Types of normal urethral discharge in men
The physiological discharge of the urethra must correspond to normal indicators, which indicate the healthy functioning of the organs of the urogenital system. These include:
- Smegma. It is a mixture of sebaceous gland secretion, dead epithelium and moisture accumulating in the foreskin. It has a whitish tint and an oily consistency. An excessive amount of such secretion can lead to serious diseases, so to prevent their development, you should follow the rules of intimate hygiene.
- Urine. A transparent liquid of a yellowish tint, in healthy people it is practically odorless and does not contain foreign inclusions. Changes in color indicators, consistency and the presence of impurities indicate the development of a pathological process in the body.
- Ejaculate. This is the fluid that is released during ejaculation in men. Normally it has a gray-white hue and the consistency of mucus. Any deviation in the appearance of sperm may be evidence of a pathology of the genitourinary system, which you should pay attention to and make an appointment with a doctor. Such discharge from the urethra is observed not only after sexual intercourse, but also in the morning - the phenomenon is called “emission” and is a spontaneous release of fluid. Mostly, wet dreams are typical for teenagers and people whose sex life is irregular.
- Prostate secretion. A viscous, whitish liquid with a specific odor.
2.1
Urethritis
In most cases, any abnormal discharge is associated with a group of diseases such as urethritis. In general, we can say that this is an inflammation of the urethra - the urinary organ. But it has different pathogens, so there are different types of it.
The main causes of urethritis:
- hypothermia;
- suffered from acute respiratory viral infections;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- increased physical activity.
All this leads to decreased immunity.
An unhealthy lifestyle can also provoke the development of the disease - a diet with a predominance of fats and carbohydrates, an excessive passion for spicy dishes (they irritate the mucous membrane, it becomes more vulnerable to attacks by bacteria and viruses).
Urethritis often develops against the background of the presence of other chronic inflammatory diseases in the body:
- 1. Specific urethritis . Inflammation of the urethra, which develops against the background of infections such as mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, genital herpes. A less common form is caused by the human papillomavirus. The main symptom is the appearance of yellow, green or gray mucus. It can be liquid or thick in consistency, heterogeneous, sometimes with lumps. It has an unpleasant aroma - sour, reminiscent of the smell of fish, and sometimes there is discharge with the smell of garlic.
- 2. Nonspecific urethritis. Caused by Escherichia coli, streptococcus or staphylococcus. It is characterized by the same symptoms as the specific one. So the pathogen can only be determined based on the results of laboratory diagnostics.
- 3. Urethritis caused by a fungus. If white discharge appears, especially in the morning, the situation indicates the growth of the Candida fungus, which provokes thrush. This type of urethritis is accompanied by itching and burning. A white coating appears on the genitals.
- 4. Urethritis caused by vaginosis. Then the discharge has a dirty white or gray tint and the smell of rotten fish. The causative agents of the disease are transmitted sexually. Symptoms of the disease intensify after sexual intercourse.
Urethritis can be treated at home, although in severe forms hospitalization is indicated. It is necessary to provide the patient with rest and bed rest. Treatment comes down mainly to the use of antibiotics.
For nonspecific bacterial urethritis, immunostimulating therapy is prescribed using Viferon and Likopid. This way the body will be more resistant to infection. Among the antibiotics prescribed are tetracyclines, cephalosporins, Clindamycin, Ofloxacin and some others.
For candidal (fungal) urethritis, Diflucan, nystatin, and other antifungal drugs are prescribed. With a specific form of the disease, everything depends on the pathogen. For example, for trichomonas, instillations of silver nitrate and protargol are prescribed, and metronidazole is used among the drugs. For gonorrhea, antibiotics from the group of penicillins and macrolides are used.
Pathological discharge from the urethra
Discharges are considered pathological if differences from natural ones are observed in:
- volume;
- color index and degree of transparency;
- the presence of foreign impurities;
- consistency (too sticky or thick);
- smell;
- episodic occurrence.
As a rule, the nature of the discharge directly depends on the type of causative agent of the pathological process, the state of immunity at the time of infection and concomitant diseases. The duration and severity of the inflammatory process are also important - the discharge can change its appearance and composition.
In some cases, discharge from the urethra is a normal physiological process, then it is not accompanied by pain, discomfort, or an unpleasant odor. But there are also pathological discharges that need to be diagnosed and treated.
The probable causes of discharge from the urethra can be infectious or non-infectious. In turn, infectious causes can be of a specific type (diseases that are transmitted through sexual contact) and a nonspecific type (which are caused by opportunistic microorganisms).
