Authors | Last updated: 2019
Modern gynecology offers many different methods of physical and chemical influence on the cervix, and all these procedures are commonly referred to in one word - cauterization. It doesn’t matter which method is used - laser, radio waves or liquid nitrogen, the goal is the same - to remove the pathological formation and relieve the woman from the unpleasant symptoms of erosion. A lot can be said about the benefits of cauterization, but it is worth mentioning the possible unwanted complications after the procedure.
Unfortunately, even the most modern methods are not absolutely safe for women. The consequences of cauterization of cervical erosion can be unpredictable, and it is difficult to predict in advance how the manipulation will affect the patient’s health. When deciding on a procedure, you should weigh the pros and cons, evaluate the possible risks and make sure there are real indications for destructive treatment. Only if you have complete information about your own health can you agree to undergo any therapy for cervical erosion.
Advantages and disadvantages
Each method of cauterization of cervical erosion has its own advantages and disadvantages. Many years of experience of specialists in the treatment of underlying cervical diseases allows us to choose the available types of cauterization. Some methods are expensive and rarely used. Others are considered budgetary and can be carried out in each medical institution. The consequences of the manipulation are also different. Cauterization in some ways does not lead to the appearance of scars on the mucous membrane, while others cause the formation of connective tissue in the treated area.
Today there is no ideal method that would suit all women without exception. Otherwise, alternative methods would not be considered by doctors. By studying each treatment option individually, we can talk about specific advantages and disadvantages.
- Cauterization of erosion using the radio wave method is performed without pain and does not require anesthesia. In the future, a woman can give birth naturally, since there are no scars left on the mucous membrane. The disadvantage is the low prevalence and high cost of treatment. The procedure is carried out more often in private clinics. It is difficult to find government medical institutions that have a radio wave apparatus.
- Removing erosion using current is a painful procedure and requires the use of anesthesia. The advantages of the procedure include extensive experience of specialists in this treatment, low cost and accessibility. The manipulation is effective and rarely leads to relapse. The disadvantage is that subsequently cicatricial deformation of the cervix occurs, and during the rehabilitation period there remains a high risk of bleeding and infection.
- Cauterization of erosion with a laser beam. The procedure can be performed without anesthesia as it is not painful. The advantages of this treatment include high efficiency, absence of bleeding, rapid recovery and minimal risk of infection. The disadvantage is the high price. In addition, most government medical institutions do not perform laser cauterization.
- Removing erosion using liquid nitrogen. The undoubted advantage is the speed of execution, high efficiency and absence of scars after recovery. The disadvantages include pronounced symptoms of the recovery period and the lack of total doctor control over the depth of penetration of low temperatures.
- Treatment with chemicals. A plus is the accessibility and possibility of carrying out the procedure for nulliparous women. This technique does not cause pain and does not involve tissue injury. The disadvantage is the low efficiency and high cost of chemicals. Often the procedure has to be repeated several times.
How long does it take for erosion to heal after cauterization?
Among all gynecological problems, cervical erosion is the most common pathology. It is found in more than half of women during routine examinations. One of the common methods of treating erosion is cauterization.
Cauterization of erosion is carried out using several methods:
- Diathermocoagulation. The basis of the diathermocoagulation method is the heating effect of electric current. Subsequently, a “crust” forms, under which healing of the affected tissue occurs. Then a scar is formed - this is a significant disadvantage of DTC.
- Cryodestruction. CD - destruction of an eroded area under the influence of liquefied nitrogen. The advantageous difference between CD (and other methods) and DTK is the absence of scar tissue after exposure.
- Chemical coagulation. Based on multiple chemical erosion treatment. solutions. This method has a significant drawback - a high probability of relapse.
- Laser exposure. This is vaporization - a method of “evaporation” of damaged tissue under the influence of laser radiation.
- Radio wave exposure. This method is the least painful and most gentle, but the most expensive. In addition to destroying erosion, the radio wave method has a disinfecting effect on fabrics.
Consequences of the effect on the cervix during cauterization by any method:
- complete recovery;
- incomplete recovery;
- recurrence.
Long-term consequences after cauterization of cervical erosion can be:
- deformation of the cervix;
- violation of cervical patency.
This provokes:
- the likelihood of spontaneous abortion due to decreased cervical tone;
- the possibility of ruptures during labor.
Due to these consequences, the use of DTC in nulliparous patients is not recommended.
What is erosion
Cervical erosion is a mucosal defect that can occur for a number of reasons.
These may be mechanical injuries, hormonal imbalances, hereditary predisposition, infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
The clinical picture of the disease, as a rule, is not clearly expressed, so most often erosion is diagnosed in an advanced or complicated form.
Cervical dysplasia is considered a dangerous complication of erosion, which can become an impetus for the development of cancer.
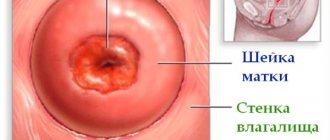
True erosion is a wound on the mucous membrane that can bleed. It is a gateway for various infectious pathogens, which, having penetrated the mucous membrane, can affect not only the cervical region, but also spread further, leading to serious diseases of the genital organs.
If true erosion is not detected and treated in time, it goes into the next stage - pseudo-erosion, accompanied by the replacement of flat epithelial cells of the mucous membrane with cylindrical ones, and this can lead to the formation of adhesions on the cervix, which can cause big problems during pregnancy and childbirth.
