Without a detailed gynecological examination, it is impossible to determine how fully the organs of the female reproductive system function. Many female pathologies are manifested by changes in the nature of vaginal discharge. For example, discharge with a jelly-like consistency, when jelly-like discharge appears, may indicate an inflammatory process in the cervix. Some women, without fully understanding the problem, try to solve it on their own, ignoring the help of specialists. Such actions can only aggravate your condition when jelly-like discharge without color appears, if leucorrhoea (as pathological vaginal discharge is called) is one of the manifestations of a gynecological disease. And its progression can threaten a woman with serious complications and reproductive dysfunction.
But the presence of transparent, jelly-like mucus coming out of the genital tract in small quantities may also indicate a change in the state of a woman’s intimate sphere, caused by natural physiological processes. How to identify indicators of normality and deviations in this situation, when thick discharge in the form of jelly, viscous odorless vaginal discharge can be symptoms and signs of a gynecological or other disease, that is, a pathological problem, and when thick discharge appears due to physiological problems that are not associated with serious diseases.
Pathological jelly-like secretion
The pathological nature of discharge in the form of jelly can most often be determined by a number of signs:
- presence of an unpleasant odor;
- associated symptoms (itching, burning sensation in the vagina, rash, irritation, pain during sex, etc.);
- unusual color and consistency of discharge (blood particles in mucus, bright color, abundance, etc.).
Jelly-like discharge in a woman can be a symptom of a disease such as endocervicitis. It is an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. In this case, there is an abundant gel-like discharge, the formation of which is associated with irritation of the glandular cells. There is sometimes pus in it, which makes vaginal discharge look like jelly.
Yellow slime
Along with changes in sexual secretion, a woman with endocervicitis is bothered by pain in the lower abdomen, during sexual intercourse, and urination.
The causes of this disease are infectious and non-infectious. The first group includes sexually transmitted infections, the development of opportunistic microflora, and viruses. Inflammatory processes in the genital organs create the most favorable environment for the development of infectious diseases. The second group consists of cervical dysplasia and trauma, as well as a number of systemic diseases.
Causes of pathological discharge
Alas, many pathological processes pass without symptoms; only a gynecological examination and laboratory tests can show their presence.
Several factors can influence the appearance of discharge in a healthy woman. These are stress, climate change, taking hormonal drugs, taking strong medications, allergic reactions. Personal hygiene can also affect the nature of the discharge.
There are some symptoms that can be used to preliminarily identify the disease. Of course, an accurate diagnosis is only possible with a doctor after examination and laboratory diagnostics, but the appearance of some can give a more or less accurate picture of the disease.
White curdled discharge with a sweet or sour odor indicates candidiasis.
. Other symptoms of candidiasis are:
- burning, itching in the vagina and external genitalia;
- swelling of the vagina after sexual intercourse;
- pain when urinating and during sexual intercourse.
Excessive yellow or bloody discharge with a foul odor may indicate bacterial vaginitis
. This is an inflammation of the vagina caused by a violation of the microflora. This means that local immunity cannot restrain the growth of pathogenic bacteria; they attack vaginal cells, and the inflammatory process begins. Characteristic symptoms of bacterial vaginitis:
- redness, itching and swelling of the genitals;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- painful intercourse;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- weakness and fatigue;
- frequent urination.
Excessive foamy leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor may indicate trichomoniasis
. The causative agent of the disease is Trichomonas. The following symptoms are also observed:
- irritation of the genitals and inner thighs;
- erosion of the mucous membranes of the intimate area;
- pain when urinating;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
Homogeneous yellow-green discharge with an unpleasant odor may be a sign of gonorrhea
. This is an acute infectious disease caused by gonococcus and sexually transmitted. Symptoms of gonorrhea are:
- itching and pain in the urethra and vagina;
- increased body temperature;
- separation of pus from the vagina;
- frequent painful urination;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- loss of appetite.
Serous-purulent discharge with blood often indicates the presence of a cyst
in the uterus or its appendages. Symptoms of a cyst, in addition to bloody discharge, are:
- discomfort in the vagina;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- increased menstrual flow;
- menstrual irregularities;
- painful menstruation.