Non-infectious causes that can lead to discharge from the urethra:
- trauma or narrowing of the urethra;
- allergic reaction;
- irritation from chemicals;
- mechanical damage (including during medical procedures).
Diseases transmitted through sexual contact often cause the following symptoms of pathology:
- The discharge is mucous in nature. Such discharge from the urethra may be clear, thick and not abundant. Characteristic of chronic chlamydia damage, and urethritis, which is caused by ureaplasmas or mycoplasmas.
- Mucous with purulent impurities. Indicate an acute form of chlamydial, ureaplasma or mycoplasma lesions.
- Purulent. Urethral discharge has a yellow-green color and a foul odor.
White discharge
White discharge from the urethra in men may indicate the presence of candidiasis. In addition to this symptom, thrush is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- unpleasant yeasty odor in the area of the head of the penis;
- whitish coating on the head;
- itching and discomfort in the groin area;
- the appearance of red spots on the head of the penis;
- pain during sex.
In addition to thrush, white discharge from the urethra can accompany pathologies that were caused by chlamydia, ureaplasma or mycoplasma, as well as inflammation of the prostate gland.
Causes of curdled discharge in men
The penis has a natural microflora, which consists of various types of bacteria and other microorganisms.
They create an environment in which other pathogenic microorganisms cannot reproduce.
Therefore, Candida albicans is extremely rare in the healthy microflora of the penis.
Hence, the main reason for the development of candidal balanoposthitis/balanitis is infection during sex with a woman who has thrush.
Among the factors contributing to fungal infection, primarily a weakened immune system .
Also, discharge can be observed during ongoing diabetes mellitus, HIV, while taking antibiotics, corticosteroids, cytostatics (chemotherapeutic drugs).
Symptoms of candida infection in men are quite pronounced.
Penile fungus is accompanied by redness and swelling of the glans.
Itching, burning when urinating and a white film-like coating appears, which can be easily removed under running water.
The appearance of cheesy discharge can be noticed 10-14 days after sex.
Discharge due to prostatitis
The acute form of prostatitis is characterized by the appearance of purulent discharge from the urethra. They are accompanied by fever, chills and pain in the perineum. The process of urination becomes painful and frequent, urine loses its transparency. The chronic form of prostatitis is characterized by the presence of clear sticky discharge from the urethra in men, but it often occurs without any symptoms. Often, discharge from the urethra appears in the morning. The pathological process is accompanied by dull pain and heaviness in the perineum and frequent painful urge to urinate.
Urology
Brown and bloody discharge after urination may appear directly from the urethra. This symptom occurs in men and women with various pathologies of the urinary system:
- Trauma to the urethra as a result of medical manipulation, urethral massage, sexual games. In this case, wounds form in the urethra that bleed from time to time.
- Inflammation of the urethra in the chronic stage. The chronic course of urethritis leads to thinning of the mucous membrane and bleeding.
- Ulcers, tumors, cysts in the urethra, which bleed when injured.
- Acute and chronic cystitis. In this case, blood may be present in the urine, as well as blood clots and brown discharge after urination.
- Urolithiasis disease. Brown discharge appears as a result of injury to the urethra by a stone.
- The appearance of blood in the urine is also observed with malignant tumors of the urinary system.
Bloody discharge
The presence of blood in the discharge of the urethra may indicate:
- the presence of glomerulonephritis (pathology of the renal glomeruli);
- infectious process (candidiasis, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea);
- traumatization during medical intervention;
- damage to blood vessels due to the passage of sand or stones;
- the presence of malignant neoplasms (dark bloody discharge).
Diagnosis of urethral discharge in men
Correct diagnosis allows you to determine an effective treatment regimen. When identifying the cause of urethral discharge in men, the doctor pays attention to the following signs:
- the presence of pain and burning sensations during urination;
- the nature of the discharge (purulent, mucous, bloody, transparent);
- the appearance of frequent urge to urinate;
- discomfort in the perineum;
- symptoms of urinary incontinence;
- increased body temperature, chills;
- the patient’s history of infectious lesions of the genitourinary tract and prostate pathologies;
- the presence of ulcers or rashes on the skin and mucous membranes.
As a rule, the specialist must clarify whether the patient’s sexual partner has changed recently. Having a new partner significantly increases the risk of sexually transmitted infections. They can cause urethral discharge in men.
Patient examination methods include:
- examination of the penis and groin area to identify pathological deformations of the penis and symptoms of various diseases;
- palpation of regional lymph nodes;
- examination of the prostate gland to obtain secretions, which are subsequently examined under a microscope;
- collection of biological material for cultural research and polymerase chain reaction;
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys, bladder and prostate;
- laboratory testing of blood and urine;
- X-ray of the urinary tract;
- computed tomography.
