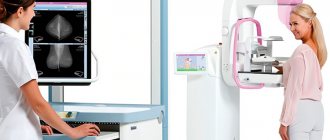
Mammography is a type of diagnosis that is a screening study of the condition of the mammary gland, the purpose of which is to identify benign and malignant neoplasms, including cancerous tumors. At what age do mammograms begin? Let's talk!
A woman needs to undergo this examination regularly for preventive purposes. Doctors recommend using this type of diagnosis no more than 1–2 times a year from 40–45 years of age. It is at this age that most cancers are detected.
Indications and contraindications
Doctors recommend that all women who have reached puberty undergo this examination once a year. But this is especially true for those over 40 years old. According to statistics, between the ages of 40 and 49 the risk of breast cancer is 1 in 69. This risk increases to 1 in 27 for women 70 and older.
Symptoms that require urgent mammography:
- nipple discharge;
- the appearance of compactions;
- chest pain;
- deformation of the breasts or nipples.
It is important to remember that the first stage of breast cancer is not accompanied by pronounced symptoms, so mammography can be preventive. If breast cancer is detected at the first stage, the patient's survival rate is 90%. The survival rate at the fourth stage is no more than 10%.
Factors that increase the risk of developing breast cancer for which regular mammography is recommended:
- hormonal deficiency;
- elderly age;
- taking hormonal medications;
- early onset of first menstruation;
- late menopause;
- obesity;
- one of the relatives had cancer.
Since during the examination the patient receives, albeit a small amount of radiation, this procedure has contraindications.
Contraindications for examination:
Contraindications and possible side effects of mammography
A contraindication to mammography is, first of all, the young age of the patient (up to 40 years). The reason for this is a much greater sensitivity to X-rays and a different structure of the breast. Images taken before age 40 have a higher risk of radiation exposure and lower diagnostic yield.
Until recently, fears about mammography were justified by an increase in procedures, a significant portion of which were mastectomies. The current level of knowledge makes it possible to abandon most surgical procedures in favor of reliable diagnostics.
When choosing mammography, you should be prepared for the fact that due to the extremely high sensitivity of the mammograph, the result may be false positive. Then an additional x-ray examination is necessary as an element of diagnosis, excluding the presence of any cause for concern. There is no need to worry about an overly positive result from this type of test.
There is another criticism of mammography: radiation is one of the best known factors in the development of cancer. This argument was advanced in the late 1970s, prompting a response from the medical community with intense research into the importance of the risk of X-ray radiation in relation to spontaneously occurring breast cancer. Studies have shown that the ratio of detection of primary to induced cancer was 50:1. Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely avoid risks, but mammography remains the safest way to detect breast cancer early.
Preparing for a breast examination
Mammography does not require complex preparation.
Before having a mammogram:
- tell your doctor about the presence of breast implants;
- do not use deodorant before the procedure;
- Make sure your chest and armpits are dry;
- remove all metal jewelry;
- if the presence of lumps is already known, the doctor can give you an anesthetic to make the procedure comfortable.
Dependence of the procedure on the day of the cycle
Experts recommend undergoing this type of examination in the first half of the cycle. This is due to the hormone progesterone. After ovulation, in the second half of the cycle, the amount of this hormone increases and it affects the mammary glands. This can make the mammogram procedure a little unpleasant for the patient and make it difficult for the doctor to make a diagnosis.
How is the procedure performed?
The procedure is carried out for 10–15 minutes. The patient stands in front of the machine, the mammologist fixes the breast and sometimes asks her to hold her breath for a while.
Breast fixation is done for several reasons:
- to level out unevenness;
- to get a clearer image;
- to increase the clarity of the image of seals;
- The smaller the layer of tissue, the less radiation is needed to scan it.
Each breast is checked separately so that their anatomical structure can be compared. Pictures are taken in two projections; sometimes it is necessary to take pictures in additional projections to clarify the diagnosis.
The video shows how mammography is done using various techniques. Video provided by Health&Life channel.