Bright yellow and green discharge in copious amounts with a very unpleasant odor signal endometritis
. This is an inflammation of the uterus caused by bacteria or injury. Symptoms of endometritis:
- acute pain in the abdomen, in its lower part;
- fever with chills;
- increased heart rate;
- painful urination;
- weakness;
- enlargement of the uterus caused by tissue inflammation;
- heavy and painful periods;
- infertility.
Brown discharge during delayed menstruation can indicate a pathological course of pregnancy, for example, an ectopic pregnancy
. The likelihood of this pathology can be judged by the following symptoms:
- absence of menstruation;
- sharp or cramping pain in the lower abdomen, usually on the side;
- toxicosis and other signs of pregnancy.
This is a very dangerous condition that requires immediate medical attention. Even if the pregnancy is intrauterine, but there is spotting, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this is a sign of a threat of miscarriage.
In any case, when unhealthy discharge appears, very careful hygiene is required, since many pathological discharges corrode the skin of the genitals. Sometimes the doctor prescribes baths with medicinal solutions and douching.
There are many traditional methods for treating discharge. They sometimes help, but sometimes they can blur the clinical picture and complicate the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. Under no circumstances should foreign objects be inserted into the vagina, as some folk recipes advise. This can harm the microflora and injure the already irritated vaginal mucosa. Therefore, even traditional methods should be used only on the recommendation of a doctor.
What to do if the nature of the discharge changes?
Many ailments, especially of the genital area, are often virtually asymptomatic, which is even more dangerous due to the lack of timely treatment. Changes in the nature of discharge are clear signs of the presence of certain health problems. Of course, it is necessary to immediately exclude the natural nature of such a phenomenon (pregnancy, menstruation, ovulation, menopause, etc.).
If you cannot find the cause on your own, you should definitely seek advice from a gynecologist. At the appointment, you need to talk in detail about the color, consistency and how the discharge smells. As a rule, such information helps to significantly narrow the list of necessary diagnostic measures, because certain diseases are characterized by specific symptoms. After taking tests, the doctor will tell you exactly the cause of changes in vaginal discharge and, if necessary, prescribe appropriate treatment.
Mucus from the vagina is secreted by all women of reproductive age. Its color and smell indicate the presence of a disease or indicate absolute health. At the same time, jelly-like discharge in women can be considered both as a variant of the norm and as a sign of pathology. It is necessary to figure out in advance in which cases medical assistance is needed and when there is no cause for alarm.
Preventive actions
The quantity and nature of vaginal secretion is very dependent on compliance with the rules of personal hygiene. Therefore, the best ways to prevent the appearance of heavy jelly discharge are to follow these simple rules:
- It is necessary to wash yourself 2 times a day using special cleansers.
- Casual relationships should not be allowed, because many diseases are sexually transmitted.
- You should use popular oral contraceptives only on the recommendation of a gynecologist.
- It is advisable to lead an active lifestyle.
- It is important to adhere to healthy eating standards.
- It is necessary to avoid stress and prevent psycho-emotional overload.
The presence of jelly-like discharge in women is not always a sign of pathology. However, this does not mean that you do not need to be careful about your health. If the condition is in doubt, it is better to visit a doctor rather than seek help on online forums. There you can find a lot of comments and advice from women, where everyone wants to share their experience, but only a specialist can provide qualified assistance.
Causes
Jelly-like discharge can appear under the influence of a number of factors:
- menstrual cycle. A thick consistency of mucus is noted during the period of ovulation and before the arrival of the regulus;
- pregnancy. With successful fertilization, the level of hormones changes significantly, for this reason the secretion becomes like jelly;
- menopause Hormonal changes occur in the body, which entails similar changes;
- discharge when excited. During sexual intercourse, a kind of lubricant is produced that protects the mucous membranes from damage and provides better glide;
- exposure to stress. The production of hormones is suppressed, the nature of secretion undergoes changes;
- taking oral contraceptives and hormonal medications;
- allergy;
- failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules. The vaginal microflora is disrupted, and as a result, secretion becomes somewhat different.