There is another type of erosion - congenital. This is the safest form of the disease, which in most cases does not require treatment, and most often goes away on its own after the girl reaches puberty.
- The most effective way to get rid of erosive lesions of the mucous membrane is the cauterization procedure.
- How dangerous is this method of treatment and is it necessary to cauterize the erosion?
- There cannot be a definite answer to this question, since everything depends on the cauterization method, the woman’s plans for childbirth later, the woman’s age, her condition and the presence of background ailments.
- There are several ways to cauterize erosion:
- Each of them has its own indications and contraindications, which the doctor must take into account when prescribing one or another treatment method.
- As with any surgical intervention, any cauterization method can have negative consequences, which will be discussed below.
What is meant by the inflammatory process?
Erosion (Latin for “corrosion”) is a chronic inflammatory process in the cervix. Characterized by the presence of a wound or ulcer on the cervix. There are 2 types of erosion :
- True . Actually erosion with an inflamed and bleeding surface. It is diagnosed extremely rarely, since in most cases it heals within 2 weeks.
- Ectopia . Pseudo-erosion. It develops as a consequence of true erosion, when healing occurs in a pathological way. In this case, the squamous epithelial cells that normally make up the outer vaginal part of the cervix are replaced by columnar epithelial cells that line the internal os of the uterus.
Pseudoerosion of the cervix is the most common gynecological pathology, which is detected during a gynecological examination in every fifth (and according to some data, every third) patient.
Erosion, as a rule, occurs against the background of an inflammatory process. If inflammation is not treated, the pathological process constantly recurs, erosions become inflamed, and, in turn, provoke inflammatory processes. In addition, the altered epithelium with false erosion does not have the ability to prevent infection from entering the uterus.
Recurrent inflammatory erosions can degenerate into cancer cells. The situation is aggravated by the fact that at an early stage, cervical cancer does not visually differ from ordinary inflammatory erosion.
Causes and treatment of pain due to cervical erosion
The manifestations and symptoms of cervical erosion are minor: rarely can a woman independently understand that a problem has arisen in the area of the cervical canal and the outer cervical surface.
Pain in the lower abdomen, which occurs with cervical erosion, is most often caused by diseases in nearby organs. If there is heavy vaginal discharge, it may be inflammation.
Sometimes abdominal troubles begin before menstruation, but this symptom is characteristic of endometriosis. If you experience any pain, you should consult a doctor who can identify the disease and prescribe treatment.
Can pain occur during erosion?
Often, a woman first learns about cervical pathology during a routine examination by a gynecologist. The reason for this is simple: cervical erosion does not hurt. In the normal uncomplicated course of the disease there will be no suspicion or discomfort.
Pain in the lower abdomen is possible due to inflammation that occurs with any genitourinary diseases: after visiting a doctor, when examined on the mirrors, the specialist will see an eroded surface on the outer part of the cervix.
The pain is not associated with erosion, but with diseases of neighboring organs, so the doctor will prescribe an examination that will help identify the causes of the pathology.
What is the cause of pain syndrome
The eroded surface on the outer part of the cervix is the result of the action of microbes. The infection causes inflammation, which causes damage to the cervical surface and cervical canal.
Sometimes primary changes occur due to injury or hormonal disorders, and microorganisms act on the cervix secondary. In any case, the infection spreads throughout the pelvic organs.
Pain in the lower abdomen due to cervical erosion occurs against the background of the following diseases:
- cystitis (acute disease or exacerbation of a chronic bladder process);
- urethritis (infection in the urethra);
- endometritis (inflammatory process inside the uterus);
- cervical canal polyp (benign neoplasm in the cervical canal);
- colpitis (vaginal infection);
- salpingitis (inflammation in the fallopian tubes);
- oophoritis (penetration of microbes into the ovaries);
- adnexitis (chronic or acute inflammatory process in the reproductive organs);
- external or internal genital endometriosis;
- uterine leiomyoma.
The intensity and severity of pain varies. A woman should pay attention to any pain that occurs in the lower abdomen. At your first visit to the doctor, the specialist will definitely ask about the nature of the pain.
What is the nature of pain against the background of erosion?
Often, periodic or constant pain in the lower abdomen is associated with the menstrual cycle, but pain can appear regardless of the menstrual days. It is imperative to pay attention to the connection with urination: with cystitis and urethritis, pain occurs when visiting the toilet. Possible options for pain in the lower abdomen:
- pulling,
- pressing,
- aching,
- stabbing,
- cutting.
Against the background of inflammation in the ovaries and uterus, hormonal problems may arise, which will be manifested by the following changes:
- the menstrual cycle is disrupted (untimely arrival of menstruation, heavy or scanty periods, pain in the first days of menstruation);
- breasts swell and hurt;
- there is no desired pregnancy.
When a woman undergoes examination and treatment for erosion on the cervical surface, it is necessary to promptly inform the doctor about all changes associated with the regularity of the menstrual cycle or any atypical symptoms.
These problems are caused by hormonal imbalances that need to be identified and treated.
What examination is required for pain syndrome?
Any pain that appears against the background of existing erosion in the cervix requires treatment. Together with your doctor, you need to identify the causative factor by performing the following studies:
- examination on mirrors and taking smears for common infections;
- general clinical urine analysis;
- bacterial cultures from the vagina and urine;
- special research for infections affecting the cervix and cervical canal (PCR for chlamydia, papillomavirus, genital herpes, mycoplasma);
- transvaginal ultrasound;
- colposcopy.
