartholinitis worsens, and resolution of the problem becomes possible only through surgical intervention. Prolonged inflammation leads to the fact that the body tries to protect other organs from the effects of infection, and therefore forms a protective capsule around the lesion, called a cyst. Inside this capsule, when favorable factors appear, pus accumulates.
- Formation of fistulas. Excess pus in the cyst leads to its rupture and the formation of a special channel (fistula), through which the pathological fluid flows. The opening of the fistula can be located on the surface of the skin or in adjacent internal organs (bladder, vagina). A fistula on the skin looks like a large ulcer through which pus leaks. Internal fistulas are very rare and are detected using a contrast study. These formations take a long time to heal and often require surgical intervention to cleanse the remaining purulent fluid.
- Development of the inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system. Vulvitis, cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, colpitis, andexitis occur if an infection from the inflamed Bartholin glands penetrates the vagina. This is facilitated either by the anatomical proximity of these 2 organs, or by the appearance of a fistula in the cyst. Patients with such complications complain of itching in the vagina, swelling of the mucous membranes of the vulva, fever, inflammation of the clitoris and labia minora. Women with inflammation of the genitourinary organs suffer from painful urination, menstrual irregularities, lower back pain, and purulent vaginal discharge.
- Sepsis. Gynecologists call this type of complications with a Bartholin gland cyst one of the most dangerous. It can only be compared with Bartholin gland cancer, which occurs due to the complete lack of treatment for cystic formations. Sepsis develops when pus destroys the walls of blood vessels, enters the bloodstream and is carried by its current to other organs and systems. Against the background of sepsis, the patient may develop purulent meningitis, and the heart is affected due to septic endocarditis. Such an acute condition is complemented by unfavorable external symptoms. The woman’s temperature rises to 40-41 °C, bruises appear all over her body, convulsions appear, blood pressure drops, and against this background a state of shock develops, consciousness is impaired (some patients even fall into a coma). Cardiopulmonary failure is added to this clinical picture.
- The Bartholin gland, in which cancer rarely forms, sometimes still undergoes malignant changes. In the first stages of development, cancerous tumors in the gland can be confused with a cyst. The symptoms of these two pathologies are similar. The patient's temperature rises, bleeding is possible, and purulent vaginal discharge appears. The Bartholin gland (photo showing the clinical manifestations of oncology), affected by cancer, is often difficult to treat due to lost time. If the diagnosis of malignant tumors is made late, the cancerous tumors metastasize to other organs (usually bone tissue or lungs).
If there is no treatment for a Bartholin gland cyst, unfavorable factors associated with it can provoke the transition of a benign formation to oncology.
If a woman develops a lump after removal of the Bartholin gland, its nature may be malignant. Cancer of the Bartholin glands affects the tissues located in the vestibule of the vagina. Most often, the tumor forms on one side, on the labia majora. Its localization in the first stages does not extend beyond the gland.
Pain after removal of the Bartholin gland can be caused by cancer that was not noticed by medical specialists in time. A woman with a malignant tumor in the vagina experiences severe discomfort at the site of the tumor. Due to the fact that the primary stage of Bartholin gland cancer is similar in its symptoms to a cyst, the doctor may confuse the diagnosis.
Treatment
If a gynecological consultation specialist during diagnostics discovers the patient’s Bartholin’s glands with inflammation, conservative and symptomatic treatment is prescribed. The absence of complications of the disease eliminates the possibility of hospitalization. The patient undergoes an outpatient therapeutic course, following all the instructions of the attending physician.
How to treat inflammation of the Bartholin glands in the hospital
Diagnosis of inflammation of the Bartholin gland, treatment, photos of pathological abnormalities from an X-ray machine - all these possibilities are now easily realized thanks to modern equipment installed in gynecological departments. Every woman, if alarming signs appear, should visit a specialized medical facility, and not self-medicate at home. After all, only in a gynecological clinic can you accurately determine the essence of the problem and undergo a course of effective treatment.
Diagnostic measures in the gynecological office (tests, x-rays, ultrasound) help the doctor detect inflammation in the Bartholin gland and develop treatment (photo) on an individual basis, taking into account the characteristics of the pathology. Treatment of bartholinitis in the day hospital of the women's department is carried out in compliance with the following methods and requirements:
- heat or cold (with ice) compresses applied to the site of inflammation;
- drug therapy using antibiotics;
- prohibition of sexual contacts until complete recovery;
- compliance with bed rest.
If a woman has an inflamed Bartholin gland, gynecologists will tell you what to do in such a situation. With such a pathology, doctors immediately recommend undergoing a course of treatment with antibiotics. Typically, broad-spectrum drugs are used for these purposes. For example:
- penicillins with a semi-synthetic composition;
- macrolides;
- cephalosporins.