Film
Film mammography is the first method of breast X-ray, which appeared in the 60s of the last century. The resulting image is recorded on film and cannot be converted into digital form. In addition, this method is 20% less accurate than digital mammography. Such devices are preserved only in government institutions, since the transition to digital equipment costs a lot of money.
Digital
To record the image, not film is used, but detectors. They convert X-rays into an electrical impulse and transmit the image to a computer.
This type of mammography is optimal for:
- patients with dense breasts;
- patients under 40 years of age;
- patients before menopause.
Microwave
Microwave mammography uses the intensity of the patient's own tissue radiation. In this case, X-ray radiation is not used. The essence of the technique is that compactions and foci of disease differ in temperature from healthy tissue. This allows them to be identified with high accuracy in the early stages.
Advantages of this method:
- safety;
- non-invasive;
- diagnosis in the early stages of the disease;
- determination of tumor growth rate;
- identifying patients at high risk of developing breast cancer.
Optical
This method uses infrared radiation passing through the breast tissue. Each type has its own differences and is selected by the doctor depending on the situation.
There can be three types:
- projection - pictures in two projections using harmless infrared radiation;
- tomographic - several dozen images are taken and superimposed to form a three-dimensional image;
- luminescent - the patient takes drugs that accumulate in the tumors, which makes them clear in the pictures.
Allows you to identify several types of neoplasms:
- calcifications;
- mastopathy;
- benign tumor;
- cancer tumor.
Advantages of this type of examination:
- safety;
- possibility of digital processing of results;
- better suited for patients under 40;
- high degree of disease detection.
Electrical impedance mammography
The examination is carried out using a multifrequency electrical impedance mammograph (MEM). The method is based on the fact that tissues have different electrical conductivity depending on the viewing angle. The patient lies down on the couch, the doctor applies a moisturizing ointment and places a sensor. The entire procedure is painless and takes no more than five minutes.
Advantages of this type of examination
- safety;
- no contraindications;
- the ability to repeat the procedure at any time;
- speed of examination;
- painlessness;
- high accuracy of results.
Magnetic resonance mammography (MRI)
Additional research method. Does not replace mammography or ultrasound. Suitable for monitoring breast implants and complementing the diagnosis.
Advantages of this type of examination:
- suitable for all types of patients;
- diagnostics of identified formations for benignity and malignancy;
- detection of relapse of breast cancer.
During the study
Before starting the study, you must remove your jewelry and undress to the waist. Choose clothes so that you can take them off comfortably.
To perform the test, the laboratory technician will ask you to stand in front of an X-ray machine - a mammograph. Your breasts will be located between special mammography platforms. The technician will adjust the level of the platforms depending on your height and help you position your arms, head and torso correctly so as not to distort the image. Warn the technician if you have breast implants.
During the examination, your breast will be compressed for a short time between the platforms of the machine. This is necessary for uniform capture of mammary gland tissue. If you feel discomfort, inform the laboratory assistant. The compression lasts several seconds.
Types of mammography
Examination using a film apparatus . It is dangerous to receive an acceptable dose of radiation exposure. Used for half a century, it is gradually being replaced by modern formats. Mammography detects the disease 1.5–3 years before the first symptoms appear.
- Digital mammography has been widely used in the last decade. It is characterized by a high-quality image, and the radiation dose is lower than with a classic examination. The technique reveals the smallest changes in tissues.
- Computer mammography appeared simultaneously with digital mammography. It is not used for mass screening of the population - it does not provide information about precancerous conditions. Effectively used for diagnosing malignant neoplasms and identifying secondary foci (metastases).
- Tomosynthesis is an advanced type of digital mammography. The procedure produces a series of high-quality images from different angles to find high-probability cancerous tumors without additional tests.
X-ray
The images are taken using a special device – a mammograph. During the procedure, the woman stands or sits in front of the machine. Each breast in turn is placed on a platform and clamped on top with a transparent plate that generates X-rays. The image is printed onto film in two projections. Using special equipment, tissue cells are removed for microscopic examination.
