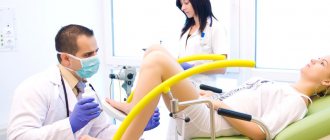
Causes of bleeding in women over 60 years of age
Uterine bleeding is bloody vaginal discharge that is not menstruation and does not relate to the postpartum period.
The medical name of the pathology is menometrorrhagia. Bleeding at 60 years of age indicates a disease affecting the reproductive organ. If a violation occurs, it is necessary to take measures to stop the bleeding and determine the cause. Menometrorrhagia is a dangerous phenomenon, and it must be eliminated under the supervision of a doctor. The appearance of red liquid during menopause is a reason to immediately contact a gynecologist. Self-medication is unacceptable, as large blood loss is possible.
Physiological features of the menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a complex process that involves 5 elements. They are all closely related. When provoking factors appear, signals are sent to the cerebral cortex, and the body reacts to them in one way or another. For example, in a stressful situation, the hypothalamus begins to produce more or less hormones than usual, resulting in hormonal imbalance.
Further, pathological changes spread to the pituitary gland, which is responsible for the synthesis of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones. These substances control follicle maturation and ovulation. The ovaries are another important organ on which the production of androgens, progesterone and estrogens, a group of female sex hormones, depends. Finally, under the influence of processes occurring in other organs, natural or pathological changes occur in the uterus.
Thus, to combat bleeding after 60 years, you need to understand why it started. Symptomatic therapy in this case is inappropriate, since it does not help restore hormonal balance. Still, the first thing to do is to stop the bleeding if it is intense. After this, the woman is sent for diagnostic procedures.
Classification of uterine bleeding
In older women, uterine bleeding is classified according to its abundance, frequency, and cause of cyclicity. By origin they can be defined as dysfunctional and ovarian.
In turn, dysfunctional discharge is divided into the following types:
- amenorrhea;
- metrorrhagia;
- two-phase MK;
- ovulatory;
- proyomenorrhea;
- anovulatory.
Older women are usually diagnosed with dysfunctional discharge. This is due to disturbances in the interaction between the pituitary gland, hypothalamus and ovaries. The occurrence of bleeding in women after 60 years of age due to hormonal imbalance is dangerous due to the high risk of the formation of malignant tumors. The cycle at this time has already completed, and the appearance of blood particles most likely indicates an abnormal process.
Causes
Benign causes of discharge in women over 60 years of age include loose mucosa associated with atrophic vaginitis, urethral caricula, trauma caused by sexual activity, cervical erosion, endometrial polyps and hyperplasia.
Estrogen replacement therapy may also cause vaginal bleeding, but any bleeding in older women should be fully investigated to rule out other causes. The evaluation includes a thorough pelvic examination with biopsy of suspicious lesions.
Clinical picture of uterine bleeding
After 60 years, a woman experiences the menopause stage. In very rare cases, menstruation may still occur. Having discovered blood particles on her underwear, a woman should monitor her condition, as well as the intensity and nature of the discharge. If they are scanty and pink, but cause pain, the cause may be damage to the vaginal mucosa. In this case, it is better to consult a doctor to make sure that everything is in order with your health.
Intense, painful bleeding that does not stop for 1-2 days or longer is a reason to immediately contact a antenatal clinic.
Symptoms characteristic of metrorrhagia:
- dizziness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- weakness;
- pale skin;
- low pressure;
- presence of blood clots;
- scanty or, on the contrary, abundant discharge;
- the appearance of blood after sexual intercourse.
These symptoms are often accompanied by irritability, anxiety, apathy, and depressive mood. The lady can determine the intensity of the discharge on her own. Bleeding is considered heavy if the pad or tampon fills within 1 hour. In this case, the risk of severe blood loss is very high.
A dangerous combination is the presence of symptoms of uterine bleeding when menstruation is absent. This may indicate internal hemorrhage, a life-threatening condition.
Dangerous symptoms
Bloody exudate that appears in menopause and postmenopause should be cause for concern if the last menstrual period was several months ago. After complete loss of reproductive function, a healthy woman should not have bleeding. If they are present, this means that an oncological process is occurring in the body or another disorder is occurring.
The appearance of spotting or brown discharge after age 60 is another cause for concern. If it is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, this may be a sign of dysplasia, endometrial hyperplasia, a malignant or benign tumor.
Normal discharge
Women of any age produce some mucus from the vagina. This is a natural process and there is no need to worry about it. The secretion is produced in the cervix and after the decline of reproductive function it becomes less, but the discharge is still present. Their task is to prevent infection from entering the body. In some women, the lack of secretion leads to the fact that the mucous membranes become thinner and dry.
The normal volume of physiological secretions is 2-6 ml per day. In healthy women they are transparent or yellowish, odorless. The consistency of the secretion should be similar to rice water, since, in addition to mucus, the liquid contains lymph and plasma. The appearance of heavy bleeding, changes in odor and color indicate pathology.
Causes of discharge
The appearance of spotting in postmenopause can be due to several reasons. One of them is the functioning of the female reproductive system. During this period, most women do not form follicles, and the ovaries become smaller. But there are exceptions when ovulation occurs from time to time, after which menstruation begins.
In medical practice, cases have been recorded of women becoming pregnant after 60 years of age. The second reason why discharge may appear is a pathological process occurring in the body.
- therapy with hormone-containing drugs;
- infection;
- chronic disease of the uterus, ovaries;
- myoma;
- polyp;
- malignant ovarian tumor;
- hyperplasia;
- endometrial injury.
Some women have blood particles in their natural mucous secretions. This is a normal phenomenon that stops over time. If blood appears regularly, you need to contact a gynecologist. Even single bloody streaks present in the mucus should alert you.