It must be taken into account that pathogenic bacteria that provoke the inflammatory process are insensitive to the components of medications. To find out the existence of this problem, culture of the purulent contents is carried out. Before the results of the diagnostic procedure are obtained, a set of antibiotics is selected experimentally.
The doctor may sometimes add imidazole, fluoroquinolone, or other antibacterial medicinal compounds to the general treatment regimen. You may also need symptomatic therapy with the use of antispasmodics and analgesics, which will help eliminate pain and relieve inflammation.
The development of purulent abscesses in the Bartholin gland is a reason for hospitalization. Women with this complication are treated in a gynecology hospital, most often undergoing surgical intervention.
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland - surgery, when is it necessary?
The first indication for surgery for acute bartholinitis is the occurrence of a purulent abscess in the cyst. When inflammation is diagnosed in the Bartholin glands, treatment is developed by the doctor according to a comprehensive scheme. During surgery, the pus is cleaned out, and postoperative therapy is based on the use of antibacterial medications. When all purulent masses have been removed from the cystic capsule, the empty cavity is washed with an antiseptic solution (hydrogen peroxide is most often used for this purpose). The final stage of surgery is the installation of drainage. If the rehabilitation period after surgery is successful, the drainage tube is removed after 1 week.
Chronic forms of bartholinitis are also treated with surgery. However, the achieved therapeutic result is not as stable as when fighting an acute inflammatory process. Opening and washing the cyst from pus in the chronic course of the pathology does not allow achieving a complete recovery. The cystic walls eventually fuse with each other, and the duct completely closes. There are only 2 ways out of this situation:
- formation of an artificial duct (marsupialization);
- complete excision of the Bartholin gland (extirpation).
Marsupialization is more often used by specialists in the field of gynecology. This method of surgical treatment is considered more gentle and is suitable for women who often experience relapses of the disease, large cysts form, and conservative therapy does not give the desired result.
Surgical procedures involve the doctor forming a new duct to remove secretions. A small incision is made in the cyst, then a tube with a ball at the end is inserted into it. The free edge of the catheter remains outside, and a balloon is inflated through it, trapped inside the cystic formation. It increases in size, fixing the catheter and preventing it from falling out. 4-5 weeks after the completed manipulations, the ball is deflated and the catheter tube is removed from the cystic cavity. In the allotted time, a new duct is formed, through which the secretion from the Bartholin glands comes out.
Removal of Bartholin's glands is a last resort measure that surgeons use very rarely. This type of operation is fraught with complications and severe bleeding, because the gland is located next to a large bundle of blood vessels. The technique is used only if it is the only possible one (for example, with frequent relapses of a purulent inflammatory process, or after an unsuccessful marsupialization procedure).
The rehabilitation period after excision of the Bartholin gland is 1 week. To speed up the healing process, the patient is prescribed UHF and magnetic therapy. It is also recommended to lubricate the operated area with special ointments with a healing effect, and to undergo the phonophoresis procedure.
Postoperative prognosis for surgery on Bartholin's glands depends on the timeliness of the woman's visit to the hospital. The sooner the patient comes to the doctor, the more favorable the result will be.
Inflammation of the Bartholin glands - treatment at home
The patient can treat the Bartholin gland with inflammation at home after agreeing on the chosen therapeutic regimen with the attending physician.
If the Bartholin gland is inflamed, first aid at home is aimed at relieving acute symptoms:
- severe pain;
- inflammation;
- swelling.
A woman should not thoughtlessly apply home treatment methods to prevent the development of a purulent process. Before using this or that therapeutic method, she needs to consult a doctor. During the period of exacerbation of the inflammatory disease and during treatment, you need to provide the body with rest, move less and lie down more, stop playing sports, and temporarily exclude intimacy with your partner. Below is a list of ways to treat an inflamed Bartholin gland at home.
- Cold. The effect of cold compresses made from frozen water helps to quickly relieve swelling during bartholinitis. Before the procedure, water is frozen in a special refrigerator container or plastic bubble. The prepared ice is wrapped in a thick cloth and applied to the inflamed area for 20-30 minutes. The procedure is repeated several times, changing the ice and taking 15-minute breaks.
- Painkillers. Long-term painkillers will alleviate a woman’s condition, remove painful manifestations, relieve swelling, and have a powerful anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effect. The best among these drugs are Diclofenac, Ketorolac and Dolaren. But it is worth paying attention to the fact that the listed drugs cannot be taken for stomach ulcers, impaired blood clotting and intestinal problems. If the patient suffers from such problems, to improve her condition with bartholinitis, it is better for her to give preference to paracetamol.
