Normally, a woman's menstrual cycle lasts 21-35 days - from the first day of one menstruation to the first day of the next. But sometimes the cycle gets shorter or longer. We will explain why this happens in the article.
Important!
We will consider the shortening and lengthening of the menstrual cycle relative to the individual norm. For example, if a woman’s cycle lasted 28 days, and then suddenly became 22 or 34, you need to look for the cause of this condition. A deviation of 2-3 days is considered normal, it occurs even in completely healthy women against the background of stress, overwork, colds and does not require treatment.
What can cause a disruption in the hormonal system?
Menstruation is a natural cycle of changing the concentration of sex hormones in the female body for the full maturation of the egg in the follicle for the purpose of subsequent conception. It lasts on average 21 - 22 days from the first day of menstruation until the first day of the next cycle. But, depending on the individual characteristics of the body, it can extend to 28 - 31 days, and this is also considered the normal limit.
The main reasons include:
- One of the most common reasons for visiting a doctor with a complaint that the monthly cycle has lengthened is taking combined oral contraceptives as prescribed by a doctor. It is important to understand that this is not necessarily the start of taking it; very often the reason is either changing one drug to another, or refusing to take it. Any change is almost 100% likely to lead to a disruption of the menstrual cycle. It should also be taken into account that oral contraceptives are taken not only for the purpose of protection, but also as a therapeutic technique for the treatment of many diseases.
- Age-related changes in the premenopausal period. In women after 50 - 55 years, a period of so-called premenopause begins, when the body begins to prepare for the involution of the reproductive system, the concentration of progesterone in the blood decreases, and as a result, a shift in the menstrual cycle quite often occurs.
- Infectious processes in the genitourinary system in the form of urethritis, cystitis, adnexitis and other diseases. They are predominantly caused by intracellular pathogens (chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma) or protozoa (trichomonas, amoeba).
- In addition to hormonal drugs, the failure of menstruation can also be affected by taking other pharmaceutical drugs, for example, antihypertensives, anticoagulants or antibacterial agents.
- A sharp change in climatic conditions due to flight to another zone.
- Bad habits (smoking tobacco, alcohol), weight gain.
- Prolonged nervous tension or emotional stress also very often leads to menstrual irregularities. The nervous system is so closely connected with the endocrine system that in recent years many scientists consider them as an inextricable complex of neuro-humoral interactions. Therefore, even slight stress can cause changes in hormonal levels in the body.
- Excessive physical activity can often cause hormonal imbalance, because muscle activity stimulates the production of growth hormone, testosterone and a number of other biologically active substances.
- Changes in diet, in particular low-calorie diets or limiting the intake of certain types of foods, can lead to hormonal imbalance.
Thus, the fact that the menstrual cycle has lengthened can have a wide variety of reasons and depend on many parameters. However, there is no urgent need to sound the alarm, since in most cases the source of the problem is quite trivial and can be easily corrected. However, in more complex cases (if the cycle does not recover on its own within 1 - 2 months), you should contact a gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Norm
It is especially worth considering cases where a cycle lasting forty days would be considered normal. Most often, this feature of the female body is inherited from mother to daughter. This deviation from the norm is not a pathology and does not bring any particular inconvenience to the woman.
The only thing that can become a problem is determining the onset of ovulation. Because of this, it may be difficult to plan a pregnancy. Special ovulation tests can help in this situation.
A menstrual cycle of 40 days is normal if such a deviation from the norm has already been observed in the family, and the doctor did not reveal any health problems during the examination.
In adolescents, when a cycle is established, an increase in the interval between menstruation may also be observed, but this is also considered normal. This phenomenon in girls can last up to three years from the onset of their first menstruation. But even in this case, it is necessary to consult a doctor to exclude pathologies that lead to prolongation of the cycle. Most often, doctors prescribe a progesterone test for such menstrual irregularities.
If your menstrual cycle is 35 days once or twice a year, then there is no reason to worry. You should consult a doctor if such a deviation occurs over a long period of time.
