A desired pregnancy is an exciting and pleasant period of life. The woman tries to act according to the doctor’s recommendations and is actively preparing to meet the long-awaited baby. However, unfortunately, there is always the possibility of spontaneous termination of pregnancy. Which weeks are the most dangerous for a developing baby? How should a woman behave during these periods and when should she seek medical help?
Which weeks are the most dangerous during pregnancy?
Pregnancy can end suddenly at any stage and in any trimester. There are so-called critical moments in the formation of the baby, which determine the possibility of bearing and further normal growth and development of the fetus.
1st trimester
The first 3 months of pregnancy are considered the most important and dangerous in a child’s life. It is at this time that the systems and tissues of the growing organism are formed, and the placental connection with the mother is formed. Serious deviations in the health of a pregnant woman can lead to consequences.
Typical complications in the second trimester of pregnancy
In the second trimester of pregnancy, the placenta and fetus continue to grow. In this case, the formation and development of higher structures of the fetal brain, neuroendocrine, and autonomic nervous system occurs. The fetus develops protective and adaptive reactions. After 19-20 weeks, the intensity of uteroplacental and fetal placental blood flow increases. The function of the placenta provides for the increasing needs of the fetus.
The most typical complications of the second trimester of pregnancy are: threat of late spontaneous miscarriage, bleeding due to placental abruption, anemia, early forms of gestosis, intrauterine infection. These complications contribute to the formation of placental insufficiency and fetal growth retardation.
Due to the increasing size of the uterus, which begins to shift the abdominal organs towards the chest, shortness of breath and heartburn may begin to bother you after 15-16 weeks. The kidneys begin to experience significant stress.
In women with extragenital diseases (kidney disease, hypertension, neurocirculatory dystonia) from 20 weeks there is a risk of developing gestosis. In this regard, you should pay attention to the appearance of edema, excessive and uneven weight gain, increased blood pressure, and the appearance of protein in the urine.
Therefore, it is important to monitor the normal development of the fetus and the course of pregnancy, as well as prevent possible complications.
A pregnant woman should visit a doctor at least once a month, and in some situations, more often. At each visit, the doctor examines the patient, monitors weight gain, measures the circumference of the abdomen and the height of the uterine fundus above the womb, determines blood pressure, and listens to the fetal heartbeat. Prescribes the necessary additional studies.
At 20-24 weeks of pregnancy, a second mandatory ultrasound examination is performed, which is necessary to determine whether the size of the fetus corresponds to the expected period of pregnancy in order to exclude delayed fetal development; detection of fetal malformations; assessing the amount of amniotic fluid; studying the condition of the placenta. Also important is a Doppler study, which is performed during ultrasound to assess the intensity of uteroplacental and fetal placental blood flow.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, in the interval from 16 to 20 weeks, for prenatal screening of possible fetal anomalies, it is advisable to determine the blood level of a-fetoprotein (AFP), free estriol E3, inhibin-A and human chorionic gonadotropin (total hCG).
If there are no contraindications, then after 17 weeks you can begin to perform a special set of physical exercises for pregnant women, which allow you to control the muscles of the perineum and abdominals. It is also important to master breathing exercises.
It is advisable to start drug prophylaxis in pregnant women at risk already from 14-16 weeks of pregnancy under the supervision of a doctor. You should not self-medicate.
After IVF
The most important and dangerous time after IVF is the period of implantation of the fertilized egg. As a rule, this moment occurs 7–10 days after fertilization.
On such days, it is important not to stop hormonal support in the form of progesterone drugs. This will prepare the uterine cavity for the attachment of the fertilized egg in the best possible way and reduce the risk of miscarriage.
It is on days 7–10 after fertilization that the success of the IVF procedure is judged. To do this, control is carried out:
- Ultrasound - checks the presence of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity;
- hCG level in the blood - its growth can be used to judge the progression of pregnancy.
To avoid the risks of bearing a fetus after IVF, you must follow all the recommendations of your gynecologist and reproductive specialist.
Critical periods of pregnancy
"Critical days" of pregnancy
Intrusive advertising has accustomed us to the cutesy euphemism “critical days.” Now, perhaps, any TV viewer, regardless of gender and age, is able to tell what these days are like in a woman’s life and what means should be used at this time to reduce discomfort and continue to enjoy life. However, not everyone knows that “critical days” (“critical periods”) is also a medical term that is used to describe the condition of pregnant women. So today we will talk about these “critical days” - critical periods of pregnancy. First, we will talk about when they arise and what they are associated with, and then we will explain how to behave in order to avoid a crisis that could lead to irreversible consequences.
