A process sticking out of the vagina
Frequently, frightened patients who have discovered a growth in their vagina come to the gynecologist.
Of course, such a discovery will scare anyone, but you shouldn’t worry ahead of time. Most likely you are faced with a benign neoplasm. The color of this process is usually pinkish or flesh-colored, if you can see it. Such formations indicate that HPV, the human papillomavirus, has been activated in the body.
Growths in the vagina, photos of which can be taken, are located near the entrance to it. There are also those that can only be detected by touch and can only be seen by a doctor during an examination, since they are located inside the vagina.
Often such neoplasms appear suddenly and a woman does not notice them until she accidentally feels them. Sometimes their appearance is accompanied by itching, burning and even spotting.
To protect yourself and your partner from HPV, you must use barrier methods of contraception, and never neglect intimate hygiene, especially after sexual intercourse.
The presence of a process in the vagina can interfere with sexual intercourse and also become an obstacle to the desired pregnancy.
Condylomas are classified as follows:
Condylomas can appear in different places - on the labia, pubis, near the anus, on the thighs. They are not dangerous in themselves, but can easily be injured upon contact and bleed.
A process from the vagina can also be malignant, so if you find one in yourself, you should definitely consult a specialist. To begin with, see a gynecologist. There are also cysts, lipomas, polyps, and warts in the vagina. So, if the growth is white, then this is a genital wart.
Sometimes women discover that they have hemorrhoids and do not immediately understand what kind of nodule it is. During the examination, the doctor, based on his many years of experience, will share his assumptions with you. And in this case, he will refer you to a proctologist to solve the problem.
Up to a certain point, HPV does not manifest itself in any way, but after some time growths appear. As we have already said, in color they are not much different from the color of the body.
Causes
The occurrence of a growth or condyloma in the vagina depends on the state of the person’s immune system. Once infected, the virus can live in the body for about three months and not make itself known. It rarely happens that within two weeks after contact with an HPV carrier, the first condylomas or papillomas appear.
Most often, a woman becomes infected with HPV if:
- her immune system is impaired;
- there are various infections in the genital tract;
- she often changes partners without thinking about safety.
Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules is also fraught with unpleasant consequences.
With a strong immune system, a woman can live her entire life and never find the appendage from the vagina. But at the same time, she is a carrier of the virus and can infect her partner. Most often, the risk of contracting HPV is higher during pregnancy, as well as during breastfeeding.
Of course, there are few women who, in such a difficult period, plunge headlong into intimate life and change partners, forgetting about everything.
So before you plan to conceive, you need to undergo all the necessary examinations.
Treatment
A process in the vagina, if it is a condyloma, usually must be removed. The final diagnosis is determined only by a gynecologist after a thorough examination.
To begin with, the doctor talks with the patient, and then conducts an examination on the chair. Then a colposcope is used to enlarge the detected formations on the walls of the vagina and cervix. Thanks to PCR diagnostics, it is possible to determine the HPV strain, because it comes in several types. For this analysis, it is necessary to take a scraping from the place where the growth is located.
Using the ELISA method, antibodies to HPV are determined. Be sure to take a smear of the flora to see if there is a bacterial infection. They also conduct an examination for the presence of oncological processes in the cervix and cervical canal - a smear for oncocytology.
The choice of therapy is also influenced by the woman’s age, her general health, and individual characteristics. Various medications are also used to support the functioning of the immune system. If the doctor deems it necessary, the growth can be treated with local means.
Removal
Quite often, gynecologists advise removing the appendage from the vagina as soon as possible using special devices used in gynecology. The operation does not last long, there are no scars left and the risk of relapse tends to zero.
Reasons for appearance
The main reasons for the appearance:
- decreased immunity;
- insufficient hygiene with profuse sweating;
- poor quality hygiene products;
- excess body weight;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- dysfunction of the sebaceous glands (clogging of the sebaceous glands);
- hormonal disorders;
- stressful conditions;
- unprotected sex with casual partners;
- the presence of infectious and inflammatory diseases (chlamydia, vulvovaginitis, gonorrhea, etc.).
Treatment of papillomas
The tumor should be removed even if it does not cause discomfort. The virus is transmitted through sexual intercourse, so the likelihood of infecting a sexual partner is too high.
It is not recommended to use pharmaceutical products for home use, as there is a risk of causing a burn to the mucous membrane.
Consultation with a dermatologist is required in the following cases:
- the presence of purulent or bloody discharge,
- inflammation of the skin in the area of the growth,
- discomfort when pressing on the papilloma,
- increase in tumor size.
Before learning how to treat the virus with drastic methods, it is necessary to transfer it to a latent form. For this purpose, medications are taken that stimulate the immune system. The greatest demand is: Likopid, Immunal, Anaferon, Estifan, Immunomax.
