CTG norms at 32 weeks of pregnancy
Pregnancy is an important stage in the life of every woman, which changes her both inside and out.
During the period of the birth of a new life, the expectant mother often listens sensitively to any changes in her body. And this is not surprising, because at this time the body of a woman and child is most susceptible to various negative influences of the external environment. One of the methods for assessing the condition of the fetus is cardiotocography. It is carried out to exclude or timely identify pathological conditions of the mother and child that pose a threat to the course of pregnancy or to the future health of the newborn baby. In this article we will talk about decoding CTG at the 32nd week of pregnancy in normal and pathological conditions.
CTG safety
As a diagnostic method, cardiotocography has no contraindications. There is scientific evidence that cardiotocography does not cause any harm or danger to the health of both the pregnant woman and the fetus.
CTG today is a fairly informative diagnostic method, however, to obtain the most reliable information, it is necessary to evaluate the data of CTG, ultrasound, Doppler, clinical studies and medical history data of the pregnant woman in total.
Indications for the procedure at 32 weeks
Cardiotocography makes it possible to identify disorders such as polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios, fetal hypoxia, intrauterine infection, abnormalities in the structure of the heart and blood vessels, and fetoplacental insufficiency.
The procedure is prescribed in the following cases:
- The presence of endocrine or systemic diseases in the mother (diabetes mellitus, anemia of various origins, etc.).
- Conditions that threaten the course of pregnancy (malpresentation of the baby, multiple and post-term pregnancy, severe toxicosis, persistent increase in body temperature, etc.).
- Previously identified abnormalities during ultrasound diagnostics (deviation of the fetal size from the norm, decrease in its motor activity, developmental delay, pathology in the amniotic fluid and placental circulatory system).
- Previously recorded cases of premature birth and spontaneous termination of pregnancy in the early stages.
- Rhesus conflict between mother and fetus.
This type of diagnosis does not require special preparatory measures. In order for the results to be most accurate, the expectant mother should lie as still as possible, so before the study it is better to go to the toilet in advance. It is prohibited to take analgesics or sedatives 11–12 hours before the start of CTG.
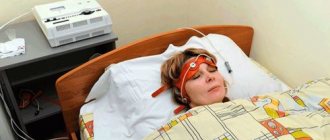
It is allowed to carry out the procedure in a position on your side or half-sitting, resting your back on a previously prepared pillow. A special device consisting of two parts is attached to the expectant mother’s belly. The first sensor is lubricated with gel and installed in the projection of the best audibility of the fetal heartbeat.
The second - to the area of the fundus of the uterus to record its excitation and further contractions. Next, the pregnant woman is offered a special button that she will press during periods when the baby moves. The appointment is made by a doctor within 30–60 minutes. A special device records all data in the form of graphs on paper tape.
Frequency of CTG
- In the normal course of pregnancy, CTG is performed every 12–15 days from 32 weeks until birth.
- In case of complicated pregnancy, the required frequency of the study is assessed by the attending physician and cardiotocography can be carried out at a frequency from once every 5–7 days to twice a day (most often this regimen is prescribed for inpatient treatment).
The most common indications for additional cardiotocography in pregnant women include:
- complicated pregnancy (preeclampsia, placenta previa, polyhydramnios, preeclampsia, oligohydramnios, multiple pregnancy, Rhesus conflict, etc.);
- complicated medical history of the pregnant woman (diabetes mellitus, diseases of the nervous system, heart pathologies, vascular diseases, systemic diseases, uterine scar, premature birth or antenatal death of the fetus in the anamnesis, etc.)
- pathologies of pregnancy and fetal development anomalies identified by ultrasound (delayed or advanced intrauterine development, which is expressed in the discrepancy between the size of the baby and the gestational age, any change in the quantitative and qualitative amniotic fluid, abnormalities in the development of the placenta and umbilical cord, premature maturation of the placenta, blood flow disorders);
- complaints from the expectant mother about changes in the child’s physical activity (excessively active movements, or, on the contrary, too sluggish and infrequent), which may indicate the presence of oxygen starvation in the child.
CTG during labor
During childbirth, cardiotocography is the most accessible and informative method for diagnosing the baby’s condition.
Normally, CTG is performed:
- immediately upon admission of a pregnant woman to the maternity ward;
- after the amniotic fluid has broken (either on its own or as a result of amniotomy);
- when stimulating labor;
- every three hours during labor.
