Histological examination of the uterine mucosa allows us to study in detail the effect of sex hormones on the endometrium. The diagnostic method is widely used to identify the causes of pathology of reproductive function. In response to cyclical changes in hormones, a restructuring of the endometrium occurs in a healthy woman’s body - within 21-28 days, its thickness and cell structure change from one to seven millimeters.
Each menstrual cycle ends with the destruction and removal of part of the epithelium of the uterine cavity, accompanied by menstrual flow. What happens when this process is disrupted? Gynecologists get the answer to this question with the help of diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity.
They prescribe treatment based on the results of histology after curettage. Only with the help of this most informative method can one distinguish malignant cells from benign ones and determine the degree of cancer germination.
Methodology
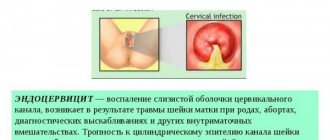
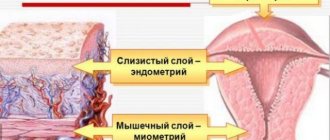
What is histology in gynecology after curettage? During curettage of the uterine cavity, the internal mucous layer of the uterus, capable of regeneration and having a complex anatomical structure, is removed. The endometrium consists of a covering epithelium, onto the surface of which the uterine glands open.
The integumentary epithelium is made up of secretory and ciliated cells. The glands are formed by cylindrical epithelium, located near the muscular layer of the uterus (myometrium), without growing into its thickness.
In case of endometriosis, the pathohistologist diagnoses the growth of glands into the myometrium; other gynecological diseases are characterized by their inherent features of tissue changes at the cellular level. These processes can only be seen under special optical instruments, after having first obtained a scraping and prepared a microspecimen.
The quality and reliability of the examination results depend on the technique of diagnostic curettage (carefully, with minimal damage to cells), proper preparation of the microspecimen:
- Fixation - the material obtained as a result of curettage is immediately immersed in chemical solutions that prevent tissue destruction. This can be a 10-20% formalin solution, 96% alcohol solution.
- Washing - in a pathohistology laboratory, the material is washed from excess fixative in ordinary water.
- Dehydration is the gradual passage of tissue through alcohol solutions with increasing concentrations. The process may take several days.
- Pouring is a complex process of transferring a drug from a mixture of alcohol and chloform into a mixture of wax and paraffin. After complete hardening in paraffin, proceed to the next stage. For urgent examination, the tissue may be frozen.
- Preparation of sections - using a special knife (microtome), paraffin blocks are cut into individual sections several micrometers thick. Dyeing – paraffin is removed, dyed with paints and reagents special for each type of fabric.
- Conclusion - after staining, the sections are washed again, dehydrated, cleared, and only after that a special balm or synthetic preparation is added to the slide with the section, covered with a coverslip, and sent for examination to a histologist.
It takes about 10-14 days to prepare a microslide; an urgent study differs in the technique of preparing the material and lasts for 40-60 minutes. Pathohistologists decipher the histology after curettage. Since the study is subjective, the skill level of the specialist plays a huge role in making a diagnosis, which determines the scope and effectiveness of therapy.
Conducting research
To conduct histology after curettage, doctors take a small piece of tissue from the patient’s uterus. Histology lasts for 5 or 10 days. If a woman requires urgent laboratory testing of tissues, it will take from 1 hour to 24 hours. It should be remembered that in this case, the histology after curettage may not be fully reliable.
Histology (both urgent and non-urgent) is carried out in several stages:
- Fixation. To ensure that the sample under study does not rot after scraping, it is subjected to processing during the study. For this, a special liquid is used that prevents the breakdown of the structure and cells.
- Wiring. The sample taken for analysis is subjected to dehydration so that it becomes denser.
- Filling. The material is impregnated with a potting agent (mostly paraffin) to make it hard.
- Cutting. Fabrics drenched in paraffin or other means are cut with a special device after drying. The result is thin plates (slices).
- Coloring. At this stage, the laboratory assistant places the resulting plates on special glasses. After this, the sections are stained with special means, which serve to study the different structures of the sample (RNA, cytoplasm, DNA, etc.).
- The final stage. Cut and stained samples of material are covered with other glass slides. This is necessary in order to preserve thin plates for a long time.
- Study. Histological samples that were obtained after all manipulations are sent to pathomorphologists or histologists. For research they use a light or electron microscope.
Histology is in many ways similar to cytological analysis, however, it examines a piece of tissue. During histology, a comparative study of healthy and pathological tissues is carried out.