It is advisable to pay attention to chronic diseases. They negatively affect the immune system, which makes the body vulnerable to the virus. Of particular danger are endocrine disorders, pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract and inflammatory pathologies.
Of particular danger are endocrine disorders, pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract and inflammatory pathologies.
Removal methods
The likelihood of papilloma degenerating into a malignant growth increases with its constant trauma. Removal of papillomas in the vagina is a mandatory procedure, since the growth inside the genital organs is regularly subjected to mechanical stress.
The following methods of eliminating neoplasms are distinguished:
- cryodestruction,
- surgical removal,
- laser therapy,
- exposure to radio waves,
- electrocoagulation.
When performing cryodestruction, a stream of liquid nitrogen is directed to the problem area. Electrocoagulation uses high temperatures. Laser removal is considered one of the most effective and painless procedures. The likelihood of relapse in this case is minimal.
Radio wave exposure is a relatively new way to eliminate viral symptoms. Very often it is practiced when they are located on the genitals.
Surgery is suitable if the tumor is too large. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia using medical instruments.
After removal, the woman must be regularly monitored by a gynecologist. During the recovery period, it is advisable to limit sexual intimacy. Poor treatment of the growth is fraught with relapses.
The disease can spread not only to the walls of the vagina, but also to the inner thighs, near the anus, and even in the esophagus.
A sample of the removed growth is sent for histological examination. It helps determine its nature of origin.
During pregnancy
After conception, the likelihood of developing HPV increases several times. This is due to a decrease in the immune system and changes in hormone levels.
Papillomas in the vagina during pregnancy can be eliminated using gentle methods. Treatment begins at 28 weeks, when the fetal life support systems are already formed.
For local use, medications are prescribed in ointment format: Acyclovir, Celandine, Viferon, Oxolinic ointment and Solcoderm. Medicines that strengthen the immune system are taken internally: Reaferon, Kipferon, Viferon and Anaferon. If possible, therapy against the virus is carried out before pregnancy. If the growths cannot be eliminated before the moment of delivery, then delivery is performed by cesarean section.
The best way to prevent the virus is to strengthen the immune system through a healthy diet, exercise and replenishing vitamin reserves.
Conclusion
Growths in the vagina and around the outer surface of the genitals are common. Reviews indicate that such neoplasms bring severe physical and psychological discomfort.
According to survey results, laser therapy is considered the most preferable method of removing them. Its advantages include a short wound healing period and a low probability of relapse.
It is highly not recommended to remove condylomas yourself. This leads to infection and the formation of pustular wounds. Correct and timely treatment of HPV helps to avoid serious consequences.
Fungus in the groin area +18
How to prevent vaginal fungus?
In the prevention of vaginal mycoses, an important element of the fight is the prevention of its relapse. In this case, it is necessary to take care of appropriate hygiene of the intimate organs. However, excessive care for cleanliness is not recommended, as this can disrupt the natural flora of the vagina. For example, the following can be harmful: douching, irrigation, vaginal rinsing.
The cleaning products used should not contain aggressive reagents, irritants, or perfumes. A natural and neutral composition is recommended.
When washing, point your hand from the urethra to the anus, and not vice versa.
Don't wear underwear that is too tight or too tight.
The use of public swimming pools, jacuzzi, etc. may contribute to the development of mycoses, so avoid visiting them, especially during treatment.
One of the most important preventive measures is the use of gynecological probiotics. They are available as oral tablets and as vaginal suppositories and capsules. The greatest effect can be obtained from the vaginal use of such drugs.
But probiotics for vaginal fungus containing lactic acid rods cannot act as an independent treatment. Such drugs should be used in combination with antifungal agents and other drugs selected by the gynecologist. In this case, they help restore the natural composition of the flora and maintain the desired pH level of the vagina.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Development of papillomas
The appearance of papillomas on the human body is provoked by a specific papillomavirus, which is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. It manifests itself in the form of growths localized on the skin or mucous membranes. Vaginal papillomas, as well as neoplasms on other genital organs and the anus, are called condylomas. They come in 2 types:
- Pointed (exophytic). Genital warts are most often benign formations. They rise above the surface of the skin and look like a sharp papilla.
- Flat (endophytic). Such papillomas grow inside the epithelium, which causes changes in it that can provoke the transformation of a benign growth into a cancerous tumor.
HPV, which causes vaginal papillomas, has more than 100 strains. Some of them are relatively harmless and appear as benign formations, others have oncogenic properties. Depending on the degree of risk of cancer cells, papillomaviruses can be divided into the following groups:
- low-tumorigenic,
- moderately oncogenic,
- highly oncogenic (strains 18 and 16 are especially dangerous for women).