Based on the examination results, the doctor will prescribe therapy that will help get rid of pain and inflammation and normalize the menstrual cycle. Then it will be necessary to prepare for the removal of cervical pathology, especially if there are significant indications for cauterization or surgery.
If, with cervical erosion, there is pain in the lower abdomen, then it is necessary to look for the cause of these problems. The doctor will prescribe diagnostic tests and treatment to relieve pain, which has nothing to do with a cervical problem, but is most often caused by inflammatory diseases of the female genitourinary organs.
We recommend reading how to use suppositories in the treatment of cervical erosion.
Source: https://gynecologyhelp.ru/eroziya-shejki-matki/boli.html
Tests before cauterization
Before cauterizing erosion, gynecologists must prescribe a preliminary examination. To avoid complications, the patient must undergo tests:
- On TORCH infections.
- Determine the type of HPV that is present in the body.
- General blood test and biochemistry.
- Vaginal smear to determine microflora and cytology.
In addition to laboratory diagnostic procedures, instrumental and hardware examinations are prescribed. The supervising method is colposcopy. This procedure allows you to determine the risk of degeneration of altered cells into a malignant tumor and choose the right treatment method.
Is it painful to cauterize erosion?
There has long been an opinion about the removal of cervical erosion that this procedure is painful and requires a long recovery. However, modern methods of treating underlying diseases make it possible to do without the use of anesthesia.
If you cauterize cervical erosion with an electric current, there will be pain. This manipulation is one of the first methods of treatment and has been used for many decades. Previously, treatment was performed only by this method, which created a stereotype about the painfulness of the procedure.
Removing erosion with modern devices destroys the myth that cauterizing the cervix is painful. Moreover, some procedures can prevent bleeding and tissue infection.
Cauterization: what is it and is it necessary to do it?
Cervical erosion is a defect of the mucous membrane that occurs under the influence of various factors. The cause may be hormonal imbalance, infection, injury or other conditions. A variety of techniques are used to treat cervical diseases, and cauterization is one of them. This term refers to one of the following methods of influencing erosion:
- Chemical coagulation - cauterization with drugs;
- Diathermoelectrocoagulation (DEC) – exposure to high frequency current;
- Argon plasma ablation - the use of argon to destroy erosion;
- Cryodestruction – use of liquid nitrogen;
- Laser vaporization – evaporation of a pathological focus with a laser beam;
- Radio wave coagulation - cutting off erosion with radio waves (modern Surgitron and Fotek devices are used).
All these manipulations are called destructive methods of treatment. In special cases, conization is performed - excision of a section of the cervix (usually with deep lesions and cancer).
On a note
To treat erosion in nulliparous women, laser, radio wave and argon plasma cauterization are used.
Destructive treatment methods are prescribed only after a complete examination of the patient, colposcopy and taking a smear for cytological examination.
Video colposcopy is a method of examining the walls of the vagina and the outer part of the cervix, which uses a special microscope and a video device that allows you to display an image on a monitor screen.
In some cases, medications are used to treat erosion. If cauterization is unavoidable, the doctor should familiarize the woman with the peculiarities of this procedure and talk about the possible consequences of the manipulation. The choice of a specific treatment method will depend on the type of pathological formation on the cervix, its size, as well as the age and reproductive status of the patient.
When to start treating erosion
So you gave birth to a baby, waited for the postpartum period, accompanied by bleeding, visited your doctor and found out about the presence of an unpleasant “sore”. You want to get rid of it quickly, but there is one thing - you are breastfeeding the baby.
Many doctors advise to refrain from any treatment during this period, because with the slightest complications, you will have to take medications, which can have a detrimental effect on the baby.
I don’t want to scare you, but as with any surgical intervention, there can be complications after treatment, after cauterization. Although they are not as scary as with NO treatment.
Also, many are tormented by the question - when to cauterize erosion? Before your period or after? There is no clear answer here. For example, regular cauterization is best done after menstruation, but there is no specific time for radio wave surgery and chemical coagulation.
That is, it all depends on which treatment method you choose.
Complications
Complications of the cauterization procedure are normal and pathological.
Normal - discharge mixed with blood, pain during the recovery period.
These phenomena are observed throughout the period of restoration of the damaged surface of the cervical mucosa.
The healing period after cauterization is about a month. Discharges are observed throughout this time, but their nature changes over time.
For up to ten days, the discharge is serous, transparent, and watery. Their number is small.
Then over the next ten days their volume increases, a little blood is added to the clear liquid, and the consistency becomes more viscous. Then for several more days there is a separation of a thick white liquid.
At the end of the healing period, the discharge is brown, in small quantities, and after DTC, small dark fragments may fall out (these are crusts falling off the forming scar).
Main methods of treatment
The altered cells of the cervix are treated using different methods. When choosing a method, the doctor takes into account:
- patient's age;
- desire to realize reproductive function in the future;
- what is the clinical picture of the disease;
- what the colposcopy showed;
- what budget does the patient have?
Diathermocoagulation
The method of removing cervical erosion by electric current has been used for many years. This technique is carried out in a day hospital and involves the use of anesthesia. Within 15-30 minutes, the doctor treats the eroded area, resulting in cell destruction. After the procedure, the woman remains under medical supervision for some time.