In case of complications, the frequency of the study is determined by the doctor or team of doctors.
Basic indicators of cardiotocography
The fetal CTG norm is a series of digital values that are examined by the doctor to confirm the normal or pathological intrauterine development of the child. During the study, the following indicators are recorded.
Basal rhythm (BHR)
To calculate this value, heart rate indicators are recorded every second, after which significant increases and decreases in the rhythm are subtracted and the average value is obtained over a time period of 10 minutes. Normally, at 32 weeks of pregnancy, the heart rate during active movements of the child is 130–180 beats, and during sleep 120–160.
If the values of the basal rhythm are within the normal range, this indicates the absence of fetal hypoxia. A heart rate higher or lower than the given indicators indicates that the baby’s body is not receiving enough oxygen, and this can have a detrimental effect on the nervous system and the overall development of the child.
Basal rate variability
Amplitude is considered to be vertical fluctuations from the main line of the heart rate, frequency is the spread of indicators per minute. Normally, the baby's heart rate in the womb should not be the same all the time. Normal cardiotocography is indicated by such concepts as undulating or saltatory rhythm, when the spread is 10–15 beats per minute, and the amplitude is 25–30 beats per minute.
Acceleration
This indicator is displayed on the graph in the form of teeth, the tops of which are directed upward. They reflect the acceleration of the heart rate. Normally, this should occur during uterine spasms, during active fetal movements, and in response to stress tests. 2-3 increases are allowed over 15 minutes.
Deceleration
The appearance of teeth on the graph, the tops of which are lowered down. This indicator reflects a decrease in heart rate. Normally, they should not be present or be mild in depth, frequency and duration. The following types of decelerations are distinguished:
- Early - occur simultaneously with the contraction, begin and end gradually. The appearance of such an indicator may be a sign of compression of the umbilical cord.
- Late - occur in response to uterine contractions, but are delayed by 0.5 minutes or more, and their peak is recorded after the maximum tension of the organ walls.
- Variable - there is no connection between the slowing of the rhythm and the occurrence of contractions. The graph displays spikes of varying shapes and durations. Such deviations from the norm occur when the umbilical cord is compressed or there is insufficient amniotic fluid.
Number of uterine contractions
Periodic spasms of the muscular membrane of this organ are a completely physiological process. The norm for 32 weeks is considered to be the duration of such contractions no more than 30 seconds, and the ratio with the basal heart rate is no higher than 15 percent.
Why is a cardiotocogram necessary?
CTG indicators during pregnancy are needed as a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the intrauterine fetus. Ultrasound or even Doppler sonography alone is not enough to know whether the baby has enough oxygen (even if the blood vessels and placenta are completely normal).
CTG of the fetus during pregnancy shows how it tolerates physical stress (in particular, its movements and contractions of the uterus), whether it can pass through the natural birth canal and remain healthy.
The only caveat: the CTG assessment should be made after 28 weeks, when there is already a close relationship between the autonomic and central nervous systems and the heart muscle, and the sleep-wake cycle has been established.
This will help eliminate false positive results.
How is CTG analysis performed, what do all these numbers mean?
1. Basal rhythm of the baby’s heart rate (usually abbreviated as “BHR”). This indicator is calculated as follows: heart rate readings are taken every second, then obvious increases and decreases are subtracted, and the arithmetic average for 10 minutes is calculated.
The norm for fetal CTG in relation to heart rate at any stage is: 119-160 beats per minute if it is known that the child is sleeping, 130-190 beats if the baby is actively moving.
On a cardiotocogram, the heart rate spread is usually written, that is, not one number is indicated, but two.
2. Variability (amplitude and frequency) of the basal rhythm. Amplitude is defined as the magnitude of the deviation from the main line of the basal rhythm along the vertical graph; frequency is the spread of the number of oscillations per minute. Depending on the variability, fetal CTG interpretation includes the following characteristics of the basal rhythm:
- monotonous (or silent): have an amplitude of 0-5 per minute
- slightly undulating: amplitude 5-10 per minute
- undulating: spread 10-15 per minute
- saltatory: 24-30 beats per minute amplitude.
Fisher's ten-point scale
Doctors use this scale to evaluate CTG results. The essence of the procedure is that each indicator is awarded from 0 to 2 points. All values are added up and determine the information content of this diagnostic method, as well as the presence or absence of pathologies.
- 1-5 points – the condition of the fetus in the uterus is poor, it experiences a pronounced lack of oxygen.