That is, all strains of the virus that cause vaginal growths are potentially dangerous and can lead to the appearance of cancer cells in the absence of appropriate treatment. Therefore, if vulvar papilloma appears, you should consult a doctor.
How does papilloma occur in the vagina? First of all, a person must become infected with papillomavirus. There are several ways of transmission of infection:
- Contact. Often papillomas at the entrance to the vagina occur as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse with a carrier of the virus. The papilloma virus is also transmitted through anal and oral sex.
- Domestic. This method of infection involves the use of personal belongings, underwear, hygiene items (soap, towels) that belong to the carrier of the virus.
- From a mother to her child. If the mother has condylomas on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, then there is a high risk of infection of the fetus during childbirth.
- Autoinfection. This method involves getting infected during depilation or shaving if there are microdamages in the vagina.
Vaginal papillomatosis is manifested by the appearance of neoplasms in the following places:
- inside the vagina,
- on the vulva,
- on the walls of the vagina,
- in the area of the vaginal vestibule,
- on the uterine cervix.
Once HPV enters the body, it remains there forever. The incubation period lasts from several weeks to several years. Only in the presence of certain factors does it become activated and manifest itself in the form of growths in the genital area.
Is it possible to prevent the disease?
The appearance of neoplasms in the vagina can be prevented. There are methods of specific and nonspecific prevention. Specific prevention of papillomavirus in the vagina is vaccination. There are two vaccines that help avoid the development of human papillomavirus infection (infection with oncogenic strains):
- Gardasil;
- Cervarix.
Girls are vaccinated three times starting from 10–11 years of age. Vaccination allows you to protect against oncogenic strains of HPV and thereby against the development of certain malignant tumors, including cervical cancer.
Methods of nonspecific prevention include barrier contraception and adherence to personal hygiene rules. Barrier contraception does not avoid all cases of infection, since even when using condoms, damaged areas of the skin may come into contact with viruses. Reduces the risk of infection by following the rules of personal hygiene, as well as strengthening the immune system - nutrition with a sufficient supply of vitamins and proteins, an active lifestyle, hardening.
Treatment of vaginal growths and diagnosis
It is impossible to delay the treatment of formations in the vagina. The earlier removal techniques are applied, the greater the likelihood of avoiding developmental pathologies. Fixing the problem yourself is fraught with negative consequences. The method of curing the disease is prescribed only by a gynecologist who has a clear clinical picture. To establish it, diagnostics are prescribed. The table describes the main methods for diagnosing the disease.
| Method | Description |
| Visual inspection | Conducted by a gynecologist along with an oral survey of the patient for symptomatic manifestations. The walls of the vagina and uterus (colposcopy) and the anus area (anoscopy) are examined. |
| PCR diagnostics | The type of HPV, quantity and effect on the body is determined, which can be done by scraping from the affected area of skin |
| ELISA | The presence and reaction of antibodies to the virus are checked |
| Cytological and histological | Cells and tissues of nodular formations are examined using a microscope |
| Oncocytology | The presence of cancer cells is determined using a smear from the cervical area and the cervical canal area |
To treat condylomas, you cannot do without antiviral tablets.
Drug treatment
To get rid of condylomas using a conservative method, antiviral drugs are used. Popular medications among consumers are Alpizarin, Lykopid or Podophyllotoxin. When prescribing such medications, the doctor takes into account the patient’s age, health status and individual sensitivity to the components. In combination with antiviral drugs, drugs to stimulate the immune system are prescribed: Cycloferon, Galavit, Immunofan. "Galaderm" is an ointment with restorative and healing properties that is applied directly to the growth.
Hardware treatment
Gynecologists recommend using hardware methods for getting rid of vaginal condylomas. Such treatment is not as long as medication, not as traumatic as a conventional operation, which is performed by a surgeon with complete excision of the condyloma, and, if necessary, with nearby tissues. Hardware techniques reduce the risk of relapse and leave no scars. It is carried out in combination with immune therapy under the supervision of a physician. The table provides descriptions of hardware methods.
| Hardware treatment method | Description |
| Laser therapy | Drying and removing the growth using a laser. Used for large diameter build-up |
| Cryodestruction | Freezing with liquid nitrogen. The procedure takes place in several stages |
| Radio wave destruction | Removes using radio waves, leaves no scars |
| Electrocoagulation | Getting rid of condylomas using elevated temperature. Skin restoration course - 14 days |
It is rational to treat extensive or aggressive neoplasms in the vagina using hardware methods.
The choice of hardware treatment technique is based on the wishes of the patient and the doctor’s recommendations. Only specialized clinics perform such procedures. You should not go to a cosmetology salon because of the risk of encountering unprofessionals. The rehabilitation course does not last long; during this period you should abstain from sexual activity. Recurrence of condylomas in the vagina means that HPV remains in the woman’s body and repeated intervention is required.
