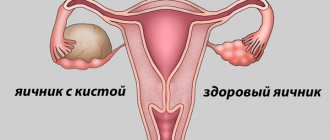
A two-chamber ovarian cyst is a phenomenon in gynecology that many women of reproductive age encounter. A benign growth, hollow inside and filled with liquid, is divided by a septum into separate cells.
The formation is more typical for the left ovary than for the right. A woman should know what it is, the reasons for the appearance of a cyst and be aware of the possible health consequences. If the formation is diagnosed late or the woman refuses to undergo the prescribed treatment, internal bleeding or the development of peritonitis if the cyst bursts cannot be ruled out.
Reasons for education
In gynecology today there is no clear answer to the question of what causes the development of two-chamber cysts. Information is constantly being studied and data is being improved.
Practicing gynecologists have identified only a few key points that can cause the appearance of formation.
- Hormonal imbalance. The reason is considered one of the main ones. Against the background of hormone imbalance, the formation of ovarian cysts cannot be ruled out.
- Physiological problems leading to menstrual irregularities. This reason largely provokes the development of a corpus luteum cyst.
- Pregnancy is one of the causes of the disease.
- Diseases of the genital organs suffered by a woman of an inflammatory nature that are of a bacterial nature.
- Surgery on the organs of the reproductive system.
These are just some of the reasons that provoke the appearance of a cyst. Gynecologists note that abortions and late puberty may be the cause of the disease.
It is also necessary to take into account the time of the onset of menstruation; there is an opinion that neoplasms appear more often if menstruation began early, at about 11 years of age.
Diseases of the reproductive system can provoke the development of benign formations.
Causes
A two-chamber cyst of the left ovary, as well as the right one, can occur due to a number of reasons. Here are the most common ones:
- Hormonal disorders, which include changes in the ratio of “female” and “male sex hormones”, lack or excess of estrogen and progesterone.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Previous surgical interventions, including abortions.
- Infectious and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs that are chronic or have not been treated properly (adnexitis, salpingoophoritis).
- The likelihood that such a cyst will appear during pregnancy is quite high. A two-chamber cyst of the right ovary can occur with excess progesterone. The right ovary is more active than the left due to the large vessels and arteries passing through it. The disease can have a negative impact on pregnancy, including the development of fetal pathologies and the threat of miscarriage, and therefore requires the most careful monitoring and treatment.
- A history of endometriosis can cause the development of multilocular cysts on the ovaries.
- Disturbances in the functioning of organs that produce hormones - the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, and thyroid gland. Diseases such as hyper- and hypothyroidism, autoimmune thyroiditis can cause disruptions in the reproductive system.
- The nervous system has a great influence on the body as a whole and on the hormonal system in particular. Therefore, stress, nervous shock, negative emotions, anxiety and fears cause disruption of chemical processes in the brain and change the ratio of hormones. As a result, various diseases in the genital area may occur.
Types of two-chamber tumors
There are several types of two-chamber ovarian cysts:
- Paraovarian. Education appears in the fetus during intrauterine development. This genetic anomaly is detected when a girl, as a rule, reaches 12-14 years of age; previously it was hidden and asymptomatic.
- Follicular. The cause of development is hormonal imbalance. Before ovulation, a follicle has already formed in the ovary; when it bursts, an egg is released. Under the influence of hormonal imbalance, without bursting, the follicle continues to grow, transforming into a cyst.
- Mucinous and serous cysts are benign formations that have the ability to transform into malignant tumors.
- The malformation is a dermoid cyst.
Education can occur on the right and left. According to doctors, it appears on the left side much more often; in this ovary, the follicle with the egg more often matures and bursts.
Double-chamber formations are considered more dangerous than single-chamber ones. It is important to identify them in the early stages, undergo adequate treatment, avoiding possible consequences.
Two-chamber (three-chamber) ovarian cyst: left, right, treatment, during pregnancy, without surgery
A two-chamber ovarian cyst is a benign tumor containing liquid contents inside. The difference from other neoplasms of this type is that the capsule is divided by a thin septum into two chambers. Women of reproductive age are more susceptible to this pathology.
Women of reproductive age are susceptible to pathology.
Symptoms that appear
A multi-chamber cyst, like other types, is difficult to detect at an early stage. Almost always it is asymptomatic and does not bother the patient until its size increases.
When the compaction reaches 4–5 cm in diameter, it begins to put pressure on the internal organs and causes discomfort.