Main symptoms
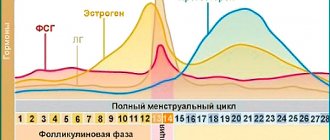
Jelly-like discharge may appear at different periods of the cycle. Normally, they protect the mucous membrane of the external genitalia from pathogenic bacteria and infections. With the onset of ovulation, the secretion becomes more viscous. At this point, a change in the consistency of the vaginal fluid is considered a physiological phenomenon.
The discharge may become thick, jelly-like, profuse and prolonged, but it is impossible to determine at home whether it indicates the onset of a pathological process. With such changes in secretion, in any case, the help of a doctor is needed. Many diseases are asymptomatic at the initial stage, and thick leucorrhoea may be the only visible sign of their development.
How to understand that jelly-like vaginal discharge is a sign of pathology?
Mucus with a jelly-like consistency and thick discharge that is released from the vagina for a number of reasons is due to:
- physiological processes;
- development of inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- infectious lesions of the intimate organs.
Having a clear idea of the nature of the discharge, which is considered normal, it is not difficult to pay attention to the deviations that have appeared. Vaginal secretion, normally secreted by the glands of the mucous membrane, meets the following characteristics:
- there is no unpleasant pungent odor from the discharge;
- the color of vaginal discharge is transparent with a slight tint of white or yellow;
- his jelly-like discharge is scanty, so there are no noticeable marks left on his underwear;
- the composition of the mucus is uniform, without the presence of clots, flakes and other inclusions;
- the woman does not feel discomfort, pain in the vulva and labia, there is no redness, swelling, or irritation;
- There is a certain periodicity in the volume of secreted mucus (a slight increase is noted during the ovulatory period, after which the volume of secreted secretion decreases again).
The nature of the discharge may change under the influence of internal and external factors, which include: errors in nutrition, poor hygiene of the intimate area, emotional shocks suffered, and a rapid change in climate zone. Vaginal secretions may become thin and watery or thick and sticky. If a woman does not notice any other pathological signs, there is no cause for concern. But it is still advisable to consult with a gynecologist, since the development of a number of gynecological diseases at the initial stage occurs without pronounced symptoms, slightly changing only the nature of vaginal discharge.
Signs of normality
Transparent jelly-like discharge can be observed in women who do not suffer from diseases of the genitourinary system. Normally they have the following characteristics:
- white and mucus-like;
- with a faint or odorless aroma;
- small volume;
- there is no itching or burning;
- body temperature does not rise.
If jelly-like discharge is observed in the middle of the cycle, then this is a sign of normal physiological processes occurring in the body. Also, their appearance does not cause concern a few days before menstruation is due to begin.
For various diseases
Abnormal vaginal discharge is usually characterized by an increase in volume, a change in color (pink, brown, yellow or green) and an unpleasant odor.
In the vast majority of cases, the development of pathology is caused by infection. In this case, there is a rotten smell of the discharge. In addition, accompanying symptoms are noted (burning and itching, swelling and redness of the skin in the genital area).
Depending on what kind of infection led to a change in the nature of secretion, the mucus may become cloudy, almost opaque, heterogeneous and thick.
Erosion
This is a pathology in which ulcerations appear on the mucous membranes of the cervix. Often the disease is asymptomatic. The appearance of secretion during erosion does not cause concern in women. Often, abundant mucus is observed before the arrival of the regulus; it is perceived as a harbinger of menstrual periods.
If an inflammatory process has begun against the background of this disease, then green mucus is observed. It may contain an admixture of pus. With bacterial vaginosis accompanying erosion, the secretion becomes gray and has a strong fishy odor.
The danger of the disease lies in the fact that when the mucous membranes of the cervix are damaged, the body becomes more susceptible to inflammatory and infectious diseases. For this reason, against the background of erosion, other pathologies are often observed that significantly aggravate the situation.
Endometritis
The inflammatory process in the mucous membranes of the uterus in the vast majority of cases is accompanied by a change in the nature of secretion. Often, jelly-like discharge is observed. Their volume is usually small.
The mucus-like secretion may contain blood clots and pus. Depending on the cause of the inflammation, the fluid from the vagina may change. If endometritis is accompanied by thrush, then curdled leucorrhoea with a sour odor is observed. In the same case, when the causative agent of the disease turns out to be a bacterial infection, the discharge becomes thicker and takes on the smell of rotten fish.