Warts in the vagina: when and how to remove
Removal is recommended if:
- symptomatic manifestations in the area of papillomas;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- injury to condylomas, which is often accompanied by inflammation;
- psychological discomfort;
- planning pregnancy (due to a natural decrease in immune defense, the growth of papillomatous formations is possible);
- preparation for childbirth in pregnant women (to reduce the risk of infection of the child).
When dealing with a problem such as warts in the vagina, a comparison of removal methods shows a variation in the effectiveness of different approaches from 30% to 90%.
However, it is impossible to achieve a 100% result if the virus persists in the body or, less commonly, is reinfected.
In this regard, relapse after removal of a wart in the vagina depends little on the choice of therapy.
There are different methods for removing condylomas.
Physical impact:
- surgically (especially when confirming malignant transformations, may require hospitalization);
- electrosurgically - through electrocoagulation, electric knife, etc. (requires anesthesia, protective equipment for personnel);
- radio waves (radio knife, Surgitron);
- cryotherapeutically - local cold action of liquid nitrogen, nitrogen oxides or carbon (to reduce damage to surrounding tissues, the surface of the formation is pre-treated with a special gel);
- laser (neodymium/carbon dioxide laser), performed under local anesthesia;
Cytotoxic effects - when using drugs podophyllotoxin, podophyllin, rarely 5-fluorouracil, destruction processes are induced in papilloma cells;
Chemical exposure - when using acids, for example, the drug Solcoderm - a combination of nitric, lactic, acetic and oxalic acid, nitric or trichloroacetic acid itself;
Intralesional administration of interferon (it is also known that local application of interferon solution to the area of the wart after laser removal reduces the likelihood of relapse);
Surgical and laser removal is carried out using special equipment.
While some drugs with cytotoxic effects (prohibited for use during pregnancy!) can be used at home.
It is recommended to remove warts in the vagina using chemical methods (chloroacetic acids) or cryotherapy.
When treating large formations using laser, cryotherapy, electrocoagulation and a number of others, scar formation is possible, which should be taken into account when choosing an intervention technique.
With extensive lesions of the skin and mucous membranes, Buschke-Levenshtein condylomas, hospitalization may be indicated.
The risk of relapse, regardless of the method used, is about 20-30%.
Care after removal of a wart in the vagina involves careful adherence to hygiene rules.
After using some methods, slight swelling and redness in the area of intervention may occur.
In order to eliminate unwanted manifestations, the doctor may prescribe local analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents.
Treatment of tumors in the vagina
The tactics for managing formations in the vagina are based on their size and structure.
Observation
In some cases, regular examinations by a gynecologist are sufficient to timely detect the growth of formations or the appearance of other complications. There is no need to remove benign vaginal tumors in the following cases:
- for small sizes;
- if it does not cause discomfort to the woman and does not cause complaints.
However, this rule does not apply to papillomas. Since a viral infection plays a role in their occurrence, the growths should be removed and a course of antiviral treatment administered in order to avoid relapse.
Drug therapy
Used to treat the following cases of vaginal tumors:
- with their suppuration, inflammation;
- if they are viral in nature - papillomas;
- after removal to prevent complications.
Removal
Surgery is necessary in the following cases:
- for papillomas;
- for large tumors, if they cause discomfort and pain;
- if malignancy is suspected.
But the method is suitable only for small-sized formations. Removal usually takes place in several treatments - two or three.
Surgical removal of vaginal formations can be carried out in the following ways:
- With a scalpel. In this case, the formation is peeled off and the bed is sutured. The vagina is tamponed to prevent bleeding. Additionally, drainage is possible - installation of a catheter for the outflow of pathological fluid (secret, blood, etc.). All tissue obtained during the operation is sent for histological examination, which makes it possible to clarify the origin and confirm the benignity of the tumor.
- Using a laser. It is used for small formations with full confidence in their benign growth. During laser removal, tumor tissue is “evaporated” and there is no material left for further histological examination.
- Cryodestruction. In this case, the tumor is treated with liquid nitrogen, which literally “freezes” the tissue, after which it is rejected. The disadvantage of the method is that there is no material to be removed for research.
- Sclerotherapy. Can be used either alone or in combination with other methods. In this case, a substance is injected into the vessels feeding the tumor, which leads to gluing of their walls. As a result, education “dries out.”
- Electrocoagulation. Involves the use of an “electric scalpel”. As a rule, it is used in combination with other methods.
Expert opinion Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
Removal of tumors with suspected or confirmed malignant growth is carried out only with a scalpel. This way, the likelihood of cell spread and metastasis is less, and the material that is sent for histological examination is not altered, which makes it possible to more accurately establish a diagnosis.