Critical periods are certain periods of pregnancy when the risk of miscarriage is especially high. As gynecologists have established, these terms are common for women included in certain “risk groups”. As a rule, the threat of miscarriage at these stages is due to normal physiological processes that become pathological under the influence of unfavorable factors. For each critical period, the most characteristic causes of termination of pregnancy can be identified. Let's look at this in more detail.
I trimester
The first critical period occurs at 2-3 weeks of pregnancy, when a woman may not even suspect that new life is beginning to grow in her body. At this stage, the fertilized egg enters the uterine cavity and is fixed in its mucous membrane - the endometrium. This process can be disrupted due to pathological changes in the woman’s genital organs, such as:
- abnormal structure of the uterus (genital infantilism, bicornuate or saddle-shaped uterus, presence of septa in the uterus);
- endometrial injuries after induced abortion;
- uterine fibroids;
- scars after cesarean section.
Another reason for spontaneous abortion in very early stages is genetic abnormalities of the fetus. Most chromosomal disorders are the result of mutations in the germ cells of the parents or the embryo (in the early stages of its development), occurring under the influence of external unfavorable factors (for example, taking certain medications, exposure to ionizing radiation, etc.). Thus, something like natural selection of future offspring occurs.
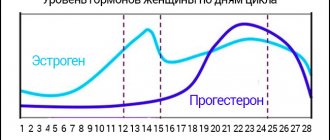
The next critical period is 8-12 weeks of pregnancy . In this case, the most common cause of miscarriage is hormonal imbalance. At this time, the “corpus luteum” that formed in place of the egg after ovulation ceases to exist, and the placenta begins to form and function. The “corpus luteum” produced progesterone, a hormone that supports pregnancy. Now the placenta takes over this function. If at the time of passing such a “relay race” the level of progesterone decreases, pregnancy is at risk. Sometimes there is a simultaneous deficiency of progesterone and estrogen. Estrogens - hormones that the ovaries produce in the first phase of the menstrual cycle - ensure the development of the uterus and the friability of the endometrium. Dysfunction of the ovaries, adrenal glands and thyroid gland, and diseases of the pituitary gland can lead to a decrease in the level of estrogens and gestagens (progesterone).
II trimester
The critical period of 18-22 weeks of pregnancy is the time of active growth of the uterus. At this stage, the danger is low position and placenta previa (complete, incomplete). If a woman experienced the pathological phenomena described above in the first trimester, and any infectious diseases were also discovered, then the placenta becomes vulnerable, and improper location can provoke its detachment and bleeding. However, most often late miscarriages are caused by a pathological condition such as isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI). Due to injuries to the isthmus and cervix (during abortion, delivery of a large fetus, the application of obstetric forceps) or congenital anomalies, the muscles in this place lose the ability to contract, the cervix opens and cannot hold the fertilized egg. Under the influence of gravity, it falls down, as a result of which labor can develop.
III trimester
The period of 28-32 weeks of pregnancy is the next stage of intensive growth of the fetus and uterus. Miscarriage at this stage can be caused by severe forms of late toxicosis, ICI, hormonal disorders, placental abruption. Termination of pregnancy at this stage is called premature birth, because the child is born viable, but his condition requires serious rehabilitation.
All trimesters of pregnancy
The days corresponding to the onset of menstruation if conception had not occurred, as well as the timing of spontaneous or artificial termination of past pregnancies, are also considered critical: it is believed that the body “retains the memory” of the need for hormonal changes.
Rules of conduct during critical periods
Typically, doctors talk about critical periods only when faced with recurrent miscarriage (i.e., repeated spontaneous abortion). For women suffering from recurrent miscarriage, during the critical periods described above, as well as on the days of expected menstruation and during the previous termination of pregnancy, it makes sense to take care of themselves: exclude serious physical activity (do not play sports, do not move furniture, etc.), do not exercise sex, try to protect yourself from nervous tension. Of course, you shouldn’t lie motionless on the couch waiting for something terrible to happen. However, you should be attentive to your health, monitor your condition during critical periods and do not neglect the consultation of specialists. By the way, these recommendations will also be useful for healthy women who do not suffer from recurrent miscarriage.
