The main reasons for the appearance
As soon as a girl begins puberty, she notices the appearance of leucorrhoea. Vaginal secretion is observed throughout the entire reproductive period and stops only at the onset of menopause. If the discharge is odorless and colorless, this is normal.
Leucorrhoea in women is produced by special glands. They contain waste products of various microorganisms that are present in the microflora, and cervical fluid, which performs a protective function.
An increase in secretion volume during certain periods of the cycle is considered normal. Similar changes are observed during the period of ovulation, when the uterus is ready for fertilization, and closer to the arrival of the regula.
Changes in leucorrhoea in volume and consistency can be caused by various pathologies. Copious discharge with an unpleasant odor may be a symptom of the disease. Therefore, it is so important to constantly monitor all the features of vaginal secretion.
Why do women douche?
Women practice douching because they mistakenly believe that it is beneficial. The most common purposes for which women undergo such procedures include:
- Vaginal hygiene;
- Removing residual bloody discharge after menstruation;
- Elimination of unpleasant odor;
- Prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs);
- Preventing pregnancy.
Gynecological practice today shows that for all these purposes, douching is of little use, and the harm from it almost always exceeds the intended benefit. Only in rare cases, in combination with other therapeutic agents and methods of douching may be advisable.
Diseases caused by heavy discharge
Abundant secretion without color or odor is often caused by diseases. There are several groups of pathologies that can lead to a change in the nature of leucorrhoea and an increase in its volume.
Inflammatory diseases
The reasons for strong discharge in women may lie in inflammatory processes occurring in the body. Among them are the following:
- Colpitis . The cause of inflammation of the vaginal mucosa is a change in the composition of the microflora and the predominance of pathogenic bacteria in it. Such violations can occur if the rules of intimate hygiene and frequent douching are neglected. Initially, profuse leucorrhoea is observed, in which pus appears over time.
- Cervicitis . The pathological process develops in the cervix. From the moment it begins, abundant secretion is observed, acquiring a pinkish tint due to damage to the blood vessels. Closer to the approach of the regula and immediately after their completion, the mucus turns brown.
- Endometritis . When the endometrium becomes inflamed, its vessels are damaged, and blood clots appear in the leucorrhoea. This symptomatology manifests itself most clearly after intimacy.
- Salpingitis . Inflammation of the fallopian tubes in acute form manifests itself in the form of a watery green secretion with a pungent aroma.
- Oophoritis. If the inflammatory process begins in the tubes of the reproductive organ, there is abundant discharge mixed with pus and an unpleasant odor.
Pathologies are often accompanied by pain localized in the lumbar and abdominal areas, as well as hyperthermia and cycle failure.
Venereal pathologies
With venereal diseases of the genital tract, as a rule, leucorrhoea appears with an admixture of pus, which has a specific aroma. Urination becomes painful, and there is discomfort in the abdominal area. Other signs of the disease appear, including itching and burning in the intimate area.
The most common STDs are the following:
- Trichomoniasis. The appearance of intense gray-yellow foamy discharge with an unpleasant aroma is noted.
- Chlamydia. Leucorrhoea acquires a mucopurulent consistency and a pungent odor. At the initial stage of development, the pathology is often asymptomatic.
- Gonorrhea. The secretion becomes yellow and quite abundant, it contains pus.
Infectious
In the presence of an infectious-inflammatory process, secretion becomes abundant, its color and smell change.
In case of disturbances in the vaginal microflora, bacterial vaginosis often develops. This process can be triggered by hormonal fluctuations, various pathologies of the genitourinary system, and the use of antibiotic medications. In this case, leucorrhoea is profuse, causing irritation in the intimate area. As a rule, they have a gray color and a pungent odor of rotten fish.
The volume of discharge also increases in the case of thrush development. The consistency of the leucorrhoea becomes cheesy and the smell sour. Associated symptoms include itching and burning.
Education mechanism
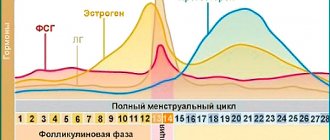
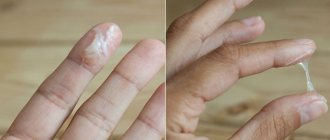
The structure of a woman’s genital organs is very interesting, each element in them performs clear functions, and for the proper functioning of the reproductive system, the full functioning of all parts is important. For example, the cervix not only connects the uterine cavity with the vagina, but also plays the role of the main protector against the entry of foreign bodies and infections into it. Inside the cervix there is a cervical canal, which is covered with epithelial cells of the glandular structure, forming branches of the glands. It is in these glands that a mucous jelly-like substance is produced, which is necessary primarily for conception: during the period of ovulation, its quantity increases significantly, it becomes more liquid, facilitating the easy movement of sperm directly into the uterus.