Possible symptoms include:
- painful sensations in the ovary where the compaction is localized.
Sometimes the pain also radiates to the lower torso or back; Pain in the lower abdomen, on the side. - during intimacy, the pain syndrome intensifies;
- disruptions occur in the menstrual cycle. It becomes shorter or, on the contrary, longer;
- the type of discharge changes, and spotting may appear in the intervals between menstruation;
- the abdominal cavity increases in size, a feeling of tightness occurs;
- intestinal function is disrupted, disorders or constipation may appear;
- With the pressure of a two-chamber ovarian cyst on the bladder, urination becomes more frequent.
In case of complications (spontaneous rupture of the membranes, twisting of the leg, infection), other signs are additionally added. The temperature rises, the pain changes from aching to acute, and bleeding appears.
Types of formations
Benign tumors have several classifications. One of them is related to the nature of the appearance. There are paraovarian and dermoid seals (congenital), follicular cyst (occurs due to hormonal disorders), serous, mucinous. In addition, pathology has a classification related to the location.
Two-chamber cyst of the left ovary
The tumor may appear in the left ovary, although this does not occur very often. The symptoms are almost identical, no matter which side the tumor appears on. But there are also differences:
When suppuration or infection occurs, vomiting may occur.
- painful sensations are felt in the left side, in the lower part.
Give into the abdominal cavity; - when suppuration or infection occurs, vomiting may occur, as well as a rise in temperature and a headache;
- blood clots are visible in the discharge;
- a woman cannot get pregnant.
It is important not to confuse a cyst on the ovary with pathologies of the pancreas or kidney. An accurate diagnosis can only be made on the basis of several types of examination.
Two-chamber cyst of the right ovary
Tumors most often occur on the right ovary. This is due to anatomical features. At the initial stage, the pathology does not manifest itself in any way. Only as the compaction grows does it cause pain, which is localized in the right side.
Often patients notice spotting in the middle of the cycle.
It is often possible to confuse a neoplasm with liver or kidney problems. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
In addition to pain in the right ovary, the patient may notice spotting in the middle of the cycle, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, disruptions in menstruation, as well as an increase in the abdominal cavity that is not associated with weight gain.
Three-chamber cyst
This is a more dangerous type of cystic formation because it contains 3 chambers. The risk of cancer cells increases. The danger is that at first it is easy to confuse a malignant and a benign neoplasm due to similar signs. Time will be lost.
Each of the chambers appears separately, and only then they merge into one tumor.
A three-chamber capsule is the same cavity filled with liquid, but divided not into 2, but into 3 parts. They are separated from each other by thin partitions. In most cases, each of the chambers appears separately, and only then they merge into one cyst.
Symptoms
A two-chamber cyst, which is small in size, does not show symptoms for a long time. A woman learns about the existing formation only during the next preventive examination by a gynecologist.
Symptoms characteristic of the pathology appear when the formation begins to increase in size.
A woman faces:
- pain in the part where the affected ovary is located, where the growth develops;
- intermenstrual bleeding of a spotting nature;
- failures of menstruation;
- periodic attacks of nausea;
- the appearance of false urges to urinate, defecate;
- problems with bowel movements;
- weight gain;
- an increase in body temperature for no particular reason;
- disorders of blood vessels, heart, tachycardia.
During palpation, the doctor feels tension in the abdominal wall. Hormonal imbalances lead to increased activity of the sebaceous glands and the appearance of inflamed acne. A woman is faced with an increase in facial hair.
Treatment and causes of multilocular ovarian cysts
A multi-chamber ovarian cyst is a benign formation that grows on the gonad. As a rule, the growth is formed from the tissues of the appendage. The pathology requires immediate treatment. This is due to the fact that there is a risk of developing serious complications.
Characteristic
The neoplasm is a kind of bubble filled with liquid. The growth of this tumor occurs due to the growth of the endometrium into the tissue of the uterine canal and other organs.
Most often, a two-chamber cyst of the right ovary appears. The intensive growth of nodes on this side is due to the proximity of a large artery, which is involved in the blood circulation process. In case of damage to the left ovary, the growth of the growth occurs much more slowly.
The danger of the pathology is that if the stem of the neoplasm ruptures or twists, bleeding can begin, and nearby tissues die.
