Views - 62,152
Assessment of UHM indicators (the abbreviation stands for uterine fundal height) is one of the most important diagnostic measures during pregnancy. Firstly, the indicator under consideration allows us to determine the age of the developing baby, secondly, to assess the condition of the fetus, and thirdly, to assume the presence of various types of deviations in the child’s development.
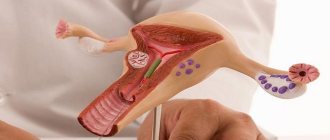
In sexually mature women, the uterus in normal condition has a length of up to 8 cm, of which about 2.5 cm is at the cervix. As the child develops, the size of the uterus also changes, and by week 40 it can reach about 40 cm. The weight of this organ also increases - before conception it is approximately 50 g, and by the third trimester it increases up to 4 kg.
- Features of changes in the uterus during pregnancy
- Deviations of VDM from the norm
- How to independently determine VDM?
Video - WMD during pregnancy by week table
Fundal height of the uterus - concept
The most significant changes affecting the female body occur in the uterus during pregnancy. From the moment of attachment of the fertilized egg until the moment of birth. To ensure a comfortable stay for the unborn child inside, the uterus is constantly expanding. When mature, it is about 8 cm long, about 2.5 of which is the cervix. With the growth and development of the embryo, the size of this organ also changes, reaching 40 cm by the 40th week. Its weight also increases from 50 grams. up to 4 kg.
For a short period of time, the size of the organ is determined by palpation through the vagina. When the 14th week arrives, the uterus reaches such a size that it extends beyond the boundaries of the pelvic area, rising higher, so that it becomes easily palpable through the abdominal wall. This concept is called the height of the uterine fundus.
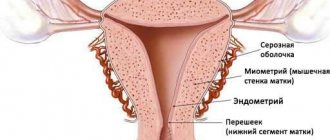
The height of the uterine fundus is the length between the pubic symphysis and the upper border of the organ, which is its bottom. It is measured in centimeters at each woman’s visit to the gynecologist and is indicated on the exchange card. It is important to monitor the dynamics of changes in order to identify any deviations in time. The size of the uterus makes it possible to determine compliance with the gestational age and date of birth.
The belly is growing but the uterus is not rising. How the uterus changes during pregnancy
The biggest changes that occur in a woman's body during pregnancy are probably related to her uterus. This is where the fertilized egg is normally attached for its further growth and development. To provide the growing fetus with the space necessary for life, the uterus constantly increases in size. As it grows, it rises higher and higher, reaching a maximum at approximately 37 weeks of pregnancy.
The lifespan of sperm is 72 hours. This means that for 3 days sperm can survive inside the uterus. If a woman is near her fertile days, the cervical mucus will be as clear and watery, and the ovarian follicle will be bulging, although it is not yet ready to be released. So the sperm will move on and on and on until it meets an egg somewhere. If the eggs are not encountered, a very small portion will fall after crossing the infundibulum of the fallopian tube.
Some may become trapped by the fimbriae, and if the fallopian tube is sufficiently closed, it may even fall on top of or near the eastern follicle in the ovary. Or perhaps the egg was released normally, transport begins, and reclamation occurs in a funnel where gravity may play a role.
The biggest changes that occur in a woman's body during pregnancy are probably related to her uterus. This is where the fertilized egg is normally attached for its further growth and development. To provide the growing fetus with the space necessary for life, the uterus constantly increases in size. As it grows, it rises higher and higher, reaching a maximum of approximately .
Hope you get the picture now. Let's say that ejaculation occurs 60 or 70 hours before ovulation. The sperm will have more than enough time to move freely, and once the egg ruptures, it can be intercepted by the sperm, although the position is not ideal. In most cases this egg would be discarded, but the human body cannot be generalized.
Fallopian tubes: 95% of all ectopic sites will occur in the fallopian tube, usually because the cilia are damaged or they are moving abnormally, and so the egg will move very slowly or not at all, and the process will continue normally, although abnormally the circumstances are clear. But the secretions can retain nutrients, and as long as the embryo is small enough, it will survive for a while. Pregnancy in this part is not viable and must be terminated as soon as possible to prevent permanent damage to the fallopian tube or even rupture. Cornum uterus or uterus from the point: 2.5% of ectopic pregnancies occur near the angle of the uterus. The survival rate up to this point is better, but not completely. Ovarius, abdominal cervix: the remaining 2.5% will occur in any of these structures. Ectopic pregnancies in the ovaries and cervix are not viable and again need to be terminated, but not in the abdominal cavity. An egg may be fertilized but fall, either due to abnormal functioning of the cilia or because fecal matter occurs in the first parts of the fallopian tube and is released into the abdominal cavity.
The size of the uterus and its height are of great diagnostic importance. They help determine the approximate duration of pregnancy and draw conclusions about its course, as well as assess the degree of development and size of the fetus and identify possible deviations in time. That is why he will examine and evaluate the size and height of the uterus at every examination of his ward.
