What does the estradiol level indicate during menopause?
The level of estradiol depends on the function of the organs that synthesize it (mainly the ovaries and adrenal cortex), on the stimulating effects of the pituitary gland, the condition of the liver, thyroid gland and some other factors.
With age, ovarian tissue receptors lose sensitivity to the effects of follicle-stimulating (FSH) and luteinizing hormones (LH). Despite their increased content, estradiol is synthesized less and less, which is manifested by irregular menstruation, anovulatory cycles, the appearance of hot flashes and other symptoms of menopause.
After 45 years, with the onset of the first delay, the levels of female sex hormones should be determined in order to make a differential diagnosis between early menopause and pregnancy. To get a complete picture of gynecological health, in addition to estradiol, it is necessary to evaluate the value of FSH and LH.
The doctor talks in detail about FSH during menopause.
How to maintain normal levels during menopause
In order not to encounter hormonal problems, you should prepare for menopause in advance. At the first symptoms of menstrual irregularities, consult a doctor. Only a qualified specialist will prescribe the correct treatment.
To maintain normal estradiol levels you need to:
- Take hormonal medications. Synthetic analogues of the natural hormone will help the body not experience stress and save a woman from rare age-related changes. Thanks to selective modulators, depression, mood swings, sleep disturbances and hot flashes are prevented. Based on the results of laboratory tests, a specific drug is prescribed in the required dosage.
- Lifestyle. Excessive physical activity should be avoided, but at the same time lead an active life. For a woman aged 50, daily walks in the fresh air for an hour and light morning exercises will be useful. You should also give up alcohol and smoking, they help reduce estrogen.
- Balanced diet. Due to the risk of osteoporosis, insufficient estrogen production and vitamin deficiency, you need to increase the amount of fruits and vegetables in your diet. The diet should consist of 70% plant products. This recommendation will help maintain the balance of estradiol and testosterone.
Don't forget to see your doctor and get tested every year.
The norm of the hormone estradiol in women during menopause
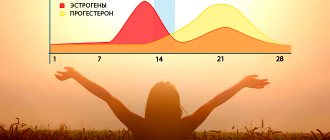
Estrogen levels fluctuate not only depending on age, but also on the phase of the menstrual cycle: the highest levels are recorded during ovulation and during pregnancy.
Since each laboratory gives its own reference values for the norm, it is not possible to talk about exact numbers. Approximate values for estradiol levels:
- follicular phase – 68-1269 pmol/l;
- ovulatory phase – 131-1655 pmol/l;
- luteal phase – 91-861 pmol/l;
- menopause – less than 73 pmol/l.
In various sources, the upper limit of normal for the menopausal period ranges from 50 to 80 pmol/l.
On a note! In order to correctly assess the functioning of the ovaries, it is advisable to have data on the level of hormones during the childbearing period of life - this is considered an individual functional norm, used for comparison with fluctuations in adulthood.
Increased estradiol during menopause
An unexpectedly high level of estrogen in women over 50 should be a reason for an in-depth examination and clarification of the nature of this condition. Possible reasons include:
- hormone-producing tumor or ovarian cyst;
- uterine fibroids;
- breast tumor;
- liver pathology;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- endometriosis;
- adrenal tumor;
- pituitary adenoma.
Some symptoms may suggest hyperestrogenemia:
- tendency to edema,
- weakness,
- decreased performance,
- disruption of the digestive system,
- insomnia,
- thickening and tenderness of the mammary glands.
To make a diagnosis and take appropriate measures, consultation with a gynecologist and determination of the levels of estradiol, FSH and LH are indicated. During menopause, the risk of developing tumor diseases increases, so such a pathology should be excluded first. For this purpose, even if a woman feels ideal, according to the medical examination program, a cytological examination of a cervical smear and mammography are performed free of charge once every 2 years.
Low estradiol during menopause
During the period of decline, the ovaries can reduce and then completely stop the synthesis of estrogen - this is a natural physiological process. Due to the wide range of effects of estradiol on the body, its absence affects all organs and systems: adipose tissue begins to actively develop - a woman gains weight sharply, the skin loses its elasticity, ages quickly, breasts lose their shape, the vaginal mucosa becomes sensitive and painful due to lack of mucus production.