Causes
Multi-chamber and two-chamber cysts of the right ovary can occur for the following reasons:
- irregular periods;
- an anomaly of the reproductive system that arose in the prenatal period;
- hormonal disorders;
- inflammation of the appendages and other organs of the genitourinary system;
- early abortion;
- miscarriage;
- surgical intervention in the reproductive system;
- pregnancy;
- disturbances in the activity of the endocrine glands.
It will be possible to accurately determine the cause of the onset of the pathological process only through a comprehensive examination.
Symptoms of pathology
At the initial stage, the disease is asymptomatic, but with further development of the multilocular cyst, the following clinical manifestations are observed:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- unstable periods;
- the stomach increases in size;
- hyperthermia;
- acyclic bleeding;
- impossibility of conception;
- weakness;
- sudden, causeless weight loss;
- male pattern hair growth;
- false urge to defecate.
All symptoms of pathology are conventionally divided into several groups:
- pain;
- hormonal imbalances;
- clinical manifestations of intoxication.
If the tumor ruptures, the woman’s condition worsens significantly. Sharp pain in the abdominal area and dizziness appear. In this case, you must contact a medical institution without delay.
Diagnosis of a two-chamber cyst
At the initial stage of diagnosing a two-chamber cyst of the left ovary, the doctor examines the woman in a chair, carefully examines the features of the clinical picture and collects an anamnesis.
In order to determine the location of the neoplasm, its size and the degree of neglect of the pathological process, the following studies are prescribed:
- Ultrasound using a transvaginal probe;
- MRI;
- blood chemistry;
- CT;
- hormone analysis;
- examination of the uterus using hysteroscopy.
To exclude the presence of malignant neoplasms, additional blood sampling can be performed to identify tumor markers. Treatment tactics are selected only after receiving the results of all diagnostic studies.
Treatment of multilocular cyst
There are several methods of treating cystic multilocular formation. Most often they resort to surgical treatment, but at the initial stage of development of the pathology, it is possible to eliminate the problem through the use of medications.
Without surgery
If the size of the tumor is small, then treatment is carried out using hormonal agents. Often, oral contraceptives Yarina or Marvelon are prescribed. Thanks to their use, the tumor volume is significantly reduced, and in some cases the growth completely resolves.
Hormonal medications based on progesterone can also be used. As a rule, the drug Duphaston is prescribed. With its help, the formation begins to gradually decrease in size.
The selection of medications should be carried out exclusively by a doctor. Hormonal drugs have a number of restrictions on their use and often cause side effects. If treated incorrectly, the condition can worsen significantly.
Sometimes Longidaza is prescribed for the treatment of ovarian cysts, so we recommend that you read additional information on its use.
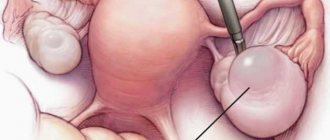
Operating
During therapy, surgical intervention is most often used. This may be abdominal surgery or laparoscopy. The use of a laparoscope allows tissue to be excised with minimal damage and under strict visual control.
During the operation, several small incisions are made in the navel area and the peritoneal cavity is filled with gas through them to ensure normal visibility. Then a special device equipped with a flashlight and camera is introduced. Due to this, the image is transmitted to the monitor screen, and the doctor can monitor the progress of all manipulations.
At the next stage, the affected tissue is removed. Next, cauterization of the damaged vessels is performed. This stops bleeding immediately and reduces the risk of infection.
With small growths, it is possible to limit ourselves to excision of only the lesions. The tissues of the appendages are not affected. In advanced cases, the tumor is removed along with the ovary. The material obtained during the operation is sent to the histology laboratory.
puncture
The procedure is carried out by introducing a special substance into the cavity of the tumor. As a result of such actions, the walls of the cyst begin to subside and the tumor regresses.
If the formation is multi-chamber, then the operation is performed with maximum caution. This is due to the fact that such a growth contains a large number of partitions.
During this procedure, it is almost impossible to exclude a malignant process and perform a biopsy. Only the contents of the tumor can be subjected to subsequent examination. A puncture is performed only if there are special indications.
Possible complications
When the pathology is neglected, there is a high risk of tumor cells degenerating into malignant ones. In order to promptly detect the onset of the oncological process, the affected tissues are collected and sent to a histology laboratory. After receiving the results of the study, the doctor makes a decision on the advisability of surgical intervention and its scope.
Cyst rupture may also occur. As a result, severe bleeding begins and the state of health deteriorates significantly.