During the recovery period, blood is released from the genital tract for 7-14 days. The patient may also experience pain during rehabilitation. Tissue healing takes an average of 3 months. Subsequently, after cauterization of the cervical erosion, a scar is formed on the mucous membrane.
The procedure is contraindicated for nulliparous girls and those who are planning a pregnancy in the future.
Diathermoexcision
Excision of the cervix does not involve cauterization of erosion, but complete removal of the pathological area of tissue. This technique is described in medical reference books, but is not usually used in practice. Diathermoexcision is a highly traumatic method of treatment and can lead to adverse consequences. If it is necessary to perform excisional intervention, alternative and more gentle methods are chosen.
Radio wave methods
Radio wave removal of cervical erosion is preferred if the patient has the appropriate budget. The procedure is expensive, but worth it. The essence of the treatment is to cauterize the tissue between the healthy and pathological layer. The liquid in the cells heats up and evaporates.
The recovery period after the procedure does not exceed one month. Immediately after cauterization of the cervix, the woman can go home. The absence of scars allows the procedure to be performed even for nulliparous patients.
Laser vaporization
Another advantageous cauterization method is laser beam treatment. The procedure involves non-contact and painless treatment. The duration of the manipulation does not exceed half an hour.
When erosion is destroyed, the laser beam simultaneously coagulates the vessels. This avoids bleeding during the recovery period. The laser also has an antiseptic effect, which reduces the risk of infection to zero. Healing of the mucous membrane lasts 1-1.5 months. The absence of scars allows laser cauterization to be prescribed to nulliparous girls.
Cryodestruction
If cervical erosion does not affect deep tissues, cryodestruction can be performed. This method involves treating pathological areas with liquid nitrogen. As a result, the changed areas are split, and healthy tissues remain uninvolved.
After cryodestruction, connective tissue does not appear on the mucosa. However, during treatment, the doctor cannot control how much internal tissue is processed. If cauterization is insufficient, the procedure must be repeated again.
Chemical coagulation
Minimal preparation for cauterization of cervical erosion is carried out if it is planned to treat the mucous membrane with medications. Unlike other procedures, this technique does not require tissue destruction using any devices. The essence of this treatment is to treat the affected mucosa with medicinal substances that contribute to the destruction of pathological cells. Chemical coagulation is carried out several times until the eroded area is completely healed, therefore it is considered a long-term and high-cost procedure.
After cauterization occurs, the tissues are completely restored, and scars do not appear on them. This makes it possible to prescribe treatment to young patients.
Pain after cauterization of cervical erosion
Methods for removing erosion: freezing, using a radio knife (Surgitron device), cauterization with electric current, laser coagulation, chemical burning with Salkovagin cream.
The consequence of the operation or when and how pain in the lower abdomen appears after cauterization of cervical erosion:
- Drawing, aching pain, as if menstruation has begun, is noted on the first day, you can take an antispasmodic,
- Irregular pain, turning into a feeling of discomfort, occurs during physical activity;
- Bloating and internal discomfort;
- Regular discharge of exudate (vaginal discharge);
Attention! Of particular danger are severe pains accompanied by discharge with the smell of rot, which is a sign of complications and requires examination by a gynecologist.
Cervical erosion (violation of the integrity or change in the mucous membrane) is found in every third woman, and is practically painless, and only routine examinations can detect the disease at an early stage and prevent malignant degeneration. The disease is practically asymptomatic, so it is worth paying attention to the signaling organism and starting treatment on time.
Pain after conization of the cervix
This is a surgical procedure during which pathological tissue is removed and the excised neck becomes cone-shaped, used for diagnosis and treatment.
If the lower abdomen hurts after conization of the cervix, the pain is nagging, like menstrual pain, and brown discharge is observed - these are normal symptoms that the conization was carried out perfectly.
Diagnosis of pain in the lower abdomen
A routine examination by a gynecologist is carried out at least once every six months. When interviewing a doctor, it is necessary to clearly give answers and describe the existing symptoms. If, for example, the uterus and cervix hurt during pregnancy, this may be a sign of cervical dilatation. Having found out why the cervix hurts, the specialist provides approximate diagnoses:
- Erythroplakia – thinning of the mucous membrane;
- Ectropion – cervical canal with signs of everted mucosa;
- Leukoplakia is a modification of epithelial skin areas that develops after operations and injuries;
- Cervical erosion;
- Pseudo-erosion, or ectopia;
- It is necessary to take a smear for flora and carry out a cytological examination;
The specialist’s diagnosis is confirmed by performing a gynecological examination of the vagina, cervix and vulva using speculum and a colposcope.
Many women believe that after a colposcopy the lower abdomen hurts and are worried about having it done, but when they begin to experience pain in the cervix when walking, they change their minds.
Even dilation of the vagina with speculums causes painful sensations for sensitive women; it is recommended to immediately tell the doctor to use a smaller size of instruments. Colposcopy is painless; the patient only experiences a feeling of anxiety, a feeling of pressure, and a slight spasm.
Attention! If a woman begins to experience sharp, causeless cramping pain, with a burning sensation when urinating, sometimes nausea and even vomiting is possible, with loss of consciousness, most likely an ovarian rupture has occurred, and an emergency call to the ambulance is required.
Pain after suturing the cervix
In patients at high risk, cervical monitoring is carried out at 12 weeks, checking how low the cervix is. The operation of suturing the cervix (suture) allows you to preserve the pregnancy, since it is the closed state, without allowing the cervix to open, that allows you to hold the fetus and protect it from infection.
