Regular visits to the gynecologist are not a whim of the doctors themselves. All representatives of the fair sex should visit a doctor several times a year. Often women neglect this instruction and come for examination only when any signs appear. However, one should not lose sight of the fact that some pathologies in the reproductive organs may not appear for a long time. This is how the fluid behind the uterus behaves, the detection of which most often comes as a surprise to the woman.
Where does free fluid come from in the pelvic cavity?
It is a generally accepted opinion that normally there should be no free fluid in any form in the retrouterine space. But, nevertheless, during ovulation, when the dominant follicle ruptures, there is a possibility that the liquid contents will enter the peritoneum. In this case, accumulation of substance behind the uterus may occur. The amount of free fluid in this situation is extremely small. A good specialist can easily distinguish such a case. Which, by the way, is considered an indicator of accomplished ovulation. Soon the fluid will disappear (dissolve or be resorbed).
Ovulation
The only cause of fluid accumulation without an accompanying disease. During the release of a mature egg, the follicle reaches a large size and ruptures to release the mature egg. At this time, it becomes possible for fluid to enter the peritoneum. What causes its accumulation behind the uterus. However, a qualified specialist will distinguish this case (indicating that ovulation has occurred) from the disease, since the amount of fluid is very small - the norm. After 2 - 3 days it will resolve.
Fluid in the retrouterine space and gynecological diseases
With this disease, endometrial cells grow in any part of the pelvis. These cells are also involved in menstruation, which means they can cause free fluid to accumulate behind the uterus. But other diseases can affect a similar process. For example, diseased organs secrete an exudative substance. If there are diseases of the pelvic organs (including reproductive organs), it is possible that the presence of free fluid will be diagnosed. Often such a symptom appears in the presence of acute endometritis, as well as in the period after an abortion. Other reasons why fluid appears in the retrouterine space are ovarian rupture (anoplexy) or its cysts, purulent salpingitis. Also, a similar symptom can result from microperforation (small tear) of the endometriosis cyst, due to which its contents leak out. Fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites) can accumulate due to malignant tumors, diffuse peritonitis, liver diseases, renal or heart failure, pelvioperitonitis and other diseases.
Types of abdominal hydrops by ultrasound
The international classification of diseases does not identify ascites as a separate disease - this condition is a complication of the last stages of other pathological processes. Based on the severity of clinical symptoms, the following forms of ascites are distinguished:
- initial – the amount of water accumulated inside the abdomen reaches 1.5 liters;
- with a moderate amount of liquid - manifested by swelling of the legs, a noticeable increase in the size of the chest, shortness of breath, heartburn, constipation, a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen;
- massive (exudate volume more than five liters) - a dangerous condition characterized by tension in the walls of the abdominal cavity, the development of insufficiency of the cardiac and respiratory systems, and infection of the transudate.
How does a normal state differ from a pathology?
First of all, the presence of concomitant symptoms that occur in the presence of a corresponding pathology. But some diseases occur in a latent form. Therefore, if the ultrasound specialist believes that there may be an abnormality, you should consult your doctor and undergo the necessary examinations. Remember that timely treatment is extremely important.
Regular visits to the gynecologist are not a whim of the doctors themselves. All representatives of the fair sex should visit a doctor several times a year. Often women neglect this instruction and come for examination only when any signs appear. However, one should not lose sight of the fact that some pathologies in the reproductive organs may not appear for a long time. This is how the fluid behind the uterus behaves, the detection of which most often comes as a surprise to the woman.
Liquid formations: natural process or pathology?
The presence of free water in the Douglas space is not a disease, but may be a symptom of pathology. Fluid behind the reproductive organ or in the paraovarian areas accumulates in the middle of the menstrual cycle, after the onset of the ovulation process. This is a normal phenomenon and does not require specific treatment. It means the release of the egg from the follicle and the possible occurrence of pregnancy.
Quite often, free fluid behind the uterus is a sign of pathology of a woman’s internal organs. It is extremely difficult to determine the exact volume of such a formation on ultrasound, because it spreads between the reproductive organs. Doctors have developed certain criteria to assess the condition of the fluid in the retrouterine space (the length of the vertical level of the formation is measured):
- accumulation of water up to 10 mm is considered insignificant;
- from 10 mm to 50 mm - moderate stage;
- more than 50 mm - significant.
The volume of water behind the uterus is compared with the woman’s menstrual cycle. If the doctor has suspicions about the cause of the presence of a large amount of water behind the uterus, he may order additional instrumental tests.
