Timely diagnosis of pathologies of the female reproductive system allows you to prescribe effective treatment and reduce the risk of infertility and other serious complications. Already in the early stages of the disease, characteristic changes in the structure of organs are possible, as shown by MRI of the uterus and ovaries. Magnetic resonance imaging is used to visualize the state of internal structures. The method does not require invasive manipulations, with the exception of intravenous injection during contrast-enhanced scanning.
Developmental anomaly (unicornuate uterus) on an MRI image (yellow arrows indicate the only developed Müllerian duct, white arrows indicate a rudiment without its own cavity)
During the scanning process, the area of interest comes under the influence of a directed electromagnetic pulse, which causes vibrations of charged particles in water molecules. The resonance of hydrogen atoms ensures that a stable signal is obtained from the tissues being studied. The intensity of the reaction directly depends on the amount of liquid in the structures under consideration. The study of soft tissue formations is more reliable compared to MRI imaging of bones and cartilage.
Indications for MRI of the pelvis
- suspicion of tumor and metastases in the pelvic organs;
- anomalies in the formation of organs in this area;
- suspicion of acute surgical pathologies, such as cyst rupture or ovarian apoplexy;
- various injuries of the pelvic organs;
- endometriosis;
- constant pain in the sacrum and pelvis of unknown origin;
- inflammatory pathologies such as adnexitis or endometritis in women and vesiculitis or prostatitis in men;
- suspicion of rectal disease;
- the likelihood of developing ovarian cysts;
- vaginal bleeding of unknown origin;
- infertility that has no objective reasons;
- tumor formations in the scrotum area.
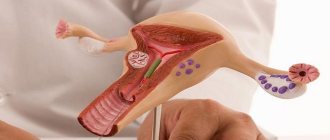
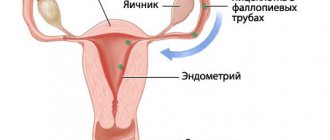
Anatomy of the uterus and ovary
In women, the pelvic area contains the organs of the genitourinary and reproductive systems. The latter includes:
- uterus;
- ovaries;
- fallopian tubes;
- vagina.
The uterus is a pear-shaped muscular organ located behind the bladder in the middle part of the pelvic region. The wide base is directed upward, the lower segment narrows and turns into a neck protruding into the vagina. The proximal part (body of the uterus) communicates with the fallopian tubes, which ensure the advancement of the egg.
The walls of the organ consist of serous, muscular and mucous membranes, and in the isthmus zone there is fiber. The inner surface of the uterus is represented by glandular columnar epithelium, the cyclic changes of which lead to monthly detachment of the functional layer and concomitant menstrual bleeding. Endometrial restoration occurs due to basal cells.
Photo MRI of the uterus, coronal plane
The muscle layer consists of smooth muscle. The cells are arranged in three layers, the thickness of the myometrium reaches 2.5 cm. Some of the muscle fibers in the area of the uterine horns pass to the fallopian tubes.
Outside, the body and posterior surface of the organ are covered with a serous membrane, which is a continuation of the peritoneum. There are vesicouterine recess and pouch of Douglas. At the edges, the serous membrane doubles and passes into broad ligaments, where nerve plexuses and blood vessels are located.
The cervix (vaginal part) has a convex shape, in the center there is a slit-like or round opening of the cervical canal. The upper section of the anatomical formation is represented by smooth muscle fibers, the lower section consists of fibrous connective tissue. The mucous membrane lining the cervical canal (endocervix) consists of columnar glandular epithelium.
The ovaries are paired formations located in the lateral sections of the small pelvis. The size of the organ changes throughout a woman's life. The formation is attached with the help of two main ligaments, one of which suspends the ovary, the second connects it to the uterus.
A series of MRI images of the pelvic organs
In the mesenteric folds of the fallopian tube there is an appendage - a round yellowish body (vestigial organ).
There are characteristic scars on the surface of the ovary, indicating the physiological processes of ovulation. The outer shell is a thin layer of epithelium, under which there is a dense connective tissue stroma. The ovarian cortex is located on the periphery of the parenchyma. Here follicles form and begin to mature, in one of which an egg develops. The inner layer of parenchyma (medullary substance) has a loose structure and contains blood and lymphatic vessels.
The mature dominant follicle bursts, the egg enters the uterine cavity through the fallopian tubes. In the case of fertilization, the zygote attaches to the endometrium, and embryo development begins.
Is magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvis safe?
MRI is absolutely harmless for any category of patients.