Cervical dilatation is isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI) or weakening of the uterine muscles. Pregnancy can shorten the cervix, which also makes surgery more difficult. If the indications for the operation and the vital activity of the fetus are confirmed, doctors apply a suture, protecting the fetus and the patient from premature birth, warning of possible pain after the operation.
Possible pain after suturing the cervix:
- Nagging pain with the tone of the uterine walls (the anterior wall of the uterus and, accordingly, the posterior wall of the uterus, these are the points of attachment of the placenta, and methods for determining the presentation of the fetus);
- The lower back begins to hurt and the lower abdomen ache;
- A feeling of heaviness, as if the fetus were pressing on a suture;
- If it hurts to sit down, try to walk around a little, stretch your legs, or better yet, if you are at home, lie down;
- If you have discharge containing a bloody clot, it is better to inform your doctor.
Helps determine how successful the suturing was: a follow-up visit to the attending physician, ultrasound diagnostics.
At week 37, the doctor will decide to remove the suture to prepare the woman for childbirth; after the procedure, the baby can be born at any time.
Attention! If nagging pain and heaviness continue for more than a few days, this is a sign of complications and you should call a doctor.
Pain after cervical biopsy
A clarifying gynecological examination if dysplasia or cancer is suspected is called a cervical biopsy. Only the results of a test for the benignity of the cells allow the gynecologist to draw up a treatment plan. The procedure is very painful and is performed under the influence of an anesthetic injection or general anesthesia.
If, after a cervical biopsy, the lower abdomen hurts and is accompanied by spotting for up to 7 days, as well as pain in the depths of the vagina and the body temperature rises to 37.5°C, these are symptoms that the biopsy was performed correctly.
Attention! In rare cases, a complication may occur, including heavy bleeding, smearing for 7 days, discharge with an unpleasant odor, fever over 37.5 ° C, you need to call a doctor.
Pain after cervical amputation
A low-traumatic surgical intervention prescribed for pathological conditions of the genital organs. Amputation is prescribed for patients:
- In the early stages of cancer, which is detected if there is pain with cervical cancer. This pain is characterized as a lumbago in the lower back, sacrum, lower abdomen, rectal area, pain in the left side and left thigh. Added to the pain are foul-smelling bleeding, spotting and leucorrhoea. In advanced cases, cervical cancer is characterized by the appearance of contact bleeding resulting from minor injuries, such as cycling, pain in the cervix when walking, etc.
- Analysis of cervical cells revealed malignant changes;
- With a hypertrophied cervix;
- With chronic endocervicitis;
- With ectropion, when the mucous membrane of the cervical canal is inverted;
- With the regular appearance of erosions;
- With a deformed cervix, when uterine prolapse is noted.
If the pain after amputation of the cervix is very severe, an anesthetic is prescribed. These pains include:
- The pain from the installed urinary catheter is temporary, as it will be removed very quickly;
- It begins as if it were shooting in the lower back;
- As if it begins to pull in the lower abdomen, in case of lifting weights of more than 4-5 kg;
- Painful dryness in the vagina and around the entrance.
Even after amputation of the cervix, a woman retains reproductive function (menstrual cycle, ovulation, fertility), and is able to give birth, the main thing is to follow the doctor’s recommendations and be careful in the postoperative period. If symptoms persist and a biopsy reveals the presence of malignant cells, a hysterectomy may be required - amputation of the patient's uterus, in which, after removal, a stump, the remnant of the genital organ, will remain.
: treatment of cervical erosion
Source: https://sheika-matka.ru/diagnostika/boli-posle-prizhiganija-jerozii/
Consequences of cauterization
As a result of cauterization of cervical erosion, consequences can always appear. The likelihood of complications for each method is different. The more traumatic method of cauterization of erosion is chosen for a woman, the higher the risk will be for her.
Before cauterizing cervical erosion, doctors examine the patient. This makes it possible to reduce the likelihood of complications and predict possible consequences. Experts will definitely tell you how to prepare for cauterization of erosion. Proper preparation is the basis for preventing complications.
Common adverse effects of cauterization are:
- infection of the tissues of the cervix and cervical canal;
- bleeding;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ and appendages;
- formation of connective tissue on the mucous membrane of the cervix;
- reappearance of the eroded area;
- menstrual irregularities;
- difficulty conceiving;
- problems during pregnancy - cervical insufficiency, cervical ruptures during childbirth;
- tissue malignancy.
Cauterization of cervical erosion: consequences and complications, recommendations for minimizing them
Among all gynecological problems, cervical erosion is the most common pathology. It is found in more than half of women during routine examinations. One of the common methods of treating erosion is cauterization.
Treatment methods for ESM and their results
Cauterization of erosion is carried out using several methods:
- Diathermocoagulation. The basis of this method is the heating effect of electric current. Subsequently, a “crust” forms, under which healing of the affected tissue occurs. Then a scar is formed - this is a significant disadvantage of DTC.
- Cryodestruction. CD - destruction of an eroded area under the influence of liquefied nitrogen. The advantageous difference between CD (and other methods) and DTK is the absence of scar tissue after exposure.
- Chemical coagulation. Based on multiple chemical erosion treatment. solutions. This method has a significant drawback - a high probability of relapse.
- Laser exposure. This is vaporization - a method of “evaporation” of damaged tissue under the influence of laser radiation.