Types of pathological discharge
Depending on what disease or disorder occurs in the body, the discharge may take the following form:
- Bloody. Brown or bright red, appearing as bleeding, spotting or pink fluid.
- Curdled. The exudate is white, with thick particles and an unpleasant sour odor.
- Purulent. With a foul odor, thick, gray-green in color.
- Mucous. With an unpleasant odor, the consistency resembles foam, and can be both abundant and scanty.
The most dangerous bleeding after 60 years is uterine bleeding with purulent admixture.
Treatment
Bleeding or other discharge that appears after 60 years of age is eliminated by addressing the cause.
Types of therapy depending on the type of pathology:
- Intense discharge. When they become abundant, the woman should take hemostatic agents. Additional prescriptions depend on the cause of the pathology.
- Curdled discharge due to thrush. Elderly patients are prescribed antifungal drugs: Pimafucin, Diflucan, Fluconazole, Nystatin.
- Ichoritis caused by dryness and thinning of the vaginal mucosa. Recommended drugs that restore microflora, hormonal agents and vaginal suppositories “Estriol”, “Ovestin”.
- Oncological process. When a malignant tumor develops, surgery, radiation and hormonal therapy are prescribed. At a later stage, the uterus and appendages are completely removed, then chemotherapy sessions are performed.
- Infectious (inflammatory) diseases. Antibacterial suppositories are prescribed: Metronidazole, Polygynax, Hexicon. The woman also takes antibiotics.
Diagnostics
To make a final diagnosis, several examinations are prescribed. In addition, the woman undergoes blood and urine tests. First, the lady is examined in a gynecological chair, then a referral is issued for the following procedures:
- MRI;
- hysteroscopy;
- colposcopy;
- transvaginal ultrasound;
- tumor markers;
- blood clotting test;
- analysis of the level of hormones necessary for the functioning of the whole body;
- saline sonohysterography;
- endometrial aspiration biopsy;
- positron emission tomography.
After all the tests, treatment is prescribed. If necessary, the lady is referred to other doctors - an endocrinologist, cardiologist, neurologist.
Treatment of urticaria in elderly women
Uterine bleeding is eliminated with drug therapy or surgery. Treatment methods are selected depending on the cause of MK:
- Polyps, suspicion of the development of malignant tumors. The cervix and uterine cavity are scraped, and samples of the material are examined. Prescribes medications with estrogen and medications to stop bleeding. Further treatment depends on whether the suspicion of cancer is confirmed.
- Myoma. The node or the entire uterus is removed, in some cases with appendages. If you have fibroids, you may experience sudden pain - this is how you can recognize this pathology.
- Forgotten spiral. Some women, having installed an IUD, forget about it or do not consider it necessary to remove it. This often leads to bleeding. If an intrauterine contraceptive is found in the uterine cavity, it is removed. After this, the woman takes anti-inflammatory drugs for some time.
- Low hemoglobin concentration. With low hemoglobin, the risk of developing melanoma increases. The condition is accompanied by dizziness, weakness and general deterioration. Injections or tablets containing iron are prescribed.
In approximately 70% of cases, elderly women who apply for uterine bleeding are diagnosed with endometrial cancer. In the initial stages, this disease can be successfully treated. Having applied too late, women are faced with the need to remove the uterus and appendages. Thus, the earlier therapy is started, the greater the chance of saving organs.
A 70-year-old woman has bleeding
Uterine bleeding is bloody vaginal discharge that is not menstruation and does not relate to the postpartum period.
The medical name of the pathology is menometrorrhagia. Bleeding at 60 years of age indicates a disease affecting the reproductive organ. If a violation occurs, it is necessary to take measures to stop the bleeding and determine the cause.
Menometrorrhagia is a dangerous phenomenon, and it must be eliminated under the supervision of a doctor. The appearance of red liquid during menopause is a reason to immediately contact a gynecologist.
Self-medication is unacceptable, as large blood loss is possible.
Physiological features of the menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a complex process that involves 5 elements. They are all closely related.
When provoking factors appear, signals are sent to the cerebral cortex, and the body reacts to them in one way or another.
For example, in a stressful situation, the hypothalamus begins to produce more or less hormones than usual, resulting in hormonal imbalance.
Further, pathological changes spread to the pituitary gland, which is responsible for the synthesis of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones. These substances control follicle maturation and ovulation.
The ovaries are another important organ on which the production of androgens, progesterone and estrogens, a group of female sex hormones, depends.
Finally, under the influence of processes occurring in other organs, natural or pathological changes occur in the uterus.
Thus, to combat bleeding after 60 years, you need to understand why it started. Symptomatic therapy in this case is inappropriate, since it does not help restore hormonal balance. Still, the first thing to do is to stop the bleeding if it is intense. After this, the woman is sent for diagnostic procedures.
Causes of bleeding related and not related to the reproductive system
All organs and systems are interconnected. Failure in the functioning of some parts of the body causes pathological changes in other tissues. As a result, various symptoms arise, which include uterine bleeding. The following reasons contribute to the appearance of this symptom:
- dysfunction of the endocrine system (increased activity of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands);
- cardiovascular pathologies (arterial hypertension);
- liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatitis, cancer);
- pathologies of the hematopoietic system, accompanied by a decrease in blood clotting (hemophilia);
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals necessary for the normal functioning of the hematopoietic and cardiovascular systems);
- infectious diseases;
- prolonged stress and psycho-emotional overload;
- depletion of the body caused by poor nutrition or cancer.