Thus, a moderate amount of jelly-like discharge in women is explained by the active work of the glandular cells of the cervical canal and is a physiological feature of the female body. The consistency and volume of vaginal discharge can vary, responding to a woman’s stressful state, environmental conditions (for example, a sudden change in weather conditions when going on vacation), and the influence of a number of medications. An increase in the amount of mucus secreted on the eve of ovulation is physiologically justified. There is a connection between the volume of discharge and a woman’s arousal: the more the body is ready for sexual intercourse, the more mucus in the vagina. Pregnancy is another factor in the increased production of viscous fluid. Moreover, the longer the gestation period, the more mucus - this is due to the activation of the production of female hormones.
The average norm is no more than half a teaspoon of discharge per day (about 2 ml). This fluid should predominantly contain cellular structures of squamous epithelium and lactobacilli.
A minimum content of opportunistic microorganisms such as streptococci and staphylococci, gardnerella, mycoplasma, and anaerobic bacteria is also acceptable. When their amount is up to 2%, we can talk about healthy vaginal microflora. This balance is ensured by an acidic environment (acidity pH level varies from 3.8 to 4.5).
Volume of discharge
The secretion of a transparent, odorless color can be abundant or scanty. Depending on the volume of leucorrhoea, the reasons for its appearance will be different.
Scarce
Previously abundant, transparent leucorrhoea often becomes scanty during certain phases of the cycle and does not indicate pathology. Scanty periods are observed during menopause, when the level of sex hormones in the female body significantly decreases, the mucous membranes become thinner, and reproductive function gradually fades away.
Often hidden sexually transmitted infections at the initial stage of development are accompanied by slight secretion, which women perceive as normal. Only after a while is a large amount of discharge observed, acquiring an uncharacteristic aroma.
Abundant
Normally, the volume of odorless discharge per day does not exceed 5 ml. The amount of secretion varies throughout the cycle. The appearance of excessively abundant discharge in women often signals problems such as:
- Erosion. In the presence of ulcerations on the cervix, there is a significant increase in the volume of secretions before the arrival of the regula.
- Salpingitis. At the initial stage of the inflammatory process, leucorrhoea becomes more abundant, and after a while it becomes yellow.
- Adnexitis. This pathology is characterized by the appearance of mucus, the consistency of which resembles snot.
- Vaginitis. The discharge not only increases in volume, but also acquires an unpleasant aroma.
Watery
Watery discharge that does not have any odor is considered normal, but only if no other clinical manifestations are noted. Transparent leucorrhoea appears after ovulation. If they acquire an uncharacteristic aroma, they may indicate the following pathologies:
- chlamydia;
- bacterial vaginosis;
- thrush;
- vulvitis
How safe are they?
Chlamydia is one of the most common pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases.
Douching is not safe and most gynecologists do not advise women to douche. The vagina contains bacteria and other microorganisms called vaginal flora. They are necessary to protect against foreign bacteria and to maintain the normal condition of the vaginal mucosa. Normal acidity is also maintained here, providing optimal conditions for harmless microflora necessary for the vagina. Douching can change this delicate balance and lead to the death and washing out of those bacteria that do not pose a danger to the body, but to some extent protect it from pathogenic microorganisms. This may increase your risk of contracting vaginal infections.
Additionally, douching may spread existing vaginal infections to the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. Simply put, if a woman has an infectious disease of the vagina and she wants to fight it with the help of douching, there is a risk that it is because of such procedures that other internal genital organs will become infected.
Consistency of secreted secretion
Copious discharge in women comes in different consistencies. Depending on these secretion features, several reasons for their appearance are identified.
Thick discharge
Normally, very thick mucus is observed at the time of ovulation and in the early stages of pregnancy. It is caused by natural physiological processes that occur in the body. In this case, purulent discharge of a thick consistency is an alarming symptom. Their appearance is often caused by sexually transmitted diseases and advanced inflammatory processes. If such clinical manifestations occur, you should seek help from a doctor without delay.