- Radio wave exposure. This method is the least painful and most gentle, but the most expensive. In addition to destroying erosion, the radio wave method has a disinfecting effect on fabrics.
Consequences of the effect on the cervix during cauterization by any method:
- complete recovery;
- incomplete recovery;
- recurrence.
Long-term consequences after cauterization of cervical erosion can be:
- deformation of the cervix;
- violation of cervical patency.
This provokes:
- the likelihood of spontaneous abortion due to decreased cervical tone;
- the possibility of ruptures during labor.
Due to these consequences, the use of DTC in nulliparous patients is not recommended.
Complications
Complications of the cauterization procedure are normal and pathological.
Normal - discharge mixed with blood, pain during the recovery period.
These phenomena are observed throughout the period of restoration of the damaged surface of the cervical mucosa.
The healing period after cauterization is about a month. Discharges are observed throughout this time, but their nature changes over time.
For up to ten days, the discharge is serous, transparent, and watery. Their number is small.
Then over the next ten days their volume increases, a little blood is added to the clear liquid, and the consistency becomes more viscous. Then for several more days there is a separation of a thick white liquid.
All this reflects the normal process of restoration of the damaged mucous membrane of the cervix.
Do not worry if small spots of blood appear during the recovery period. This is the norm. If the bleeding exceeds menstrual bleeding, you need to see a doctor.
Pain is also possible during healing. If your stomach hurts after cauterization of cervical erosion, this is also normal during the period of restoration of the integrity of the damaged surface.
But if the pain is excessive, does not go away after a month, or is accompanied by bleeding, you should consult a specialist.
The range of pathological complications is much wider:
- relapse of cervical erosion after cauterization (most often this occurs after DTK and chemical coagulation);
- scarring (this is typical for DTC);
- inflammation (if infection occurs, erosion may recur);
- endometriosis (a rare complication that involves the growth of the endometrium from the uterus into the cervical canal).
Special situations
Many women are concerned about discomfort and discharge after the procedure for treating erosion by cauterization. Which of these situations are normal, and which ones should you immediately consult a doctor?
Menstrual cycle changes
A change in cycle during the recovery period is a normal situation. In this case, menstruation can occur either earlier or later than usual.
During cauterization, the body is exposed to stress, and stress often affects the frequency of menstruation.
If this does not happen, you need to consult a doctor.
Discharge
In general, discharge, especially in the first two weeks after exposure, is absolutely normal, even if it is bloody.
In case of excessively heavy bleeding (exceeding menstrual bleeding), you should consult a doctor, since blood after cauterization of cervical erosion may indicate damage to a large blood vessel in the process.
It makes sense to go to the doctor if the discharge has a yellowish or greenish color and a strong unpleasant odor , since this is a sign of an inflammatory process, which means that an infection has joined, and there is a high probability of relapse of erosion.
Infection
Erosion itself is a gateway to infections. And the surface after its removal - even more so.
The following signs indicate infection:
- copious yellowish or greenish discharge;
- unpleasant odor of discharge;
- abdominal pain (although this phenomenon can be observed without any infection);
- phenomena of general intoxication (fever, weakness, headache, chills).
If such symptoms occur you should consult a doctor promptly , since infections in the gynecological area are fraught with consequences such as recurrent erosion.
Bleeding
Bleeding after cauterization of cervical erosion is a normal phenomenon after the procedure , because the erosion itself and its removal are damage to the mucous membrane of the cervix.
The duration of bleeding after destruction of erosion is two weeks.
You should be concerned if bleeding is greater than normal for a particular patient's period, as this will indicate possible damage to a major blood vessel.
Relapse of erosion
Can cervical erosion reappear after cauterization? Yes. If, after the destruction procedure, erosive changes are again detected on the cervix, then the following reasons for relapse are possible :
- under-examination before cauterization;
- viral infection;
- precancer;
- cancer.
For this purpose, a preventive examination is carried out after a month, then after 3 months, and then a year after destruction.
Thrush
After any intervention that violates the integrity of the mucous membrane, there is a risk of infection, including fungal infection.
Often, after cauterization of erosion, the patient notices the appearance of symptoms :
- pulling pain in the lower abdomen;
- white, cheesy discharge;
- pain after sexual intercourse.
These signs indicate candidiasis, or “thrush”.
If thrush is detected after cauterization of cervical erosion and such symptoms, you should contact a gynecologist and begin treatment in a timely manner.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, usually similar to that during menstruation, of low intensity, is present during recovery after the destruction procedure. Normally, they should go away a month after cauterization.
Pain that is too severe or does not go away for a long time is a reason to visit a gynecologist.
Pregnancy and childbirth after the procedure
Therapy for erosion through destruction is not a reason to give up the prospect of becoming a mother.
Some treatment methods are contraindicated for women who are just planning a pregnancy.
This is diathermocoagulation, which leaves behind significant scar changes on the cervix, which subsequently leads to its deformation.
This can lead to miscarriage during pregnancy, and during childbirth - to ruptures, bleeding, and injury to the fetus.
For them, there are other methods of treating eroded areas of the cervix, for example, laser vaporization or radio wave treatment.
Recommendations for minimizing undesirable outcomes
To reduce the risk of developing unpleasant complications of cauterization, you must carefully follow your doctor’s advice for at least 1–2 months :
- exclude sexual contacts;
- maintain hygiene;
- do not be exposed to excessive temperatures;
- do not lift heavy things;
- do not use tampons;
- eat a nutritious, varied diet;
- do not visit the beach, pool, or swim in open water.