The nervous system becomes less adapted to stressful situations, which causes mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and insomnia. Decreased memory, performance, and concentration make a negative contribution to the emotional background.
Hot flashes are often the first and main reason for visiting a doctor - severe discomfort from this symptom reduces the quality of life. Increased sweating, changes in blood pressure, tachycardia, periodic nausea can also be symptoms of estrogen deficiency.
Hidden from view, but no less important aspects of menopause are the development of osteoporosis, an increased risk of bone fractures, as well as the progression of atherosclerosis, leading to diseases of the cardiovascular system. Having lost the protection of estrogen, blood vessels begin to quickly accumulate cholesterol in their walls, which turns into plaques.
To prevent all these phenomena, it is advisable to increase estradiol during menopause by introducing the hormones necessary for the body from the outside.
Estradiol preparations for menopause
After the onset of menopause, estradiol in the blood may be less than 50 pmol/l and decrease to zero. In order to maintain normal levels of sex hormones in a woman’s body, hormone replacement therapy can be used to reduce symptoms caused by their deficiency. Treatment is prescribed exclusively by a doctor, taking into account possible contraindications.
Symptoms of horse racing
When there is an excess or deficiency of estradiol, the body begins to send signals, symptoms of inflammatory diseases and pathologies of the genitourinary system appear. Early diagnosis will help prevent irreversible consequences.
Elevated
Hyperestrogenism is an increased level of estradiol. It can normally fluctuate and increase 3 times before ovulation to trigger follicle rupture and prepare the body for pregnancy.
Increased estradiol during menopause and during a woman’s fertile period can provoke the following diseases and symptoms:
- Endometriosis. Due to too high activity of female hormones, the reproductive system begins to form cysts on the ovaries, and the endometrium develops too quickly. The formations can reach 10 cm in size, in some cases surgery will be required. The disease also sometimes causes problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Adenomyosis. In this disease, the growth of the endometrium connects with the myometrium - the tissues of the uterus. Symptoms appear most clearly during the period of ovulation. Growths and nodes form on the walls of the uterus, requiring surgical removal. The main symptom is abdominal pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
- Estrogen-secreting tumors. Formed on the ovaries, they can cause early puberty in girls. If not treated in a timely manner, a benign tumor sometimes develops into a malignant one. In the presence of an estrogen-secreting tumor, a woman experiences heavy menstruation or cycle disturbances with a long absence of bleeding.
- Chorionepithelioma. This is a malignant tumor in the uterus caused by excessive production of estrogen. In this case, the symptoms are clearly expressed: periods are very painful, the cycle is disrupted, and abdominal pain appears constantly.
- Hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex. Symptoms may not be noticeable. Excessive production of glucocorticoids can only be detected by testing. Due to high estradiol, metabolism is disrupted, a woman quickly and without reason gains excess weight.
Also, high levels can provoke diseases of the endocrine system, disrupt the functioning of the liver, kidneys and other internal organs. It is impossible to determine a specific problem based on symptoms; only laboratory tests will help.
Due to the surges, a woman experiences menstruation disorders, breast tenderness, sleep disturbances and insomnia, depression and poor condition of hair, skin and nails.
Reduced
With low estrogen levels, the likelihood of miscarriage increases. Insufficient production of estradiol can make conception impossible and childbearing very difficult. Estrogens are responsible for the formation of the placenta and the normal course of pregnancy.
Symptoms of low estradiol during menopause:
- menstrual irregularities;
- severe pain during bleeding;
- insufficient moisture of the vaginal mucosa;
- lack of sexual desire;
- decreased performance, fatigue;
- blood pressure surges;
- frequent headaches;
- body weight deficiency;
- fragility of the skeletal system.
Low estrogen even shows up externally. In a woman of the male type, the hips become narrower and the shoulders become wider. Whiskers with coarse hairs may begin to appear on the face. If a woman cannot get pregnant for a long time, then she should consult a doctor to prescribe estrogen-containing drugs.