Cervicitis
The development of pathology most often begins with an inflammatory process in the cervical canal (endocervicitis). Only after a while does the lesion become larger and the inflammation spreads to the vaginal part. As a result, cervicitis develops.
This disease is characterized by the appearance of a gel-like secretion from the vagina. The maximum volume of mucus is observed in the first days after the end of regulation. Associated clinical manifestations are pain in the lower abdomen, frequent but false urge to urinate, itching, irritation and discomfort after sexual intercourse. Often, intimate intimacy causes a pink secretion streaked with blood.
Pathological vaginal discharge
By the nature of the discharge, you can assess the condition of the female genital organs. Healthy discharge is formed in a small volume, it is transparent, odorless and not accompanied by pain or itching. When the type of discharge changes, this indicates the presence of a pathological process in the female genital organs.
You should be concerned if the discharge changes in consistency, acquires a strange color or smell, or changes in intensity. Often such discharge is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, itching, pain in the perineum, irritation of the external genital organs, and discomfort when urinating.
Discharge in pregnant women
Pregnancy is an exciting and worrying stage of life for a woman. During this period, a number of changes occur in the body, which are extremely important to monitor closely. Uncharacteristic vaginal secretions can be either normal or a sign of serious danger. Only with a timely response to pathological processes will it be possible to save the fetus.
Immediately after successful fertilization, the amount of normal secretion of a transparent color increases significantly. The mucus becomes thicker. Often, pregnant women experience jelly-like discharge. Such changes are not cause for concern and are considered a natural reaction of the body to hormonal fluctuations.
A signal to contact a gynecologist is leucorrhoea with blood streaks. Such symptoms indicate an increased risk of spontaneous miscarriage and possible ectopic pregnancy.
Thick, jelly-like discharge that turns yellow in color is also a concern. Often they signal the penetration of infection into the genitourinary system. In order not to harm the growing body, you need to immediately begin therapy, which is carried out under strict medical supervision.
Vaginal secretions acquire a thick consistency in the second trimester. It indicates a healthy pregnancy. If bloody inclusions are noted in it, then the woman is indicated for urgent hospitalization. The presence of blood in the leucorrhoea is a harbinger of premature birth.
Prevention and treatment
The main goal of therapy is to eliminate the factor that provoked the change in the nature of vaginal secretions. As a rule, a number of drugs are prescribed that help eliminate infections and inflammation, suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, restore healthy vaginal microflora and strengthen the immune system. In some cases, drug therapy is ineffective, and surgical intervention is resorted to. For example, with erosion of the cervix, the ulcerations are cauterized.
Most often, the following groups of drugs are prescribed during treatment:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- medications with antifungal effects;
- immunomodulators;
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
After taking the medications, the doctor prescribes vaginal suppositories and other drugs that have a local effect. With their help, it is possible to suppress the activity of pathogenic bacteria and restore normal microflora.
During the treatment process, it is also recommended to stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking, and to exclude spicy and fatty foods from the diet. You should not have sex until you have fully recovered.
To avoid the development of diseases that can lead to the appearance of a jelly-like secretion, it is recommended to adhere to a number of recommendations. Among the main preventive measures are the following:
- Use barrier contraception.
- Avoid promiscuous intimate relationships.
- Make dietary adjustments. The menu should be healthy, complete and balanced.
- Wash yourself twice a day and use special intimate hygiene products. The use of soap is strongly discouraged.
- Replace panty liners promptly.
- The selection of oral contraceptives should be carried out only with a doctor.
- Do not self-medicate any disease.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Spend more time outdoors and lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Regularly undergo examinations with a gynecologist.
Jelly-like secretion is most often a normal variant. Such discharge appears during the period of ovulation, pregnancy and as the critical days approach. In the absence of pathological changes, leucorrhoea has a uniform consistency and no odor. If the mucus gives off an unpleasant aroma, it has changed its color, become more abundant, or acquired a different structure, then you should consult a gynecologist. Such clinical manifestations in most cases indicate the development of the disease.
The presence of discharge in women, which has a transparent structure, a small volume and a normal odor, is a completely normal physiological sign. This secretion is produced by the glands so that pathogenic microflora naturally leaves the genitals. The protection created by nature helps the female body protect itself from many infections. However, when the color, consistency and smell of the secretion changes, this should definitely alert you. Jelly-like discharge in women is often a sign of gynecological disorders.