The exception is pregnant women: during this period it is better to refuse to conduct a study with contrast, and in the first trimester - to refrain from MRI at all. Equipment for magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetom Aera MRI scanner (1.5 Tesla)
- Expert level research
- Exceptionally high image quality
- Comfortable conditions for patients with limited mobility
- Maximum patient weight: 180 kg
MRI scanner Siemens Magnetom Essenza (1.5 Tesla)
- New generation tomograph
- High image quality and data accuracy
- Suitable for patients with claustrophobia
- Maximum patient weight: 130 kg
MRI scanner Basda BTI-050 (0.5 Tesla)
- Excellent quality, image clarity
- Helps examine seriously ill and injured people
- Maximum patient weight 135-140 kg
MRI of the uterus, how is it done?
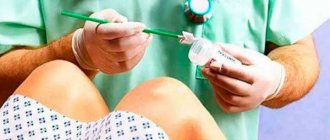
After preliminary preparation, the patient lies face up on the mobile tomograph table. The body and limbs are fixed using holding devices and special rollers. To increase the information content of the study, it is necessary to remain still while an MRI of the uterus is taken.
To protect against the noise of the operating device, headphones are used; communication with the patient is maintained through an intercom. During the procedure, the doctor and x-ray technicians are behind a transparent partition.
Dermoid cyst (teratoma) of the ovary on an MRI image
The table with the patient is rolled into the tomograph tube, having previously installed gradient magnetic coils in the area of interest. Generators located in the tunnel induce a uniform constant field necessary to create resonance of charged particles. Sensitive detectors record the response and transmit it for subsequent analysis. Using complex algorithms, the data is converted into layer-by-layer images reflecting the condition of the uterus, ovaries and adjacent anatomical structures.
Scanning is carried out in axial, sagittal and coronal projections. If necessary, a 3D model of the studied area is reconstructed, which makes it possible to clarify the localization of the pathological process and the interaction of affected and healthy tissues.
Contrast MRI is used in the diagnosis of vascular pathologies and neoplasms of the uterus and ovaries. The patient is given an intravenous catheter before the scan. After a series of native images, the procedure is paused and an injection of gadolinium solution is made using an automatic device. Filling the vascular bed and intercellular space in the area under consideration, the drug “colors” the circulatory network and visualizes the slightest changes in the structure of the uterus and ovaries.
MRI of the pelvic organs with bolus enhancement
Scanning is continued 10 minutes after administration of the contrast solution.
Contraindications to MRI of the pelvic organs
This study cannot be performed on patients with pacemakers, metal implants or fragments in the body, as well as metal-ceramic prostheses.
In addition, there are restrictions on the patient’s weight:
- for a clinic on the street. Clara Zetkin - maximum weight 120 kg, maximum circumference more than 140 cm;
- for the clinic on Volgogradsky Prospekt - maximum weight 120 kg, maximum circumference 120 cm;
- for the clinic on Yaroslavskaya street - maximum patient weight 200 kg, maximum body circumference in the largest dimension 140 cm;
- for the clinic on Simferopol Boulevard - maximum weight 180 kg, provided that the maximum body circumference in the largest dimension is no more than 130 cm, if the circumference is less than 130 cm, then the maximum weight is 200 kg.
Preparing for MRI of the pelvic organs
- It is not advisable to undergo the procedure with a full stomach, so on the day of the examination it is best not to eat at all or limit yourself to a very light breakfast.
- Two days before the test, you must exclude from your diet foods that stimulate the formation of gases (legumes, cabbage, foods rich in fiber).
- The bladder should not be full before the examination. A large amount of liquid in it will lead to insufficient clarity of images and will cause discomfort to the patient, except for examination of the bladder.
- MRI of the rectum for constipation requires a bowel movement on the day of the study.
- MRI of the ovaries, uterus and fallopian tubes is performed in the second week of the menstrual cycle (days 6-9)
- Antispasmodic (like ultrasound OBP) - in 1 hour.
Diseases of the uterus and ovarian appendages
Pathological processes affecting the organs of the reproductive system have different pathogenesis. Depending on the etiology there are:
- oncological diseases;
- inflammatory processes;
- congenital developmental anomalies;
- infectious diseases;
- pathologies of the circulatory system;
- consequences of injuries;
- dystrophic and degenerative processes, etc.