Indications
What does histology show after curettage? Histological examination of scrapings is an important, indispensable stage in the diagnosis and treatment of uterine bleeding. Menstrual irregularities, infertility, menopausal and juvenile bleeding, benign and malignant neoplasms are a consequence of the abnormal structure of the endometrium and impaired hormone production.
Inflammatory processes have their own histological picture. Using histology after curettage, the cause of termination of pregnancy is clarified. To obtain most scrapings, separate curettage of the uterine cavity (the lining of the uterus separate from the cervical canal) is performed under the control of a hysteroscope.
The contents are collected in different containers, without mixing with each other, and sent for histological examination after curettage. Accompanied by indicating where the material was obtained, a brief gynecological history of the patient, the day of the menstrual cycle, and the date of onset of pathological manifestations of the disease. The timing of the intervention relative to the phase of the menstrual cycle is also important:
- For bleeding associated with lack of ovulation, scraping is done a few days before the upcoming menstruation.
- If endometrial hyperplasia is suspected, on the first day of the onset of menstruation or bleeding the day before.
- For the diagnosis of neoplasms, the day of the menstrual cycle does not matter.
- The presence of hyperpolymenorrhea suggests conducting a study on the 5th day from the start of menstruation.
- Bleeding is a direct indication for emergency curettage.
When describing drugs, the term menstrual cycle phase is used. The fact is that the intermenstrual period has several phases: menstrual bleeding (at this time the destroyed endometrium is rejected 1-4 days), proliferation (growth of a new layer of cells 5-14 days), secretion (active work of the glands, changes in blood vessels 15-28 days ). If the production of hormones is disrupted, there is a failure in the restructuring of the endometrium - one of the phases may be delayed, shortened, disappeared, or proceed with more rapid growth.
Result
The histological results after curettage and their interpretation are of interest to many patients. Each disease has its own characteristic transformations of the endometrial structure. Typical for persistence of the corpus luteum (long-term existence) are pronounced secretory changes in the glands and a decidual reaction of the endometrial stroma. This occurs as a result of a violation of gonadotropic stimulation of progesterone synthesis.
The results of a scraping study with dysfunctional uterine bleeding indicate hyperplasia (pathological proliferation of normal cells) of the endometrium and the absence of a secretion phase.
With prolonged exposure to low levels of estrogen, scrapings are diagnosed with glandular hyperplasia; this condition often accompanies menopause. It can be cystic - the glands grow in the form of cavities. Atypical hyperplasia involves the presence of enlarged nuclei with a changed shape in the cell, irregularly shaped glands. After menopause, endometrial atrophy occurs.
The occurrence of ovulation is indicated with 90% accuracy by secretory changes in the endometrium, removed during curettage of the uterine cavity two to three days before the onset of menstruation. With the help of histologists, they confirm the diagnosis of a chronic inflammatory process in the uterus, an interrupted pregnancy, determine the presence and nature of polyps, benign and malignant processes.
If the histological results after curettage describe uneven infiltration of glands in combination with damaged fibroblast stroma or a desmoplastic reaction, pronounced aggregation of glands with the formation of a lattice pattern in place of the stroma, its replacement with a large amount of desquamated epithelium - we can talk about a malignant transformation of the endometrium into adenocarcinoma (cancer) .
Curettage is an operation to remove the functional layer of the endometrium from the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. It is carried out with the aim of eliminating pathological formations, which often cause infertility. And in order to determine what caused the deviations in the functioning of the reproductive system, histology is performed after curettage.
To do this, samples of biomaterial taken from the patient are sent for examination to a laboratory, where they are carefully studied. After 2 weeks, the woman receives the results and transcript of the analysis, where you can see whether malignant cells or neoplasms are present in the reproductive system. The causes of the pathology also become known. With this conclusion, you should definitely visit a gynecologist to discuss the further course of treatment.
Histology after a frozen pregnancy: interpretation of the results
Based on the results of histology, after curettage of a frozen pregnancy, the doctor may prescribe additional examination or treatment. Most often, additional tests are required to confirm the biopsy. These include:
- study of the hormonal background of the expectant mother - tests for estrogens, progesterone, testosterone, FSH, LH, cortisol, prolactin and other hormones;
- examination for TORCH infection;
- spermogram for the spouse;
- immunogram to establish immune status.
The results of fetal histology after a frozen pregnancy can be deciphered by the attending physician; it is difficult to understand the pathological terms on your own.