- 6-7 points – mild hypoxia, borderline state.
- 8-10 points – the child’s body does not experience oxygen starvation and is in excellent condition.
Fetal health indicator (FSI)
This value is calculated automatically. The following PSP options are distinguished:
- Less than 1 is normal. However, if the CTG value is from 0.8 to 1.0 during pregnancy, it is recommended to repeat it.
- From 1 to 2 – initial changes in the general condition of the fetus. Outpatient treatment and control cardiotocography after one week are recommended.
- From 2 to 3 – the child’s condition is serious. Urgent hospitalization and immediate initiation of treatment are required.
- More than 3 – the condition is extremely serious. The question of emergency management of childbirth is raised.
Fetal reactivity index and non-stress test
The first indicator reflects the state of the fetal nervous system in response to external influences. Such stressful situations primarily affect the state of the cardiovascular system. Points are used for calculation, where:
- 0 – complete absence of response to external stimulus.
- 1 – pronounced decrease in reactivity.
- 2 – noticeable decrease in reactivity.
- 3 – moderately expressed response to external influence.
- 4 – initial degree of pathological reactivity.
- 5 – adequate response to external influences.
A non-stress test is carried out to assess the state of the baby’s cardiovascular system during his voluntary movements. Normally, such a test should be negative, which implies the presence of 2 or 3 increases in heart rate by 15 beats, lasting no more than 20 seconds.
Despite the large number of indicators, cardiotocography is only an additional diagnostic method. For a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the mother and fetus, other instrumental examinations, laboratory test data and consultation with an experienced specialist are necessary.
Source of the article: https://apkhleb.ru/prochee/normy-ktg-32-nedele-beremennosti
What is CTG?
Cardiotocography, or CTG, is a diagnostic method that provides a functional assessment of the current condition of the fetus.
The baby's condition is assessed based on cardiac performance indicators depending on his activity. Two graphs are simultaneously applied to special calibration paper - contractions of the uterus and the heartbeat of the child.
Most often, non-stress cardiotocography is used, when the study is carried out in natural conditions.
In some cases (as an additional method), the stress cardiotocography method is used, when the child’s cardiac activity is examined in response to external stimuli - sound (acoustic test) or mechanical (fetal palpation). This also includes CTG in a situation of simulating labor (mammary test, as well as oxytocin test).
Purposes of CTG
Cardiotocography is performed to evaluate:
— features of the child’s cardiac activity (heart rate, changes in heart rate as a reaction to stimuli);
- frequency of uterine contractions;
- motor activity of the fetus;
- adequacy of the response of the fetal organ systems (mainly cardiovascular) to uterine contractions.
The results of cardiotocography, together with the results of ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound, allow timely detection of such serious disorders as:
— intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
- various anomalies in the development of the heart and vascular system of the fetus;
All of the conditions described above can seriously affect the child’s health, so their timely identification will help to take the necessary measures in time.
When, how and why is CTG done during pregnancy?
CTG is performed on all women without exception during a normal pregnancy three times in the third trimester and always during childbirth. Cardiotocography is indicated from 32 weeks. According to indications, the study can be carried out from 28 weeks of pregnancy. Previously, this is uninformative, since only by the 28th week does the fetal heart begin to be regulated by the autonomic nervous system, and its heart rate begins to respond to the movements it makes. In addition, by the 32nd week of gestation, the baby’s sleep-wake cycle is formed.
If a woman has problems or abnormalities were detected on a previous CTG, the study is repeated more often.
In case of intrauterine hypoxia, the study is carried out daily or every other day until the fetal condition normalizes or until the issue of the need for emergency delivery is decided.
In physiological labor, CTG is performed every 3 hours. If complications occur, more often (it is advisable to conduct the period of contractions under constant CTG monitoring).
Indications for unscheduled CTG include:
- late gestosis (arterial hypertension, edema, protein in the urine)
- arterial hypertension of any etiology
- anemia
- polyhydramnios
- oligohydramnios
- multiple pregnancy
- Rhesus conflict pregnancy
- post-maturity
- threat of premature birth;
- assessment of the effectiveness of treatment of fetoplacental insufficiency and fetal hypoxia;
- fetal malnutrition
- severe extragenital pathology of the mother
In case of multiple pregnancy, the study is carried out separately for each baby.
There are 2 ways of performing CTG: external (indirect) and internal (direct).