Surgical operations for malignant tumors of the vagina can be extensive - with the removal of not only vaginal tissue, but also adjacent organs. In this case, sexual life in the future is possible only after reconstructive operations with an imitation of the vagina, for example, from part of the intestine. Also, tissue irradiation, chemotherapy and other methods of influencing cancer cells are used to treat malignant tumors.
Watch this video about how and when condylomas are removed using the coagulation method:
Reasons why a process appears in the vagina
Growths at the entrance to the vagina are a symptom that indicates the presence of the human papillomavirus or diseases of the internal organs. In most cases, the formations are benign and do not pose a threat to the patient’s life.
Reasons for education
Sometimes women notice that some processes in the vagina are progressing in growth and causing some discomfort. Unpleasant symptoms indicate the development of an internal disease and require immediate medical attention.
What can cause the appearance of shoots on a thin stalk:
- problems with immunity; recent viral infections;
- excess weight and excessive sweating;
- improper care of the genitals;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- changes in hormonal levels after childbirth;
- frequent stress and anxiety;
- infection with sexually transmitted infections through unprotected sexual intercourse;
- infectious pathologies, for example, gonorrhea or chlamydia.
Types of processes
If you look at the photo of the formations, you can see that the growths come in different colors, shapes and textures. Therefore, sometimes making an accurate diagnosis can be difficult.
What diseases can long shoots in the vagina indicate:
- HPV. A small process is observed at the entrance to the vagina, which is accompanied by itching, burning during urination, and redness inside the vagina. If treatment is not timely, the situation may become more complicated and progress to a malignant stage. Therefore, in this case, it is recommended to undergo a thorough diagnosis in time and begin comprehensive treatment.
- Wen. Localization of wen is the surface of the labia and the vaginal wall. The appearance of the formation is not complemented by auxiliary symptoms; most often the development of the growth occurs without pronounced symptoms. Wen has a round shape and soft consistency. The growth is removed surgically after a comprehensive examination.
- Cyst. Cystic formations appear spontaneously and most often do not give any negative symptoms. A woman may experience discomfort during sexual intercourse. Since, increasing in size, the cyst prevents the normal continuation of intimate life. In such cases, an examination by a gynecologist and surgical intervention are required.
- Wart. A long skin growth may be a common wart. In such cases, the growth causes discomfort during sexual intercourse, the patient experiences pain and itching in the problem area. The appendage may increase in size, swell and bleed. In these cases, surgical removal of the formation is required.
- Herpes. Genital herpes is transmitted sexually and is expressed in the idea of vesicular growths filled with fluid. Formations appear both in the vagina and on the inside of the thigh. After some time, the bubble bursts, and ulcers form in its place. The situation requires medical intervention.
- Malignant formations. At the initial stages of development of the pathology, symptoms are practically not observed. Significant changes occur at stages 2 and 3 of cancer. Symptoms manifest themselves in the form of pain that radiates to the pelvis and does not stop after taking analgesics. The woman also has problems with defecation and urination, and there may be blood streaks in the excrement. In some cases, there is an increase in temperature and distinct palpation of the inguinal lymph nodes.
Diagnostics
Advice from a dermatologist... Itching, rashes and flaking of the skin signals that the body is SCREAMS at the top of its lungs about problems. We asked the chief physician, Sergei Vladimirovich Rykov, what these symptoms indicate... Read more.
..
To clarify the diagnosis, a woman should contact a gynecologist, who will conduct a thorough examination and refer her for diagnostic procedures. Based on the test results, further treatment tactics will be determined.
What diagnostic measures are carried out:
- In-person inspection of the problem area. The doctor examines the problem area, feels the lymph nodes, and the groin area. Additionally, colposcopy and anoscopy are performed.
- Taking a smear. This tactic will help determine the presence of infectious lesions and fungal pathologies.
- ELISA. Tests help determine the presence or absence of antibodies to the virus.
- Histological examination. Removal of the formation and further examination of it for the presence of cancer cells.
Therapy
What options and types of treatment can the doctor offer:
- For HPV, a complex of drug treatments is prescribed, which consists of antiviral agents, immunostimulating drugs and healing ointments.
- Fats and cysts are removed surgically. The removal method is determined by the doctor, depending on the condition of the growth. If the formation is small, the surgeon may suggest drug therapy using absorbable ointments. However, this option does not guarantee complete removal of the growth.
- Warts can be difficult to treat in some cases. For complete removal, surgical methods and subsequent courses of immunostimulating drugs are used.
- Genital herpes is treated with antiviral drugs.
Various methods are used to remove the growth, which may vary depending on the age of the patient or the characteristics of her body.
What are the main options for removing growths used in medicine:
- Laser. One of the most common and painless methods, it helps eliminate small formations, leaving virtually no traces of scars.