Classification of uterine bleeding
In older women, uterine bleeding is classified according to its abundance, frequency, and cause of cyclicity. By origin they can be defined as dysfunctional and ovarian.
In turn, dysfunctional discharge is divided into the following types:
- amenorrhea;
- metrorrhagia;
- two-phase MK;
- ovulatory;
- proyomenorrhea;
- anovulatory.
Older women are usually diagnosed with dysfunctional discharge. This is due to disturbances in the interaction between the pituitary gland, hypothalamus and ovaries.
The occurrence of bleeding in women after 60 years of age due to hormonal imbalance is dangerous due to the high risk of the formation of malignant tumors.
The cycle at this time has already completed, and the appearance of blood particles most likely indicates an abnormal process.
How to treat bleeding?
Treatment for postmenopausal bleeding depends on the cause of its occurrence. For example, in the case of atrophic vaginitis, hormone replacement therapy is used to compensate for estrogen deficiency.
For minor atrophic changes in the vagina, moisturizers and lubricants are suitable.
If the cause of bleeding during menopause is fibroids, analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and in justified cases, hormonal drugs. It can also be removed surgically.
Clinical picture of uterine bleeding
After 60 years, a woman experiences the menopause stage. In very rare cases, menstruation may still occur.
Having discovered blood particles on her underwear, a woman should monitor her condition, as well as the intensity and nature of the discharge.
If they are scanty and pink, but cause pain, the cause may be damage to the vaginal mucosa. In this case, it is better to consult a doctor to make sure that everything is in order with your health.
Intense, painful bleeding that does not stop for 1-2 days or longer is a reason to immediately contact a antenatal clinic.
Symptoms characteristic of metrorrhagia:
- dizziness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- weakness;
- pale skin;
- low pressure;
- presence of blood clots;
- scanty or, on the contrary, abundant discharge;
- the appearance of blood after sexual intercourse.
These symptoms are often accompanied by irritability, anxiety, apathy, and depressive mood. The lady can determine the intensity of the discharge on her own. Bleeding is considered heavy if the pad or tampon fills within 1 hour. In this case, the risk of severe blood loss is very high.
A dangerous combination is the presence of symptoms of uterine bleeding when menstruation is absent. This may indicate internal hemorrhage, a life-threatening condition.
About the norm of sugar and symptoms of its increase
For each age, there is a certain norm for glucose in the blood; its excess or sharp drop is already a symptom of the disease. For women over 60 years of age, the acceptable norm is 6.0 mmol/l. Minor deviations up or down are possible, since in addition to medical standards, physiological features are taken into account.
Normally, blood sugar levels increase gradually with age. This is understandable: the older a person is, the more strength is required for the normal functioning of the body. However, if growth occurs “intermittently” against the background of age-related changes and hormonal “changes”, it is advisable to contact a specialist to identify/refute the diagnosis of “diabetes mellitus” if:
- the appearance of excess weight, subject to proper nutrition,
- decreased visual acuity,
- increased drowsiness,
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating,
- an increase in blood pressure that has not previously been observed,
- swelling of the face and neck,
- dry skin,
- the appearance of small boils,
- the presence of fungal diseases,
- problems with oral health,
- temporary loss of sensation in the arms or legs.
The danger of diabetes lies in the ability to “mask” symptoms as signs of other diseases. Often women over 60 mistake dry skin and swelling for signs of aging; furunculosis is associated with an illiterate choice of hygiene products. As a result, the patient reaches a specialist in a moderate or severe stage of the disease, when inpatient treatment is required.
Signs of diabetes in women - all in one article
In the moderate form of diabetes, in addition to the above symptoms, the following are observed:
- metallic taste in the mouth,
- increased irritability, causeless mood swings,
- dry mouth, low amount of saliva,
- fragility of hair and nails,
- sleep disturbance,
- increase or loss of appetite.
The appearance of symptoms in a complex is a reason to immediately go to the hospital. Even if diabetes is not diagnosed, treatment will likely be needed. Such signs do not appear out of nowhere; therefore, therapy will be required to get rid of the disease itself and the causes of its development.
Normal discharge
Women of any age produce some mucus from the vagina. This is a natural process and there is no need to worry about it.
The secretion is produced in the cervix and after the decline of reproductive function it becomes less, but the discharge is still present. Their task is to prevent infection from entering the body.
In some women, the lack of secretion leads to the fact that the mucous membranes become thinner and dry.
The normal volume of physiological secretions is 2-6 ml per day. In healthy women they are transparent or yellowish, odorless. The consistency of the secretion should be similar to rice water, since, in addition to mucus, the liquid contains lymph and plasma. The appearance of heavy bleeding, changes in odor and color indicate pathology.
Types of pathological discharge
Depending on what disease or disorder occurs in the body, the discharge may take the following form:
- Bloody. Brown or bright red, appearing as bleeding, spotting or pink fluid.
- Curdled. The exudate is white, with thick particles and an unpleasant sour odor.
- Purulent. With a foul odor, thick, gray-green in color.
- Mucous. With an unpleasant odor, the consistency resembles foam, and can be both abundant and scanty.
The most dangerous bleeding after 60 years is uterine bleeding with purulent admixture.
Diagnostics
To make a final diagnosis, several examinations are prescribed. In addition, the woman undergoes blood and urine tests. First, the lady is examined in a gynecological chair, then a referral is issued for the following procedures:
- MRI;
- hysteroscopy;
- colposcopy;
- transvaginal ultrasound;
- tumor markers;
- blood clotting test;
- analysis of the level of hormones necessary for the functioning of the whole body;
- saline sonohysterography;
- endometrial aspiration biopsy;
- positron emission tomography.