This area is covered by a membrane called the peritoneum. The visceral peritoneum covers the intestines and the lower part of the stomach and its rich blood vessels. This is why implantation can occur. The fertilized egg will be attached to it, and soon the placenta will break the vessels and use them. The embryo and then the fetus will be protected by something called the amniotic sac, which will contain amniotic fluid.
This is very rare. Eggs that enter the abdominal cavity are absorbed rather than implanted. But with modern medicine, you can keep one or both. Now, why is pregnancy impossible without a uterus? Let's say a woman has no uterus due to a hysterectomy. Intermediate hysterectomy: where the uterus is removed but the cervix and fallopian tubes remain. Radical hysterectomy: where the uterus, cervix, and upper third of the vagina are removed. General hysterectomy: where the uterus and cervix are taken. . The ovaries will remain under any of these 3 procedures and the mature eggs will fall directly into the abdominal cavity if there are no fallopian tubes, or will be caught by the fallopian tubes but either remain inside, dissolve, or fall into the abdominal cavity and dissolve.
In the early stages, the size of the uterus is determined by finger palpation through the vagina. But from the second trimester, after approximately 13-14 weeks, the uterus extends beyond the border of the pelvic region, rising higher, and it can already be felt through the abdominal wall. Now the gynecologist will measure it every time, or more precisely, the height of the bottom.
And what to do if we have sex and ejaculate. Any of these three procedures would leave the vagina closed, completely sealed and therefore no room for sperm to enter, not even into the abdominal cavity. But just for the sake of argument, let's say there's a small discovery, the Neck remains, and it wasn't sealed properly.
The uterus contracts to make it easier for sperm to travel up the fallopian tube. Without a uterus this will not happen. And why is a fallopian tube so important if you can actually carry out a pregnancy in the abdomen? Remember those nutrient secretions in the fallopian tubes? These secretions provide additional nutrition to the egg and sperm to ensure survival. It also changes the chemical balance of the membrane in every sperm that reaches this point, they will become hyperactive and move harder and faster.
The height of the uterine fundus () is the distance between the upper point of the pubic symphysis and the highest point of the uterus, which is its fundus. It is measured in centimeters in the position of a pregnant woman, lying on her back, using a special pelvis meter or a regular measuring tape. The doctor enters all the indicators into your chart each time in order to be able to compare them and track the dynamics.
The proteins in their membrane begin to change and when they reach the egg, their heads will open and so chemicals will be released to break down and penetrate through the thick layers of the egg until they reach the inner membrane. One will be able to pass. Without the fallopian tubes, egg survival is greatly reduced. The sperm cannot move fast enough to meet the egg before it is too late, and thus fertilization is impossible.
I hope this information answered your question. Pregnancy is divided into three trimesters. This division is useful, especially when describing symptoms that a woman may experience. By the time the pregnancy reaches the 28th day or the end of the 4th week, it is firmly established in the lining of the uterine cavity and is visible to the naked eye. Extremely important changes occur in a woman's body at this early stage, although she may not know she is pregnant until she misses her first period.
To evaluate the indicators, use a table that shows the standards for compliance with the gestational age of pregnancy:
As you can see, the height of the uterine fundus in centimeters approximately corresponds to the gestational age in weeks, plus or minus 2-3 cm. This range of fluctuations in UMR values takes into account the individual characteristics of each pregnant woman, in particular, her physiological parameters.
The embryo is about an inch and a half long and already has a recognizable head, nervous system, body and the beginning of minute buds. By the end of the fourth week, the heart begins to beat, although it is not yet visible on an ultrasound scan. It is usually around this time that a woman begins to suspect that she may be pregnant when she misses her first period.
The embryo measures about one and a half inches. Material organs continue to form, the digestive, respiratory and urinary systems are formed. The eyelids have formed but will not open for several weeks. Ears, ankles, fingers and toes are barely distinguishable at this stage, and it is at this time that the proportion of hearing, which is responsible for balance and hearing, also grows.
A significant discrepancy between the height of the uterine fundus and the norms at a particular stage of pregnancy gives the doctor reason to suspect something is wrong. If the indicators are too high, we can talk about or too much. Underestimated indicators of the fetus may indicate low rates of fetal development, its transverse or oblique location.
However, do not rush to panic and draw premature conclusions if your uterine fundus height does not correspond to the due date. Firstly, often the reason for the differences is an error in determining the gestational age. Secondly, in the case of inflated indicators, the reason can be doubly pleasant - this is development. Thirdly, indicators of the height of the uterine fundus themselves are not very informative. It is necessary to evaluate the dynamics, and if from week to week or from month to month the uterus rises higher and higher, as it should be, then there is most likely no reason for concern. However, if any violation is suspected, the doctor will refer you for additional tests (ultrasound, Doppler, CTG, etc.), and this should not be neglected.