A large three-chamber ovarian cyst is especially dangerous. The likelihood of it breaking is quite high. In this case, the heartbeat becomes rapid, weakness, a feeling of discomfort in the rectum, sharp pain in the lower abdomen appear, and blood pressure decreases.
At the onset of the purulent process in the cavity of the neoplasm, a significant deterioration in well-being, loss of strength, increased body temperature, and throbbing pain in the abdominal area are noted. A blood test reveals leukocytosis.
In addition, serious consequences such as tubo-ovarian abscess and hemorrhage may occur.
A multilocular cyst is a serious disease that requires immediate treatment. Most often it is performed surgically. Sometimes it is possible to eliminate the pathology with the help of hormonal medications, but only at the initial stage of its development. In the absence of proper therapy, there is a risk of developing serious complications.
Source: https://TopGinekolog.ru/bolezni/kista-yaichnika/mnogokamernaya
Diagnostics
During an examination by a gynecologist, a specialist can determine the formation if it is already large in size or suspect its presence based on the symptoms present in the patient. To confirm the preliminary diagnosis, a number of studies are prescribed:
- Ultrasound with transvaginal, abdominal sensors.
- Laparoscopy, which allows you to identify the growth and remove it.
- CT results show the structure and exact size of the formation.
- The procedure for puncturing the posterior vaginal fornix allows one to accurately diagnose the presence of a formation, its size and the possibility of complications in the form of bleeding into the retroperitoneal space.
Additionally, a general blood and urine test is prescribed. This allows you to assess the woman’s condition.
The doctor must make sure that there is no risk of developing a malignant tumor; in addition, the woman is tested for tumor markers.
ᐈ What is an ovarian cyst? ➡【How is it dangerous?】
№❶ What is an ovarian cyst and why is it dangerous?
Menu
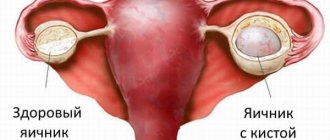
An ovarian cyst (ovarian retention cyst) is a benign tumor-like formation in the ovary, filled with fluid. Ovarian cysts occupy the second place among neoplasms of the female genital organs. Most often develop in women of reproductive age.
Ovarian cysts are cavities filled with liquid or semi-liquid contents that form inside the ovary or on its surface.
The process of degeneration of normal ovarian tissue into tumor formation can occur from any cellular element contained in germ cells, which causes a variety of shapes and structures of cysts.
- the presence of rudimentary remains and dystopia of embryonic elements;
- inflammatory processes in the ovaries and fallopian tubes, which provoke implantation of sections of epithelial tissue of the uterus and fallopian tubes on the surface of the ovary;
- disturbance of hormonal balance towards the predominance of gonadotropic hormones;
- endocrine metabolic disorders;
- taking certain medications;
- stimulation of ovulation;
- trophoblastic disease and other factors.
The development of ovarian cysts is facilitated by the absence of orgasm with pronounced sexual arousal, interrupted sexual intercourse, and uterine tumors.
Ovarian cysts do not have the ability to proliferate; they are formed as a result of retention of excess fluid in preformed cavities. In the development of ovarian cysts, congestive hyperemia of the pelvic organs, the development of adhesions, and inflammation of the peritoneum covering the ovary play an important role.
Any medical problem has a huge number of manifestations. However, there are some symptoms that you should definitely consult a doctor if you encounter them.
Main symptoms of ovarian cysts:
- acute pain (occurs when the cyst ruptures, turns around the suspensory ligament, or changes in size);
- aching pain of varying intensity, a feeling of pressure in the hypogastric region;
- menstrual irregularities;
- bloody issues;
- signs of pregnancy (breast engorgement, nausea);
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- dysuric phenomena.
Ovarian retention cysts are divided into:
- Follicular cysts. They are formed from mature follicles that for some reason did not burst. Most often multiple. Found in almost every ovary.
- Corpus luteum cysts. Formed at the site of a ruptured follicle. Most often found between the ages of 16 and 45 years.
- Endometrioid or “chocolate” cysts. They are a type of endometriosis. Often form adhesions with surrounding tissues. The hemorrhagic contents of the cysts are the color of chocolate or tar.
- Paraovarian cysts. Develops from the epididymis between the ages of 20 and 30.
- Dermoid cysts or mature teratomas. They are formed at a young age from integumentary epithelial cells that enter the period of fetal development. The cells grow, multiply and form differentiated tissues (cartilage, hair, etc.) surrounded by a dense capsule.