Digital
Mammography is based on the principle of converting X-rays into a digital signal. The image is displayed on the computer screen in several projections at once. You can enlarge pictures, change brightness and contrast, and make copies. The need for re-examination is minimal. The analysis is deciphered automatically. The result is sent by email to other doctors if necessary.
Computer
Advanced digital breast mammography creates three-dimensional images on a computer in three dimensions. The images are positioned at different heights and are constantly shifted to illustrate the breast in cross-section. When screening with tomosynthesis, the radiation dose is higher than during a classic examination, but within the acceptable range.
What is mammography?
Mammography is an x-ray examination. Breast mammography is performed using a mammograph, which is radiological equipment with extremely high sensitivity. The device takes sequential X-ray images of the breast, which makes it possible to recognize most changes before the appearance of any clinical symptoms. During the examination, the mammograph takes 4 x-rays of the same area, differing in the angle of exposure.
The main principle of mammography is that different tissues absorb radiation differently and therefore produce different images in the resulting image. A mamogram can reveal any abnormalities in the structure of the breast. Microcalcifications detected in this way may (but not necessarily) indicate the development of a tumor and initiate further examination to determine the cause of the changes.
Mammograph
During a mammogram, the breast is fixed at the top and bottom and compressed using equipment. The pressure required to perform the test may cause discomfort in patients, especially those who are sensitive to pain. However, this is necessary because it allows you to minimize the radiation dose while increasing resolution and contrast, and also eliminates the formation of “blind spots” in the image caused by inaccurate adhesion of the skin to the base of the detector.
Because age is a factor in changes in breast structure, it is recommended that you bring your previous images (if you have had a previous mammogram) for comparison. Changes in imaging may also be caused by using equipment that is calibrated differently, so it is recommended that additional mammograms be taken at the same center.
In its history, mammography has been criticized many times because this examination can be painful due to the high sensitivity of the breast. Moreover, the detected changes did not always turn out to be a real threat. False diagnoses are frightening and cause women to undergo repeated testing or even a biopsy of a benign lesion that would never have been detected without a mammogram, but may never have caused symptoms of the disease. However, it is most advisable in this case to check even minor changes.
What a mammogram can show
The procedure helps detect changes in breast tissue and diagnose cancer at an early stage, when there are no symptoms yet. After menopause, the risk of developing tumors is higher. Without observation and treatment, benign lesions degenerate into malignant ones.
At an early stage, breast cancer is successfully treated - 98% of women make a full recovery.
Screening
The doctor evaluates the general appearance of the structure of the mammary gland, checks the breast for the presence of suspicious nodes and lumps (cysts, calcifications, benign or malignant lesions).
Diagnostic
A mammogram is done if cancer is suspected. The diagnostic procedure will determine the stage of oncology. Doctors prescribe a referral for mammography to monitor the effectiveness of treatment with hormones or chemotherapy. The study will show whether the surgeon cut out all the malignant cells during the operation.
Main objectives of mammography
Today, the mammography procedure is the main diagnostic method that can detect various pathologies of the mammary glands, including cancerous tumors. This is a screening diagnostic method carried out for prevention. Unlike ultrasound diagnostics, which are prescribed according to indications, all women over a certain age are required to undergo x-rays, even if they do not have any manifestations of the disease. If a woman has any lumps in her breasts, discharge from the nipples, or pain, it is better to undergo an unscheduled mammography procedure. Based on its results, the mammologist will make a preliminary diagnosis, which will be confirmed or refuted by the ultrasound procedure. There is no need to conduct research often; it is enough to visit a mammologist’s office every year. Such a screening study will help identify the disease at a stage when the tumor has already begun to develop, but there are no symptoms yet.
This asymptomatic period can last about two years, and when the disease manifests itself, it will no longer be possible to cure it completely. Complete removal of the mammary glands followed by chemotherapy will be required. This treatment is considered effective, but cases of relapse, unfortunately, are not uncommon. With mammography, the disease can be detected even when therapeutic methods are effective and the risk of complications is minimal.