After all the tests, treatment is prescribed. If necessary, the lady is referred to other doctors - an endocrinologist, cardiologist, neurologist.
Treatment of urticaria in elderly women
Uterine bleeding is eliminated with drug therapy or surgery. Treatment methods are selected depending on the cause of MK:
- Polyps, suspicion of the development of malignant tumors. The cervix and uterine cavity are scraped, and samples of the material are examined. Prescribes medications with estrogen and medications to stop bleeding. Further treatment depends on whether the suspicion of cancer is confirmed.
- Myoma. The node or the entire uterus is removed, in some cases with appendages. If you have fibroids, you may experience sudden pain - this is how you can recognize this pathology.
- Forgotten spiral. Some women, having installed an IUD, forget about it or do not consider it necessary to remove it. This often leads to bleeding. If an intrauterine contraceptive is found in the uterine cavity, it is removed. After this, the woman takes anti-inflammatory drugs for some time.
- Low hemoglobin concentration. With low hemoglobin, the risk of developing melanoma increases. The condition is accompanied by dizziness, weakness and general deterioration. Injections or tablets containing iron are prescribed.
In approximately 70% of cases, elderly women who apply for uterine bleeding are diagnosed with endometrial cancer. In the initial stages, this disease can be successfully treated. Having applied too late, women are faced with the need to remove the uterus and appendages. Thus, the earlier therapy is started, the greater the chance of saving organs.
Consequences
Bleeding from the uterine cavity can lead to various complications. One of the dangerous ones is posthemorrhagic anemia or hemorrhagic shock. This occurs with heavy discharge.
Read more How menopause is expressed in men
Infection of the body in an ascending manner also often occurs. As a result, secondary complications develop in the form of purulent myometritis or the formation of pus on myomatous nodes.
If fibroids are not detected in a timely manner, the woman experiences severe pain in the abdominal area and bloody discharge. Symptoms are caused by the rejection of the fibromatous node and its release into the uterine cavity. The complication is dangerous and requires surgical removal.
Bleeding that is atypical in nature should alert a woman during any period of menopause. It is important to immediately contact a gynecologist to prevent the development of complications.
Uterine bleeding (menometrorrhagia) is bleeding from the uterus not associated with menstruation and physiological blood loss after childbirth. In old age, menometrorrhagia may indicate the presence of a serious disease, so it is important to recognize bleeding in time and take measures to stop it.
Older women experience bleeding during menopause and menopause. During this period, women need to be more attentive to their body and be able to independently distinguish menometrorrhagia from menstruation. Stopping bleeding and treating the cause can only be done by a doctor; home treatment is unacceptable.
Source: https://g-women.ru/klimaks/krovotechenie-u-zhenshchin-posle-60-let.html
Consequences
Do not underestimate the danger of bleeding after 60 years. A careless attitude towards your health can cause death, regardless of what caused the bleeding.
Pathology leads to the following complications:
- hemorrhagic shock;
- anemia;
- hemorrhagic syndrome;
- ascending infection is the cause of purulent inflammation and other diseases;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen.
A common cause of bloody particles is uterine fibroids. In its advanced state, this tumor causes pain. You should not wait until the pathology begins to threaten your life. For uterine bleeding, you should not use any folk remedies. The pathologies that usually cause the appearance of blood cannot be eliminated by using infusions, decoctions and lotions. Only the help of doctors will help maintain health. If you can drink some kind of tincture, the gynecologist will tell you about it.
Among the serious consequences of bleeding is the degeneration of benign tumors. If treatment is delayed, the process may spread to other organs, and then even removal of the uterus and appendages will not help.
Postmenopause is a period when you need to treat your health very carefully and responsibly. By monitoring atypical phenomena and deviations from normal well-being, a woman is doing the right thing. It’s better to spend a little time and go to an appointment: even if it turns out that there are no serious illnesses, the doctor will give recommendations on how to improve your well-being.
Symptoms and causes of bleeding from the uterus in old age
Uterine bleeding (menometrorrhagia) is bleeding from the uterus not associated with menstruation and physiological blood loss after childbirth. In old age, menometrorrhagia may indicate the presence of a serious disease, so it is important to recognize bleeding in time and take measures to stop it.
Older women experience bleeding during menopause and menopause. During this period, women need to be more attentive to their body and be able to independently distinguish menometrorrhagia from menstruation. Stopping bleeding and treating the cause can only be done by a doctor; home treatment is unacceptable.
Symptoms of uterine bleeding
At a young age, women have menstruation at regular intervals, so the sudden appearance of blood is always alarming. In old age, the situation is more complicated: since menstruation is irregular, women often mistake bleeding from the uterus for it. The following symptoms may indicate menometrorrhagia:
- Copious discharge with clots;
- Menstruation for more than a week;
- Decreased blood pressure;
- Weakness and dizziness;
- Pale skin.
With menometrorrhagia, the cervix bleeds profusely; within an hour, a pad or tampon can be completely filled. There are a large number of clots in the blood. Heavy bleeding forces you to wake up at night and change pads. General health deteriorates significantly, weakness is felt, dizziness appears. Large blood loss leads to a decrease in blood pressure, and signs of anemia appear.
If you experience weakness, dizziness, pain in the lower abdomen, and there is no bloody discharge with clots, internal bleeding is possible. This situation requires immediate hospitalization. It is necessary to urgently call an ambulance and remain calm until it arrives.
If you have at least one symptom of bleeding from the cervix, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible and get tested to confirm the diagnosis. Home treatment using folk remedies may not give the desired effect and may worsen the situation. Moreover, stopping the bleeding does not at all indicate the elimination of the cause, which may be a serious illness.