Decoding the result
Determining the exact volume of fluid behind the uterus using ultrasound data can be difficult due to the two-dimensional nature of the image. In addition, the fluid spreads between the organs, which also makes it difficult to determine its exact volume. In modern medicine, it is customary to distinguish the height of the formation, correlating the volume of liquid with it. With a height of up to 10 mm, the volume of liquid is considered insignificant, from 10 to 50 mm - moderate. At a height of more than 50 mm, the volume of fluid behind the uterus, diagnosed by ultrasound, is considered significant.
The appearance of fluid behind the uterus can be caused by a serious illness. One of which is pelvic inflammation, which often requires hospitalization.
Sometimes during an ultrasound, the doctor detects free fluid in the retrouterine space. Normally there should be no fluid, so it may be evidence of a disease.
Ovulation process as one of the reasons
Ovulation is a natural process in which water accumulates in the pouch of Douglas. It does not cause serious problems, since a small amount of liquid is formed. The ovulation process occurs as follows:
- follicles are formed first;
- one of the vesicles outstrips the growth of the others, and the formation of an egg occurs in it;
- liquid formation reaches up to 20-25 mm in diameter;
- then the follicle ruptures so that the egg leaves the membrane and begins to move towards the reproductive organ.
In a healthy woman, the ovulation process occurs monthly. When a cell is released from the follicle and travels to the uterus, this is ovulation. There is fluid in the follicle, but it is very small. If the bubble ruptures, water can enter the abdominal cavity. On an ultrasound, the doctor will see a small amount of it, which is normal. The liquid resolves after a few days and does not cause any discomfort to the woman. In addition to ovulation, the formation of water in the retrouterine space can occur for such natural reasons as early puberty, menstruation.
Signs of ascites
In the early stages of the development of this condition, patients do not have any complaints; the accumulation of free fluid can only be detected using ultrasound. Visible symptoms appear when the amount of transudate exceeds one and a half liters, the person feels:
- increase in the abdominal region and body weight;
- deterioration in general health;
- feeling of fullness in the abdominal cavity;
- swelling of the lower extremities and scrotal tissue (in men);
- burping;
- heartburn;
- nausea;
- difficulty breathing;
- flatulence;
- tachycardia;
- protrusion of the umbilical node;
- discomfort and pain in the abdomen;
- stool and urinary disorders.
If an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity shows existing excess moisture, the attending physician must accurately determine the root cause of the pathological condition. Pumping out accumulated transudate is not an effective method of treating ascites.
Formation of hemorrhage in the pouch of Douglas
The fluid behind the uterus may be bloody. This kind of education is not the norm. The occurrence of bloody discharge in the pouch of Douglas means the presence of a pathology that can lead to the formation of apoplexy. Causes of hemorrhage:
- vessel rupture;
- the presence of a follicle cyst;
- ovarian cyst or stroma.
After the integrity of the ovarian tissue is broken, water is released into the abdominal cavity. The formation of bloody fluid in the retrouterine space causes pain, weakness, and dizziness. In this case, the woman experiences discharge of a characteristic color - red or dark brown.
Liquid in the space of Douglas may turn into clots. The main reasons for this phenomenon are:
- permanent injuries;
- hard sex;
- lifting weights;
- hyperemia;
- inflammatory process;
- dilated vessels.
Such pathologies cannot be allowed to occur. If a girl knows about the presence of diseases in the female part, then she should visit a gynecologist and be treated to prevent apoplexy and subsequent penetration of fluid into the retrouterine space.
Other conditions for the formation of pathology
The formation of water in the Douglas space is often the cause of some pathological process occurring in the internal reproductive organs of a woman. Doctors identify many diseases that can lead to fluid accumulation. These include the following pathologies:
- inflammatory process in the surface layer of the endometrium (endometritis);
- inflammation in the kidneys, liver, heart failure lead to the formation of ascites, as a result of which free fluid flows into the pelvic organs;
- benign formations characterized by limited growth of the endometrium in the form of a tubercle on a thin stalk;
- an infectious disease accompanied by unilateral or bilateral inflammation of the fallopian tubes (salpingitis);
- adnexitis (inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes);
- oophoritis.
The formation of fluid in the pouch of Douglas may indicate the presence of an ectopic pregnancy, in which a pregnancy test will show a positive result. In addition, this phenomenon causes endometriosis, the appearance of endometrioid cysts on the ovaries, and a condition after an abortion. If you find an accumulation of fluid behind the uterus on an ultrasound, you should not panic. A competent doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment, consult the patient and give recommendations on tactics for the woman’s further actions.
It is often discovered that fluid has accumulated in the retrouterine space, but one should not panic, because this does not always mean that a pathological process or something extraordinary is taking place.