Women should undergo an annual preventive examination from the moment they turn 40 years old. But there is a special group of patients for whom mammography can be prescribed from an earlier age. These are women who have already suffered from breast cancer, as well as those representatives of the fairer sex whose close blood relatives have encountered this disease. The attending mammologist or gynecologist will tell you when such women should start monitoring their health.
Rules for the procedure
Mammography is done to detect pathological changes in the mammary gland in women after 35 years.
The procedure is prescribed when warning signs appear:
clear or bloody discharge from the nipples;
Young women undergo ultrasound examinations, but if family members have had cases of breast cancer, the doctor additionally prescribes a mammogram and schedules examinations.
The procedure is allowed for women over 30 years of age after breast surgery, for hormonal disorders and infertility.
What day of the cycle?
It is recommended to undergo examination 5–12 days after menstruation, when good conditions are created for visualization of the mammary glands. In the second phase, the woman’s hormonal background changes, the breasts swell and become painful. During menopause, mammography is done at any time.
How often can you have a breast mammogram?
Women after 40 years of age are recommended to undergo examinations annually, after menopause - 2 times a year. For young girls with breast diseases or at risk, the frequency of mammography is determined by the doctor. During a diagnostic examination, it is allowed to take pictures as many times as necessary for doctors to make an unambiguous verdict.
Contraindications to mammography
There are no special cases where mammography can significantly harm a woman’s health. However, for some patients, conducting the study may be difficult. This applies to ladies who have breast implants.
Not every specialist will be able to conduct a correct study of a woman who has undergone plastic surgery for breast augmentation. A radiologist with extensive experience knows how to properly straighten the mammary gland, with what force to compress the breast, so that the images are high-quality and informative.
Silicone implants
Therefore, if a woman has implants in the mammary glands, she should talk in advance with the specialist who will conduct the study and find out whether this will become an obstacle to performing mammography. If the doctor doubts his abilities or says that implants are a contraindication to the procedure, it is better to go to another clinic.
It is also not recommended for women to undergo mammography while they are expecting a baby. X-ray is radiation, the effect of which on an adult is not very destructive, but the fetus may suffer. Radiation received by a baby in the womb can lead to congenital pathologies and anomalies. Therefore, during pregnancy it is better to avoid mammography. The best type of examination will be ultrasound diagnostics, which is safe for both mother and baby. If its results are disappointing, further examinations and diagnostics will be carried out only after birth.
It is also important to be confident in the specialist’s qualifications when interpreting mammography results. The quality of the resulting images is not always ideal, and only an experienced doctor will be able to distinguish artificial interference (sweat, deodorant, perfume, etc.) from real tumors in the mammary glands.
Risks and limitations
A mammogram may give a false result (positive or negative). Reliability depends on the examination method and the experience of the radiologist. Age and density of the mammary glands affect the accuracy of the image.
What to do if mammography reveals pathology of the mammary glands?
First of all, do not panic if you are told that a mammogram has revealed darkening (mass formation) or some abnormalities have been identified. Detection of a formation does not mean that a mammogram reveals breast cancer. In the vast majority of cases, various benign (harmless) processes and formations are identified in this way. In some cases, it may simply be an area of thickened or denser breast tissue, a cyst, or a benign tumor such as a fibroadenoma. If a suspicious area is detected during a mammogram, the patient may be advised to undergo additional examination of this area using breast ultrasound or another examination method. In this case, the radiologist redirects the patient to a specialized specialist involved in breast pathology. Most often, this is an experienced surgeon or mammologist, who subsequently performs a biopsy of the suspicious area.
Fig.5 Mammogram for breast cancer
A breast biopsy is the removal of a piece of breast tissue for examination under a microscope. The biopsy can be done through conventional surgery, in which an incision is made and the suspicious area is removed, or the same procedure can be done using a stereotactic needle biopsy. Stereotactic biopsy is a technique for obtaining a sample of suspicious tissue without the need for traditional surgery. In this case, a special machine and computer mammography apparatus are used, which make it possible to reliably determine the nature of the breast lesion, and then obtain very thin sections of breast tissue for examination under a microscope. This procedure is carried out under local anesthesia of the puncture area and, as a rule, is absolutely painless.