Dangerous weeks for childbirth
Pregnancy is considered full-term from 37 weeks. At this time, the baby is ready to be born; its organs and systems are able to function independently without the help of the mother.
The following periods are considered statistically dangerous for childbirth:
- From 22 to 27 weeks. The criterion for the viability of a baby at this stage of pregnancy is a weight of more than 500 g. In practice, there are cases of successful nursing of children 600–800 g without serious consequences for their development.
- From 28 to 33 weeks. During this period, premature spontaneous rupture of the membranes often occurs. The amniotic fluid either completely pours out or begins to leak slowly. Since the baby's lungs are not yet capable of independent breathing, he will need respiratory support in the first minutes after birth.
- From 34 to 37 weeks. The child’s lungs are formed, but they are not yet working at full strength. Therefore, children born at 8 months of pregnancy also require constant monitoring of respiratory functions.
One of the reasons for premature birth is the high weight of the fetus. A large fetus may be due to genetic characteristics or the fact that the mother eats everything in large quantities. This can lead to complications for the woman herself if she develops gestational diabetes.
Individual hazards
There are also individual dangerous periods, which are quite difficult to explain in the dry language of medical science, but every doctor knows about their existence. If a woman’s previous pregnancy ended in miscarriage or fetal death, for example, at the 16th week of pregnancy, then the 16th week of the subsequent pregnancy will be the most dangerous for a particular woman. Quite often, a negative scenario is repeated within a week. Therefore, when registering, be sure to remember in as much detail as possible at what dates and how your previous pregnancies ended. This information will help your doctor plan how to protect you and your baby during your own “crisis period.”
How to avoid problems during dangerous periods
To reduce risks during dangerous days during pregnancy, you must follow the following rules:
- Completely eliminate alcohol and nicotine.
- Try to minimize heavy physical activity - if your constant work involves heavy lifting or other intense activity, you should switch to light work. But don’t forget about activity - walking, gymnastics for pregnant women, swimming will help keep your body in good shape.
- Avoid stress, eliminate conflicts at work and in the family, but at the same time, you should not worry too much about your condition. You need to rest and relax more.
- Follow all instructions of your attending physicians - take prescribed medications, do not cancel them yourself.
- Be sure to undergo prescribed examinations - blood tests, ultrasound, and scheduled visits to the obstetrician-gynecologist.
If any suspicious signs appear, you should consult a doctor or the nearest emergency room.
It is important to experience the most dangerous weeks during pregnancy in complete calm. Any excitement can provoke the development of problems. If you follow all the recommendations, there is no point in worrying unnecessarily.
Photo: ru.freepik.com, pixabay.com/ru, yandex.ru
Other threatening stages of pregnancy
The additional likelihood of miscarriage increases if there is a history of termination of pregnancy. In such cases, the dangerous period is considered to be the week in which fetal death, miscarriage, or the onset of premature delivery occurred.
Doctors say that the main reason for the repetition of this situation is the woman’s psychological mood. Having experienced such a loss, on a subconscious level she expects the situation to repeat itself within an identical time frame.
That is why hospitalization is recommended for expectant mothers. Thus, women will feel calmer and more confident, because qualified doctors will help them at any time.
Women with a history of hyperandrogenism have a high chance of miscarriage.
Hyperandrogenism is a condition in which the concentration of male sex hormones is increased. Such patients need to be constantly monitored by a gynecologist, regularly donate blood for hormones and adjust their amounts.
During such a pregnancy, additional phases are distinguished when male sex hormones begin to be synthesized in the child’s body:
- 13 weeks – the beginning of testosterone production in the child’s body;
- 20-24 weeks – the adrenal cortex begins to produce cortisol, male hormones;
- 28 weeks – an increase in male hormones is observed due to increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone, which is produced in the pituitary gland of the baby.
To prevent miscarriage, check your hormonal levels regularly.
Useful video about dangerous weeks of pregnancy
List of sources:
- Obstetrics and gynecology. Directory for practicing doctors Remedium-Doctor. - M.: Remedium, 2021. - 352 p.
- Gitun, Tatyana Vasilievna Diagnostic reference book for obstetrician-gynecologist // M.: Astrel, AST, 2021. - 203 p.
- Serova, V.N. Obstetrics and gynecology. Clinical recommendations // M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2021. - 656 p.
Author
Anastasia Krasikova
Gynecologist
Share