The first method is the most common. It is used without restrictions for all pregnant women. It has no contraindications or side effects. During the procedure, sensors are placed on the pregnant woman’s stomach and do not cause discomfort to either her or the baby. The study is carried out using a special device. It consists of two sensors and a data recorder. Both sensors are attached to the pregnant woman’s belly with a special belt.
One ultrasonic sensor. It allows you to record the fetal heart rate. The second sensor is a strain gauge. Records uterine contractions. A remote control with a button is placed in the pregnant woman's hand to record fetal movements.
The optimal time for conducting the study is daytime from 9 to 14 and evening hours from 19 to 24.
One of the main conditions for conducting the study is the convenience of the expectant mother. She should take a comfortable position, sitting on a chair, lying on her back or side. She should not experience discomfort throughout the entire procedure. The duration of the study is usually 20-40 minutes. This is due to the frequency of periods of sleep (usually no more than 30 minutes) and wakefulness of the fetus. Registration of the basal rhythm of the fetal heart rate is carried out for at least 20 minutes until 2 movements are recorded lasting at least 15 seconds and causing an acceleration of the heart rate by 15 heartbeats per minute.
In case of unsatisfactory results of conventional (non-stress) CTG, special tests (functional tests) may be prescribed.
The second method is used extremely rarely, mainly at the time of childbirth. For the study, a catheter or strain gauge is inserted into the uterine cavity, which records intrauterine pressure, and an ECG electrode, which is attached to the fetal head and records the heart rate.
CTG is carried out to assess the condition of the fetus in the third trimester of pregnancy and during the process (during contractions and between contractions), identifying threatening conditions and deciding on medication or emergency delivery.
If unsatisfactory results of non-stress CTG are obtained, tests (functional tests) are used, which is called stress CTG. These tests include: oxytocin, mammary, acoustic, atropine and others.
Decoding the CTG result provides information about the cardiac activity of the fetus
CTG of uterine tone and fetal heart rate: 6, 7, 8, 9 points
Update: December 2018
When the expectant mother feels the movements of the fetus, it is wonderful: the pregnant woman knows that the baby is doing well. But it is impossible to assess the possible onset of intrauterine suffering in a child based on motor activity.
In order to detect and prevent problems in time, it is necessary to use ultrasound research methods (CTG, ultrasound and Doppler). Fetal cardiotocography (CTG) is a simple and accessible method for assessing a baby’s heartbeat, with which you can notice the initial signs of oxygen deficiency.
In addition, it is possible to identify changes in the muscle tone of a woman’s uterus, which can cause premature birth. CTG is a technique for recording uterine tone and heart rate on special calibration paper. That is, there are 2 graphs; some devices can record the child’s physical activity:
- heartbeats recorded by ultrasound
- uterine tone determined by a strain gauge
Is cardiotocography harmful to the fetus?
This is an absolutely safe procedure for both the fetus and the woman, does not cause discomfort and can be performed according to indications even daily (in case of fetal hypoxia), to assess the effectiveness of the therapy and make a decision on emergency delivery.
Indications for CTG
The most informative method is in the last trimester of pregnancy.
It is after 30 weeks that biori are fully established and a specific reflex is formed (increased heart rate with fetal movements), by which one can judge the full support and normal intrauterine development of the child (see calculator for calculating the gestational age). The main indications for CTG during pregnancy include:
| Complicated pregnancy:
|
Diseases in the fetus identified by ultrasound examination:
| Serious illnesses in a pregnant woman:
|
In the cases listed in the table, CTG should be performed more often, up to daily. The condition of the fetus and the effectiveness of labor can also be assessed by cardiotocography in real time.
Research methodology
Most often, the examination is carried out at 32 - 34 weeks of pregnancy. CTG is performed in the pregnant woman's supine position with a small bolster under her right side (the optimal position is a slight turn to the left side). It is possible to perform CTG in a position lying on your side, or sitting, leaning back in a chair.
- First, the doctor uses a stethoscope to find the point on the abdomen where the baby's heart can best be heard.
- An ultrasound probe is placed on this site, and a probe is placed on the fundus of the uterus to assess muscle tone.
- To notice the baby's movements, the woman is given a special device with a button that she will press when she feels intrauterine movements.
- Recording time is 40-60 minutes.
When CTG is done, the study is carried out using sensors with a frequency of ultrasonic waves of 1.5-2 MHz, which is absolutely safe for the fetus even with prolonged exposure. Any modern device has the ability to assess the vital functions of two fetuses at the same time, which is used in women with twins.