- Nitrogen. In this case, the shoots are removed using liquid nitrogen; the procedure takes place in several stages; after the process, a course of preventive therapy is prescribed.
- Radio wave method. The formation is removed using a radio wave, which leaves no scars or traces of surgery.
- Electrocoagulator. The process is removed using a current; at the initial stage, a crust appears at the site of formation. A couple of weeks after the procedure, the crust disappears, and a pinkish scar forms in its place.
After removing the growth, you must follow all the recommendations of the gynecologist and come for dressings, if necessary. In the first 2 weeks, you should abstain from sexual intercourse and cancel intense workouts in the gym.
Precautionary measures
To avoid reappearance of the growth, you should follow the recommendations of gynecologists:
- Monitor the area after removal of the appendix, check regularly with a doctor, apply dressings and medicinal compresses with the products prescribed by the gynecologist.
- Maintain personal hygiene, take a shower 2 times a day, and change your underwear in a timely manner.
- Strengthen your immune system, take multivitamins, lead a healthy lifestyle, get rid of bad habits.
- Protect yourself during sexual intercourse, use antiseptics, for example, miramistin or hydrogen peroxide, and be checked for sexually transmitted infections every six months.
- Treat viral infections in a timely manner, strengthen the body.
Conclusion
Doctors warn! Shocking statistics - it has been established that more than 74% of skin diseases are a sign of parasite infection (Accarida, Giardia, Toxocara).
Worms cause enormous harm to the body, and the first to suffer is our immune system, which should protect the body from various diseases.
The head of the Institute of Parasitology shared the secret of how to quickly get rid of them and cleanse your skin, it turns out that it’s enough... Read more...
If, after removing the appendage, a formation begins to appear in its place again, you should consult a doctor. In this case, the doctor will determine further tactics of action.
Source: https://venbolezni.com/problemy-u-zhenshhin/prichinyi-pochemu-poyavlyaetsya-otrostok-vo-vlagalishhe.html
Diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis, a gynecologist needs a complete diagnosis:
- History of the disease. It includes knowledge of information:
- how long ago the growths appeared;
- whether there were unprotected intimate relationships;
- how long ago the last act of this kind took place.
- Examination by a gynecologist. In this case, the affected epithelial cells are collected for subsequent PCR analysis.
- PCR diagnostics. In this analysis, the number of pathogens and the type of papilloma viral infection are determined.
- Linked immunosorbent assay. It is necessary to confirm the presence of antibodies to the virus in a person. Based on which, one can judge the degree of development of HPV in the human body.
- Colposcopy. Inspection of the vaginal walls to determine damaged areas. It is carried out using a special colposcope device and staining the cervix with iodine solution.
- Anoscopy. Involves examining the anal area for the presence of papillomas.
- Cytological examination. Study of cells under a microscope, detection of damaged areas and their characteristics.
- Histological analysis. Studying the structure of damaged areas.
- Oncocytology. Study of cells in scrapings from the cervix and cervical canal under microscope magnification.
When papillomatosis is confirmed, timely treatment and correct selection of therapy are necessary.
Major diseases
- HPV (human papilloma virus). A growth formed inside the female genitalia is medically called condyloma. The incubation period can last from 2 weeks to 3 months. During the formation of condyloma, a woman experiences itching, pain and burning. The mucous membrane may become swollen and red. The growths often emit an unpleasant odor. Untreated condylomas can cause cervical erosion, dysplasia and oncology.
- Lipoma. Wen is localized on the walls of the vagina and labia. Education occurs asymptomatically. The growth has an oval or round shape. There is no pain when palpated. If the lipoma is located outside the vagina, then when examining it, the woman will be able to notice yellow contents inside the seal. The patient is not recommended to squeeze the contents out of the seal, use burning devices, rip off the growth on her own, and take medications until a doctor makes an accurate diagnosis.
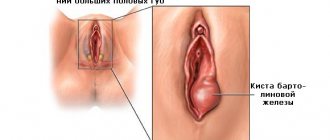
- Cyst. The formation of a vaginal cyst is asymptomatic and is detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist. When the growth reaches a large size, it can fester and make sexual life difficult (due to pain). The cyst is examined using colposcopy. The cyst has a round shape, and its structure is soft-elastic.
- Polyp. Characterized by a single growth in the area of the uterus and vagina. Multiple formations - uterine polyposis. If left untreated, polyps cause infertility. There are adenomatous polyps (grows in the mucous membrane and covers the inner surface of the uterus) and glandular polyps (formed from endometrial tissue and glands). Symptoms of formation: spotting and spotting during the intermenstrual period, discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse, nagging pain in the lower abdomen and menstrual irregularities.