To understand what is written in the pathologist's report, it is necessary to understand what the normal endometrium looks like during pregnancy.
Before implantation of the embryo, under the influence of progesterone, spiral arteries grow from the thickness of the endometrium. They are necessary for the nutrition of the future embryo. After implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium, morphological changes occur. Fibroblast cells increase in connective tissue and acquire the ability to synthesize protein. Such cells are called decidual, and the epithelium containing them is called the decidual (or falling) membrane. Depending on the location of the shell, there are several types:
- basal - between the embryo and myometrium;
- capsular - between the embryo and the lumen of the uterus;
- parietal, or parietal - the remaining gap between the first two.
The chorion is the rudiment of the placenta, which connects the embryo with the vessels of the uterine wall and provides nutrition. In histology, decidual tissue of the chorionic villus refers to the area of the membrane in which the placenta should have formed.
Trophoblasts are cells that provide nutrition to the embryo in the early stages of development. They secrete proteolytic enzymes that help dissolve endometrial tissue and implant into the embryo. In histology, altered decidual tissue with trophoblast cells indicates that a disruption in the development of the embryo occurred in the early stages, which did not allow it to attach normally to the uterine cavity.
Spiral arteries with gestational restructuring are a sign of the beginning of placenta formation. This conclusion is typical for pregnancy after 5 weeks. But the nature of the changes in the vessels may be different. If the adjustment is not complete in accordance with the term, this can cause termination of pregnancy. Studies have shown that if such a pregnancy continues, there is a high chance of developing gestosis at the beginning of the 2nd trimester.
Chorionic villi can transform into bubbles with fluid - cysts. This condition is shown in histology as a partial simple hydatidiform mole. It cannot be called a full pregnancy. The condition is characterized by severe toxicosis and the risk of massive bleeding. The fetus dies in the early stages, so only pathologically altered trophoblast tissues develop in the uterus. The causes of the pathology are associated with:
- chromosomal abnormalities;
- influence of viruses;
- hypoestrogenism;
- multiple abortions;
- young age of the expectant mother;
- after 35 years of age.
In this condition, there is also a violation of the maturation and differentiation of chorionic villi, which may be an indirect sign of chromosomal abnormalities in the development of the embryo.
Endometritis in histology after cleaning a frozen pregnancy
Chronic endometritis is one of the main causes of missed abortion in a short term. With repeated anembryonia, up to 63% of pregnancy pathologies are associated with it. Endometrial tissue is characterized by inflammatory changes that affect different layers.
Focal productive deciduitis indicates a pronounced inflammatory reaction that affected the developing membrane of the embryo. In endometrial tissues, the formation of microthrombi and pronounced inflammatory infiltration are sometimes noticeable.
The main morphological signs of endometritis are:
- diffuse lymphocytic infiltration with an admixture of neutrophils, polymorphonuclear cells, histiocytes, plasma cells;
- productive basal deciduitis, plasma cells in the endometrial stroma;
- stromal fibrosis in focal or diffuse form;
- sclerotic changes in the spiral arteries;
- vascular growth in the chorion is impaired, there are signs of dystrophy and fibrosis;
- hypoplasia or necrotic changes in the chorionic villi;
- decidual tissue with focal micromorphological infiltration;
- Sludge syndrome of erythrocytes in the vessels of the developing intervillous space.
All these changes speak in favor of chronic inflammation of the endometrium, which will become an obstacle to subsequent conception. Therefore, women with a similar histological finding need to establish the type of infection and select the appropriate treatment. This will increase the chances of successful conception and reduce the risks of pregnancy complications in later stages.
Villusitis and intervillusitis of the placenta in histology after frozen pregnancy
Examination of tissue obtained after curettage is a mandatory diagnostic step after fetal loss. After a frozen pregnancy, histology of the placenta often reveals villusitis and intervillusitis. What do these concepts mean?
A frozen pregnancy is a consequence of chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus or chronic endometritis. Other causes of miscarriage are identified less frequently. Inflammation of the chorion, and later – of the placenta, can have different localizations.
- The chorionic villus (Latin villus) can become inflamed in isolation, then villusitis is detected.
- When there is inflammation of the intervillous space, placental intervillusitis is recorded in histology.
- Lesions of the basal lamina are described as basal deciduitis.
- Productive choriodeciditis is the involvement of the chorionic plate.