The circulatory system is established and the heart is beating strongly. The lungs, which form as tiny solid organs on each side of the midline for about seven weeks, continue to grow rapidly but remain at this level. The embryo's head is still very large in size in relation to the body, although the face begins to take on a noticeable shape with depressions present where the eyes would be and shaped nostrils. The two sides of the upper and lower jaw are also fused so that the mouth can be recognized.
Shoulders, elbows, hips and knees begin to become apparent and the limbs continue to develop rapidly. Because the spine is fully formed at this stage, the embryo is able to make very small movements, although the mother is not yet aware of these movements for many weeks.
Please also note that 2-4 weeks before labor begins, the baby begins to descend into the pelvis, which we call. At the same time, the uterus also decreases slightly and the IMD accordingly decreases by several centimeters, which can be seen in the table.
Especially for
— Elena Kichak
During pregnancy, a woman experiences many changes, both physical and mental. In order to bear a small miracle in her womb, a woman’s body is completely rebuilt.
A woman at this stage of pregnancy may develop so-called morning sickness. She may also notice fatigue, urinary frequency, and tender, enlarged breasts. Nowadays, many women develop lower abdominal pain, this is due to stretching of the pelvic ligaments and muscles. There is often a creamy white discharge from the vagina.
At this stage, the rapidly growing pregnancy is no longer medically related to the embryo, but ends in fetal status. Now about three and a half inches, we can say that they have reached a major milestone where all the vital organs have formed and are starting to function.
The fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus, becomes a fetus, and with further development turns into a child. If you want to see the outline of your baby, then make an appointment as prescribed by your doctor.
The child grows and develops, which affects the functioning of the entire body of the expectant mother. The most striking female organ, the uterus, which is home to the baby for the entire period of pregnancy, undergoes the most significant changes. The development of the embryo and gestation of the fetus occurs in the uterus.
During the critical period until the end of the 12th week, congenital anomalies may occur. However, it is reassuring to note that once the organ has been properly formed, it cannot cause much harm. The growing fetus's kidneys begin to produce urine by the end of the 12th week, and soft nails form at the ends of the fingers and toes. The buds that will eventually form the 20 baby teeth already exist in the gums, and the genitals have developed, although they are not yet visible on the ultrasound scan.
The face is properly formed and the head begins to take on a more rounded appearance, but still leans forward. The inner ear is properly formed and the outer ear continues to take its special shape. The fetus continues to flex its limbs, but the mother does not feel any movement.
Initially, its shape resembles a pear, and later becomes ovoid. The uterus also increases in proportion to the development of the child, although initially its changes are completely invisible. A large number of pregnant women are interested in the structure and features of changes in the uterus during pregnancy.
Changes in the uterus during pregnancy
In the uterus, changes begin to occur immediately after fertilization. As soon as the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus, the body immediately receives a signal that it is necessary to gather all its strength and concentrate in order to save this small and fragile life.
The uterus is now enlarged by pregnancy and can be felt in the lower abdomen as a very soft tumor arising from the pelvic cavity. Other physical changes that appear to the mother at this stage are changes in the size and shape of the breasts. There is a very definite enlargement of the breasts and an increase in the size and number of veins on the surface of the breasts. Small, raised pink nodules known as Montgomery bumps also form on the areola, which is the area of pink, tender skin surrounding the nipple.
The formation of these bumps can very often be one of the most reliable early signs of a first pregnancy. However, they are not as reliable a diagnostic feature in subsequent pregnancies because they do not disappear completely after delivery.
The uterus will be slightly bulging where the egg is implanted throughout your pregnancy. Gradually, the uterus will become more swollen, filled with fluid, and swell. If before pregnancy the uterus weighed approximately 50-100 g, then by the end of pregnancy, due to all the changes and increases, its weight will reach a kilogram.
At the beginning of pregnancy, the uterus is still very small, and it is not yet possible to detect it by palpation. Only at 3-4 months does it increase to approximately the size of a newborn’s head and is palpable. The shape of the uterus also changes several times. If initially its shape is pear-shaped, then by 2-3 months it becomes spherical, and then becomes ovoid. It is this form that persists until the very end of pregnancy.
Morning sickness usually occurs sometime after the 12th week and very rarely persists throughout pregnancy. Second trimester. The fruit continues to grow and develop rapidly. All limbs are correctly formed and the joints move vigorously. The fingers and toes are properly shaped and the nails are fully formed. Although the head continues to be quite large in relation to body size, rapid body growth is observed at this stage. All primary sexual characteristics are in place, and the sex of the fetus is obvious even to an untrained observer.
Throughout pregnancy, the uterus stretches and grows in proportion to the growth of the baby inside it. In addition, the uterus is constantly shifting. If the uterus is located in the abdominal cavity, at the beginning its bottom rises and it occupies the space between the navel and pubis.
Throughout pregnancy, the fundus of the uterus rises, and by the 9th month it reaches the lower edge of the chest. Due to its large size, at the end of pregnancy the uterus puts pressure on the diaphragm and makes it difficult for the mother to breathe. In addition, the uterus puts pressure on other internal organs - the bladder, intestines and stomach. For this reason, there is frequent urination or other digestive problems.