When jelly-like discharge does not require treatment
There is no need to worry about transparent or jelly-like secretion with small white fragments in the following cases:
- Present in small volumes and lacking color. A small amount of snow-white clots is quite acceptable.
- A clear, odorless, jelly-like discharge is indicated.
- There is no irritation on the external genitalia.
- There is no discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen.
An important point: the listed signs are quite subjective and can be assessed in completely different ways. In most cases, only a gynecologist can find the answer to the question of whether jelly-like discharge is normal or pathological.
The body of each representative of the fair sex is unique, so gel-like transparent discharge can be a constant companion for many women, but for some it will act as a sign of a serious illness. Ignoring the symptom can cause health problems, so it is better not to postpone a visit to the gynecologist.
Menstrual cycle
Each woman's menstrual cycle is individual. It can range from 21 to 28 days (in some cases a little more, but not much). Such indicators are considered the norm.
The duration of menstruation can also vary from 3 to 7-8 days, which is also not a pathology. Many women experience nagging pain in the lower abdomen a day or two before the onset of their period. A mucous-bloody discharge appears, quite scanty and in most cases odorless.
On the due day, menstruation begins, and the discharge becomes completely bloody, with only a small amount of mucous secretion. This is the tearing away of the productive layer of the endometrium, which was preparing to receive a fertilized egg. And since conception did not occur, its further presence in the uterus is unjustified. After all, in the next cycle the process will repeat again.
Common Causes of Jelly-like Discharge
Several factors can cause changes in mucus secretion:
- Menstrual cycle. Mucus is thicker during ovulation. Sometimes you can even notice lumps of mucus in the middle of the cycle.
- Onset of pregnancy. As soon as the egg is fertilized, the hormonal levels begin to change, and a viscous jelly-like discharge appears.
- Menopause. With the onset of menopause, hormonal levels are also subject to significant changes, which entails characteristic changes in discharge.
- Discharge during sexual arousal. This is how nature intended that during sexual intercourse, natural lubrication is produced, which protects the vagina from injury.
- Exposure to stress. When a woman is in an unfavorable psycho-emotional environment, this disrupts the production of many hormones.
- The use of hormone replacement therapy and oral contraceptives.
- Allergic manifestations. The delicate skin in the labia area can be irritated by the use of unsuitable intimate hygiene products or by the use of pads.
- Insufficient hygiene. Failure to comply with the rules of care for the external genitalia causes a disruption of the microflora, as a result of which the composition of the secretion changes.
There are some pathologies that provoke the appearance of discharge with the presence of blood and lumps of leucorrhoea, similar in consistency to jelly:
- diseases of the fallopian tubes;
- infectious and inflammatory processes;
- the predominance of pathogenic flora in the vagina;
- damage to endometrioid type cells.
Most often, such disorders occur due to infectious and inflammatory diseases, as well as changes in the functioning of the endocrine system.
Types of vaginal discharge
Depending on quantity
produced mucus, pathological discharge is divided into scanty and abundant.
Scanty is a discharge that is not enough for the normal functioning of the vagina and external genitalia. The mucous membranes begin to dry out and crack. During sexual intercourse, friction and pain are felt. Scanty discharge is the result of hormonal changes due to age, endocrine disease, or taking hormonal medications.
Heavy discharge is a discharge that leads to a constant feeling of moisture in the vagina. They are noticeable on underwear. Heavy discharge can be diagnosed in young women during ovulation in the middle of the menstrual cycle; it is transparent and does not have an unpleasant odor. During pregnancy, especially before childbirth, the discharge also becomes more abundant. These are healthy discharges and should not be feared. If the consistency, volume, color or smell of the discharge changes, this indicates the beginning of a pathological process.
By consistency
The discharge can be watery, mucous, curdled or foamy.