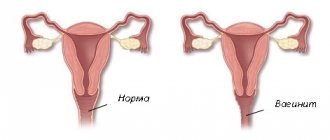
Discharge from the urethra in women
The cause of discharge from the urethra in women, as a rule, is disorders in the functioning of the urinary system. This may be an infectious process caused by an STD, or a consequence of other pathologies and anomalies of the genitourinary system. Liquid is released from the external opening of the canal and comes in a variety of colors, consistencies and turbidities. A similar sign of a pathological process in the body is characteristic of people of all ages.
Transparent discharge from the urethra occurs in women three to four days before ovulation. This discharge lasts for several days and is considered physiologically normal, since the root cause of its appearance is changes in the balance of hormones. A similar mucous discharge is released from the vaginal cavity at this time. Not very abundant discharge from the urethra, almost odorless, is also observed after coitus - this indicates strong arousal and is considered a completely healthy phenomenon.
Discharge from the urethra during pregnancy is diagnosed quite often. This sign indicates an inflammatory process of the urethral mucosa. This occurs due to infection of the mucous membranes with various types of bacteria. The pathology also occurs in non-pregnant girls due to the fact that the anatomical structure of the urethra makes the female sex very susceptible to the negative effects of infectious agents.
Factors that contribute to the development of the disease are:
- general and local hypothermia;
- trauma to the genital organs;
- state of immunodeficiency;
- promiscuous sexual life and its consequences;
- inflammatory process of the genitourinary system;
- vaginal dysbiosis;
- the presence of urolithiasis.
In addition to discharge, the pathological process may be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and burning in the urethra.
Causes
Discharge from the urethra of women has different causes - we list the main ones:
- Cystitis. Kidney stones descend down the urethra, injuring it - this contributes to the development of inflammation;
- A number of sexually transmitted diseases. Increased secretion in women, if accompanied by frequent urination, may be a consequence of the proliferation of trichomonas, chlamydia and a number of other microorganisms. For example, gonococcus, the causative agent of gonorrhea, also causes discharge;
- Decreased immunity;
- Mechanical damage to the urinary canal. Occurs after accidents or disruption of the integrity of the mucous membrane during medical procedures;
- Spending a long time in the cold. This affects the activity of bacteria in the body in women;
- Poor nutrition – when a woman eats sour, fatty or bitter foods in excessive quantities.
- Cancerous formations in the urethra also contribute to the appearance of inflammation in it.
The main causes of discharge are various sexually transmitted diseases. A woman becomes infected through unprotected sexual intercourse. In addition, the disease is affected by personal hygiene rules, non-compliance with which leads to infection of the urethral canal.
We must remember: prolonged emotional stress in itself can cause frequent urination. But if discharge is added to it, then this, as a rule, is already a sign of an infectious disease.
Diagnosis of urethral discharge in women
The doctor interviews the patient. During the conversation, the specialist finds out all the necessary information - complaints, accompanying symptoms, duration of signs of pathology. After collecting anamnestic data, urethroscopy (examination of the urethra using a cytoscope) follows. To establish a reliable diagnosis, the patient will need to submit biomaterial for laboratory testing (urethral smear). Subsequently, the smear is examined under a microscope.
In addition to the microscopic research method, the following are used:
- blood test for the presence of sexually transmitted infections (enzyme immunoassay);
- cultural method (bacterial culture allows you to determine the resistance of bacteria to antibacterial drugs);
- ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system;
- general blood and urine analysis.
Timely diagnosis and establishment of the cause of the disease will help to take timely measures to eliminate the disease and maintain the health of yourself and your sexual partner. It should be understood that self-medication is strictly excluded - not only will it not help, but it can also lead to chronicity of the pathological process. If suspicious discharge appears, you must immediately contact a qualified specialist.
Diagnostics
First, the doctor interviews the patient. He learns from her about accompanying symptoms, complaints, and the duration of signs of the disease. After this, diagnostics is carried out: smear microscopy is performed. Sometimes the urethra is examined using a special device - a cystoscope.
Additional methods of examining the genitourinary system are also used to confirm the diagnosis:
- Bacterial culture;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- Urine and blood tests.
Based on all examinations, the doctor can make a diagnosis.
Many diseases of the genitourinary system manifest themselves insignificantly in the initial stages. You should contact a competent specialist as soon as possible: he will help relieve the symptoms of the disease.