Following these recommendations will minimize the risk of infection, bleeding and possible relapse.
The choice of treatment method will depend on your medical history and health status.
Not all methods of cauterization can be used if a woman has not yet given birth, but is only planning a pregnancy.
Source: https://beautyladi.ru/posledstviya-prizhiganiya-erozii-shejki-matki/
How to diagnose
The disease can be suspected based on characteristic symptoms:
- Contact bleeding – dark red, scarlet, bloody. They occur when the organ is damaged during sex, examination by a doctor, vaginal ultrasound, douching, etc.
- Dyspareunia. Pain during sexual intercourse is associated with damage to the mucous layer of the organ and the development of the inflammatory process.
The birth defect often remains asymptomatic and is discovered accidentally during examination by a gynecologist.
The following methods help clarify the diagnosis:
- Pap smear. This analysis allows you to evaluate the cellular composition of the defect, identify signs of deep tissue damage and HPV infection, and detect carcinoma.
- colposcopy. If erosion is suspected, the cervix must be examined under magnification. The examination allows you to determine the type of defect and identify associated deviations.
- biopsy. It is carried out from suspicious areas of the organ after colposcopy.
- tests for infections. Screening for HPV, chlamydia and other STIs is indicated. A general assessment of the microflora of the genital tract is required (a culture for microorganisms is taken).
Radio wave conization of the cervix: indications and features
Based on the results of the examination, the tactics for managing the woman are determined.
Nagging pain in the lower abdomen after cauterization of erosion
The manifestations and symptoms of cervical erosion are minor: rarely can a woman independently understand that a problem has arisen in the area of the cervical canal and the outer cervical surface.
Pain in the lower abdomen, which occurs with cervical erosion, is most often caused by diseases in nearby organs. If there is heavy vaginal discharge, it may be inflammation.
Sometimes abdominal troubles begin before menstruation, but this symptom is characteristic of endometriosis. If you experience any pain, you should consult a doctor who can identify the disease and prescribe treatment.
Diagnosis of pain in the lower abdomen by a specialist
A routine examination by a gynecologist is carried out at least once every six months. When interviewing a doctor, it is necessary to clearly give answers and describe the existing symptoms. If, for example, the uterus and cervix hurt during pregnancy, this may be a sign of cervical dilatation. Having found out why the cervix hurts, the specialist provides approximate diagnoses:
- Erythroplakia – thinning of the mucous membrane;
- Ectropion – cervical canal with signs of everted mucosa;
- Leukoplakia is a modification of epithelial skin areas that develops after operations and injuries;
- Cervical erosion;
- Pseudo-erosion, or ectopia;
- It is necessary to take a smear for flora and carry out a cytological examination;
The specialist’s diagnosis is confirmed by performing a gynecological examination of the vagina, cervix and vulva using speculum and a colposcope.
Many women believe that after a colposcopy the lower abdomen hurts and are worried about having it done, but when they begin to experience pain in the cervix when walking, they change their minds.
Even dilation of the vagina with speculums causes painful sensations for sensitive women; it is recommended to immediately tell the doctor to use a smaller size of instruments. Colposcopy is painless; the patient only experiences a feeling of anxiety, a feeling of pressure, and a slight spasm.
Pain due to cervical erosion
Before a planned cauterization operation, carefully listen to the body's signals, remembering what hurts when you have cervical erosion. Having already established a diagnosis:
- Sexual intercourse is a likely cause of pain, with possible blood-like discharge;
- Urination with pain;
- Unexpected dull pain in the abdomen due to cervical erosion, similar to pain during menstruation (monthly uterine cycle);
- Associated brown discharge;
Since the process is inflammatory, there is an increased temperature.
Despite doctors’ assurances that it is painless, there are cases of why cervical erosion hurts:
- Infliction of mechanical injury during sexual intercourse;
- If the nature of erosion is infectious;
- The cervix has the appearance of pasty, red, loose, inflamed flesh, is painful without intervention, tissue softening is observed;
- The cervical pharynx has uneven edges, with numerous ulcers.
It is necessary to get rid of erosion in any case, even for nulliparous girls, since the tissues of the cervix, when the process is advanced, are more susceptible to injury, have a long healing process, and begin to hurt.
There is no need to resist, refusing to perform the operation, because tissue changes will grow until they lead to huge complications.
In gynecology, gentle treatment methods have been developed that do not injure the cervix of a nulliparous girl, for example, burns with chemical agents (Vagonostil and Vulvostimulin). With this treatment, there are practically no scars left.
Diagnostics
Since endometriosis is often asymptomatic, or its symptoms are similar to other diseases of the female reproductive system, objective examination data play a key role in diagnosis:
- examination in a chair using mirrors;
- colposcopy - examination of cervical tissue under a microscope;
- cytomorphological study - histological study of materials obtained from a biopsy;
- diagnostic curettage of the cervical canal – is carried out if it is necessary to obtain cells from the canal mucosa.
To make an accurate diagnosis, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, radiography and endoscopy are performed. But these measures are considered auxiliary, since they make it possible to confirm or refute the presence of endometriotic lesions in neighboring organs.