Estradiol: main tasks in the female body
Estradiol is essential for women for the normal functioning of both the reproductive system and the entire body. For example, estradiol helps to activate the contractile function of the myocardium, strengthen vascular walls and reduce cholesterol levels in the blood.
This hormone also increases the tone of the smooth muscle fibers of the intestinal wall and bladder, which improves the functioning of these organs.
In addition to smooth muscles, estradiol has a positive effect on the activity of skeletal muscles, promoting their regular contraction and relaxation. Thus, the endurance and resistance to stress of the human body increases, and the body becomes elastic.
In addition to a good mood, estradiol helps women be beautiful and sexy. This is explained by the fact that this hormone allows the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics, such as round breasts, steep hips, thin waist, smooth skin, soft voice, etc. The significant importance of estradiol in the formation of libido is also noted.
Numerous medical studies have shown that estradiol helps maintain a fit body shape and weight. For example, in women of menopausal age, as a result of a decrease in the level of estradiol in the blood, the problem of excess weight and brittle bones often arises.
Estradiol plays an important role in creating favorable conditions for fertilization, loosening the endometrium so that successful implantation of the zygote occurs.
Estradiol and the menstrual cycle: relationship
Estradiol is synthesized and released into the blood throughout the entire monthly cycle, only in different quantities. Its synthesis occurs in the ovaries, adrenal cortex and adipose tissue, and during pregnancy - in the fetal place.
During the follicular phase of the monthly cycle, estradiol is produced in minimal quantities, under the influence of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones. Before the ovulatory phase, the amount of the hormone increases three times, after which it decreases, reaching a minimum level before menstruation.
Estradiol can be converted into estrone and estriol throughout the monthly cycle.
Also, the level of estradiol in women changes with every hour of the day. The largest amount of the hormone is synthesized between 15 and 18 hours of the day, and the smallest - between 24 and 2 am.
General information about the hormone
Estrogens are the main support of the female body. This group includes three hormones: estradiol, estriol and estrone. The latter have virtually no effect on the functioning of the female body. Estradiol has the greatest activity and impact.
Functions
Estradiol is a steroid sex hormone that directly affects the menstrual cycle, the likelihood of conception and the course of pregnancy. Production occurs in the follicles, corpus luteum and placenta, with a small amount secreted by the adrenal glands. Regulation of processes occurs in the pituitary gland of the brain.
Women have many times more estradiol in their bodies than men. Due to an imbalance between estradiol and testosterone, negative hormonal changes occur.
Already in childhood, from 8-14 years of age, when the first menstrual blood appears in a girl, estrogens are actively produced, and puberty begins. With increasing physical activity and heavy sports loads, the amount of the hormone decreases.
- Accelerates metabolic processes. If there is a metabolic disorder, a woman may gain weight. Estradiol helps maintain good physical shape and protects against bone fragility and osteoporosis.
- Helps break down fat. However, if you abuse fatty foods and consume large amounts of carbohydrates, the level of female hormones can fall, which leads to weight gain. Obesity can contribute to the cessation of menstruation.
- Lowers cholesterol levels. Estradiol can also reduce appetite and protect against the formation of cholesterol plaques.
- Maintains water-salt balance. However, reduced estrogen levels lead to the formation of edema. Estradiol helps retain water and calcium in the body.
- Improves the functioning of the cardiovascular system. The hormone prevents the development of coronary heart disease in women by improving metabolism on the walls of blood vessels.
- Immunostimulating effect. A normal level of female hormone in the blood increases the body’s resistance to pathogenic bacteria and strengthens the immune system.
- Protects against cancer. In a healthy woman, the risk of gastrointestinal cancer is minimal.
- Prevents Alzheimer's disease. Protection consists of strengthening the central nervous system; estradiol also helps to recover faster from head injuries and ischemic diseases, stroke.
- Responsible for the beauty and health of a woman. Estradiol is a hormone of sexuality and good mood. It is responsible for the formation of sexual desire and psychological state.
It is important to maintain a balance at a normal level: in women there is low testosterone and high estrogen, in men it is the opposite.