- Liquid discharge
- watery and mucous - odorless and colorless is considered normal. Watery discharge occurs in the middle of the cycle during ovulation; mucous discharge appears during sexual intercourse and serves as a lubricant. - Thick, cheesy discharge
indicates the presence of a fungal infection. Doctors usually diagnose candidiasis. The discharge resembles liquid cottage cheese, it is not uniform in consistency. - Foamy discharge
indicates the presence of a bacterial infection. This is especially dangerous if they have an unpleasant odor or distinct color. Foamy discharge is a hallmark of trichomoniasis.
Based on the color of the discharge, there are clear (normal), white, bloody, yellow, green and brown:
- Clear discharge
is normal. They are usually invisible on underwear and on the body. - Thick white discharge
indicates the presence of candidiasis (thrush). In a healthy state, white discharge may appear before childbirth. - Bloody and brown discharge
is the most dangerous, as it signals the presence of blood in the vagina. Normally, they occur only during menstruation. When taking hormonal contraception, especially in the first months, the appearance of intermenstrual bleeding is acceptable; this is considered normal and indicates the body’s adaptation to artificial hormones. In other cases, spotting indicates the presence of a serious pathology or the onset of bleeding. - Yellow and green discharge
indicates the presence of an infectious-inflammatory process.
Discharge like jelly in diseases
If jelly-like discharge appears due to the development of any disease, the woman will definitely notice a change in color, a significant increase in volume, the presence of pieces in the discharge, and an unpleasant odor.
Most often, the cause of this phenomenon is a pathological process caused by infection. If the genitals smell unpleasantly of rotten meat, then this is a sign of an infectious process. Associated symptoms: severe itching and burning in the external genital area, white clots in large quantities in the discharge of women. In advanced cases, women complain of discomfort due to the fact that the genitals are too dry. Often there is a change in color and swelling in the labia area.
Pathological causes of jelly-like discharge
Before listing the most common pathological causes of discharge with a thick consistency in the form of jelly, it is worth understanding that clear, odorless jelly-like discharge is often observed during the period of ovulation. That is why you should pay attention to other symptoms and signs that accompany thick discharge. The presence of jelly-like discharge in large quantities, when thick and abundant discharge, all this may indicate the development of a gynecological disease, especially if the discharge has noticeably changed color, it has become greenish, yellow or pink and has acquired a distinct unpleasant odor.
Most often, this disease develops against the background of infection. The discomfort of a woman when her intimate organs are infected is expressed not only by the presence of copious vaginal discharge with a specific rotten odor. Often there is itching and burning in the vagina, vulva, and labia. As a result of the action of pathological agents, the tissues of the perineum become irritated, swell, and turn red. Depending on the type of infection and the progression of the pathology, the nature of the discharge changes, it becomes less transparent, its jelly-like structure thickens, becomes heterogeneous, and acquires various shades, from slightly yellow to pronounced greenish, with purulent inclusions.
A genital tract infection can be caused by:
- gardnerella;
- Trichomonas,
- chlamydia;
- cytomegalovirus;
- gonococci;
- ureoplasma;
- mycoplasmas.
Having penetrated inside, these pathogenic bacteria actively multiply and cause a number of disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system. Therapy should be carried out using special antibacterial drugs, which are selected by the treating gynecologist depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. When heavy vaginal discharge appears, women often note the presence of other unpleasant symptoms:
- painful sensations during sexual intercourse;
- pain every time you urinate;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- discomfort in the vagina.
Such symptoms can be a sign of many pathologies, in particular endocervicitis. This is a gynecological disease in which an inflammatory process develops in the tissues of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. One of the manifestations of endocervicitis is the occurrence of profuse mucous discharge from the genital tract in a woman. Their intensity depends on the degree of inflammation progression.
Normally, the glandular cells of the cervical canal produce a small amount of secretion, but during inflammation it mixes with inflammatory mucus, including purulent impurities, so women often complain of a viscous jelly-like discharge with a pronounced yellow tint.
If the disease progresses and there is no proper treatment, the mucous membrane of the cervical canal changes, microulcers appear that begin to bleed.
In such advanced cases, a woman develops a pinkish discharge due to the presence of blood streaks in the secreted mucus. The pathology of endocervicitis can develop:
- against the background of erosive lesions of the cervix;
- due to improper use of the intrauterine device;
- as a result of injury to cervical tissue during incorrect gynecological manipulations, after childbirth, or abortion.