It is possible that there is nothing unusual in this phenomenon; the fluid in the retrouterine space is due to the cyclical processes occurring in the female body.
At the same time, these symptoms may also indicate the presence of a disease. Under normal conditions, a small amount of water is allowed in the pelvis behind the uterus. At the same time, it is considered completely natural that after ovulation a certain amount of free fluid collects behind the uterus. Compared to other periods, there is more of this liquid.
It should be noted that this is a sign of ovulation. When the dominant follicle ruptures in the ovary during ovulation, the contents sometimes enter the pelvic area and accumulate behind the uterus. After some time, resorption occurs, and nothing is determined during an ultrasound.
Fluid appears in the retrouterine space if a woman is menstruating. In this case, there is a reflux of blood into the peritoneal cavity. It should be noted that this condition does not pose any threat to the woman. Simply, during menstruation, the endometrium can be moved into the peritoneum with menstrual blood.
What does an ultrasound show?
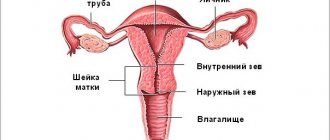
If we talk about the structure of the female body, the uterus is a pear-shaped cavity. The main task of this organ is to bear and protect the fetus throughout the entire pregnancy.
The postuterine space, or as it is also called in medicine, the space of Douglas, surrounds the uterus and is limited by the layers of the peritoneum and the anterior surface of the rectum. Usually, when liquid appears there, it accumulates in the lower part of the space in a small depression.
The transducer used to perform ultrasound is a microphone that can detect high-frequency sound waves, somewhat similar to a submarine's echo sounder. These waves are inaccessible to the human ear. Ultrasound not only sends high-frequency waves into the body, but also tracks how the wave reflects off the tissues and organs inside each of us. The received data is displayed on the monitor in the form of a picture.
The intensity of reflection depends on the density of tissue, its structure, as well as many other indicators, and is determined through frequency, amplitude, signal travel time, and characteristics of the wave itself. If there is no fluid in the retrouterine space, then the cavity of this space itself will not be detected on ultrasound. Therefore, any experienced ultrasound specialist can always determine whether there is such a liquid or not.
It is difficult to find out in any other way than ultrasound about the presence of fluid in the pouch of Douglas. It is not surprising that many women are unaware of its existence before research.
Although this symptom may be decisive for more serious examinations and tests, which should not be postponed under any circumstances. After all, sometimes it is quite difficult to accurately determine what has accumulated in the cavity: inflammatory exudate, transudate, blood or something else.
Causes
In addition to the mentioned cases, which are natural moments in the life of every woman and are periodically repeated, the appearance of fluid in the retrouterine space can also occur due to illness. It is possible that there is an inflammatory process in the woman’s genitals that is progressing. In this case, it is very likely that inflammatory exudate occurs behind the uterus.
If acute endometritis has developed, and this is especially true for the period after an abortion, then free fluid often collects in the pelvis. When performing an ultrasound scan, such fluid can be detected in a number of diseases. For example, if there is peritonitis, purulent salpingitis, ascites, hemoperetonium. With endometriosis and pelvioperitonitis, as well as a number of other pathological conditions, such fluid is also found.
Thus, with the formation of endometriotic cysts, abdominal pain becomes more pronounced and irritation of the peritoneum occurs. As a result, microperforation of the cysts occurs, so the contents leak into the abdominal cavity, so a certain amount of free water forms behind the uterus. If there is heavy bleeding in the abdominal cavity, then in this case, fluid accumulates in the retrouterine space.
If purulent salpingitis has developed, often the accumulated pus breaks through and ends up in the peritoneum. This condition leads to diffuse peritonitis, and then immediate surgical intervention is necessary. You should know that such a development of events is quite rare for pus coming out of the fallopian tube to enter the uterus or pelvic area.
An ultrasound echogram can reveal pelvioperitonitis in the abdominal area. In this case, peritoneal fluid can also enter the place behind the uterus. Moreover, the quantity is always different. Sometimes this is very small, sometimes the volume of liquid is quite significant.
What else could fluid collected in the pelvic cavity indicate? It is possible that the patient suffers from an oncological disease that occurs secretly. Something similar is observed with ovarian tumors. In addition, the development of oncology can be supplemented by ascites, that is, the accumulation of transudate in the abdominal cavity.