During adolescence, estradiol provides:
- normal development of the genitourinary system, formation of the mammary glands;
- formation of a strong skeleton, strengthening of bones;
- female pattern hair growth;
- distribution of adipose tissue and the formation of a proportional female figure;
- rapid growth in the period up to 16 years.
Already at the age of a girl of about 10 years, estrogen prepares her body for bearing a child: wide hips are formed, the breasts swell for subsequent feeding of the baby.
Effect on the menstrual cycle
The female sex hormone is synthesized throughout the menstrual cycle. Over the course of a month, its level may change daily.
During the follicular phase of the monthly cycle, estradiol is produced in minimal quantities under the influence of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormone. Before ovulation, the amount of the hormone increases 3 times, after which it decreases, reaching a minimum before menstruation.
Factors affecting the level of estradiol in the body
Once again, I would like to say that the norms of the hormone estradiol in women can change under the influence of various factors, namely:
- phase of the menstrual cycle;
- age;
- pregnancy;
- changes in climatic conditions;
- fluctuations in body weight;
- harmful environmental factors
- psycho-emotional shock;
- bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking);
- taking medications.
Each of these facts, as a rule, causes fluctuations in the level of estradiol in the blood within the acceptable range.
Blood test for estradiol
In a blood test, the level of this hormone is usually displayed in picograms per milliliter (pc/ml), but this indicator can also be expressed in picomoles per liter (pmol/l).
A blood test for estradiol is prescribed by specialists in such cases as:
- hormonal imbalance in the body, as a result of which the monthly cycle is disrupted;
- lack of ovulation;
- infertility;
- disruption of the sex glands;
- periodic uterine bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle;
- pronounced manifestations of premenstrual syndrome;
- malfunction of the pituitary gland;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- fragility of bone tissue;
- ovarian neoplasms;
- adrenal neoplasms;
- preparation for in vitro fertilization.
In order for the result of a blood test for estradiol to be as objective as possible, when preparing for the study, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- 2-3 days before the study it is not recommended to transfer;
- 24 hours before blood sampling, limit physical and mental stress;
- Avoid having sex 24 hours before;
- 24 hours before blood sampling, smoking and drinking alcohol are prohibited;
- If you are taking any medications, notify the doctor who ordered the tests. In this case, temporary discontinuation of the drugs may be considered, since they may distort the results of the study for estradiol;
- The last meal should be no later than 12 hours before blood sampling. The analysis is carried out strictly on an empty stomach.
Diagnosis of jumps
First of all, a woman needs to see a doctor - a gynecologist or endocrinologist. The specialist will prescribe a full blood examination and additional diagnostics. You cannot self-medicate, otherwise there is a possibility of aggravating the situation and leading to hormonal imbalance.
Indications for diagnosis:
- male pattern hair growth;
- increased activity of the sebaceous glands;
- threat of miscarriage and premature maturation of the placenta;
- menstrual irregularities;
- tumor processes of the genitourinary system;
- menopause symptoms;
- premenstrual syndrome.
The analysis must be taken on days 3-5 of the cycle. Also, as an additional study, ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs may be prescribed.
What is estradiol?
Estradiol is a steroid sex hormone. It is produced by the ovaries, adrenal cortex, peripheral tissues, and placenta. This hormone plays an important role in the proper development of all genital organs and characteristics of a woman, as well as in the functioning of her reproductive system.
Fluctuations in estradiol occur predominantly during the menstrual cycle, consistent with the level of follicle-stimulating hormone and progesterone. The highest level of estradiol is during ovulation, and it remains the same and even higher if pregnancy occurs.
There are three types of estrogens in a woman's body:
- Estradiol is a positive type of estrogen that is involved in more than 400 vital functions of the female body. With normal levels of estradiol, a woman has good vision, elastic skin, free of “hormonal” rashes, normal body weight and strong bones. This type of estrogen cannot be synthesized from other hormones.
- Estrone is a bad type of estrogen that can provoke cancer (cervical cancer) during menopause. It is mainly produced by adipose tissue, therefore, during menopause, increased physical activity is especially important to prevent the subcutaneous fat layer from increasing.