The child's face has matured to the point where he can smile and frown. Small fluffy hair covers the entire surface of the body, including the face. Eyebrows and eyelashes begin to grow at about 16 weeks. It is during this second trimester that many women are at their peak both physically and emotionally. Their body has adjusted perfectly to being pregnant, and any nausea they may have experienced in the first 12 weeks has disappeared.
Hair appears on the head of the fetus, which now grows rapidly in both length and weight. Because he still has a relatively large amount of amniotic fluid to move around in, he can move and rotate freely and exercise his limbs very intensively.
In the process of bearing a child, the flexible fibers of the uterus and some of the ligaments that support the uterus become softer and even stretch, which, in turn, can cause pulling in a woman. But such pain can also be caused by other, more dangerous reasons, so be sure to consult a doctor and tell him what is bothering you. After all, for example, similar pains are observed with, which can lead to early termination of pregnancy or.
During pregnancy, blood circulation increases in the uterus and throughout the body. This is how the child receives the right amount of nutrients and oxygen. This is how the mother feeds her baby. The condition and health of the child directly depends on the mother’s mood, her state of health and the food consumed.
What happens to the baby in the uterus during pregnancy
After 35 weeks, the baby takes its final position in the uterus and the woman becomes a little easier. At 38 weeks, the uterus reaches its highest location, the baby moves down, pressing against the outer wall of the birth canal, thus preparing to be born. After the uterus descends, the pressure on the diaphragm decreases and the woman becomes able to breathe easier and more freely.
As soon as the uterus has dropped to its proper place, you can expect birth in the next 1-3 weeks. Over the entire period of pregnancy, the uterus has increased in weight to about 1 kg, its muscles can sometimes contract slightly - training contractions. Some mothers feel them from 20-21 weeks.
Just a couple of weeks before giving birth, women may experience false contractions - stronger contractions of the uterus that go away after some time. In this way, the uterus trains in preparation for the upcoming birth. Real contractions begin after the mucous plug, which has been covering the entrance to the uterus throughout pregnancy, comes away. At the same time, your water may break. And this all happens at approximately 38-40 weeks.
Fundal height of the uterus by week
Every week, along with the growth of the baby, the height of the fundus of the uterus should also increase. This makes it possible to determine the correct development of the fetus, the amount of amniotic fluid and tell whether the pregnancy has stopped.
The doctor is obliged to indicate this indicator each time in the pregnant woman’s chart.
Interesting! The approximate length of the VDM corresponds to the period by week, that is, at 25 weeks it will reach approximately 25 cm. An error of 1 - 2 cm in both directions is allowed.
At week 20, the border of the uterus reaches the navel, the woman clearly feels the movements of the fetus in the abdomen. The child’s position at this stage of development is not yet stable; he turns over all the time, kicks with different strength and localization.
If the height of the uterus deviates by a couple of centimeters, the woman is sent for an additional ultrasound examination and the blood circulation in the umbilical cord and placenta is studied. When determining such symptoms, a common deviation is oligohydramnios and delay in embryo development. A small amount of water especially affects the child in the womb; he becomes cramped, and therefore his growth slows down. But don’t be too nervous and stress yourself out; stress is also passed on to the fetus. Typically, the amount of fluid in the amniotic sac normalizes after 1 to 2 weeks and the baby quickly reaches the appropriate developmental stage.
Throughout the entire period of bearing a child, the uterus constantly increases in size, and accordingly the value of the UMR increases. But in the last weeks, when the fetus, preparing for birth, descends into the pelvic area, it may become smaller. Then the shape of the abdomen changes noticeably; it drops lower and no longer puts pressure on the ribs, making it easier for the woman to breathe. The position of the baby in the uterus can be easily determined by a qualified doctor. It is easily palpable during examination on the couch, which is a mandatory part of a visit to the gynecologist.
Abdominal drooping in the early stages - 30 or 35 weeks - may indicate possible premature birth. If the VDM has become smaller, and the pregnant woman’s condition has improved, this is a huge cause for concern.
The table below will tell you about the normal values of abdominal circumference and centimeters of uterine fundal height by week:
The data in the tables are not exact indicators, the structure of each person is unique, if in doubt, consult your doctor.
If signs of premature birth appear, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound for a more accurate diagnosis. It will show the amount of amniotic fluid, the condition of the cervix, its readiness for childbirth - possible opening and length.
Deviations of VDM from the norm
The average normal indicators of VDM by week are shown in the following table.
Table. WYD by week
| Gestation period, weeks | VDM, cm | Gestation period, weeks | VDM, cm |
| 8-9 | 8-9 | 26-27 | 28-28 |
| 10-11 | 10-11 | 28-29 | 26-31 |
| 12-13 | 10-11 | 30-31 | 29-32 |
| 14-15 | 12-13 | 32-33 | 31-33 |
| 16-17 | 14-19 | 34-35 | 32-33 |
| 18-19 | 16-21 | 36-37 | 32-37 |
| 20-21 | 18-24 | 38-39 | 35-38 |
| 22-23 | 21-25 | 40-41 | 34-35 |
| 24-25 | 23-27 |
In general, the GMR indicator may change under the influence of the following factors:
- size of the developing fetus;
- individual anatomical features of the maternal body;
- baby's position;
- number of developing babies;
- volume of amniotic (amniotic, intrauterine) fluid.