There are similar diseases
Differential diagnosis is important for separating cervical endometriosis from other pathologies with similar symptoms - cervicitis of a specific and nonspecific nature, cysts with hemorrhagic contents, cancerous tumors, etc. If necessary, the woman is referred to specialized specialists - an oncologist and a dermatovenerologist.
Pain in the postoperative period and during recovery after cauterization of erosion
Methods for removing erosion: freezing, using a radio knife (Surgitron device), cauterization with electric current, laser coagulation, chemical burning with Salkovagin cream.
The consequence of the operation or when and how pain in the lower abdomen appears after cauterization of cervical erosion:
- Drawing, aching pain, as if menstruation has begun, is noted on the first day, you can take an antispasmodic,
- Irregular pain, turning into a feeling of discomfort, occurs during physical activity;
- Bloating and internal discomfort;
- Regular discharge of exudate (vaginal discharge);
Suturing the cervix
In patients at high risk, cervical monitoring is carried out at 12 weeks, checking how low the cervix is. The operation of suturing the cervix (suture) allows you to preserve the pregnancy, since it is the closed state, without allowing the cervix to open, that allows you to hold the fetus and protect it from infection.
Cervical dilatation is isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI) or weakening of the uterine muscles. Pregnancy can shorten the cervix, which also makes surgery more difficult. If the indications for the operation and the vital activity of the fetus are confirmed, doctors apply a suture, protecting the fetus and the patient from premature birth, warning of possible pain after the operation.
Possible pain after suturing the cervix:
- Nagging pain with the tone of the uterine walls (the anterior wall of the uterus and, accordingly, the posterior wall of the uterus, these are the points of attachment of the placenta, and methods for determining the presentation of the fetus);
- The lower back begins to hurt and the lower abdomen ache;
- A feeling of heaviness, as if the fetus were pressing on a suture;
- If it hurts to sit down, try to walk around a little, stretch your legs, or better yet, if you are at home, lie down;
- If you have discharge containing a bloody clot, it is better to inform your doctor.
Helps determine how successful the suturing was: a follow-up visit to the attending physician, ultrasound diagnostics.
At week 37, the doctor will decide to remove the suture to prepare the woman for childbirth; after the procedure, the baby can be born at any time.
Cervical biopsy
A clarifying gynecological examination if dysplasia or cancer is suspected is called a cervical biopsy. Only the results of a test for the benignity of the cells allow the gynecologist to draw up a treatment plan. The procedure is very painful and is performed under the influence of an anesthetic injection or general anesthesia.
Source: https://gpk1.ru/bolezni/boli-posle-prizhiganiya.html
Let's sum it up
The opinion that cauterization of altered cervical tissue is dangerous and painful is a big misconception. It is based on the fact that previously, removal of the pathological area was performed exclusively with the help of current. Medicine does not stand still, which means that every year new methods of treating underlying diseases appear - painless, safe, low-traumatic and effective.
If cervical erosion is detected, an extensive examination must be performed. Some cases do not require cauterization, and pathological areas are eliminated with the help of drug therapy and lifestyle adjustments.
Erosion: forms, signs and causes
The first form is an ulcer that occurs on the walls of the cervix due to damaged epithelial cells as a result of mechanical action, for example, surgical abortion, traumatic insertion of a tampon, or rough sexual intercourse. In the absence of infections and hormonal disorders, such erosion can heal on its own. But the second form, false erosion, is much more dangerous.
It is a response to the formation of cervical defects. In their place, the mucous membrane begins to grow and a large inflamed area forms. Such erosion should be treated to prevent it from growing. After all, places of damage are a very favorable environment for various types of infections.
The insidiousness of this disease is that it practically does not manifest itself, especially in the early stages. Sometimes there may be spotting after intercourse or simply for no reason in the middle of the cycle. As a rule, women do not pay attention to this, and only learn about the existence of erosion at a scheduled appointment with a gynecologist. However, the absence of symptoms does not mean that you should ignore this fact and postpone treatment. Many nulliparous women do this because there is an opinion that cauterization can lead to complications during childbirth. Let's figure out how true this is.
Early consequences of cauterization, or what to expect in the first month after the procedure
The rehabilitation period after treatment of erosion is 4–8 weeks. Its duration directly depends on the chosen method of therapy. The body recovers most quickly after radio wave and laser coagulation (3-4 weeks). After DEC, rehabilitation can take up to 2-3 months.
Discharge after cauterization
During the first two weeks after treatment of erosion, a woman may feel an increase in natural discharge. This is a completely normal process that occurs during the gradual healing of a mucosal defect. In the first days there will be moderate bloody or slightly brown discharge without an unpleasant odor. After 3–5 days, the discharge will become lighter, less abundant, and then practically disappear. After the next menstruation, the woman’s condition should completely return to normal.
Important aspects:
- After using DEC, a scab forms on the cervix, which comes off after 10–14 days. All this time, the woman may experience bleeding;
- After cryodestruction, the appearance of copious watery discharge (hydrorrhea) is noted within 4–6 weeks.
The discharge that occurs after cauterization should not be accompanied by itching, burning or other unpleasant sensations. The appearance of such symptoms indicates a possible infection and indicates the development of complications.
On a note
According to patient reviews, after radio wave and laser therapy, heavy discharge persists for no more than 14 days and does not cause significant discomfort.
After cauterization of the erosion, bloody discharge will be observed for 1-1.5 months: at first watery, then it will acquire a pinkish tint with blood clots, and after 3-4 weeks during the healing process it will turn brown.