If an ultrasound is performed on a patient of childbearing age, and free fluid is found in the pelvis, and a fertilized egg surrounded by blood clots is detected outside the uterus, the doctor will most likely diagnose an ectopic pregnancy. Accumulation of water is also caused by other reasons, in particular, diseases of various organs of the abdominal cavity, for example, similar symptoms can accompany liver disease.
As a rule, a woman learns about the presence of fluid in the retrouterine space when an ultrasound is performed. And if the disease has a hidden course, then this diagnosis is of particular value, since it immediately indicates the presence of serious health problems.
This allows the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and determine what type of therapy is optimal. If an ultrasound showed that there is fluid in the retrouterine space, but there are no other signs of the disease, then there is no need to worry about this; most likely, everything is in order with the patient’s health.
Contributing Factors
Today, doctors name factors that may explain why fluid accumulates in the retrouterine space. Although they are indirect, they should not be ignored. Here we are talking about the notorious bad habits, promiscuity in women, leading to complications in the sexual sphere and many diseases.
Alcohol abuse also falls into the category of bad habits. Surgeries on the uterus are also a contributing factor. Particular attention should be paid to a sedentary lifestyle, a meager diet lacking the necessary set of vitamins and microelements. All this is an essential prerequisite for the accumulation of fluid behind the uterus.
Still, most often, a complication occurs when there is a hormonal change before menopause, when the patient is prescribed hormonal therapy. In some cases, the presence of fluid is diagnosed even without special studies. The fact is that the uterus sometimes greatly enlarges, causing deformation of the abdominal cavity, which is noticeable during a routine gynecological examination.
In addition to the increase, other symptoms also occur. For example, pain of varying intensity, copious watery discharge, impaired urination. It may be rapid or defined as difficult.
The condition is often accompanied by an increase in temperature. You need to monitor your health and regularly visit a doctor for preventive purposes.
2015 - 2021, . All rights reserved.
Sometimes a situation arises when, during an ultrasound examination, the doctor detects a small amount of fluid in the retrouterine space. Let’s look at what this entails and what problems it poses in detail.
If illness is to blame: pathological causes of fluid accumulation
All of the above cases, which lead to the appearance of fluid in the retrouterine space, do not require medical intervention. The causes associated with diseases should be treated completely differently. Of course, fluid is only a symptom and may be a sign of the following health problems:
- inflammation in the uterus. Its characteristic symptoms are low-grade fever, pain in the lower abdomen, and serous-purulent discharge. Antibiotics will be prescribed for treatment. Symptomatic therapy is carried out using painkillers and restoratives;
- polyps on the uterus. Symptoms of this pathology are prolonged and heavy menstruation, bleeding between periods, pain during sexual intercourse, spotting after sex, problems with conception. Treatment can be done with hormones, or the polyp can be removed hysteroscopically;
- diseases of organs located adjacent to the uterus. So, with pelvioperitonitis, peritoneal fluid appears in the space behind the uterus. A diseased liver can provoke its appearance. This also happens with heart or kidney failure. The organs in which the inflammatory process has begun release exudate - it “finds” free space and fills it. Treatment depends on the diagnosis;
- apoplexy (rupture) of the ovary. The leading symptoms are severe pain and bleeding. Weakness occurs, blood pressure drops, temperature rises, and vomiting occurs once. Surgical treatment (laparoscopy);
- endometriotic cyst on the ovary. Due to microcracks on the surface of the cyst, menstrual blood flows out of its cavity and can enter the retrouterine cavity. The following symptoms help identify this disease: pain in the abdomen, disruption of the menstrual cycle, heavy bleeding during menstruation. Conservative treatment includes taking hormonal drugs, NSAIDs, painkillers, vitamins and immunomodulators. If it does not produce results, then the cyst is removed (sometimes together with the ovary) or a puncture is performed;
- purulent salpingitis. When the pyosalpinx ruptures, pus enters the abdominal cavity and into the “pocket” located on the back of the uterus. The patient develops additional symptoms - fever, stomach pain. Leukocytes increase in the blood. Urgent surgical intervention is required. Excess fluid will be removed, and then the woman will undergo long-term treatment to relieve inflammation and antimicrobial therapy;
- malignant tumors in the abdominal cavity or pelvis. With a tumor localized on the ovary, ascites often develops and fluid collects in the cavity of Douglas. Complex treatment - surgery, chemotherapy;
- if a woman has had an abortion, then when performing an ultrasound, the doctor can also detect fluid in the described area.
Presence of liquid under normal conditions
The retrouterine space itself is located behind the uterus and is limited by the peritoneum. Fluid accumulation is possible in the lower part of this cavity.
Sometimes minor fluid in the retrouterine space can be caused by natural causes and does not threaten serious problems.