Under certain circumstances, the VDM value may deviate from the average norm. Information on this matter is consecrated in the table.
Table. Reasons for deviation of VDM from the norm
| VDM is below normal | The GMR indicator exceeds the norm |
| Insufficient amniotic fluid | Excessive amount of amniotic fluid |
| Wide pelvis as an anatomical feature in large girls | Narrow pelvis |
| Imprecise definition of deadline | Multiple pregnancy |
| Delays in the formation of the child | Extra large baby size |
| Incorrect positioning of the developing child |
Along with the AMF indicator, specialists usually simultaneously determine the content of amniotic fluid, on which the processes of fetal development largely depend. The amount of intrauterine water depends on a number of indicators, for example, the total thickness of subcutaneous fat, the individual characteristics of the female body, etc.
By the end of pregnancy, using the mentioned indicators, you can determine the approximate weight of the baby. To do this, you need to subtract from the GMR the value obtained by measuring the volume of the maternal abdomen.
Table. Composition of amniotic water by streamester
Features of changes in the height of the uterine fundus
During all 9 months, as was said, the uterus gradually grows. At the beginning of pregnancy, it occupies the pelvic area and is shaped like a pear, about the size of a goose egg. By the end of the 8th week, the organ grows approximately three times its normal size and acquires a rounded shape. Starting from 4 months, which corresponds to 12 weeks, it is centered in the pelvic area and becomes symmetrical. After this, it gradually extends beyond the pelvis, rises above the pubic bone and becomes palpable when palpated.
Approaching 25 - 26 weeks, the uterus takes on a shape similar to an egg, its lower part is noticeably narrower than the upper. By the end of pregnancy, it acquires significant volume and weight, thickens, and acquires a developed vascular system.
What determines the height of the uterine fundus?
The height of the uterine fundus by week of pregnancy, as well as the circumference of the pregnant woman’s abdomen, depend on many factors and may differ from norms and standards. The position and characteristics of the abdomen depend on the following circumstances:
- fruit size;
- position of the baby in the womb;
- physical characteristics of the mother's body;
- pelvis shape;
- weight gain;
- number of kids;
- location and condition of the placenta;
- heredity;
- amount of amniotic fluid.
Reference! VDM not only helps monitor the development of the child, but can also approximately determine his weight before birth.
Determining the amount of amniotic fluid is very important for the normal development of the embryo. It depends on the individual characteristics of the body structure of the expectant mother and the thickness of the fat layer.
Table of AMD during pregnancy by week
The table allows you to compare normal indicators with individual parameters:
| Gestation period (weeks) | Height (cm) | Coolant (cm) |
| 14 | 8 | — |
| 18 | 12-19 | — |
| 20 | 18-21 | 70-74 |
| 22 | 22-23 | 72-77 |
| 24 | 23-25 | 76-80 |
| 26 | 26-28 | 78-82 |
| 28 | 27-30 | 80-84 |
| 30 | 28-31 | 82-86 |
| 32 | 30-32 | 84-88 |
| 34 | 31-33 | 86-90 |
| 36 | 32-35 | 88-92 |
| 38 | 36-38 | 90-94 |
| 40 | 38-40 | 94-100 |
If the height of the uterine fundus does not correspond to the gestational age, then the interpretation cannot be based only on these numbers. The standards were created in order to suspect pathology and carry out further diagnostic measures. When determining the urinary tract at the beginning of the first trimester, the uterus should come out from behind the pubic bone; if this does not happen, then an ectopic pregnancy is suspected when the egg is fertilized in the fallopian tube. Subsequently, a decrease indicates malnutrition - developmental delay, oligohydramnios, or indicates transverse presentation.
If the uterus is high, then the development of more than one child inside the womb, a large fetus or polyhydramnios is possible. Rarely, if the indicators are too high, chorionepithelioma (a tumor in the tissues of the placenta) can be diagnosed, which threatens the life of the baby.
After 38 weeks, the abdominal circumference drops, the baby descends towards the cervix, he is preparing to pass through the birth canal and be born. In case of early reduction, additional studies should be performed to detect pathologies or infectious foci that affect pregnancy.
Deviations in the height of the uterine fundus during pregnancy
Deviation in the height of the uterus is a signal for an examination of the woman and her baby, as well as a reason to take preventive measures to maintain pregnancy. The height of the uterine fundus may be more or less than normal, as indicated by its deviations; we will consider it below.