- Genital wart. The growth causes discomfort, pain, and clings to underwear. The disease is transmitted through sexual and household contact. Condyloma has a pointed, papillary and flat shape. The base of the wart can be wide or thin. Papillomas are located on the labia minora and majora, mucosal walls, near the anus, in the groin and pubic area. Main symptoms: swelling, itching, redness, copious discharge with a pungent odor, possible bleeding, pain.
- Herpes. Genital herpes is a disease caused by herpes simplex viruses. The growths are filled with fluid and are localized on the thighs, pubis, anus, vagina and cervix. During the formation of a vesicle, the patient feels itching. After 7 days, the growth bursts, forming an ulcer.
- Haemorrhoids. The growth in this case is localized between the entrance to the vagina and the anus, and its shape resembles a nodule. Symptoms of the disease: varicose veins in the perineal area, pain in the lower abdomen, vaginal discharge, discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Types of growths are classified according to:
- sizes (small, medium, large);
- form;
- color;
- structure (hard, loose).
Formations can be located:
- Inside the vagina. The patient can observe this type of formation only in a photo taken during ultrasound diagnostics. Only a doctor can detect such formations during examination or palpation.
- Outside at the entrance to the labia, on the pubis, near the anus, on the thighs.
Symptoms of vaginal papilloma
Often, with HPV in women, the formation of papillomas is asymptomatic at first.
In case of prolonged development and progression of the disease, symptoms may appear:
- There is a feeling of itching and burning in the vagina.
- Bleeding may occur.
- Detection of growths in the vagina upon palpation.
Depending on the speed of development of the disease, a diagnostic examination of the patient will be necessary, followed by removal or treatment of the growths.
Review of antiviral drugs
There are drugs that only affect the infection. These include Isoprinosine. However, you can also use universal medications: Panavir, Viferon. They perform two functions: they help increase the body’s defenses and block the activity of the virus. If highly specialized drugs are used, it is recommended to use immunostimulants along with them.
Isoprinosine contains the substance inosine pranobex. As a result of taking this drug, there is a decrease in the intensity of the manifestations of the disease. Under the influence of the active substance, the virus stops reproducing. Among the indications for use, human papillomavirus infection can be found. This drug is not prescribed to children under 3 years of age, patients with renal failure, urolithiasis, gout, or arrhythmia. It should not be taken by pregnant women and women during lactation.
Viferon contains recombinant human interferon alpha-2b. It has an immunostimulating and antiviral effect. The drug is indicated for the treatment of papillomas in the vagina and prevents the development of almost any viral infections. The advantage of this remedy is the absence of contraindications. They only note the likelihood of developing an individual reaction, which happens in rare cases.
Panavir contains a hexose glycoside. The product helps increase the body's resistance to various viruses:
- papillomavirus;
- cytomegalovirus;
- herpes;
- encephalitis.
The drug is not prescribed for diseases of the kidneys, spleen, in childhood and during lactation
Panavir can be used during pregnancy, but this should be done with caution, since there is no data on the effect of the drug on the fetus and the woman’s body during pregnancy
Why do vaginal papillomas occur?
Human papillomavirus infection has an incubation period ranging from 2 weeks to several years. Very often it causes the development of formations such as papillomas or condylomas in the vagina. This pathogen enters the body through sexual intercourse and unprotected partners. The disease can develop against the background of reduced immunity or inflammatory processes.
Of particular importance is the presence of disease-provoking factors:
- endometritis;
- inflammation of the ovaries;
- vulvovaginitis;
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea.
They lead to the rapid development of the virus inside the female body.
The development of papillomas in the vagina is also promoted by:
- early intimate life;
- avitaminosis;
- dysbiosis in the vagina;
- nervous shocks.
- decreased immune strength in the body;
- taking corticosteroids;
- performing surgical interventions on infected skin;
- pregnancy.
Papillomavirus has about a hundred different strains, of which only a few are capable of leading to the emergence and development of papillomas.
When the virus enters healthy tissue, a number of processes occur:
- The pathogen penetrates the basal layer of the dermis.
- Damages the cell membrane.
- Viral DNA is introduced into the center of the cell.
- The virus is waiting for favorable conditions.
If the carrier of the papilloma virus has a strong immune system, then the infection may not show its negative effects for a long time.
Diagnostic methods
To find out what kind of disease this is and make the correct diagnosis, research is carried out:
- the doctor needs to examine the patient for the presence of papillomas;
- PCR is carried out;
- cytological examination;
- molecular biological testing;
- histological examination;
- colcoscopy in women.
A thorough examination is necessary to determine whether it is syphilis. The symptoms of the diseases are very similar, especially at the beginning of the disease. Differential staining of the genital organs is also carried out, so that where the most papillomas occur.