Fluid in the retrouterine space during ovulation
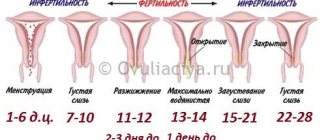
Perhaps this is due to a rupture of the follicle. Let us recall how the ovulation process occurs:
- Fluid sacs called follicles develop in the ovary.
- One vesicle is ahead of the others in growth and serves as a shell for the formation of the egg. The remaining bubbles gradually decrease in size and disappear.
- The follicle reaches 20-25 mm in diameter, which indicates the full development of the cell.
- The vesicle bursts, the cell leaves the membrane, moving towards the uterus.
This process is cyclical and occurs every month. It lasts after the end of menstruation until the middle of the cycle. The process of cell release is called ovulation. It is at the moment of rupture that a certain amount of fluid may enter the abdominal cavity. But there is very little of this fluid in the follicle and even its entry into the area behind the uterus will not cause alarm.
The doctor will determine such content to be normative and timely (in the middle of the cycle). After a couple of days, the liquid will resolve.
Other natural causes
Fluid in the retrouterine space may also appear during some natural processes, which should not cause fear:
- Period. During bleeding, blood may flow into this cavity. There's no need to worry. During menstruation, the endometrium, along with secretions, moves into the abdominal cavity.
- Young girls or girls going through early puberty may experience excess fluid in the cavity. The doctor will check and diagnose the norm.
If a similar problem is detected on an ultrasound, if it is not accompanied by signs of instability of the process (temperature, pain), the doctor determines 2-3 days for observation. If the fluid was absorbed during a repeat ultrasound, the process proceeded rhythmically. If it remains, additional tests and examinations are carried out to identify the problem. Often it can be caused by a disease, and a very serious one that requires immediate intervention.
Important
It is better not to wait and at the first symptoms of one of the diseases listed below, visit the hospital and undergo examination and treatment if necessary.
There is fluid, but no problem
Nothing “like that” should be found in the cavity of Douglas. However, there are a few cases where a small amount of fluid may still be present in the retrouterine space, and this is completely normal and does not require treatment. The natural processes that occur in a woman’s body are to blame for its accumulation, namely:
- throwing in a small portion of blood during menstruation (which is completely safe). During menstruation, the endometrium, along with menstrual blood, penetrates into the abdominal cavity;
- ovulation. When the capsule of the follicle bursts and the mature egg comes out to meet the sperm, a small part of the fluid that is released can also enter the space behind the uterus. After a couple of days it is absorbed;
- period of puberty in girls and young girls.
If the diagnostician saw fluid in the retrouterine space (in a small amount) during an ultrasound examination of the patient, then he does not immediately make a final diagnosis. The doctor watches for some time to see how the situation develops further. If a subsequent ultrasound reveals that the fluid has resolved, this indicates that everything is “going according to plan”: ovulation has completed normally.
Fluid in the retrouterine space during inflammation
In addition to natural causes, a small amount of fluid in the retrouterine space collects in some diseases caused by inflammatory processes. Inflammation of any organs of the genital and urinary system can cause accumulation:
- uterus;
- Fallopian tube;
- ovaries;
- bladder.
Features of treatment
With such diseases, the fluid cannot be absorbed on its own. The doctor will refer the patient for an ultrasound and will monitor the situation during the course of treatment.
It is necessary to reduce and observe the fluid in the retrouterine space in a small amount. Additional tests are performed to confirm inflammation. Having made an accurate diagnosis, the specialist will prescribe antibacterial drugs. Treatment features may vary depending on the complexity of the case:
- When the disease is detected at the initial stage, the doctor prescribes several types of antibiotics. If taking medications does not have an effect, antibiotics are administered through a dropper or injection.
- In advanced situations, when there are purulent accumulations in the tissues, surgery is prescribed. It is necessary to open the abscess in order to prevent the abdominal cavity from filling with pus, which will lead to dire consequences. If the abscess is on the ovary or uterus, it is sometimes possible to remove the affected organ if it cannot be preserved.
- It is mandatory to prescribe tests for the partner. He can act as a carrier of infection. If it is not eliminated, a similar type of disease may recur in a woman.
Inflammatory process
The presence of fluid not due to ovulation is associated with inflammation of the following organs:
- fallopian tube;
- ovaries;
- Bladder;
- uterine cavity.
The fluid will not be able to resolve on its own, so it can be observed during each ultrasound examination. To accurately determine the disease, the gynecologist will order additional tests (urine, blood); if they confirm inflammation, antibacterial drugs will be prescribed.