A decrease in value is a signal of the following pathologies:
- oligohydramnios – decreased level of amniotic fluid in the bladder;
- fetoplacental insufficiency – unfavorable conditions for the fetus;
- premature aging, thinning of the placenta is a dangerous condition that threatens the life of the unborn child;
- fetal malnutrition – slowing of development;
- gestosis is a complication characterized by swelling, increased pressure and the detection of protein in the urine;
- antenatal death - death in the womb;
- post-term for more than two weeks;
- intrauterine infection of the fetus.
Pregnancy, even during a normal course, can be accompanied by a small VDM, for example, if the due date is incorrectly determined, or if the volume of the pregnant woman’s pelvis is wide.
Increased belly size, reasons:
- multiple pregnancy;
- large fruit;
- transverse or oblique position of the child;
- trophoblastic disease of the placenta;
- chorylnepithelioma – malignant formation;
- polyhydramnios;
- overweight woman;
- large weight gain during pregnancy;
- placenta previa;
- narrow pelvis;
- swelling and thickening of the placenta.
How is the height of the uterine fundus measured and what does this indicator mean?
The height of the uterine fundus is an indicator by which the gynecologist judges the correct development of the baby and pregnancy in general. Every expectant mother should know what this indicator means, how to measure it and what is considered normal.
General characteristics of the concept
As pregnancy progresses, a lot changes in a woman’s body. Internal changes are often associated with the fact that as the fetus develops, the uterus acquires the appropriate size and other organs move to give it enough space.
The distance from the pubic bone to the highest point where the uterus can be felt is called its height. It turns out that the height of the uterine fundus is the size to which the uterus grows during pregnancy.
This is one of the possible indirect indicators by which the level of fetal development can be determined.
Measuring the height of the uterine fundus: with a doctor and independently
In the first trimester, the enlarged uterus can be felt by a gynecologist through the vagina. You should not do this on your own for a short period of time. But as the fetus grows, this is easier to do - at the beginning of the second trimester, the uterus extends beyond the boundaries of the pelvic bones, and it is easy to feel it through the abdomen.
During the appointment, the doctor feels the abdomen and measures it with a centimeter tape, then writes down the results. At home, you can try to repeat its actions.
Before taking measurements, you need to empty your bladder - otherwise the readings may be inaccurate.
To measure the height of the uterine fundus, you will need a centimeter tape - the most common one used by seamstresses to take measurements. You will need to lie on your back and straighten your legs.
Then gently palpate the abdomen with your fingers, starting from the pubic joint upward. The abdomen will be quite hard to a certain point. This point is the fundus of the uterus. Then you need to measure the distance from the beginning of the path to this point.
This indicator is the height of the uterine fundus.
Watch the video that shows how to measure correctly:
Norms for the height of the uterine fundus at different stages
What can be considered normal in a particular case depends on several factors:
- number of pods;
- child's size;
- intrauterine position of the child;
- individual characteristics of a woman’s body;
- presence of pathological conditions.
If there is only one child, the size is within the normal range, the position in the womb is correct and the woman does not have any features affecting the size of the uterus (for example, there is no polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, and her height is average and her build is normal), then the indicator will be equal to:
- 6 cm at 16 weeks;
- 12-14 cm at 20 weeks;
- 20 cm at 24 weeks;
- 24-26 cm at 28 weeks;
- 28-30 cm at 32 weeks;
- 32-34 cm at 36 weeks;
- 28-30 cm at 40 weeks.
It is also considered normal if the indicator is approximately equal to the gestational age in terms of weeks: how many weeks is the indicator in centimeters.
The height of the uterine fundus is constantly increasing. It decreases by a couple of centimeters only a few days before giving birth.
With multiple pregnancies, the picture changes somewhat. At week 16, the normal range is from 15 to 28 centimeters. Indicators may exceed the norm by 2 to 12 cm compared to a singleton pregnancy.
It is not uncommon that up to 28 and even up to 30 weeks of pregnancy with twins, indicators barely exceed the norm for pregnant women with one child. There is no need to panic: babies may lie and develop differently, but it is better not to refuse additional examination.
If deviations exceed 3 cm, our doctors may be puzzled by finding the reasons and send the expectant mother for additional examinations and even prescribe treatment.
Often examinations show that everything is fine with the children, but still gynecologists stubbornly prescribe Actovegin, Curantil and other unnecessary therapy in this situation.
Therefore, in civilized countries they do not rely on this indicator and do not measure it at all.
Many accredited obstetricians and gynecologists consider the measurement of fundal height to be an ancient teaching of the Soviet medical school, and therefore they rely only on the results of fetal ultrasound.
Possible reasons for indicators below normal
There are cases when, when measured, the height of the uterine fundus is less than normal.
Incorrect determination of the deadline is one of the most common reasons. If a woman comes to the LCD for the first time to register in the second trimester, and not before 12 weeks, as expected, then the doctor is not always able to accurately calculate how many weeks the pregnancy has already lasted.
Basically, in the situation under consideration, this happens due to the woman having an unstable or long menstrual cycle, as well as in its absence, for example, if the next pregnancy occurred while breastfeeding the previous baby and menstruation has not yet occurred after childbirth.