Why does the uterus bleed in old age?
In women aged 45-55 years, bleeding from the cervix is associated with irregular release of hormones, disruption of the ovulation cycle, development of the corpus luteum, and folliculogenesis.
Spontaneous bleeding indicates a decline in ovarian function during menopause. In addition to hormonal imbalances, bleeding can be caused by diseases of the genital organs. Common causes of menometrorrhagia in old age are:
- Uterine fibroids;
- Endometriosis;
- Uterine polyps;
- Malignant neoplasms of the genital organs.
Cervical fibroids occur as a result of active division of uterine cells, leading to the formation of a benign tumor from muscle tissue. Active cell division is stimulated by increased secretion of estrogen. The reasons for the development of fibroids are stress, numerous abortions, infertility, hereditary predisposition, diabetes and obesity.
Bloody discharge after 60 years: causes of uterine bleeding in old age
Bleeding after 60 years in women is considered a reason for mandatory consultation with a doctor, although this may not be seriously dangerous. Minimal disturbances in female reproductive functions at the time of menopause are easily treated and disappear without a trace.
But sometimes bleeding after menopause indicates the presence of serious diseases that develop in the endometrium of the uterus until the appearance of tumors.
Causes of bleeding after 60 years
In reality, bleeding in postmenopause should disappear, since this period is the end of all female reproductive functions. At this time, bruising with menstruation stops completely, the endometrial mucosa in the uterus becomes thinner, the ovaries become smaller, follicles do not appear and pregnancy becomes impossible.
It seems that during this period there is a lull in the female body, and you don’t have to worry about the condition of your organs.
But this is far from true; often it is during menopause that problems arise that make women worry and seek qualified help. Discharges that appear during menopause containing blood are almost always associated with pathological causes. The most common of them, which cause bleeding after 60 years, are the following:
- treatment with hormonal drugs;
- infectious processes;
- chronic diseases in the reproductive organs;
- damage to the endometrial mucosa;
- the appearance of a polyp;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- myoma;
- malignant neoplasms.
The appearance of blood in mucus in women of reproductive age is a natural phenomenon that occurs along with menstruation. This happens due to the separation of the mucous layer in the endometrium when there was no conception, and the body suffers damage to small blood vessels, which leads to the appearance of blood in the uterine secretions.
Since these processes are not performed during menopause, the endometrial layer intended for the development of pregnancy no longer grows or separates. Sex hormones, which are actively involved in cyclical processes, are also no longer created by the body, which is the cause of menopause.
During menopause, mucous discharge becomes sporadic and vaginal dryness, which accompanies changes in the body at this time, is a natural phenomenon.
Due to the changes that occur in the reproductive system, there should be no blood loss during menopause. And not only strong ones, manifested in the form of menstruation, even streaks of blood in the mucus at this age should alert you and serve as a reason to perform an examination.
We recommend: How is kraurosis treated in women after 60 years of age?
Degree of discharge during menopause
Bleeding after menopause is not always an indicator of diseases that occur in the reproductive system. Some blood is released from the urethra, urinary tract or intestines. During menopause, a normal imbalance with a minimal supply of necessary hormones causes the appearance of pathological processes in these organs.
To understand gynecological problems, you can use a tampon by placing it in the vagina. If after some time it remains clean, then the reason for such manifestations must be sought elsewhere.
What does the degree of discharge during menopause indicate?
Despite the fact that many women at this time experience vaginal dryness, which causes discomfort, the cervix still continues to synthesize mucus in small quantities.
If it is of the usual color and normal consistency and does not cause discomfort, then its manifestation is also considered normal. But if there is blood in them, then this signals a pathological process that has developed in the body.
Blood streaks can be provoked by hormonal medications that are used to treat any diseases or severe syndromes that accompany menopause. In these situations, the doctor often prescribes hormones to alleviate menopausal syndrome.
Despite such situations, hormonal drugs can affect the body in different ways. Estrogen saturation can cause endometrial growth and minimal blood flow. By stopping the drug, you can quickly get rid of the problem situation.
The brown color of the discharge may be the cause of oxidative processes, since the cervical canal narrows during menopause, the discharge from the uterus cannot leave quickly and oxidizes. In such situations, the doctor will successfully select the necessary medications to correct the body’s hormonal levels.
At the time of menopause, when washing, you may notice that the vagina bleeds a little, which is a sign of mechanical injury to the mucous membrane. As soon as the hormones necessary to maintain reproductive functions cease to be released, the mucous membrane becomes thin and vulnerable, which leads to damage during hygiene procedures.
The same uncharacteristic discharge is possible after sex or during an examination by a gynecologist. This cannot be ignored, since damage to the cervix can cause cancer. It is much worse if blood streaks appear due to the formation of cervical erosion.
We recommend: What diseases are common in women after 60 years of age?
Diseases that can affect menopause
Diseases caused by various infections appear during menopause and do not always depend on sexual life, which may not exist at all. The reason for their appearance is a violation of the vaginal microflora, in which, due to a decrease in local immunity, the defenses cannot protect the body from attack by microorganisms.
Often, when previously unusual discharge occurs, bacteria appear on the vaginal mucosa, causing gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and bacterial vaginitis. For example, ordinary thrush or vaginitis, in addition to cheesy white discharge, manifests itself as mucus and blood.
One of the reasons for such phenomena may be a polyp in the cervix or on the endometrial mucosa. Hormonal imbalance, provoked by the decline of ovarian function, causes the lining of the uterus to grow or the appearance of elevations in its cavity, which leads to the formation of polyps.
Mucous discharge with blood streaks can be observed during vigorous exercise or when separated from the mucous membrane under one’s body weight.