- Thecal lutein cysts. They occur in the early stages of pregnancy as a result of a malfunction of the corpus luteum, which does not produce the required amount of hormones for the normal course of pregnancy. They are rare and more often characteristic of multiple pregnancies.
Follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts form a group of functional ovarian cysts - the most common tumor formations of the ovaries. A functional ovarian cyst is a formation that forms during the normal menstrual cycle and often does not manifest itself clinically. Dissolve on their own in 1-2 months.
Despite the fact that many ovarian cysts resolve on their own, some of them can lead to the development of unpleasant complications.
Complications of ovarian cysts:
- Torsion of the cyst pedicle
- Capsule rupture
- Cyst suppuration
- Hemorrhages into the cyst formation cavity
- Impaired functioning of adjacent organs
- Malignancy (degeneration of cells into malignant formations)
Torsion of the cyst stalk is a serious consequence of an ovarian cyst. Pathology can lead to an increase in tumor formation as a result of impaired venous circulation, tissue edema and hemorrhage. Clinically, this is manifested by signs of an acute abdomen.
To establish a diagnosis, a gynecologist conducts a gynecological examination, collects anamnesis, analyzes the symptoms of an ovarian cyst, and prescribes laboratory and instrumental examinations.
An important criterion for laboratory diagnosis is a blood test. Allows you to detect the presence of tumor markers. Histological examination of tissue helps determine the type of cyst, its structure and features.
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the type of cyst, duration of the disease, signs of ovarian cysts, clinical manifestations, age and health characteristics of the patient.
Drug treatment of ovarian cysts is aimed at restoring hormonal levels and treating inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs. If the presence of functional cysts is suspected during puberty, hormonal therapy is prescribed.
If drug treatment is not effective, clinical symptoms appear, or the cyst increases in size, removal of the ovarian cyst is prescribed.
- ovarian resection;
- laparoscopy.
When choosing a method of surgical treatment, preference is given to laparoscopic intervention in the scope of enucleation of the cyst within healthy tissue.
After surgical treatment, therapy is carried out aimed at normalizing the menstrual cycle: cyclic vitamin therapy, nootropic drugs, combined oral contraceptives for at least three months.
The main method of preventing the development of ovarian cysts is regular preventive visits to the gynecologist. Experts recommend at least once a year to undergo ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs, mammography, tests for tumor markers, smears for microflora, etc.
Gynecologists note the positive role of long-term use of complex oral contraceptives in the prevention of ovarian cysts.
For any irregularities in the menstrual cycle, pain or other symptoms of damage to the reproductive system, you must immediately make an appointment with a specialist. Also, those women who have already encountered such a medical problem as an ovarian cyst need to remember: the risk of recurrence of the pathological process is quite high.
Remember, only a timely examination, an attentive and sensitive attitude to your health can promptly diagnose and carry out adequate treatment of an ovarian cyst. In Kiev, at the MEDICOM clinic, you can undergo a complete diagnosis of the genitourinary system, undergo an individual course of treatment, restore your health and restore the joy of life.
The specialists of the MEDICOM clinic have a high level of qualifications, many years of experience, as well as an arsenal of the latest equipment.
They successfully diagnose and treat a wide range of diseases of the female reproductive system, using all the capabilities that modern gynecology provides.
You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling one of the phone numbers listed on the clinic’s website.
all specialists
Source: https://medikom.ua/ru/chto-takoe-kista-yaichnika-chem-ona-opasna/
Treatment methods
Therapy for pathology begins with balancing the woman’s hormonal levels. This is precisely the problem that becomes key. It is solved by prescribing combined oral contraceptives. As soon as the hormonal levels return to normal, the tumor will begin to decrease in size or completely resolve on its own.
Selecting medications on your own is strictly prohibited. This is done by a specialist based on the obtained tests. Doctors often use another effective technique by prescribing a medicine containing the hormone progesterone. It helps to reduce the size of the cyst, and in the future it can resolve on its own.
If the treatment used does not provide the necessary effectiveness, the cyst is removed surgically. This decision of the attending physician is dictated by the parameters of the tumor, if it is more than 10 cm, and the onset of internal bleeding. The laparoscopy method is used. In the presence of an ovarian cyst, it is the least traumatic. The woman quickly recovers from it.
Treatment
Often, such two-chamber cysts, as well as their size, depend directly on the imbalance of hormones in a woman’s body. Due to this, the main treatment consists of taking hormonal drugs, in the form of oral contraceptives in tablets. Such means may be Yarina, Marvelon, Janine, as well as others.