Because of this, actual performance may differ from what was incorrectly assumed to be the case.
Oligohydramnios (insufficient amount of amniotic fluid) can also cause a downward deviation in the indicator: there is little water, therefore, the uterus does not increase in size.
May occur due to dehydration, nicotine use and certain medications (for example, ACE inhibitors). An additional symptom of severe oligohydramnios is pain when the fetus moves.
To detect oligohydramnios, a routine ultrasound is sufficient.
A wide pelvis with low fundal heights has a simple explanation: the uterus has enough space between the pelvic bones, so it does not need to rise. It is not a pathology.
In addition to a wide pelvis, there may be other physiological features: a miniature figure, the influence of a genetic factor, etc.
Incorrect (transverse or oblique) position of the fetus can also cause a low rate. The explanation is simple - due to this position of the child, the uterus grows not upward, but to the sides.
Fetal growth retardation is the most unpleasant possible reason when a child does not gain enough weight while in the womb.
In addition to physiological reasons (short stature of the mother or father), there may be disturbances in the development of the placenta or umbilical cord, the presence of infection, bad habits, as well as blood thickening and, as a consequence, insufficient nutrition of the fetus with nutrients and oxygen. There may not be any obvious symptoms, but during the examination the doctor will notice that the fetus may be delayed in development and will prescribe an ultrasound.
It is believed that the low weight of the expectant mother is the main sign that the baby will be born with low birth weight. Although sometimes this is true, you should not consider this a determining factor. On the contrary, many large women give birth to small, low-weight babies.
Possible reasons for indicators above normal
If the height of the uterine fundus exceeds the norm, then there may also be several reasons for this.
If the fetus exceeds the norms for its development for a given period, it is logical that the uterus will be larger than usual. This often applies to those who had a similar situation in their family in the older generation, and the large size of the fetus is due to genetics.
The second reason is the presence of two, three or more fetuses in the uterus. Each of them needs space, and each of them grows - therefore the uterus increases significantly.
A woman’s narrow pelvis can prevent the uterus from expanding in width, and it will take the space it needs from above. Therefore, the height of the bottom will be higher than usual.
Another reason is polyhydramnios, a large amount of amniotic fluid. Determining their volume can be difficult. Symptoms include gurgling sounds, pain and heaviness, large abdominal volume at the level of the navel, shortness of breath due to pressure on the diaphragm.
If these symptoms appear against the background of diabetes mellitus, infectious diseases, disorders of the heart and blood vessels, as well as Rh conflict, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound.
Also, polyhydramnios can develop during multiple pregnancies, disorders of fetal formation, due to a large fetus, and in later stages - due to impaired swallowing function in the child.
By itself, the indicator of the height of the uterine fundus carries very little information. It cannot be used to objectively judge the normal course of pregnancy and the full development of the fetus, and, if necessary, to identify pathology in time and take the necessary measures. For this there is an ultrasound of the fetus.
Source: //zaletela.net/zdorove/vysota-stoyaniya-dna-matki.html
How to measure the height of the uterine fundus
To measure the VMR, the woman must take a lying position, sitting on the couch. You need to relax, stretch your legs, and your bladder should be empty. Through a digital examination, the gynecologist will determine the highest point of the uterus and, using a centimeter tape, measure the distance to the pubis.
Such an examination often causes mistrust among women who are not aware of its significance. Of course, ultrasound examination is much more effective and more accurate in determining the condition of the baby and the characteristics of the uterus. But, since changes in the AMR must be constantly monitored, it is not possible to do ultrasound constantly. Manual inspection is safe and always available.
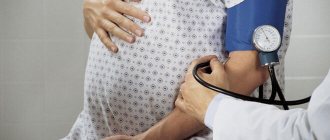
Reference! Simultaneously with the height of the uterus, the gynecologist measures the abdominal circumference, weight of the pregnant woman and blood pressure.
All this is important for assessing the condition of the expectant mother and her child. They help to take timely measures to eliminate possible pathologies and carry out prevention.
Features of measuring abdominal circumference and VSD of the uterus in pregnant women
An integral procedure performed by a gynecologist when a woman visits a consultation during pregnancy is to measure the height of the uterine fundus. By this term, obstetricians mean the distance from the pubis to the highest point of the reproductive organ, protruding in front above the small pelvis.
Belly size at different stages of pregnancy
The abdomen becomes clearly visible at week 20 in patients who were quite small up to this point. It gradually increases and becomes a certain shape. The specialist records changes at each consultation visit.
During this manipulation, he focuses on such parameters as abdominal circumference and VSD.
The doctor compares the results with earlier studies, evaluates the dynamics and, based on the obtained indicators, draws conclusions about pregnancy and fetal development. With the help of this manipulation, it is possible to determine oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, as well as the approximate weight of the child.
If the size increases quickly or slowly, this is an indication for a study to exclude developmental deviations.
Why measure?