Mucous
Such secretion is a normal phenomenon and causes absolutely no concern. The main thing is that it does not have any odor and is not accompanied by itching, discomfort and other unpleasant sensations.
If additional symptoms are present, it is no longer possible to consider mucous leucorrhoea as a variant of the norm.
Curdled
Discharge that acquires a cheesy consistency signals the development of candidiasis. This disease develops due to the active proliferation of candida fungi. These microorganisms can remain in the vaginal microflora for a long time and not make themselves felt in any way. When favorable conditions are created, their rapid development begins. In this case, a change in the consistency of secretion is noted. In addition, discharge from thrush acquires a pronounced sour odor. Severe itching and burning appear in the intimate area.
What You Can Do About Hostile Cervical Mucus
Treatment for hostile cervical mucus largely depends on what is causing the problem, what is causing the condition.
- If you have an active infection, see your doctor. You may need an antifungal drug or antibiotic. You can also see a nutritionist or naturopath for herbal antibacterial therapy.
- Quit smoking.
- Drink plenty of fluids to maintain proper hydration levels.
- Your doctor may prescribe low doses of estrogen for a short period of time to correct hormonal imbalances.
- Eat whole foods. Diet when planning pregnancy should be based on the exclusion of processed foods and dairy products, if possible. Your diet can definitely improve the pH of your cervical mucus—eating alkalizing foods like vegetables and berries, as well as leafy greens.
- Avoid any medication that may dry out mucous membranes. Talk to your doctor about reducing your dosage.
- There is evidence that to increase the amount of mucus, you can take drugs with guaifenesin - this is a mucolytic drug taken orally. Although there have been no studies to prove that it successfully thins cervical mucus in the same way it thins respiratory mucus when coughing.
- If you feel you need it, use a fertility-friendly lubricant during sex. Lubricants should only be water-based with a neutral pH.
- Evening primrose oil (from the seeds of Oenothera biennis) taken orally has been reported to improve the quality of cervical mucus. But as with many herbal remedies, there hasn't been enough research to demonstrate its effectiveness in improving hostile cervical mucus.
- Options for eliminating antisperm antibodies are systemic enzyme therapy under the guidance of a physician, or a course of tribulus under the supervision of a naturopath.
During pregnancy and after childbirth
In addition to normal leucorrhoea, dangerous ones can also be discharged from the vagina during pregnancy. Leaving this unattended is strictly prohibited. Often, during pregnancy, the body's protective functions are suppressed, the vaginal microflora is disrupted, which in turn leads to the development of candidiasis and bacterial vaginosis. Inflammatory and sexually transmitted diseases are not uncommon during this period.
With successful fertilization, the amount of secretion increases. In addition, it becomes thicker. Such symptoms are considered the absolute norm and are observed throughout the first trimester. Also, profuse leucorrhoea begins to appear closer to the expected birth. They are caused by the release of the mucus plug, which protects the reproductive organ from various infections.
The presence of blood in the mucus is observed during erosion. Such clinical manifestations may also signal an ectopic pregnancy. In addition to changes in the nature of secretion, pain in the abdominal area is noted.
Blood in the leucorrhoea can also be observed in the case of partial placental abruption. In this case, the woman needs to be urgently hospitalized. There is a high risk of spontaneous miscarriage and the onset of severe uterine bleeding.
After the end of labor for six weeks, women discharge lochia from the vagina, visually similar to menstruation. Gradually they become less abundant, first acquire a yellowish tint, and then take on a normal appearance.
What is the best way to practice vaginal hygiene?
Washing with regular baby soap is quite enough for hygiene of the female genital organs.
Regularly washing the labia majora with warm water and a gentle soap during baths and showers is enough to keep the outside of the vagina clean and healthy. In addition, doctors advise women to avoid scented tampons, pillows, powders and sprays. These drugs can contribute to the introduction of infectious agents into the vagina.
Most doctors believe that a healthy woman's vagina can clean itself completely on its own. Women do not need to douche to wash away blood, semen, or vaginal discharge. The vagina naturally gets rid of everything unnecessary on its own. Also, it's important to note that even a healthy, clean vagina may have a slight odor—this is normal.
After menstruation, before and in the middle of the cycle
The nature of secretion after menstruation and before it is significantly different. On the first day of menstruation, brown spotting may be observed, which gradually takes on the appearance of normal regula. Immediately after their completion, the amount of mucus becomes minimal, it liquefies and by the middle of the cycle significantly increases in volume.