- Estriol is a pregnancy marker, produced only in women of reproductive age.
Norm
After 30-35 years, a woman’s estrogen level drops. This is due to age-related changes in the body and depletion of the follicular reserves of the reproductive system.
During menopause
The norm of estradiol during menopause can vary from 10 to 95 pmol/ml. At the initial stage of menopause (premenopause), the level will be higher, and if there have been no periods for more than a year, the level will be lower.
During pregnancy and lactation
During pregnancy, a woman's estrogen level is at its highest. This is the only period when rapid jumps and growth of estradiol benefit the body. During pregnancy, the hormone is produced in the fetal sac.
The concentration of estrogen can reach several thousand. A normal level is considered to be between 200 and 40,000 pmol/ml. The longer the period, the higher the estrogen level. Closer to childbirth, progesterone also increases.
During lactation, the norm of estradiol is practically no different from the usual prenatal level:
- follicular phase: 20-140 pmol/ml;
- luteal phase: 40-340 pmol/ml.
Immediately after childbirth, the level of female sex hormones drops several dozen times. During breastfeeding, estradiol may be produced less than normal due to the high content of progesterone.
How to find out the level of estradiol during menopause?
Estradiol levels undergo correction during menopause: the hormone can either increase or decrease. To find out the level of estradiol, you need to take a test for this hormone. For research, blood is taken from a vein. The woman is advised not to eat several hours before blood sampling, stop taking hormonal medications, eliminate various stress-forming factors, exercise, and not smoke.
Using an analysis of estradiol levels, the following characteristics of the female body can be determined:
- assess ovarian function;
- identify the causes of delayed menstruation.
For women over fifty years of age who have entered menopause, it is very important to obtain the results of an estradiol test in order to understand whether immediate menopausal changes have occurred in her body.
During menopause, the level of estradiol decreases - it can be in the range from zero to 54 pg/ml, although the norm for estradiol in women with undiminished sexual function is twice as high, and during pregnancy it even jumps 4-10 times more.
It is worth noting that doctors have not yet decided on the norm of the hormone estradiol, therefore in some medical literature a level of 36 units is considered low, while other experts consider the figure 82 to be low. Therefore, laboratories in which women take a blood test for estradiol are obliged not only indicate the unit of measurement, but also the reference values that the clinic adheres to.
But doctors still, when assessing the health status of a 50-year-old woman, do not rely on the results of just one analysis, but carry out a whole series of diagnostic procedures that should indicate the decline of sexual function. Only after receiving such data can we talk about the onset of menopause.
By the way, if menstruation is delayed at 40-45 years, a woman may suspect early menopause, but a high level of the hormone estradiol, on the contrary, indicates that pregnancy has occurred. Such late cases of pregnancy, although rare, are quite well known in practical medicine.
What hormones does it affect?
Estradiol not only helps a woman look attractive, but also stimulates the production of a number of other hormones: corticotropin, aldosterone, somatropin and oxytocin. When diagnosing female diseases, you need to pay attention to the indicators and interaction of estrogens with testosterone, progesterone and prolactin.
- Testosterone. The ratio of male to female hormones should be 1 to 7-10. If this indicator is lower, then the woman has symptoms of hormonal imbalance.
- Progesterone. These are the two main hormones that help during pregnancy and lactation. Their indicators fluctuate depending on the phase of the cycle. During menopause, progesterone may decrease due to inflammatory diseases. When estradiol is low, progesterone levels rise.
- LH (luteinizing hormone) and FSH (follicle stimulating hormone). These hormones themselves influence estradiol more than it influences them. They participate in the synthesis and secretion of female hormones and help the formation of follicle maturation. LH acts on the membrane cells, stimulating the production of androgens, FSH acts on granule cells to ensure the conversion of androgens into estrogens.