Types of devices
Medical facilities have various options for assessing your baby's heartbeat. Most often, the doctor simply listens to the baby’s heart rhythm using an obstetric stethoscope, but if there is any doubt (or if there is evidence), it is necessary to use a special device. What types of CTG devices are there?
- CTG without automatic analysis
These outdated devices are generally quite rare in modern hospitals, but they can still be found in remote corners of our country. The main inconvenience of these devices is that the doctor must independently evaluate the fetal heartbeat graph. If the doctor has experience and masters this technique, then the effectiveness of these devices is no lower than that of new CTG devices.
- CTG with computer analysis
Modern cardiotocographs not only record the graph, but also independently process the data. The doctor only needs to read the finished result and decide on the need for treatment. This version of CTG is used most often in medicine.
The modern mobile era offers an excellent option for monitoring the baby using a special sensor attached to the skin of the abdomen and a smartphone connected to the Internet. Information about the fetal heartbeat in real time is transmitted to the web portal, processed and provided in the form of a ready-made report to the doctor. Unfortunately, online CTG is still rarely used.
Interpretation of CTG: pathology or normal
The table below shows the assessment of the fetal condition according to CTG, proposed by Dr. Savelyeva, which takes into account all indicators:
- basal rhythm - average fetal heart rate
- variability - change in the frequency and amplitude of the heart rhythm (deviation from the basal rhythm frequency
- acceleration - acceleration of the heart rate from the basal rate by more than 15 beats, lasting over 10-15 seconds.
- deceleration - a decrease in the fetal heart rate from the basal rate by more than 15 beats, lasting more than 10 seconds.
- fetal motor activity
A bad CTG during pregnancy will occur if the following indicators are detected:
- prolonged increase in fetal heart rate (tachycardia) more than 160 beats per minute
- decrease in baby's heart rate to less than 110 beats per minute
- increased rhythm variability with an amplitude of more than 25 beats per minute
- reduction in variability below 5 beats per minute
- sinusoidal rhythm, in which a uniform and monotonous heartbeat occurs without any fluctuations or changes in variability
- appearance of decelerations
| 2 points | 1 point | 0 points | |
| Basal rhythm , beats/min | 110-160 | 100-110 or 160-170 | less than 100 or more than 170 |
| variability (number of deviations from the basal rhythm per minute) | more than 6 | 3-6 | less than 3 |
| Amplitude of oscillations (deviations from the basal rhythm) | 10-25 | 5-9 or more than 25 | less than 5 or sinusoidal rhythm |
| Accelerations | regular, 2 or more | intermittent or absent | none |
| Decelerations | absent, appear simultaneously with uterine contractions | rare and short | pronounced and long-lasting |
After counting the points, the condition of the fetus is assessed:
- 5 or less - state of fetal hypoxia, the child experiences oxygen starvation
- 6, 7 points - the first signs of fetal hypoxia
- 8, 9, 10 points - no hypoxia, the child feels well
Motor activity is not taken into account in Savelyeva’s method, but you should know that increased, excessive fetal mobility or, conversely, its absence, indicates the presence of oxygen starvation in the fetus.
However, even when deviations are detected, this does not always indicate serious problems in the child. It is necessary to take into account not only CTG during pregnancy, the interpretation of which will indicate the presence of hypoxia in the baby, but also the duration of pregnancy, the presence of complications in the pregnant woman, data from ultrasound examinations and Doppler measurements.
How to prepare for the procedure
The results of CTG directly depend on the condition of the mother, so food intake before the test should be moderate, otherwise increased blood sugar can lead to excessive fetal activity and poor cardiotocography results. The optimal result will be two hours after eating.
Distortion of research results may result from:
- consuming large amounts of food before the examination;
- coincidence of the time of the procedure with the baby’s sleep period;
- overweight of the expectant mother;
- excessive fetal activity;
- the presence of more than one fetus in the uterus;
- Incorrect mounting of sensors.
The pregnant woman should be warned that the procedure takes a long period of time and it is recommended to visit the toilet before starting it.
Decoding the results
A result of more than 9 points on a 10-point scale is normal
Based on the results of the study, the doctor receives a tape on which curves with different amplitudes are displayed. Using them, the specialist deciphers the result.