The cause of bleeding in women after 60 years of age may be fibroids, which are a benign neoplasm. Despite the fact that the menopause period causes its decrease, sometimes at this age it manifests its activity in the form of previously unusual discharge.
Their manifestation is especially caused by taking hormonal drugs that help eliminate menopausal syndrome, or taking natural hormones.
Often during menopause, cell growth occurs in the uterine cavity - hyperplasia. This is a growth of cells that is benign in nature, but can sometimes turn into a malignant state. Almost always, such cases provoke severe bleeding from the uterus, in which blood clots and tissue particles from the uterine epithelium are observed.
If this disease existed before the onset of menopause, then when it occurs, the disease subsides and is not acute. But the changes that occur in the body at this time may be one of the reasons for the increase in activity and cause an exacerbation.
What can be done if bleeding occurs?
The first thing that needs to be done in this situation is to identify the source that provoked the bleeding and the reason that led to such manifestations. How successfully one can get rid of it depends on timely and competently performed diagnosis. The most commonly used method is curettage as a diagnostic method.
There is also a possibility that after curettage, the mucus secretion goes away forever, since such methods have a therapeutic effect. Women who have reached 60 years of age will benefit from taking medications based on androgens that suppress sexual function. To get rid of the general menopausal syndrome, simple sedatives are used.
In addition to treatment performed against the main disease, the doctor needs to pay attention to methods aimed at improving the health of the body. To do this, you need to include vegetables, fruits and dairy products in your diet.
To prevent the unpleasant effects of menopause and accompanying changes in the bones, you need to do therapeutic exercises. An active lifestyle and a positive attitude will prolong the feeling of youth and live the menopause period with dignity.
We recommend: How to protect older people from coronavirus?
What discharge is likely during menopause?
Age-related changes in hormonal levels lead to the fact that with the onset of menopause, a woman develops specific diseases related to disruption of the functioning of various organs. In particular, the uterus and ovaries become smaller, and the synthesis of mucus in the cervix decreases.
Because of this, the volume of normal discharge during menopause decreases. But due to vaginal dryness, the risk of inflammatory diseases and tumors increases. Pathological discharge is likely. You need to pay attention to the change in their character during menopause.
Normal discharge
Vaginal discharge in a woman of any age is considered an indicator of reproductive health. The decline of the reproductive function of the body affects the formation of mucus in the cervix.
It continues to play a protective role, preventing infectious agents from entering the organs. But its volume becomes smaller, to the point that at this time women develop vaginal dryness.
It is believed that during menopause, mucous discharge is considered normal if its amount is no more than 2 ml per day, it is transparent, but may have a slight yellow tint due to the oxidation of mucus in the air. Moreover, they should not have a strong odor.
The discharge contains not only mucus, but also plasma and lymph, so its consistency resembles rice water. Normal discharge during menopause does not cause discomfort or irritation of the genital organs in women.
Physiological features of the menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a complex mechanism where there is a direct and inverse relationship between levels of regulation. For a simpler understanding, this mechanism can be compared to a five-story building, where each floor interacts with the floor below and above. None of these floors are capable of functioning independently.
Table No. 1. Interaction of “floors” of the menstrual cycle.
The ovaries, just like the uterus, are subject to the influence of other levels of regulation located higher.
- FGS (follicle stimulating hormone). This hormone is responsible for the mechanism of follicle maturation in the ovaries.
- LH (luteinizing). The peak production of this hormone provokes ovulation, which means the release of an egg from the ovaries.
Note. Uterine bleeding is one of the most common symptoms with which a woman consults a doctor. This symptom can appear both in very young representatives of the fairer sex, and in women who have been in menopause for more than 20 years.
There can be many reasons for the appearance of such a dangerous symptom, so treatment is aimed at identifying the root cause, and then eliminating the symptom itself.
Sometimes in women during menopause, bleeding is not a serious reason to sound the alarm, as minor changes in reproductive function can contribute to it. Such bleeding is easily amenable to conservative therapy and disappears completely in a short time.
Classification of uterine bleeding
Abnormal bleeding is classified by doctors using many criteria.
These include:
The following are distinguished by origin:
- uterine;
- ovarian;
- iatrogenic;
- dysfunctional.
At the same time, dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB) is divided according to the nature of cyclicity disorders.
The classification of uterine bleeding depends on numerous criteria: age, frequency, abundance.
Table No. 2. Classification of dysfunctional uterine bleeding:
Blood loss from the uterus can be diagnosed in women of any age, and they have their own characteristics.
Taking these criteria into account, we distinguish:
- Juvenile bleeding. It is observed in girls under 18 years of age.
- Reproductive. Appears in women aged 18 years and before menopause.
- Peri- and postmenopause. During this period, as a rule, dysfunctional MVs appear, which is caused by a disorder of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis.
Attention. The risk of bleeding in older women is due to the risk of developing malignant tumors. Indeed, during menopause, the monthly cycle completely stops, and the appearance of blood discharge in frequent cases indicates the development of some serious pathology.
Etiology of uterine bleeding
The appearance of bloody discharge in older women almost always means danger, since it is often a sign of the development of cancer. If a problem arises, you should immediately sound the alarm; frivolity can lead to the most unpredictable consequences.
Abnormal bleeding from the uterus can be called any physiological blood discharge that appears regardless of the regularity of the menstrual cycle.
Gynecologists include abnormal discharge:
- if their duration is 7 or more days;
- blood loss volume is more than 80 ml per day;
- the time period between bleeding is less than 21 days (menstrual cycle).