Estradiol in menopause: hormonal characteristics
During menopause, the level of estradiol has a special effect on the body. And this is quite normal, because in the premenopausal period it was this hormone that was responsible for maintaining a woman’s sexual function and her ability to bear children. With the onset of menopause, estradiol becomes the first hormone that upsets its balance in a woman’s body and leads to her aging. The consequences of estrogen deficiency during menopause are as follows:
- the appearance of skin problems: excessive dryness and thinning of the skin, the appearance of the first senile wrinkles;
- provoking the appearance of moles and papillomas, even if the woman has not previously suffered from them;
- fluctuations in blood pressure;
- headaches, vascular spasms;
- violation of coordination of certain actions;
- the appearance of periodic nausea;
- the appearance of hot flashes - increased blood circulation in the face, neck, décolleté;
- increased sweating, especially in the evening and at night;
- rapid fatigue, decreased performance, weakened memory, inability to concentrate;
- increased bone fragility;
- disturbance of heart rhythm, the appearance of tachycardia.
Estradiol deficiency provokes a number of disorders in the body that are characteristic of the menopause period. The manifestation of these disorders is directly proportional to the level of estradiol - the lower the level of the hormone in the blood, the more pronounced the menopausal changes.
- Since estradiol is produced mainly by the ovaries, as their function fades, adipose tissue tries to take over the production of estradiol. The compensatory component in this case is negligible and does not satisfy the woman’s hormonal needs, but the level of adipose tissue increases significantly. It is for this reason that women over 50 years of age noticeably gain weight, and even thin representatives of the fair sex can notice fat deposits.
- Also, with a decrease in estradiol levels, noticeable changes occur in the vagina: dryness and discomfort appear during sexual intercourse. In normal concentrations, estradiol is able to regulate mucus production, since a healthy vaginal environment is important for reproductive function, but with a deficiency of the hormone, the opposite processes occur.
- In addition to all its functions, estradiol also affects a woman’s mammary glands. With a high level of the hormone, they remain elastic, and with a decrease in the concentration of estrogen in the blood, the breasts gradually become flabby and heavy.
- A woman's sexual desires also depend on her hormonal levels. With a high level of estrogen during ovulation, a woman most of all wants intimacy, which is dictated by the need to procreate. When estradiol levels decrease, the desire for sexual contact weakens significantly.
- Since hormones affect not only the reproductive system, but also the body as a whole, the level of estradiol cannot but affect the blood count. When the hormone content in the blood decreases, its viscosity increases and cholesterol levels rise. This automatically puts a woman in a risk group, so doctors recommend that after 50 years of age not only control the level of cholesterol in the blood, but also take statins if it increases.
- Estradiol also affects the functioning of the sweat glands. With a deficiency of the hormone, the removal of water from the body increases, and the woman not only often goes to the toilet, but also feels the removal of fluid through the sweat glands. About 80 percent of women reported excessive sweating as a sign of menopause.
- With a lack of estrogen in the blood, calcium absorption is worse, and it is even excreted in small quantities. If you do not take calcium supplements and eat little dairy products, a woman during menopause faces increased fragility of bones and decreased elasticity of the skin. It is for these reasons that many more fractures are recorded in women during the decline of sexual function than in representatives capable of reproducing offspring.
- And the last area in which the lack of hormones manifests itself is emotional. If previously a woman had a stable nervous system response to almost any stressful situation, then during menopause any little thing can throw a woman out of balance and provoke stress.
Reviews
Many women are advised to choose hormonal therapy for its effectiveness. However, in old age it is already difficult to take a large number of medications; they can suffer from heart pain and problems with blood pressure.
I only recently found out what menopause is. I wasn’t even interested in this topic, I thought I was still young. But when my periods stopped coming, I was very upset. I advise you to consult a doctor in advance and prepare psychologically for accepting age. Now I have to constantly take hormones, antidepressants and vitamins. I didn't think it would be so emotionally difficult.
I can't take hormones and my estrogen levels are very low. I had to deceive the body and take plant drops. Unfortunately, they practically do not help, although my neighbor has completely different results. It’s a pity that I didn’t take care of my health when I was young.
I think that I am still young and beautiful. But judging by my mother, in 5 years I will reach menopause. I started preparing now: I changed my diet, joined the gym and am more often in the fresh air. Next week I will go to the doctor and start taking vitamins.