Important! In the case of normalization of hormonal levels, it is much easier to achieve a reduction in the size of the pathology, as well as its complete resorption.
It is important to note that the selection of medications for treatment should be carried out exclusively by the attending physician, taking into account all the data he received after diagnosis. In addition, there is a method in which therapy is carried out using only the hormone progesterone. Its production in the body occurs during pregnancy, as well as in the second phase of the cycle. For this, the drug Duphaston is usually used.
What could be the danger?
A small cystic cavity does not cause discomfort or anxiety about your health. As soon as the formation reaches 7-10 cm, the woman should understand that there is a risk:
- rupture of the tumor, when its capsule is torn, all the internal contents pass into the abdominal cavity.;
- torsion of the tumor - this is caused by the fact that the growth of the tumor makes the ovary heavier; it twists around the ligaments that attach it to the walls of the abdomen.
- suppuration of the ovary and fallopian tubes with surrounding tissues.
Regular visits to the doctor, the correct selection of contraceptive methods, and control of the menstrual cycle are a small part of the preventive methods that should be adopted by a woman who wants to maintain reproductive health.
Double chamber ovarian cyst
A benign neoplasm that has several partitions inside it dividing it into parts is a two-chamber ovarian cyst. Inside this formation there is a liquid that may contain blood inclusions. Most often, the diagnosis of this pathology is observed in young women under 40 years of age, at the very peak of reproductive activity.
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Kinds
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Complications
Causes
At the moment, the exact causes of the development of this disease have not yet been established. But the most likely cause is considered to be hormonal imbalances, which cause the formation of other types of cysts. That is why we can identify a number of factors that cause the risk of developing a two-chamber cyst:
- disruptions in the endocrine system that cause hormonal fluctuations;
- during pregnancy, most often cyst formation occurs on the left side;
- disruptions or changes in the menstrual cycle, in most cases these are physiological reasons, which are explained by the formation of a corpus luteum cyst.
Source: gidpain.ru
Also, operations on the pelvic organs or severe inflammatory processes can trigger the development of formation. Very often, such cysts form after incompletely treated chronic diseases, such as adnexitis or salpingoophoritis. A history of endometriosis also increases the risk of cyst formation.
In addition, stress, severe shocks or negative emotions can also cause the formation of any type of cyst. By causing disruptions in the chemical processes of the brain, they influence changes in the concentration of hormones in the body.
The above factors do not always influence the formation of a cyst; in addition, it can be single-chamber. But it is still necessary to know the reasons that increase the risk of formation, because they may be the main direction in properly selected therapy.
Symptoms
The extent to which a woman experiences symptoms depends on the size of the cyst. If it is small in size, it may not bother a woman, so it can only be diagnosed with an ultrasound examination. But as soon as an increase in liquid exudate occurs, the following symptoms appear inside:
- painful pulling sensations in the lower abdomen, which intensify in the middle of the menstrual cycle or during physical activity, including during sexual intercourse;
- the appearance of spotting that is not associated with menstrual flow;
- menstruation disorders;
- feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen;
- the appearance of flatulence, constipation;
- feeling sick or vomiting;
- the appearance of excess kilograms;
- increase in body temperature by several degrees;
- development of tachycardia;
- excessive activity of the sebaceous glands.
The appearance of acute pain indicates the development of an emergency situation in which the cyst ruptures or the blood supply is disrupted. Due to the twisting of blood vessels, blood may stop flowing to the affected ovary, which will cause not only acute pain, but also an increase in body temperature and loss of consciousness.
Kinds
The formation of a paraovarian cyst occurs during intrauterine development. This cyst is one of the genetic abnormalities that are diagnosed during puberty.
A follicular cyst is formed due to hormonal imbalance. Due to hormonal disorders, the dominant follicle does not rupture, which is why it continues to grow and increase in size, ultimately transforming into a two-chamber tumor.
A serous two-chamber cyst is a benign tumor that, if left untreated, can become malignant. They reach the largest sizes, sometimes up to 30 cm in diameter, which is why treatment is only possible through surgery.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of a two-chamber cyst of the left or right ovary is carried out using ultrasound. Before this, a gynecological examination, collection of anamnesis, and the patient’s main complaints are mandatory. When performing an ultrasound, abdominal and vaginal sensors can be used.