Bleeding from the uterus can be called abnormal if it occurs outside the periodicity of the menstrual cycle.
For a complete and accurate diagnosis of an anomaly, doctors take into account such indicators as frequency, regularity or irregularity of occurrence, volume of blood loss, duration, relationship with reproductive age and hormonal levels.
The causes of blood loss can be divided into 2 groups:
- Associated with reproductive diseases.
- Associated with systemic disorders.
As for bleeding associated with systemic disorders, in this case the provoking factors are:
- blood diseases with thrombocytopenia;
- bleeding disorders;
- vascular pathologies;
- numerous infectious diseases.
Reproductive diseases that cause bleeding from the uterus are varied. These can be inflammatory, atrophic and hypertrophic changes in the uterus and genital organs. Hormonal imbalances also often cause bleeding.
Pathological conditions in older women are caused by the following diseases:
- uterine fibroids (leiomyoma, fibromyoma);
- polyps;
- endometriosis;
- ovulatory dysfunction;
- iatrogenic MK;
- endometrial cancer;
- IUD standing in the uterus for a long time;
- cervical diseases;
- tumor formations;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- endometrial hyperplasia.
Attention. The main difference between bleeding from the uterus in women in old age is the risk of developing cancer.
During menopause, a reproductive lull occurs in the female body.
During menopause, a woman should no longer experience any bleeding from the uterus, since all reproductive processes stop. During this period, all processes of the menstrual cycle stop.
Pregnancy is impossible in this case, since the endometrial mucosa of the uterus becomes thin, the ovaries become smaller, sex hormones are not produced, and the process of follicle formation stops. But menopause does not always become a lull for the female body; spotting in old age makes you worry and seek help from doctors, because urinary tract always means a pathological condition.
Important. Even the slightest discharge containing droplets of blood is considered a pathology.
Myoma
A benign tumor appears in the muscle layer of the uterus (myometrium) - this is a fibroid. Among all requests from patients over 50 years of age, fibroids are diagnosed in 80%.
During reproductive age, fibroids may not show any signs of themselves, and with the cessation of the menstrual cycle, a woman notices the appearance of bloody discharge.
Treatment of fibroids is carried out only by surgical removal of tumors.
The growth of a benign tumor is influenced by sex hormones, therefore, with the onset of menopause and the cessation of the production of these hormones, fibroids stop their development. If there is further growth of the tumor, pain and frequent bleeding, this may indicate the development of a malignant tumor.
Attention. Patients with large fibroids during menopause are offered to undergo treatment based on surgical removal of the tumor. Sometimes a decision is made to remove the uterus completely, depending on the size of the fibroids.
The reasons for the development of fibroids are as follows:
Polyps
A polyp is a kind of convex thickening that has a glandular or fibrous structure. Formed in a specific area of the genital organ. The formation of polyps is accompanied by bleeding from the uterus.
If a woman is of reproductive age, she takes this bleeding as a normal menstrual cycle, however, it has a longer duration (7 or more days). In this case, polyps cause severe pain, especially disturbing during sexual intercourse.
In such situations, the doctor prescribes radical treatment based on surgical removal of the tumors.
In medicine, there are 2 types of polyps – glandular and fibrous.
Ultrasound examination allows diagnosing polyps. Therefore, a woman during menopause should visit a gynecologist at least 2 times a year and undergo a full diagnosis.
Discharge in women after 50-55 years
A woman’s natural desire is to always be beautiful and attractive. But with age, this desire becomes more and more difficult to combine with reality. After all, no one has yet managed to avoid the age-related changes that inexorably occur after 40 years.
However, you can have an attractive appearance, despite the natural processes of gradual aging. To do this, it is important for a woman to first monitor her health.
In particular, elastic skin, muscle tone, energy and overall well-being largely depend on the production of female sex hormones. After forty, hormonal levels begin to decrease significantly, and the processes that accompany menopause begin.
And at the age of 50-55, menopause occurs, which leaves a noticeable mark on the appearance and well-being of mature beauties.
These processes cannot be changed. But, at the same time, approaching adulthood, a woman should pay more attention to herself, her appearance and health. It is important to choose the right cosmetics, undergo anti-aging procedures, eat right, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
And most importantly, you should pay special attention to your health. In particular, you should pay attention to all changes that are associated with the functioning of the female genitourinary system and endocrine glands. If you notice discharge in the middle of your cycle at the age of 50, its nature is previously unknown to the woman, you should know what this could mean.
Many ladies often do not pay any attention to the appearance of discharge. It’s easier to write off new symptoms as another manifestation of menopause. In fact, experienced doctors and gynecologists strongly recommend not to joke with your health.
At the age of 50, you should leave unnecessary embarrassment aside and, at the first warning signs, you should go to see your gynecologist.
It is the specialist’s job to determine the seriousness of the situation, and the woman just needs to notice the changes in time and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Normal discharge
Representatives of the fairer sex do not always understand why they need to visit a gynecologist regularly, especially when there is no pain. Short-term discharge is not always paid attention to. Based on medical practice, this frivolity often has a number of serious consequences that could have been avoided.
[ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1]
In a woman, the presence of discharge at 50 years old may be due to the fact that menopause has not yet occurred. In this case, natural renewal of the walls of the cervix and ovaries can still occur, at which time the old layers of the endometrium are rejected.
As a result, regular periods are observed. But during menopause, the periodicity of discharge changes, menstruation can occur once every 2-4 months, it can be more abundant or, conversely, scanty. After 55 years, women may have discharge of a different nature.
For example, neoplasms such as:
- Pus lumps or mucus
- White copious mucus
- curdled lumps,
- Bloody discharge.