Endocervicitis requires not only symptomatic treatment, eliminating unpleasant pain and discomfort. Therapy should be aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process, restoring the integrity of the mucosa and its functions. Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, healing drugs are used. It is important for every woman to understand that the appearance of vaginal jelly-like mucus, which differs in consistency and color from physiological secretions, requires contacting a gynecologist. Timeliness in this matter will help eliminate the progression of many pathological conditions.
Based on all of the above, we can conclude that normally a woman should have clear, odorless discharge.
But what kind of discharge there will be on a certain day of the menstrual cycle can be influenced by a number of different kinds of factors. At different phases of the monthly cycle, vaginal mucus can change its color to a yellowish or clearly yellow color, become white or pale, and the discharge can become thick or thin. You should also take into account the fact that the transparency of the discharge, its color and smell may change while taking hormonal birth control pills and other hormonal drugs. Only after eliminating the factors described above, you should seek help from a doctor if thick and clear-looking discharge appears, especially if there are other unpleasant symptoms or abdominal pain.
Source: womanchoise.ru
Similar articles
- Transparent, odorless discharge in women: causes, whether it is necessary to treat Transparent, odorless discharge is not considered dangerous: it is an excess of mucous secretion secreted by the glands located at the entrance to the vagina. Its purpose is to maintain an appropriate level of moisture in the vagina, fluctuations of which can...
- Why is there white and thick discharge after ovulation, reasons? The ovulation period is the time when a mature egg is released from the follicle in one of the female ovaries, ready for the fertilization process. During the process of the release of the egg and its movement through the fallopian tube into the cavity...
- Discharge with a fishy smell, causes and treatment, how to get rid of it Any woman, faced with excessive vaginal discharge, always tries to get rid of it. This is especially true in cases where the discharge has a sharp, unpleasant odor, reminiscent of fish. Some patients use various deodorizing products for intimate hygiene...
Discharge in pregnant women
Waiting for the birth of a baby is a very anxious period in the life of every woman. Over the course of 9 long months, a lot of changes occur in the body’s functioning. Every expectant mother should be especially attentive to any changes.
Suspicious jelly-like vaginal discharge during pregnancy can be either completely normal or act as a symptom of pathology, and sometimes be a sign of premature birth.
With the onset of pregnancy, the amount of transparent secretion increases sharply. The mucus acquires a thicker structure. Often pregnant women experience jelly discharge. Such changes usually do not cause concern to gynecologists, because such a secretion is a normal reaction of the body to fluctuations in hormonal levels.
However, if mucous discharge during pregnancy contains blood or pieces of curd, you should immediately contact an antenatal clinic. Such symptoms may indicate a great threat to further pregnancy.
Thick mucus with a yellow tint should cause concern - most often it is a sign of the development of an infectious process. It is impossible to do without the use of antibiotics.
Vaginal secretions become very thick in the second trimester of pregnancy. It is a sign that everything is fine with both mother and baby. Blood that is released along with mucus is an alarming symptom that should be a reason to go to the hospital. The presence of brown discharge should not cause anxiety before childbirth - this is a completely normal process, indicating the preparation of the uterus.
Types of jelly type vaginal discharge
Jelly-type vaginal discharge may differ in color, microbiological component, density and viscosity of mucus, smell, and also have a different nature of origin.
Transparent
Jelly-like discharge in women, which is completely transparent, in most cases is not a sign of a pathological condition of the organs of the reproductive system. This type of mucus, which has no color, is secreted due to unstable hormonal levels.
In later stages of pregnancy, jelly discharge may become more abundant. Transparent mucus, which has nothing to do with the painful condition of the vagina, uterus and its appendages, should not have an unpleasant odor, impurities of blood or other biological fluids.
Yellow
The appearance of jelly discharge with a rich yellow tint indicates the beginning of an acute inflammatory process of bacterial origin. In most cases, this symptom is caused by infectious microorganisms in the form of Staphylococcus aureus, gonococcus, streptococcus, and is also accompanied by the following signs of the disease:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- feeling of pain inside the vagina;
- discomfort during urination;
- disgusting putrid odor of mucous secretions, as well as admixtures of pus;
- increase in body temperature.