As an additional study, a puncture of the posterior vaginal vault is prescribed, as a result of which a ruptured cyst can be diagnosed. One of the most informative methods is diagnostic laparoscopy, during which it becomes possible to remove the formation.
Of the non-invasive techniques, computed tomography is considered the most informative. Using tomography, you can find out the location of the cyst, its structure and size.
General laboratory tests are also prescribed, which help assess the condition of the body as a whole. These include:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- blood test for tumor markers.
An analysis of the concentration of hormones in the blood is mandatory. You may also need to donate blood to check your hCG level to rule out the development of an ectopic pregnancy. After all, this condition has similar symptoms to the acute form of the cyst.
Treatment
For proper treatment, the doctor selects the necessary medications that will help stop the growth of the cyst, and then completely get rid of it. If the cyst is small in size, conservative treatment is prescribed, which includes taking hormonal medications. In most cases, the results of therapy appear after several months of treatment.
If this type of therapy does not help, then drugs that contain progesterone are prescribed. The most prominent representative of such medications is Duphaston. If a woman has an ovarian cyst, increasing progesterone levels will help reduce its size.
Since hormonal drugs have a large number of side effects, they should be taken only after a doctor’s prescription and in the dosage that was selected.
If conservative treatment does not produce results or the cyst has reached too large a size, surgical treatment methods are turned to. For this, a laparoscopic method is used, which helps to avoid incisions on the anterior abdominal wall.
Complications
The most severe outcome is the malignancy of a two-chamber ovarian cyst, that is, the acquisition of a malignant nature. But this complication is extremely rare. To exclude malignancy, the resulting fluid from the cyst is sent for histological examination, which helps determine the nature of the formation.
Also dangerous is rupture of the formation, as a result of which blood can enter the abdominal cavity. Suppuration of the ovary or tubo-ovarian process, which is characterized by purulent lesions of the ovary and fallopian tube, may also develop.
In order to avoid the development of complications from a two-chamber ovarian formation, it is necessary to monitor your health and regularly see a gynecologist. For any irregularities in the menstrual cycle or general condition, you should also consult a doctor to determine the cause of the disturbances as soon as possible.
Source: https://pro-md.ru/ivf/infertility/female-factor/kista-dvuhkamernaya-yaichnika/
What are the risks to education?
Lack of treatment can lead to the following consequences:
- the pathology threatens to rupture the cyst when the capsule is filled with a large amount of exudate. Tears are caused by physical stress and inflammation. Ruptures cause paroxysmal pain radiating to the rectum, deterioration of well-being, increased heart rate and decreased blood pressure. When there are ruptures in the left ovary, signs of an attack of appendicitis appear. When cysts on the right ovary rupture, a pain syndrome characteristic of pancreatic pathology occurs. A rupture threatens peritonitis and requires immediate treatment;
- suppuration of an ovarian cyst occurs when a secondary bacterial infection is attached. The patient's body temperature rises, signs of intoxication appear: nausea, vomiting, and pain increases. In such cases, the patient is hospitalized, undergoes laparoscopy and antibiotic therapy;
- torsion aggravates the nature of the disease; without timely surgical treatment, necrosis of the neoplasm develops;
- a two-chamber cyst, in contrast to a single-chamber formation, more often degenerates into oncology . The transition process occurs abruptly, and in order not to miss a dangerous trend, the pathology should be treated in a timely manner.
The size of the cyst varies from 5 mm to 20 cm in diameter, depending on the type of cystic formation. According to statistics, such neoplasms are diagnosed in more than 45% of women of different age categories.
Associated symptoms
The pathology is not characterized by pronounced clinical symptoms - the signs of the disease can be attributed to many gynecological problems.
A small cyst may go unnoticed by a woman, and unpleasant symptoms appear as it grows:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, intensifying at the beginning of menstruation, during physical activity and during sexual intercourse;
- the menstrual cycle is disrupted, the volume of discharge increases;
- spotting appears between periods;
- state of tension, distension in the lower peritoneum;
- digestive disorder.
NOTE!
Stressful conditions and emotional disorders negatively affect brain chemistry. This disrupts the concentration of hormones in the blood and gives impetus to the development of abnormal processes.
Causes
Most often, the pathology develops due to hormonal imbalance caused by:
- endocrine disorders;
- pregnancy;
- surgeries on the reproductive organs;
- inflammatory pathologies;
- chronic diseases.
Predisposing factors are early sexual intercourse, smoking, alcohol, unhealthy diet and poor environment.