Measuring VMR is considered a procedure that is performed by a gynecologist every time a pregnant woman comes to a consultation. Based on the results obtained, it is possible to diagnose intrauterine growth retardation at an early stage.
However, each patient’s pregnancy progresses differently, and there is no need to compare the results obtained with the table and draw conclusions on your own.
Height
In women from the second trimester, during examination, the gynecologist assesses where the fundus of the uterus is located. At week 16 it is located between the navel and pubic area. When measuring the VSD, it is clear that the cavity itself is located two fingers below the navel and the stomach grows to a large size.
At the 24th week, the VSD of the uterus is noted at the level of the navel, and at the 28th week it rises 2-3 fingers above it. At 32 weeks, the VSD of the reproductive organ occurs between the bunch and the xiphoid process. At 36, this indicator reaches the highest level, that is, the xiphoid process.
The abdominal circumference of the expectant mother is 90 cm, the navel becomes smoothed and protrudes noticeably.
Shortly before labor, the navel of all expectant mothers protrudes, but lowers due to the pressing of the baby's head to the entrance to the pelvis.
How to measure
In medical practice, the height of the fundus of the uterus is the distance that can be measured between the upper wall of the reproductive organ and the edge of the pubic area. With the gradual development of the fetus, the size of the organ increases and its bottom is determined through the abdominal wall.
Until this day, all measurements of the growth of the child's place are carried out by a doctor during a vaginal examination and determining the distance to the cervix.
To determine the height of the uterine fundus, some manipulations are performed:
- the patient takes off her clothes and sits on the couch;
- Using a centimeter tape, the gynecologist measures the distance from the upper edge of the pubic area to the most protruding point of the bottom of the genital organ.
- the obtained research result is recorded in the mother’s exchange card and the card located in the medical institution.
Altitude table by week
Starting from the second trimester, the size increases and its bottom begins to extend beyond the pelvis. When making such changes, the specialist easily palpates the uterine area through the peritoneal wall.
Gradually, during pregnancy, the height of the fundus of the reproductive organ increases noticeably. The following factors may influence these results:
- a woman bears two or three fetuses;
- amount of amniotic fluid;
- the size of the child and the features of its location.
When assessing the obtained indicators, the obstetrician focuses on the individual characteristics of the course of pregnancy. For this reason, indicators may differ from the norm for AMD by week in patients with the same period.
This phenomenon is not considered an anomaly and does not cause any suspicion to the gynecologist.
After the manipulations, the gynecologist compares the results of the study with the table “Height of the uterine fundus by week” and draws conclusions.
Abdominal circumference
The size of the reproductive organ gradually increases depending on the week of pregnancy. Changes of this nature are due to both the active growth of the child and an increase in the volume of the placenta, fetal membranes and amniotic fluid.
Until the end of the first trimester, the dimensions do not extend beyond the pelvic bones, so it is problematic to establish the presence of the fetus by ordinary palpation.
Starting from the 13th-14th, the bottom of the uterus begins to rise above the pubic symphysis. It is recommended to start measuring your abdominal circumference at 20.
It is from this time that it acquires a rounded shape and is clearly visible to others. In the future, at each consultation visit, the woman’s circumference is measured.
To carry out the procedure, a regular measuring tape is required. Using the obtained indicators, it is possible to establish the approximate weight of the fetus and the due date.
Circumference table
Various factors are taken into account in the process of determining the circumference. Attention is paid to both the woman’s physique and her weight.
In medical practice, doctors use a table that shows the abdominal circumference by week.
Measurement Rules
The main condition for the procedure is that the expectant mother must be in a horizontal position. Measurement in this state makes it possible to exclude the influence on the final parameters of the examination of the anterior wall of the peritoneum and the spine.
To obtain accurate results, it is important that the pregnant woman's bowels and bladder are empty.
The algorithm for measuring abdominal circumference is as follows:
- during the procedure, the doctor uses a measuring tape;
- it is positioned in such a way that the measuring tape is located strictly at the navel and passes through the point of the deepest vertebral curvature.
By fulfilling such requirements, the doctor is able to obtain accurate and reliable results.
Belly shape
Specialists in the field of gynecology pay attention not only to the size, but also to the shape of the abdomen. The correct shape is very important; it should be ovoid, slightly pointed towards the top for first-time mothers. Multiparous women's characteristics change. The abdomen may be round or even slightly angular, this is due to weak abdominal muscles, a large fetus and polyhydramnios. Carrying a hero by a fragile woman also affects the shape of the uterus. The pear-shaped belly is caused by weak muscles that are unable to withstand the load.
With a narrow pelvis and multiple pregnancies, the abdomen is pointed and the size is correspondingly larger. A small, inconspicuous tummy can signal oligohydramnios.
Lack of symmetry may be a signal of abnormal positioning of the fetus. For example, a transverse position can give an oval shape. All this can be clearly seen in the photo.
From all that has been said, we can conclude that the size and shape of the uterus is a necessary criterion when examining and examining a pregnant woman. With their help, you can identify and prevent the development of defects and stunting in a child.