Yellow jelly-type discharge is a symptom of an infectious infection in a woman’s reproductive system, which threatens not only the health of the pregnant woman herself, but also the healthy development of the fetus. In this case, an urgent examination by a gynecologist is required.
White
Jelly-like discharge in women, which has a completely white color, is not an indicator of the normal functioning of the genitourinary system. Such symptoms indicate a possible infection of the vagina with fungal microorganisms of the genus Candida.
These are representatives of pathogenic microflora that cause candidiasis. This disease also has a common name “thrush”. The disease is characterized by regular secretion of white jelly-like mucus, a burning sensation, pain, and excessive dryness inside the vagina.
Depending on the severity of the disease, the whitish discharge may have a thinner consistency. In most cases, white jelly-type mucus caused by candidiasis is a consequence of the pathogenic activity of fungal microorganisms.
These discharges have a distinct yeasty odor. This is one of the main signs of thrush, which occurs as a negative consequence of previous antibiotic therapy, severely weakened immunity, and unstable hormonal levels.
Gray, greenish
Jelly-type vaginal discharge, which has a completely gray or greenish tint, is the first sign of putrefactive processes that occur in the tissues of the female reproductive system.
In most cases, mucus of this color has a sharp and unpleasant smell of rotten fish and contains an increased concentration of pathogenic microorganisms that pose a threat to the human body.
Gray and greenish discharge may indicate a pathological condition of the child, fetal death, or the onset of necrotic processes.
A pregnant woman who discovers a similar symptom should be immediately hospitalized in a gynecological department. You will need to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis of the whole body, establish the cause of the appearance of gray or greenish discharge, and also make sure that the fetus is safe.
Brown
Jelly-like discharge in women, which has a brown tint, indicates that the mucous contents contain blood. This symptom indicates the presence of cracks and ulcerative formations localized on the mucous membrane of the internal genital organs. In this case, the woman’s reproductive system suffers from an acute or chronic inflammatory process.
Brown jelly-type discharge may also be accompanied by the following additional symptoms:
- cramps in the lower abdomen;
- cutting pain inside the vagina;
- unpleasant odor of mucous discharge;
- redness of the vaginal walls;
- increased body temperature;
- general malaise.
Brown, jelly-like discharge coming from the vagina can be a harbinger of the imminent onset of bleeding, and also indicate pathology in the development of the fetus. The appearance of these symptoms is a reason for hospitalization of the pregnant woman in a hospital setting.
Thick
Too thick jelly-type discharge indicates an acute and extensive inflammatory process that occurs in the tissues of the female reproductive system. Especially if the release of mucous contents is accompanied by aching, cramping or cutting pain in the lower abdomen spreading to the vaginal cavity.
With smell
Based on the primary smell of mucous discharge from the vagina, one can suspect the reason that caused its sudden appearance.
In case of infection of the reproductive system with dangerous infectious microorganisms in the form of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Streptococcus, gonococcus, the jelly-type mucus has an unpleasant putrefactive odor and may contain impurities of ichor and pus.
Damage to the vaginal mucosa by colonies of the fungus causes a pungent aroma of fresh yeast. In the latter case, the discharge may have a foamy appearance, which indicates a high concentration of pathogenic microorganisms, and also indicates the height of the disease.
Diagnosis of pathology
Every woman should understand that it is impossible to independently identify the reason why clear, jelly-colored vaginal discharge occurs. Only a specialist can determine the correct diagnosis after the diagnosis has been carried out:
- Anamnesis collection. The doctor asks the patient about her existing complaints.
- Examination on the chair. Using gynecological devices, the doctor evaluates the vaginal mucosa.
- Bimanual examination. The gynecologist palpates the genitals and vagina. This allows us to determine the structure of the reproductive system.
- Smear collection. Laboratory analysis is done to determine the microflora of the vagina.
- Colposcopy. It is carried out with the aim of identifying the nature of erosion on the neck.
- Ultrasound. Diagnostics allows us to identify the presence or absence of pathologies in the uterus and ovaries.
As soon as the results of all tests are ready, the gynecologist will be able to make a diagnosis, based on which he will prescribe the correct treatment. Complex therapy is usually selected.
Medications are prescribed on an individual basis - the flora that provoked the appearance of transparent jelly-like discharge is taken into account.