Detailed interpretation of analysis results
When talking about hormonal imbalances during menopause, it is necessary first of all to correctly interpret the results. It is very important not just to state that estradiol in the blood is increased or decreased, but to be aware of the consequences that arise when hormonal levels deviate.
If estradiol is normal in women around 54, but as a result of the analysis the hormone is elevated, then this may indicate the following pathologies:
- ovarian cyst or ovarian tumor;
- myomatous node;
- liver pathologies;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- neoplasms in the breast.
With elevated levels of estradiol, women suffer from swelling, weakness, digestive disorders, insomnia, become irritable, and feel pain in the mammary glands. If estrogen is elevated, this cannot be ignored: it is recommended to comprehensively examine the body, find out the cause, and minimize the consequences of hormone deficiency. During menopause, this is especially important, since a woman’s body becomes more vulnerable to various types of lesions - tumors, severe chronic pathologies, etc.
If the hormone is low, this can also lead to certain disorders.
Estradiol levels are considered too low if they are below 6-9 pg/ml. In this case, doctors carry out replacement therapy to prevent gynecological, endocrine, oncological and metabolic disorders.
Normalization of hormonal levels
- If the hormone level is reduced to a critical point, hormonal correction is necessary. The scope of medical care can be determined after receiving the test results. Under the supervision of a gynecologist, the woman is prescribed a course of hormone replacement therapy; traditional medicine - infusion of linden, sage, and hops - will also be useful. After the examination, patients may be prescribed one of the following drugs - Trisequence, Cycloprogynova, Estraderm, Estrimax, Climen, Climodien, Cliogest, Menorest, Octodiol, Pauzogest, etc. It is recommended to maintain a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, rationalize your diet, and get sufficient physical activity.
- If estradiol levels are elevated, conservative treatment (Clomiphene citrate) under the supervision of a physician is also recommended to minimize the negative manifestations of menopause.
Hormonal imbalance, namely a discrepancy with the norm of estradiol, is the first sign of menopause. Still invisible outwardly, they are already felt by a woman in the slightest manifestations. Of course, hormone deficiency is inevitable, as is the onset of menopause, but it is better to survive this period with minimal consequences for the body. That is why a modern woman during menopause should take sufficient care of her health, monitor hormone levels, and, if necessary, undergo treatment from a doctor.
Educational video on this topic:
Sources:
https://mirmam.pro/estradiol-pri-klimakse https://adella.ru/health/estradiol.html https://vklimakse.ru/norma-estradiola-pri-menopauze.html
Treatment
Therapy is prescribed only after receiving test results and a collected medical history. Hormonal pills have many contraindications and side effects. In old age, in the presence of chronic pathologies, herbal medicine is recommended.
Traditional
Treatment for menopause is prescribed depending on the diagnosis - high or low estradiol. An increased level can be observed only at first, when menstruation has not yet stopped.
Traditionally, to normalize hormonal levels, the following are prescribed:
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT). These are drugs from the group of selective modulators - synthetic developed estrogens. This treatment has the highest effectiveness, but is contraindicated in severe cardiovascular diseases. The drugs are based on estradiol, which helps increase the level of female sex hormones. The most popular drugs: Klimonorm, Tibolon, Kliogest and others. The duration of treatment therapy can reach 3-4 years.
- Herbal medicine. If a history of chronic diseases is detected, the doctor will suggest an alternative option - phytohormones. Their effectiveness is minimal, but with long-term use, due to the cumulative effect, estrogen levels may increase. This is a long-term, but safest method of treatment. Estradiol is found in mint, flaxseed, sage and other plants.
- Preparations with biosphonates. This is an additional treatment that helps strengthen the skeletal system during estradiol surges. These medications reduce the risk of fractures. The following drugs help protect against osteoporosis: Ferrum Lek, Fosamax, Actonel, Boniva and others.
- Other hormones. It is rare to suppress estrogen activity during menopause; usually this indicator is low in older women. When its level increases, taking analogues of gonadotropin releasing hormone, medroxyprogesterone, and norethisterone is indicated. Such drugs are prescribed by prescription, as they have a long list of contraindications and side effects.