In addition to diseases related to the sexual sphere, some somatic diseases can also increase the length of the cycle. For example, some pathologies of the liver and thyroid gland.
Diagnostic examination methods
If disturbances in the hormonal system become persistent, the woman begins to wonder why the monthly cycle is lengthening, because this causes some discomfort. Therefore, it is imperative to contact a gynecologist, and if necessary, then to doctors of related specialties (since the cause is not necessarily related to the reproductive system). Examinations that will need to be completed first:
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs (uterus, ovaries, appendages, urinary tract).
- Blood test for hormone concentrations. First of all, a sample is taken for estrogen and progesterone (the doctor must first tell you in detail which day of the cycle you need to donate blood). Then, if the reason for the failure of menstruation remains unclear, a study is prescribed for other hormones - mainly thyroxine, T4 and other thyroid hormones, releasing factors, lactotropic hormone, luteinizing hormone.
- Examination by a specialist on a gynecological chair with the possibility of collecting material for sowing the pathogen.
- Referral for consultation to a related specialist (if the cause has not been identified): cardiologist, therapist, neurologist or endocrinologist.
In most cases, taking an anamnesis with a detailed questioning of the medical history and the above listed diagnostic methods allow the doctor to get an answer to the question of why the menstrual cycle has lengthened and to find out the cause of the hormonal imbalance. In exceptional cases, further examination may be indicated using highly specialized diagnostic methods, such as cytological examination, immunohistochemistry, computed tomography, and so on.
We recommend reading the article about frequent periods. From it you will learn about the reasons for frequent menstruation - hormonal imbalance, tumors, gynecological diseases, possible pregnancy, as well as the influence of stress.
Why does the menstrual cycle change from 28 days to 25 days?
Failure of the menstrual cycle is the most common reason for a woman to visit a gynecologist.
This is due to the fact that the hormonal system in women is a rather fragile thing, susceptible to external unfavorable factors, which reacts to them by changing the concentration of sex hormones in the blood.
Many women ask the question, should they immediately run to the doctor if their menstrual cycle has lengthened, or can they deal with the problem on their own?
Read in this article
Menstruation on the 22-24th day of the cycle - worry or rejoice, norms and deviations
Menstruation on days 22-24 of the cycle is considered a sign of a good female body. Deviation up or down by 3 days is allowed. In general, even a delay of a week can be justified and not always alarming.
By now, the female body has been studied so well that, it would seem, there should be no questions about the duration of the menstrual cycle.
However, some girls are concerned whether it is normal or not if menstruation begins on days 22-24.
Normal cycle length
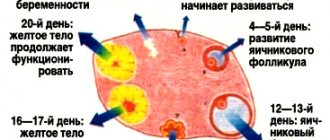
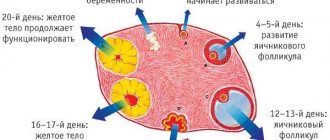
Cyclic transformations occur in the female body every month. During the first 10-15 days, he prepares for a future pregnancy; during the next 11-16 days, he tries to preserve it or tear off the unusable layer of the endometrium in order to begin a new stage. Conventionally, the cycle is divided into 2 parts. In the middle, this is 1-2 days, ovulation occurs. The egg leaves the follicle in search of sperm.
Source: https://ginekologiya-urologiya.ru/menstruaciya/pochemu-menyaetsya-tsikl-mesyachnyh-s-28-dnej-na-25-dnej
General recommendations of gynecologists for hormonal imbalance
If a shift in the menstrual cycle is detected, a woman does not need to immediately run to the doctor. Often, lengthening is caused by ordinary reasons that can be easily corrected on your own. First, you need to think and try to remember what has changed in your lifestyle recently. Analyze and try to eliminate the factor that disrupts the balance of the hormonal system.
In addition, you need to follow general recommendations for correcting your lifestyle and daily routine:
- The most important factor is to limit neuro-emotional tension as much as possible in everyday life and avoid stress as much as possible.