Cytological examination is a more complex and thorough diagnostic method. With its help, doctors can detect precancerous formations and understand how severely affected areas of the skin are.
There is also a method for detecting the disease before manifestations appear on the skin. For this purpose, molecular biological research is carried out. With its help, you can find out the type of virus that affected a person.
Finally, PCR helps determine the type of virus and how highly carcinogenic it is.
Treatment methods
When papillomas occur in the vagina, it is necessary to begin treatment as soon as possible. To do this, you should not only get rid of genital growths, but also weaken the effect of the virus. First of all, treatment of papillomas located in the vagina should begin with diagnosis. This should be done by a qualified doctor - a dermatovenerologist. After a clinical examination, he prescribes a series of studies to identify the nature of the formation and strains of viruses. After this, the attending physician will prescribe complex therapy, which is aimed at:
- fight against the virus;
- increasing the immune properties of the body;
- removal of papillomas in the vagina.
To cure papillomavirus and transfer it to an inactive (latent) phase, drug therapy is required. For this purpose, special antiviral agents are used, which are produced in the form of ointments, sprays, tablets and injection solutions.
For papillomas in the vagina, treatment is carried out using the following drugs:
- Likopid (tablets for internal use).
- Alpizarin (tablets).
- Interferon and analogues (Viferon, Anaferon).
- Solcoderm (ointment, suitable for pregnant women).
- Riodoxol.
Immunomodulators - drugs that increase the body's protective properties - also help treat papillomas in the vagina. The most popular of them:
- Immunal.
- Immunomax.
- Lycopid.
- Estifan.
But drug treatment when vulvar papilloma appears is most often ineffective and is used rather as an additional treatment. It is necessary to remove the growth to avoid injury and further growth. To treat formations in the vagina, radical methods are used:
- Electrocoagulation. This is the cauterization of condylomas using high temperature.
- Chemical cauterization.
- Cryodestruction. This is freezing the growth with liquid nitrogen.
- Laser removal. Often gives 100% relief from papillomas. Relapses are rare.
- Surgical removal. This is an operation that is performed under anesthesia. With this method, the formation is excised with a scalpel.
All these procedures are carried out only in specialized institutions - beauty salons or clinics. They are performed by an experienced specialist (doctor or cosmetologist).
Treatment of vaginal growths in most cases has favorable prognoses. Before treating papillomas, it is necessary to understand their nature (malignant or benign), and also find out which strain of the virus provoked their appearance. A doctor will help you figure this out, but self-medication in this case can lead to complications.
Types of growths in the vagina, locations
Depending on the cause, growths can be divided into certain types, which affect not only the size of the growths, but also their location.
Human papillomavirus
The papilloma virus can occur in almost any person who does not use personal protective equipment during sexual intercourse. In some cases, papilloma can occur even with the use of a condom.
The growth is most often located at the entrance to the vagina. Also, small papillomas can appear on the walls of the vagina and on the cervix.
Externally, the formation has the appearance of small scallops, which, when pressed, can provoke the formation of painful symptoms. Papilloma is contagious and can be transmitted to other people after close contact.
Lipoma
Lipoma most often appears at the entrance to the vagina or on the labia; outwardly it looks like a small growth, which has a soft consistency and changes its shape when pressed. It can occur in both single and multiple quantities.
Cyst
The most common types of formations that appear in the vagina of women. A cyst can form on absolutely any part of the mucous membrane. However, tumors most often appear on the uterus, fallopian tubes, or Bartholin glands. A cyst can also appear on the walls of the internal genital organs.
It has the appearance of a small dense formation, which upon palpation does not cause the woman any discomfort. It tends to increase in size or disappear completely on its own.
Polyp
Most often, this type of formation occurs in women who have previously given birth. The disease occurs without visible symptoms and is classified as benign growths. Growths most often appear in the area of the vaginal opening, but can also form on the walls.
When there is a large accumulation of polyps, they cause discomfort and become an obstacle to normal sexual life. In some cases, the disease may manifest itself in the form of bleeding and pain during movement. Polyps can become damaged and cause an unpleasant odor in the genital area.
Genital wart
This type of disease is a virus and can occur on any part of the mucous membrane of the genital organs.
Externally, the formation is small in size, which most often does not differ from the natural color of the skin. Genital warts, or also called condylomas, can appear in the following places: clitoris, labia, vaginal opening, cervix, anus.
Other reasons
Growths sometimes appear for reasons that do not pose any particular harm to health:
- cysts;
- polyps;
- shellfish
These defects are not accompanied by alarming symptoms and are not accompanied by discomfort. Nevertheless, it is recommended to remove them, since with strong magnification such neoplasms block the birth canal and interfere with conception. If growths appear at the entrance to the vagina, you need to visit a gynecologist or venereologist. Only timely medical care will help avoid dire consequences.