Treatment of the inflammatory process of the pelvic organs should begin immediately after examination by a doctor. At the initial stage of the disease, the doctor may prescribe one or several types of antibiotics. If such treatment is ineffective or for another reason why oral administration of drugs is impossible, the patient must be hospitalized. In the hospital, antibiotics are administered by injection or IV.
With such a disease, there is a need to treat the partner, since it is often the partner who becomes the carrier of the infection. Neglecting its treatment can provoke a recurrence of the disease.
Surgery involves opening the abscess or eliminating perforation. That is, the operation is prescribed for advanced cases when there is a large accumulation of pus in the tissues. This is necessary to eliminate the abscess before it ruptures and fills the abdominal cavity with pus. If abscesses form on the uterus or ovaries, removal of the affected organ may be prescribed.
What are the dangers of an ectopic pregnancy?
Another case when fluid forms in the retrouterine space is during an ectopic pregnancy. As we know, the egg in the genital tract meets male cells, with one of which contact occurs and, as a result, fertilization occurs. Next, the fertilized egg enters the uterus. There it should attach to its wall. But there are situations when the egg is attached to the wall of the fallopian tube. Such improper implantation provokes a rupture of the tube wall, which causes fluid to flow behind the uterus.
This is diagnosed through tests, analyzes and ultrasound. But ectopic conception shows painful signs long before excess fluid accumulates. Therefore, it will not be possible to miss this moment and detect it only with an ultrasound.
Can fluid be found behind the uterus in a pregnant woman?
Fluid in the retrouterine space during pregnancy is detected only if the fertilized egg is attached in the wrong place, that is, during an ectopic pregnancy. This will inevitably lead to a rupture of the wall of the fallopian tube, which is why fluid will penetrate behind the uterus. But an “incorrect” conception is usually detected (by pain, poor health, spotting) long before excess fluid accumulates.
Free fluid in a woman's abdomen, behind the uterus, is often found on ultrasound. If there is little fluid, its presence is not considered a pathology. Often fluid accumulates after menstruation or during ovulation. But in some cases, fluid behind the uterus on ultrasound data should be a cause for concern.
Bloody fluid - causes and treatment
Fluid in the retrouterine space, the reasons for its appearance - all this can be diagnosed by a doctor. Here we are considering general cases, one of them is hemorrhage into the ovary (apoplexy). This is possible under the following circumstances:
- ovarian stroma;
- a blood vessel ruptured;
- follicle cyst;
- ovarian cyst.
In this case, hemorrhage occurs directly in the ovary, and after the tissue of the latter is destroyed, it passes into the abdominal cavity. The fluid observed on ultrasound is bloody in nature. This is predominantly blood, often with clots. This disorder can be detected by the following symptoms:
- pain in the abdominal area, in the lumbar region;
- discharge of bloody mucus from the vagina;
- weakness, dizziness.
Any reason can cause fluid in the retrouterine space in the form of blood clots: trauma, rough sexual intercourse, severe physical exertion. Any such action causes disturbances in the vascular system or ovarian tissues. If a girl has some abnormalities, in the form of dilated vessels, small cystic deformation of the ovary, hyperemia, or even an inflammatory process, she is considered predisposed to apoplexy.
This is a very serious disease that requires urgent treatment and consultation with a doctor. Treatment occurs in stages: stopping bleeding, restoring tissue of the damaged ovary, stabilizing the body due to large blood loss.
Symptoms
Many health problems that are accompanied by the accumulation of fluid in the pelvis occur without visible symptoms or abnormalities.
Often, patients complain of aching or tingling pain in the lower abdomen; depending on the initial disease, the following may also be observed:
- Leucorrhoea of a non-standard nature from the vagina.
- Non-cyclical periods, poor ovulation or its complete absence.
- High body temperature.
- Feeling of tightness in the sacral spine.
- Causticity, numbness in the arms and legs.
- The appearance of a slight tingling sensation in the lower abdomen.
This symptomatology is caused by dysfunction of the internal organs, due to the fact that fluid accumulated in the pelvis disrupts the flow of oxygen and nutrients.
What should you be wary of?
In cases where free effusion in the pelvis has not manifested itself in any way for many years or months, the diagnosis becomes significantly more complicated and additional tests will be required for an accurate diagnosis. The sooner the patient sees a doctor, the better and more effective the treatment will be.
The following warning signs should alert you:
- Physical or mental impairment.
- Puffiness, swelling of the face and limbs.
- Uncharacteristic bloating, feeling of tightness.
- High body temperature.
- Pain of varying degrees in the lumbar region.