By the time ovulation occurs, the secretion becomes viscous and similar to egg white. Thanks to this, it is easier for sperm to reach a mature egg, and the most favorable period for conception begins.
Discharge at the end of the cycle also becomes abundant and signals the imminent arrival of menstruation. A few days before the onset of critical days, a small amount of blood is often noted in them, indicating the onset of endometrial rejection.
Such changes occur monthly; this is the norm for a healthy woman. But if an infection has entered the body or a gynecological pathology has begun to develop, the nature of the leucorrhoea may remain unchanged for a long time, which in itself is an alarming signal. Often the mucus acquires an uncharacteristic color and a pungent aroma. The clinical picture is complemented by accompanying symptoms.
How common are these procedures?
The prevalence of douching varies between developed and developing countries. Thus, in developed countries, about 30% of women regularly douche, while in developing countries the number of women using this procedure reaches 50-75%. Every second African woman, for example, douches at least once a month. In post-Soviet countries and some others, where such procedures are used by doctors as part of treatment, the percentage of mature women who douche is the highest - 90-97%.
Options for where inflammation develops
Discharge in the form of jelly of an atypical color or smell indicates not only problems in the vagina. The following cases may occur:
- the most common inflammatory processes - the culprits of leucorrhoea - include diseases of the vagina, including its dysbiosis;
- Possible problems in the fallopian tubes. During the inflammatory process, a process of narrowing of the lumen of the tube due to edema is observed. The contents of the tubes unevenly enter the uterus, and then are released into the vagina in portions;
- if the endometrial cells of the uterus are affected, leucorrhoea may also appear;
- when the cervical canal is inflamed, glandular cells excessively produce mucus, and the volume of vaginal discharge increases significantly;
- It is possible that vestibular leucorrhoea may form when the vestibule of the vagina does not function properly.
In general, in adolescence, more than half of all complaints about leucorrhoea are explained by disruptions not in the sexual sphere, but, for example, in the endocrine system, or allergic reactions. Only a third of all patients in this age group have problems with gynecology, and in most cases due to infections.
During menopause, vaginal discharge changes in character due to atrophy of the genital mucosa, but oncological pathologies are no longer excluded.
Natural discharge can suddenly change to heavy and even purulent if a foreign body remains in the vagina for a long time. For example, a hygienic tampon (gynecologists allow it to remain in a woman’s body for no more than 8 hours) or a vaginal ring to protect against unwanted pregnancy.
If a woman is generally healthy, then the initial imbalance in the vaginal microflora levels out on its own, and soon the discharge takes on its usual appearance. But if infections occur, it is no longer possible to do without qualified medical care.
Possible options
Scanty, odorless discharge, not accompanied by pain and discomfort, can be not only completely transparent, but actually white. This is a normal natural process.
A pathological process in a woman’s body can only be indicated by white discharge of a cheesy structure, against the background of noticeable itching of the genitals. These symptoms clearly indicate excessive activity of Candida type fungi in the vagina. This disease is familiar to most women, like thrush.
Very often, an inflammatory process of this nature occurs against the background of irrational use of antibiotics.
Candidiasis is diagnosed quite simply due to its clear characteristic symptoms. Treatment consists of local antifungal therapy (suppositories, suppositories), taking medications that suppress Candida fungi in the gastrointestinal tract and the subsequent restoration of healthy vaginal microflora. Unfortunately, candidiasis has a tendency to frequent relapses and become chronic.
Yellow
Jelly-like discharge can become a rich yellow, and sometimes a distinctly greenish tint in case of infectious diseases of the genital organs. In this case, a purulent process is clearly present.
If the leucorrhoea becomes more abundant and thinner, maintaining a yellow color, most likely, a sexually transmitted disease is occurring - trichomoniasis. Typical symptoms also include burning, itching, and problems with urination. The discharge in this case soon becomes like foam with a strong unpleasant odor. Treatment must be timely and complete, otherwise the disease may become chronic.
If the yellow discharge is similar in consistency to thick cream, and the woman feels very bad, even feverish, the culprit is gonorrhea. This dangerous disease threatens reproductive function and often causes further infertility.
Sources:
https://topginekolog.ru/vydeleniya/zheleobraznye https://ovydeleniyah.ru/u-zhenshhin/zheleobraznye.html https://venerbol.ru/vydeleniya/zheleobraznye-u-zhenshchin-bez-zapaha-chto-ehto- takoe.html