Women should pay equal attention to spotting and heavy discharge. Often they can be signals of the development of diseases of the genitourinary system, hormonal imbalance, or infection.
But at the same time, such discharge is mainly accompanied by an unpleasant odor, itching, a feeling of discomfort or pain.
Timely consultation with a doctor will allow you to defeat the disease in the early stages.
But you shouldn’t attribute every appearance of formations after fifty to a serious illness, get scared, and panic. At this age, due to changes in hormonal levels, a change in the nature of menstruation may be observed. They can be weak or intense, with rich bloody formations or, on the contrary, weakly intense.
It is best to visit your gynecologist in the initial stages of menopause. He will be able to tell a woman with discharge whether this is normal, what the further development of the picture may be, what medications can relieve the discomfort.
Usually, a doctor can clearly explain what is considered normal after 50 years in women, and what is a pathology.
It is better to visit a gynecologist on your own, rather than using recommendations given to a friend or colleague. After all, the gynecologist makes prescriptions based on the characteristics of each patient separately. This takes into account factors such as:
- Body weight, excess weight,
- General health
- The presence of chronic diseases,
- Tendency to allergic reactions,
- Lifestyle, bad habits,
- Previously suffered diseases (surgeries), including on the female part,
- The nature of menstruation during life, the peculiarities of the cycle, etc.
Therefore, for correct diagnosis, you should not use the advice of “women’s radio”, but be guided by the recommendations of specialists issued after a direct examination of the patient.
Types of pathological discharge
It is very important to maintain women's health to be attentive to all processes that occur in the body. In particular, you should notice new symptoms, formations, sensations that did not appear before.
There are cases when women, noticing bleeding at the age of 50, attributed it to the fact that menopause had not yet ended.
At the same time, the cutting pain in the lower abdomen, difficulty urinating, and general malaise were ignored by the ladies, silently enduring the torment. However, such symptoms can be clear signals of the development of pathologies.
After all, menopause itself is a natural process. And in most cases, it does not cause significant painful sensations.
If dirty green discharge is observed in women aged 55, this is a sure sign of the development of pathological processes. Such formations are called purulent and generally have a strong, unpleasant odor. Can be caused by diseases such as:
- Vaginitis,
- Chlamydia,
- Gonorrhea, etc.
Dark brown discharge can often be observed in women after 50 years of age. If you notice such marks on your underwear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Since the brown color of the formations is a signal of the development of pathologies in the internal genital organs.
This may be a signal of the development of polyps in the uterus. In this case, at 50 years of age, the discharge consists of thickened blood and mucus.
A brown color may be observed with the development of vaginal dryness, which is common at this age, or with the development of endometrial atrophy on the walls of the uterus.
A symptom of uterine fibroids is usually heavy bleeding. If they are detected, you cannot postpone a visit to the gynecologist. The sooner the body is examined and tests are done, the higher the likelihood of successful treatment.
In any case, an adult woman should know that there are no non-serious diseases. Any deviation from the norm must be promptly corrected. Negligent attitude towards one's own health is the main factor in the high mortality rate of women from diseases of the mammary glands and genitourinary system.
[ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1]
Causes of discharge
There are many reasons that can trigger the appearance of normal and abnormal fluids that are released during the day.
First of all, their appearance is influenced by significant changes in hormonal levels during menopause. At this time, there is an intensive stage of preparing the body for menopause, and the reproductive function of the body is completed.
Hormones are released in smaller quantities, which disrupts the functioning of internal organs and systems.
The reasons for the release of purulent mucus or a bloody substance may also lie in the contact of bacteria with the mucous membranes of the female genital organs and the development of infection.
However, you should know that any woman can develop an infection, even with careful adherence to hygiene rules.
Although, during menopause, it is recommended to increase self-care, use medicinal herbs while bathing, and keep your clothes clean.
Discharges often appear with the development of inflammatory processes in the internal genital organs. The cervix and ovaries are very susceptible to the slightest internal and external negative influences. Even basic hypothermia can lead to the development of many diseases.
With the development of sexually transmitted infections in women, noticeable symptoms also appear, such as:
- Increased body temperature
- Cutting pain in the lower abdomen, in the back (lower back),
- Difficulty and painful urination,
- General weakness, nausea.
In case of these phenomena, you should not drink painkillers randomly. The best way out is to immediately make an appointment with a gynecologist.
Signs of pathological discharge
Every woman who closely monitors her health can determine the presence of pathological processes in the body. First of all, you should be alarmed if the discharge at 50 years old smells bad, with a pungent odor. The smell is often compared to hydrogen sulfide, missing eggs, and fish.
You should also be concerned about bleeding at the age of 50, which does not have the character of regular menstruation. This may be a signal of damage to the walls of the internal genital organs, the development of fibroids, cervical cancer and other serious diseases.
Women often ask why there is foul discharge at 55, if all hygiene rules are strictly followed. To which doctors claim that these are clear signs of pathological processes. Often it is the smell that does not give a woman the opportunity to ignore the problem.
Diagnosis of discharge
Normally, there should not be a trace of blood between periods. If bleeding begins, you should consult a doctor. Many serious diseases associated with problems of the female genital organs begin with similar symptoms.
An experienced gynecologist will be able to assess the situation during the examination, take the necessary smears and material for laboratory tests. After receiving the results of the treatment, it will be possible to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Treatment and prevention of discharge
Treatment is always determined individually. But first of all, the doctor will strive to normalize the woman’s hormonal levels and strengthen her immunity.
At an appointment with a gynecologist, the patient can ask all questions about the prescribed treatment. It is also advisable to learn about the possible consequences, precautions and other issues to watch out for during menopause.