- Vaginal mucus has changed its shape, character, and smell.
- Sharp pain during menstruation (presence of blood clots).
- No sexual desire.
- Discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse.
When and which doctor should I contact?
There is no treatment for free fluid in the pelvic area. The doctor must find out the cause of this condition and prescribe therapy for a specific disease.
- Initially, it is recommended to consult a general practitioner, who, after an initial examination and medical history, will refer the woman to a gynecologist and phlebologist.
- The gynecologist will definitely perform an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, in which free fluid in the pelvis may be a symptom of endometriosis. In this case, the gynecologist will prescribe standard drug treatment, which most often includes hormonal therapy. If it does not bring the expected results, surgical intervention will be prescribed. This includes operations to eliminate common foci of endometriosis, most often the operation is performed laparoscopically.
- If the cause of the appearance of free fluid in the pelvis turns out to be foci of inflammation, the therapist will refer the patient to another highly specialized doctor to treat a specific disease.
Other types of diseases
If free fluid accumulates in the retrouterine space and rectal cavity, this may be caused by acute inflammation of the pelvic organs. The name of the disease is purulent salpingitis. On ultrasound, it looks like dilation of the fallopian tubes (enlargement or lengthening) and the presence of fluid. This disease can be identified by the following signs:
- pain;
- sensitivity, discomfort when moving the cervix;
- temperature increase.
When taking tests, the diagnosis will be confirmed by a large number of leukocytes, ESR and detection of pus during puncture of the posterior fornix. Treatment involves surgery. In this case, excess fluid is necessarily removed, acute manifestations of inflammation are stopped, the effects of microbes are suppressed, the lesion is treated, and metabolic disorders are corrected. The treatment takes a long time and includes a rehabilitation period under the supervision of a doctor to ensure that all organs return to a normal rhythm.
So, fluid in the retrouterine space after ovulation or during follicle rupture should not cause alarm. It is within normal limits and disappears quickly. But there are also many serious reasons, which are also accompanied by the collection of fluid into the cavity. Therefore, it is worth visiting a gynecologist regularly, even if there are no problems, so as not to miss a deviation in the usual operation of all systems. If you have pain or other unpleasant symptoms, there is no need to delay contacting a gynecologist.
Fluid behind the uterus cannot be called a disease. Rather, it is a harbinger of another gynecological disorder or a prerequisite for an emerging female disease. If the accumulation of water behind the uterus is the result of a disease, then such pronounced signs appear as pain when urinating, grayish discharge both during and after sexual intercourse. Fluid in the posterior fornix needs to be treated.
Fluid in the uterus is most often observed in premenopausal women who have had an unsuccessful pregnancy (miscarriage), surgery (abortion or curettage), and may be a consequence of childbirth. Most often, there are no signs of the disease: no pain, no discomfort, no discharge. Fluid in the uterus is usually detected in girls and women planning to become pregnant after undergoing an ultrasound.
Acute purulent salpingitis
Acute purulent salpingitis is an acute inflammation of the pelvic organs. An ultrasound examination will show expansion, thickening, and elongation of the fallopian tubes, which are characterized by a decrease in echogenicity. There is an accumulation of free fluid in the rectal uterine cavity.
Symptoms of the disease:
- abdominal pain;
- sensitivity during cervical movement;
- elevated temperature;
- leukocytes more than 10500;
- the presence of pus during puncture of the posterior fornix;
- ESR >15 mm/h.
Treatment of salpingitis is carried out in 3 stages:
- Preparing for surgery.
- Removal of purulent fluid and treatment of the lesion.
- Rehabilitation after surgery.
Before surgery, acute manifestations of inflammation are stopped, the aggression of microbial pathogens is suppressed, and metabolic disorders are corrected.
For more effective treatment, if discomfort, pain or symptoms of the disease appear, you should not delay or try to treat yourself using traditional medicine or, especially, prescribe yourself medications. Once every six months you need to visit a gynecologist and, if necessary, undergo an ultrasound. The initial stage of almost any disease is treatable, so do not neglect your health.
Fluid detected on an ultrasound in the retrouterine space may be a completely harmless phenomenon or, conversely, indicate the presence of certain diseases.
But how to determine how dangerous this symptom is and when urgent treatment is needed? First of all, it should be said that if a few milliliters of fluid are detected during a pelvic ultrasound 14-15 days after the start of the cycle, then nothing bad happens.
At this time, the woman’s body has just undergone ovulation - the process when an egg is released into the abdominal cavity from the ovary after the rupture of a mature follicle filled with fluid.