Fortunately, most breast biopsies performed reveal the benign nature of the lesions being studied. While mammography is not accurate enough to confirm or rule out breast cancer, it is currently the best way to screen for breast cancer. Since its increased routine use, mammography has made it possible to detect breast cancer at an earlier stage, less advanced and smaller in size. Mammography has allowed more women to survive through early diagnosis and timely treatment. Therefore, the use of conventional mammography is still encouraged by most clinicians, as it is still the best alternative in diagnosing breast cancer.
Mammography as a method of screening for breast cancer (presentation)
Preparing for breast mammography
2-3 days before the procedure, eliminate caffeinated drinks from your diet.
How long to wait for the result
The result will usually be ready in a few days, however, in our country there are medical institutions in which expectations for the result of mammography are reduced to an absolute minimum.
The specialists of the Russian Doctor company recommend to their patients only proven medical institutions and experienced specialists. With us you can completely trust the results of mammography and other examinations.
Unfortunately, our site is not compatible with your browser. Please update it to any other version. For example, Google Chrome, or you can check your browser on the Yandex service.
How to pass correctly
Before entering the office, undress to the waist and gather up your loose hair. Wear a lead apron to protect other organs from radiation.
How long
Preventive mammography of the mammary glands takes 10–20 minutes. If the images are of poor quality, the procedure is repeated. Computed tomography to confirm the diagnosis and search for metastases lasts up to 2 hours.
How dangerous is mammography?
Because mammography uses X-rays, there are minimal radiation side effects on the body. However, the amount of radiation used in mammography is minimal and approved by major national and international regulatory authorities. However, patients who are pregnant or may be pregnant are advised to alert their practitioner or radiologist because the radiation may pose a risk to the developing fetus.
Results and transcript
The conclusion is issued by a radiologist after analyzing the images obtained. Interpretation of mammography of the mammary glands takes from one hour to several days. Private clinics send descriptions by email. If the result is questionable, the doctor recommends that the patient undergo other types of examination. A woman should have a repeat mammogram in 4–6 months.
The radiologist analyzes the condition of the breast tissue, its structure, the presence of metals and calcium. In the image you can see compactions and darkening in the mammary gland, which indicate pathological processes. Vessels, ducts and lymph nodes are viewed.
When decoding images, a scale is used to determine changes:
The result does not provide information.
Calcifications
Calcium deposits appear on the image as white spots or stripes. Often observed after 50 years. Small accumulations, similar to grains of salt, signal the development of a cancerous tumor. Large calcifications are benign - they are found even in normal conditions.
Creams and deodorants that women apply to their skin before the test make diagnosis difficult.
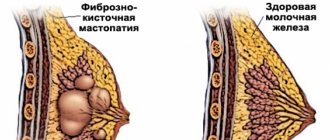
Seals and lumps
The likelihood of cancer is indicated by a blurry light area with uneven borders. A round spot on a mammogram with clear contours indicates a benign lesion. A mobile lump can be easily felt when palpating the mammary gland and does not degenerate into a malignant formation.
Mastopathy is characterized by thickening of the mammary glands. In the nodular form, a cyst is formed - a cavity with clear liquid; it rarely degenerates into cancer.
How and when does a patient receive mammography results?
Mammogram results can be provided to the patient either by the radiologist at the end of the mammogram or by the physician who ordered the mammogram. Most often, the results are announced by the attending physician, after discussing them with the radiologist. In some cases, due to busyness or other reasons, the patient may receive study data with results by email. Very often, when a formation in a suspicious area is detected on mammography, the information is announced immediately in person or by telephone, since further assessment of this area requires greater efficiency. If there are no results for some time (more than 4-5 days) after the study, it is advisable for the patient to contact the attending physician again for clarification and cannot rely on the fact that if the doctor does not report the results, then everything is fine.
Fig.4 Analysis of mammography results