Common benign diseases of the uterus and ovaries include:
- myoma is a neoplasm located deep in the muscular layer or on the border with the internal one;
- endometriosis, adenomyosis - hormonal-dependent processes of proliferation of the mucous membrane, in the second case, hyperplasia of the smooth muscles of the uterus is observed;
- endometrial polyps - focal formations on a stalk, develop from the basal layer;
- follicular ovarian cysts are benign neoplasms that develop when ovulation is disrupted;
- teratomas - arise from ovarian tissue, forming a capsule filled with liquid contents;
- fibrothecomas – tumor formations from the connective tissue base of the ovary;
- cystadenomas are single- or multi-chamber thin-walled cysts.
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs (PID) are classified into a separate group, including damage to the uterus, appendages, ovaries, peritoneum and fiber.
Endometrioid tumor on MRI images (shown by an arrow) in sagittal (a) and coronal (b) projections
The following pathologies are most often diagnosed:
- endometritis – inflammation of the inner layer;
- myometritis – affects the smooth muscles of the uterus;
- endomyometritis - inflammation of the endometrium and muscle layer;
- oophoritis - occurs in the ovaries, can be one- or two-sided;
- salpingitis - inflammation of the fallopian tubes;
- pelvioperitonitis – affects the pelvic peritoneum;
- adnexitis - changes affect the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
A complication of the inflammatory process in the vagina can be erosion of the cervix. In some cases, with a long course of the disease, malignancy of the affected area is observed, and the pathology turns into cancer.
Polycystic ovary syndrome on an MRI image
Malignant tumors are localized in the area of the appendages, body and cervix, and grow into surrounding tissues. The initial stage of ovarian cancer is characterized by unilateral lesions, then growth of atypical cells is observed on the other side.
Characteristic symptoms of diseases of the uterus and appendages are:
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- pathological nature of vaginal discharge;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- heavy vaginal bleeding.
To select an effective treatment method, timely differential diagnosis of the pathological process is necessary. MRI of the uterus and ovaries is done to detect the disease at an early stage, which helps prevent the development of complications.
Doctors provide consultations in the following clinics:
"SM-Clinic" on the street. Novocheremushkinskaya (metro station “New Cheryomushki”)
- Bikineeva Dina Ilyinichna
"SM-Clinic" on Volgogradsky Prospekt (metro station "Textilshchiki")
- Atyasova Elena Viktorovna
- Babaeva Renata Magamedovna
- Bikineeva Dina Ilyinichna
- Blinova Elena Nikolaevna
- Kobriseva Yulia Alexandrovna
- Muratkhodzhaeva Malika Farkhadovna
- Mukhin Vyacheslav Yurievich
"SM-Clinic" on the street. Yaroslavskaya (metro station "VDNH")
- Bashirova Naima Magomedovna
- Muratkhodzhaeva Malika Farkhadovna
- Panfilov Oleg Nikolaevich
"SM-Clinic" on the street. Clara Zetkin (metro station "Voikovskaya")
- Azaryan Samvel Amirkhanovich
- Ivanova Irina Vladimirovna (MRI diagnostician)
- Ikonnikova Nina Yurievna
- Kiseleva Elizaveta Alexandrovna
- Muratkhodzhaeva Malika Farkhadovna
- Nikonorova Tatyana Alekseevna
- Panfilov Oleg Nikolaevich
"SM-Clinic" on Simferopol Boulevard (metro station "Sevastopolskaya")
- Atyasova Elena Viktorovna
- Bashirova Naima Magomedovna
- Brindar Nina Ganovna
- Gudimov Yakov Alexandrovich
- Makarov Artem Mikhailovich
- Soldatkina Elena Vladimirovna
Children's department on the street. Novocheremushkinskaya (metro station “New Cheryomushki”)
- Bikineeva Dina Ilyinichna
Children's department on Volgogradsky Prospekt (Textilshchiki metro station)
- Atyasova Elena Viktorovna
- Babaeva Renata Magamedovna
- Bikineeva Dina Ilyinichna
- Blinova Elena Nikolaevna
- Kobriseva Yulia Alexandrovna
- Muratkhodzhaeva Malika Farkhadovna
- Mukhin Vyacheslav Yurievich
Children's department on Simferopol Boulevard (metro station Sevastopolskaya)
- Atyasova Elena Viktorovna
- Bashirova Naima Magomedovna
- Brindar Nina Ganovna
- Gudimov Yakov Alexandrovich
- Makarov Artem Mikhailovich
- Soldatkina Elena Vladimirovna
Children's department on the street. Yaroslavskaya (metro station "VDNH")
- Bashirova Naima Magomedovna