- Ointments. Wound-healing, antimicrobial, regenerating agents in the form of ointments will help cope with suppuration, stimulate and strengthen the immune system, relieve inflammation, and promote rapid healing of wounds and purulent ulcers. Among the numerous pharmaceutical medications recommended for inflammation of the Bartholin glands, the best are Vishnevsky Ointment, Levomikol and Levosin. Ointments for bartholinitis should not be rubbed into the skin over the inflamed area. The drug is applied to a gauze bandage and carefully applied to the affected area.
- Natural immunoregulators. Saturating a female body weakened by illness with a complex of microelements and vitamins will help restore and strengthen the immune system. During drug treatment of bartholinitis, it is recommended to eat foods enriched with vitamins A, C, E (antioxidants). Their deficiency in the body leads to disruption of immune processes, reduces cell protection, provokes protracted illnesses, frequent infections and constant relapses of inflammation and suppuration. Vitamin supplements are taken before meals or during meals, because this is how they are better absorbed.
- Antiseptic solutions. Irrigation of the affected areas with disinfectant solutions of Miramistin, Chlorhexidine or decoctions based on natural herbs, chamomile, calendula, oak bark will help destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
- Vaginal suppositories. Thanks to suppositories for inflammation of the Bartholin gland, treatment at home becomes effective and demonstrates a quick and expected therapeutic result. Most often, for home treatment of pathologies of the bulbovaginal glands of the vestibule, medications in the form of suppositories are used - Terzhinan or Metrogyl. Terzhinan contains antibiotics, therefore it has a fungicidal and antibacterial effect on the body. Another component of the medication, prednisolone, helps relieve inflammation. You need to insert the suppositories deep into the vagina before going to bed, taking a lying position. Metrogyl or medicinal compositions of similar action (Klion, Metronidazole, Trichopolum) contain active ingredients that kill the causative agents of trichomoniasis. These suppositories are used 1-2 times a day, 1 piece at a time.
The therapeutic effect on inflamed Bartholin glands will become more powerful and effective if you use medicines from the folk piggy bank as an addition to the main methods. Salt lotions, baths with the addition of buds and leaves of chamomile, birch, celandine, oak bark, yarrow, and St. John's wort help well. Teas and decoctions made from rose hips, with the addition of lemon, young birch leaves, elderflower, sage, oregano, linden blossom, and St. John's wort will help strengthen the immune system and eliminate inflammation.
Contraindications
A hollow node appears due to blockage of the Bartholin gland, which moisturizes the vagina. Accordingly, if it does not function, this place will dry out and the woman will feel discomfort. The doctor will prescribe surgery to remove a Bartholin gland cyst if several problems arise:
- swelling in the labia minora area - when inflammation spreads to other parts of the genital organ;
- abscess - occurs when the body does not function properly or an infection has entered it;
- discomfort – if a woman feels pain when walking or having sexual intercourse;
- tumor breakthrough - when the cyst reaches a large size, the tissue holding it back bursts.
If the patient suffers from at least one of these signs, it is better to have surgery and forget about the disease. If the tumor progresses quietly, surgical intervention can be avoided. Perhaps it will subside on its own after a while. However, this disease has a high relapse rate, so it is not a fact that the problem will not appear again.
Removal of a pathological neoplasm cannot be done without surgery. During the operation, anesthetics are used to dull the pain. The patient may have a congenital allergy to anesthesia and similar drugs. In this case, it is better to refuse the operation.
Anesthesia itself puts a strain on the cardiovascular system, and many people refuse it on their own. That is, the cyst removal procedure can be completed without painkillers. Then the patient will have to endure. According to women who have already experienced the operation, the pain threshold of the operation is quite tolerable.
Contraindications to cyst removal can be objectively divided into two groups:
- general - this includes the state of the body as a whole, when the patient is suffering from any infectious or chronic diseases;
- local - this category includes disorders of the intimate and genitourinary areas.
If there are additional problems, there is a risk of complications after surgery. There are no other contraindications, since the operation is not classified as severe and does not last long.
Preparation stage
Before removing a cyst, you need to consider some nuances. Treatment can be done in two ways, with the most commonly used outpatient approach. That is, the patient is at home and takes the medications prescribed by the doctor. She should come for examination periodically so that the doctor can monitor changes.
If they go for the worse, the patient is offered surgery. In this case, a little preparation is needed. Serious surgical preparation is not required for this, since the procedure is one of the easiest and lasts for an hour.
Before the operation, the patient needs to be examined in the clinic. Go through a routine gynecological examination and then laboratory tests. Doctors will determine possible contraindications, although they are rare.
Before the operation itself, the patient should also take into account some points:
- the intimate area needs to be put in order, that is, washed well, and all hair removed from it. This will greatly facilitate the surgeon’s work and protect the body from infection;
- Before the procedure, you need to empty your bladder, that is, go to the toilet.