- Stabilize your diet, consume more natural foods high in microelements, vitamins and antioxidants. Avoid spicy, smoked and salty foods and stop drinking coffee and alcohol.
- Get plenty of rest, and spend at least 8-9 hours a day on sleep.
- If a woman is involved in sports or another type of physical activity, training should temporarily be switched to a lighter mode or even take a break so that the body gains strength.
- Limit self-administration of medications, with the exception of if they are taken as prescribed by a doctor. Consult a specialist if you suspect that hormonal imbalance is caused by treatment for another disease.
To summarize, we can say that prolongation of the menstrual cycle is not a condition that requires urgent consultation with a doctor. However, you need to be on your guard, and if symptoms do not go away or new ones appear, you should not postpone your visit to the clinic. After all, it’s better not to joke with your health, but you need to treat your body with care.
Why does the menstrual cycle change? What does it depend on?
24.10.2018
The menstrual cycle is a reproductive mechanism launched in the body of every healthy woman of fertile (childbearing age), ensuring a woman’s ability to conceive and bear a child.
The stability and regularity of this cycle affects a woman’s overall well-being, her condition, activity and mood.
How does this happen
The functioning of the menstrual cycle depends on the central nervous system and hormonal levels - the balance of sex hormones - progesterone and estrogen, the production of which is responsible for the ovaries.
Depending on the hormones produced by the ovaries, hormones of the main gland - the pituitary gland - appear, but if there are few female sex hormones, then the pituitary gland stimulates their greater production, and this also happens in the opposite case.
The pituitary gland, as part of stimulating the normal menstrual cycle (MC), acts in three directions:
- stimulates the release of the follicle, the maturation of the egg in the first half of the MC;
- stimulates the release of the egg and the production of progesterone in the future, if conception has occurred;
- promotes the production of prolactin - to provide the baby with breast milk after childbirth.
The pituitary gland is affected by the central nervous system (CNS) and its department, which corrects the functioning of the endocrine system - the hypothalamus. It is in this area that hormones that inhibit or inhibit, depending on the need, the production of gonadotropic pituitary hormones are not located and are constantly produced. At the head of the entire hierarchy is the cerebral cortex.
Ovarian cyst
Often, due to impaired maturation of the follicular component and accumulation of fluid in the cavity, a benign formation appears - a cyst.
It can often be diagnosed in fertile women. The cyst may disappear and appear on its own. The disease occurs in 70 percent of women. Ovarian cysts are classified according to the area of occurrence:
- follicular;
- corpus luteum cyst;
- paraovarian.
If the cyst does not go away within 1-2 cycles or does not disappear after childbirth in pregnant women, it must be removed surgically.
Failures in the cycle, why they happen
We can observe irregular cycles in most women. Few people can boast that their periods begin on the same day of the month. Why is this happening? The first and obvious reason: ideally, the menstrual cycle lasts 28 days.
Therefore, if your period began on January 6, then after 28 days it will begin on February 3–4, and then on March 1–2 and March 31–April 1. After all, each month has a different number of days, and the cycle can normally be delayed by 1-2 days. On average, it is expected that the cycle can be from 24 to 35 days.
For many women, their cycle changes every month.
Another reason is disorders in the woman’s body.
This includes nervous experiences, malfunction of the pituitary gland, ailments of the hormonal system, infections, inflammation, bad habits, excessive physical activity, heavy lifting, taking certain medications, blood diseases, exacerbations of chronic diseases, oncology, etc. The cycle can be affected by unsuccessful surgical interventions for gynecological problems, as well as trauma and damage to the uterus, diseases of the appendages, hypothermia.
What types of MC violations are there?
Since the mechanism of the cycle’s functioning is triggered by different parts of the body, the classification of MC disorders is based on where exactly the regulation is disrupted. Cycle failures are distinguished at levels:
- cortex and hypothalamus;
- pituitary gland;
- ovaries;
- uterus;
- thyroid gland;
- adrenal glands
If violations occur in one of the listed departments, the MC also fails. After stressful situations, severe fright or prolonged nervous tension, the pituitary gland suffers, not releasing the required amount of hormone for the cyclic maturation of the egg. There is no ovulation - no menstruation occurs either.