Key indicators for assessing the result:
- Heart rate (HR), or basal rhythm. Normally, at rest, the fetal heart rate is in the range of 120–160 beats per minute.
- The height of deviations from the average frequency of contractions of the heart muscle. Normally, variability does not go beyond 5–25 beats per minute.
- Slow heart rate. On the tape, the curve goes down, forming a depression. Normally they should be absent.
- Acceleration of heart rate. On the tape, the curve forms a jagged pattern. Normally, two or more accelerations are recorded for every 10 minutes of the study.
- Contractile activity of the uterus. The norm is no more than 15% of heart rate, duration is from ½ minute.
The result is assessed on a 10-point Savelyeva scale, where:
- Less than 5 points – poor CTG. Indicates the presence of acute oxygen starvation - hypoxia. The condition requires emergency assistance in the form of stimulation of labor.
- An indicator of 6–7 points indicates the initial stage of oxygen starvation of the fetus. In this case, treatment in the antenatal department of a hospital is recommended. After a short period of time, the procedure is scheduled.
- From 8 points is the norm.
If CTG is poor, it is important to exclude measurement error, which may arise as a result of the pregnant woman’s uncomfortable posture during the procedure.
CTG results alone are not enough to make a diagnosis, much less make a decision about surgical delivery. In addition to CTG, there are a number of other studies that can confirm or refute the results obtained, for example, Doppler or ultrasound.
Significance of the procedure
A study using a cardiotocograph is of high importance in assessing the condition of the fetus. Along with procedures such as ultrasound, Doppler, in-depth electrocardiography, it allows you to promptly suspect abnormalities in the baby’s cardiovascular activity and take measures to correct them.
During multiple pregnancies, when it is not possible to evaluate the heart function of each baby using a stethoscope, CTG is the only correct way to assess their condition.
If a woman is carrying identical twins, using a stethoscope to evaluate heart function is unacceptable, as the results obtained will be false.
Childbirth is also not complete without CTG. With its help, the doctor assesses the condition of the fetus during contractions and between them, determines the most suitable period for inducing labor, if necessary, and calculates the dosage of drugs.
Is it possible to refuse a CTG examination during pregnancy?
Some expectant mothers are distrustful of this type of procedure. Especially sensitive pregnant women do not like to lie in one position for a long time; others are embarrassed by wires.
It is impossible to prohibit a woman from refusing the procedure, but only with the help of CTG can one really assess the child’s condition, record and take into account his physical activity, and record possible uterine tone or oxygen starvation.
For active expectant mothers who find it difficult to spend a lot of time without moving, modern clinics offer wireless CTG sensors and even sensors that allow recording in water.
Early diagnosis of possible pathologies allows you to correct the baby’s health even at the stage of pregnancy and successfully complete the pregnancy.
CTG technique
CTG can be performed on pregnant women in the following positions:
- in a lying position on the left side;
- lying on your back (then a small cushion is placed under the pregnant woman’s right side);
- sitting on a chair, with your back supported.
The position is chosen depending on how best the fetal heartbeat can be heard.
The device has two sensors - ultrasonic and strain gauge. The doctor listens to the fetal heartbeat using a stethoscope and determines the point where it can be heard best. An ultrasonic sensor is installed in this place and secured with a special soft belt. The strain gauge sensor is installed in the lower abdomen, at the bottom of the uterus, most often on the right, and is also fixed.
The expectant mother is given a small oblong-shaped device with a button in her right hand, which she presses every time she feels the baby move.
The research procedure takes on average 30–40 minutes; it can be shortened or increased in duration depending on the results.
Does cardiotocography harm the fetus?
In cases where daily monitoring of CTG results is necessary, expectant mothers may worry about the negative impact of the device on the child. Experts assure that the device is completely harmless. Even carrying out the procedure every day does not harm the baby or cause him discomfort.
The benefits of intrauterine examination of the fetus many times exceed all possible risks and concerns of expectant mothers about the CTG procedure. Minor discomfort in a woman during the procedure can only be caused by prolonged lack of movement.
Cardiotocography allows you to identify dangerous conditions at the earliest stages, prevent possible negative consequences for the fetus and pregnancy as a whole, and reduce the risk of their reappearance. But it should be remembered that one study is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. Additionally, tests, ultrasound and Doppler measurements are always prescribed.
Source of the article: https://www.baby.ru/wiki/kak-delaut-ktg-ploda-na-kakom-sroke-io-cem-govorat-rezul-taty/