It is precisely this fluid that can temporarily accumulate in the retrouterine space. After a few days, this fluid will resorb or resolve. The appearance of fluid in other cases indicates the need for a more thorough examination of the condition of nearby organs.
Factors contributing to the appearance of fluid in the uterine wall
There are a number of factors known that contribute to the formation of fluid in the uterus:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse
- Disturbed diet
- Disturbed sleep patterns
- Hormonal disbalance
- Bad habits
- Alcohol or nicotine addiction
- Lack of physical activity, passive activity
- Nervous breakdowns, stress.
The diagnosis of serosometer (fluid accumulation in the uterus) is made when deformation of the abdominal part and an increase in the size of the uterus occur. In addition to deformation, there are a number of other symptoms that are possible with fluid accumulation:
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Copious watery discharge
- Problems with urination (frequency and pain)
- Slight increase in body temperature.
Due to the peculiarities of anatomy, fluid accumulation is observed in absolutely healthy representatives of the fair sex.
Treatment methods
Accumulated fluid behind the back wall of the uterus can form when there is heavy bleeding in the peritoneum. Fluid behind the uterus can sometimes be pus that has leaked into the abdominal cavity due to purulent salpingitis.
Free fluid in rare cases can be considered normal, although, naturally, gynecologists note the absence of fluid behind the uterine wall as normal.
During the second stage of the cycle, water may be produced during ovulation, and in the first phase it may be due to the release of blood into the abdominal cavity during the menstrual cycle.
Experts advise regularly undergoing examinations and preventing the occurrence of infections and chronic inflammation. If any disease is nevertheless discovered, the next check by a gynecologist should be done no earlier than two months after treatment. To undergo the examination, you must take an immune test and a smear to check for the presence of chlamydia in the body.
The accumulation of fluid in the uterus may be the result of acute endometritis. Another reason is a rupture of one of the ovaries or a cyst. There are also a number of other organ diseases that do not relate to the female reproductive system. Therefore, a comprehensive examination of the whole body is recommended.
The fluid may be the result of a collection of liquid blood, medically called a hemometer. The postpartum result of fluid accumulation in the posterior wall of the uterus may be a disrupted flow of lochia waste - lochometre.
Experts are not against it when a woman undergoes herbal treatment for the purpose of prevention. Recommended herbal decoctions include red brush and hogweed, calendula, sweet clover, coltsfoot, chamomile and sage, woodland mallow and centaury, rosemary, oak bark with cinquefoil and knotweed. Douching can also be used as a preventive measure. Consuming herbal decoctions, of course, will not cause harm to the body, but before taking the course, you should definitely consult with your doctor.
Diagnostics
Free fluid in the cavity of the pelvic organs is not a separate disease, but is a symptom of one of the dangerous diseases. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnosis of the body to identify possible prerequisites for such a condition.
To do this, the doctor will initially prescribe:
- Blood chemistry;
- Laboratory testing for tumor markers.
- Puncture using a large needle to check for the presence of fungi, viruses, and pathogens in the free fluid.
As statistics show, quite often the accumulation of free fluid is a symptom of the development of an inflammatory process in the peritoneum and pelvic organs. Also, with the use of modern diagnostic devices, it is possible to determine the presence of lymph or blood in internal organs and tissues.
Free fluid can be represented in the pelvic cavity by blood, pus, and in some cases fibrosis or serosis.
With the help of modern diagnostic tools and research measures, you can easily determine the form of the liquid and formulate the best treatment.
Laboratory research
A high-quality diagnosis of various pathologies can be carried out using additional laboratory measures:
- The puncture taken earlier is sent for cytological examination. This allows us to identify a description of various pathological processes developing in the body, including malignant and benign formations.
- Carrying out catheterization using a special drainage system. This method is used when there is a large accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the pelvic organs. If the volume of free fluid is less than 20 ml, such a study is not possible.
- To identify the causes of the formation of pathologies, in some cases fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy is prescribed - a study that allows to exclude or prove erosions, gastric ulcers, tumors in the duodenum. They can cause the formation of metastases and the accumulation of free fluid in the pelvic organs.
- A mammogram of the mammary glands will be required to exclude pathological changes.
- It may be necessary to perform a hysteroscopy as an additional procedure, which will show deviations in the condition of the uterine walls. In this case, a laparoscopic diagnostic procedure is also performed.
Timely diagnosis of the pelvic organs allows us to identify the root causes of the appearance of free fluid in the pelvic organs. Depending on age, reproductive capacity and laboratory test results, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
The results of the study will show the doctor all the necessary information about the condition of the body before prescribing the most effective treatment regimen.