If the function of the hypothalamus is impaired, the ovaries may reduce estrogen production, so egg maturation will not occur within a given cycle.
Perhaps the malfunction in the MC is associated with damage to the ovaries up to their fibrosis, which results in a decrease in the number of follicles ready to create an egg during the menstrual cycle.
Follicles are formed individually during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus.
How to determine that a failure has occurred in the MC
MC disorders are divided into the complete absence of menstruation - amenorrhea and the presence of scanty discharge of a non-menstrual type at inopportune times.
Another intermediate failure is observed if the intervals between previously regularly occurring menstruation have changed, the intensity of bleeding has increased or decreased, and erratic menstruation has appeared.
The main obvious signs of failure:
- the volume of discharge changes – hyper- or hypomenorrhea;
- the period of discharge has shortened - if previously menstruation lasted for 7 days, now this period has been reduced to 3-4, for example;
- the discharge period has increased;
- The usual rhythm of menstruation has been disrupted - periods appear either twice a month, or there is a 90-day break.
Hypomenorrhea - scarcity of discharge occurs due to decreased activity of the pituitary gland and hardening of the ovaries. Menorrhagia is prolonged heavy menstruation, accompanied by pain and blood loss, lasting up to 2 weeks.
Such phenomena occur during the formation of a cycle in adolescence and during hormonal decline in the premenopausal period.
At fertile age, such disruptions occur from chronic diseases of the uterus, fibroids and the presence of polyps.
Any cycle disturbances require attention and timely consultation with your gynecologist.
Source: https://wmedik.ru/zabolevaniya/pochemu-menyaetsya-cikl-mesyachnyx.html
Why the menstrual cycle has lengthened: reasons for the failure
Regular cyclical changes that occur monthly in a woman’s body indicate the health of the reproductive system. Sometimes there are malfunctions in it: prolonged menstruation is observed. A woman notices that her menstrual cycle has increased. The reasons for such violations are varied. They often indicate the onset of a pathological process.
Causes of cycle disruption
Among the main reasons why irregular menstruation and a long cycle are observed are the following:
- taking oral contraception. A process in which the cycle increases monthly can be triggered by both the beginning of the use of contraceptive drugs and their replacement;
- changes in hormonal levels during menopause;
- infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- taking antibiotic, antihypertensive, hormonal medications and anticoagulants;
- changes in climatic conditions;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- following a strict diet;
- excessive physical activity;
- chronic inflammation of the reproductive system.
Under the influence of these factors, the cycle lengthens. Often, painful, heavy menstruation appears against the background of systematic delays.
Why does the cycle lengthen?
An increase in the duration of the menstrual cycle may be associated with the following conditions:
- Pregnancy . The first thing that should be excluded is a woman of reproductive age who is sexually active - even if she uses contraceptives or condoms. If menstruation is delayed by more than three days, you first need to take a pregnancy test, and then look for other reasons.
- Climax . As it approaches, menstruation may come rarely - once every two to three months. Sometimes the interval reaches six months. If there are no periods for 12 months, they speak of menopause.
- Ovarian cyst . Functional ovarian cysts (follicular and luteal) often delay menstruation by several days or even weeks. After a delay, periods come heavy and prolonged, often turning into uterine bleeding.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome . With PCOS, menstruation comes rarely and becomes scanty. Sometimes there are no periods for six months or more.
- Stress . Any negative situation affects the course of the menstrual cycle, inhibits the maturation of follicles and delays menstruation.
- Somatic diseases . A previous cold, exacerbation of gastritis, bronchitis or inflammation of the kidneys - the disease interferes with the normal course of the cycle and lengthens it.
Uterine fibroids, endometriosis and endometrial hyperplasia usually do not affect the length of the menstrual cycle. These diseases change the nature of menstruation - making them heavy, prolonged and painful, but they usually come regularly. If menstruation has lengthened due to fibroids or endometriosis, you need to look for another reason.
Phases of the menstrual cycle
There are several phases of the menstrual cycle. In some of them mucus begins to be produced, and at a certain period menstruation appears.
As a result of hormonal imbalance, changes occur in the body; phases may become longer.
Follicular
This stage begins at the moment when spotting (menstruation) appears. At the same time, a follicle develops in the ovaries, which is a kind of sac from which a fertilized egg will be released after a certain period.
The phase ends at the time of ovulation. If the cycle is disrupted and there is insufficient estrogen production, the period may be longer than usual. Sometimes the ovulation process does not occur at all.
Ovulatory
The cyclical nature of changes in the female body is normal. After the end of menstrual bleeding and the follicular phase, the uterus is ready to receive a fertilized egg. The moment the fertilized egg leaves the follicle, the process of ovulation begins.
The duration of ovulation is only 1–2 days. At this moment the chances of getting pregnant are greatest.
Luteal
This is the last phase, during which a corpus luteum begins to form in the appendages in place of the released fertilized egg. The process begins immediately after ovulation is completed. The duration of the period varies from 10 to 14 days.
At this moment, progesterone begins to be intensively produced, which is necessary for successful implantation of the egg and the normal course of pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, then under the influence of hormones the endometrium begins to gradually be rejected. Minor discomfort may occur. Severe pain indicates problems with the reproductive system.
Why does the cycle get shorter?
Practice shows that shortening the menstrual cycle is less common than lengthening it. Here's what it could be:
- Climax . At 40-50 years old, first of all, you should think about age-related changes in the body. During this period, the level of sex hormones gradually decreases. Menstruation comes more often or less frequently, its volume changes - it decreases or increases. At the same time, there may be other symptoms of early menopause: hot flashes, sudden mood swings, insomnia, increased blood pressure, etc.
- Luteal phase deficiency . By this term, doctors understand a condition in which the second phase of the cycle (after ovulation) becomes short - less than 12 days. NFL is often accompanied by miscarriage because the thickness of the endometrium is insufficient for fetal development.
Sometimes women mistake uterine bleeding for premature menstruation. They assume that your period came ahead of schedule - but in fact, this spotting has nothing to do with the normal cycle. They, as a rule, differ in the volume and duration of discharge - they can be longer or shorter, scanty or abundant. Bleeding can be caused by fibroids, endometriosis, polyp, ovarian cyst, interrupted pregnancy and many other conditions.
Pathological disorders
The reasons for a long menstrual cycle may lie in pathological processes occurring in the body. Among the main ones, the following stand out:
- ovarian pathology;
- disruption of communication between the pituitary gland and hypothalamus;
- malfunction of the adrenal glands;
- polyps on the endometrium;
- myoma;
- inflammatory processes in the reproductive organ;
- malignant formations in the genitourinary system;
- complications after curettage, abortion;
- disruption of the blood clotting process.
Treatment and prevention
It is extremely important to immediately find out why your menstrual cycle is shifting. The tactics of therapy directly depend on the reason that led to such changes. If they are observed as a result of taking oral contraceptives, then the contraceptive is canceled or replaced
Hormone levels are normalized with the help of hormonal medications. If the inflammatory process begins, antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. When tumors grow in the organ cavity, they resort to surgical intervention.
In order to prevent cyclic disorders, a woman should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Do not have a promiscuous sex life and avoid casual relationships.
- Follow the rules of intimate hygiene.
- Be systematically examined by a gynecologist.
- Do not resort to uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives.
- If uncharacteristic symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately.
Complications
Depending on the reasons for the lengthening of the menstrual cycle, different complications develop. As a result of such changes, ovulation is often absent for a long time, which in turn leads to infertility.
If such disorders provoke inflammatory diseases of the uterus, then there is a risk of accumulation of pus in the organ cavity. Often the development of these pathologies leads to bleeding. In this case, the woman needs urgent hospitalization. Self-medication can be fatal.