Histological definitions differ depending on the type of cellular reaction and the state of the blood vessels. In the histologist's conclusion you can see the following descriptions of the material:
- productive intervillusitis - this means that macrophages and plasma cells predominate between the chorionic villi; when infected by viruses, macrophages and monocytes predominate; with villous necrosis, destructive changes are observed;
- subchorial intervillusitis of the placenta - an inflammatory reaction that indicates an ascending infection, manifests itself in the form of a large accumulation of leukocytes (marginal standing) in the intervillous space;
- purulent subchorionic intervillusitis is a bacterial lesion with the presence of a large number of polymorphonuclear leukocytes.
Pathological changes may appear in the decidual membrane. Then they talk about focal exudative deciduitis, combined with villusite. Exudate can be of different nature:
- serous;
- fibrinous;
- purulent;
- putrefactive;
- hemorrhagic;
- catarrhal;
- mixed.
Sometimes accumulations of red blood cells are observed, which indicate hemorrhage and focal serous deciduitis.
The cause of focal productive villusitis in the placenta is infection. Pathogens penetrate upward from the vagina or are already in the uterus at the time of conception in chronic endometritis. Depending on the type of infection, certain cellular responses predominate.
With parietal intervillusitis and basal deciduitis, microbial associations with bacteria of different types are revealed. This may be an opportunistic nonspecific flora:
- staphylococci;
- coli;
- pneumococci;
- enterobacter;
- streptococci;
- Klebsiella;
- candida.
In large-focal chronic productive intervillusitis, inflammation is observed in a large number of villi; for such a histologist’s conclusion, it is necessary that more than 10 villi be involved in the reaction. The cause of damage in this case is often various types of viruses:
- cytomegalovirus;
- herpes simplex;
- rubella;
- varicella zoster (a type of herpes virus).
Less commonly, the cause is toxoplasma and spirochetes (the causative agent of syphilis). With a mycotic lesion, chronic intervillusitis occurs without productive villusitis. Similar changes appear during infection with chlamydia, protozoa, rickettsia, measles virus and Epstein-Barr virus. In this case, microorganisms penetrate into the uterine cavity not only by ascending, but also by hematogenous route. Chronic inflammation caused by bacteria or viruses will not allow the embryo to develop normally and must be treated. Additional examination (microbiological, PCR diagnostics) may be required to accurately determine the type of infection and select appropriate medications.
Histological terminology is often difficult to decipher, so it is impossible to independently evaluate the results of the study. To eliminate mistakes and choose the right tactics for planning the next pregnancy, the attending physician must know the conclusion of pathologists.
Yulia Shevchenko, obstetrician-gynecologist, especially for Mirmam.pro
Features after scraping
Curettage (cleaning the inner surface of the uterus from various pathologies using a surgical device - a curette) with further histology is carried out:
- in case of a frozen pregnancy or stillbirth of a baby;
- excessive growth of the endometrium;
- suspected uterine cancer;
- frequent intermenstrual bleeding;
- preparation for surgery;
- the need to remove a polyp on or inside the cervix;
- infertility;
- after a miscarriage, since parts of the fetal tissue may remain in the cavity of the reproductive organ, which can cause infection;
- chronic endometritis;
- bloody discharge during menopause.
Histology after curettage shows the exact causes of dangerous diseases of the female reproductive system, as well as their nature.
The most common ones that cause pathological growths include:
- secretion of estrogen in greater quantities than progesterone;
- disruption of the endocrine glands;
- consequences of abortion;
- severe and frequent stress;
- sexually transmitted diseases, inflammation, infections of the female reproductive system.
After hysteroscopy with curettage has been performed, the gynecologist prescribes treatment based on the results of the tests obtained. In a woman (if all the doctor’s recommendations are followed and postoperative therapy is carried out correctly), a new layer of endometrium grows in the uterine cavity.
To obtain the most informative and reliable results of the study, you need to prepare for curettage, following all the doctor’s recommendations.
Histology in gynecology after curettage
Histological examination of the uterine mucosa allows us to study in detail the effect of sex hormones on the endometrium.
The diagnostic method is widely used to identify the causes of pathology of reproductive function. In response to cyclical changes in hormones, a restructuring of the endometrium occurs in a healthy woman’s body - within 21-28 days, its thickness and cell structure change from one to seven millimeters. Each menstrual cycle ends with the destruction and removal of part of the epithelium of the uterine cavity, accompanied by menstrual flow. What happens when this process is disrupted? Gynecologists get the answer to this question with the help of diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity.
They prescribe treatment based on the results of histology after curettage. Only with the help of this most informative method can one distinguish malignant cells from benign ones and determine the degree of cancer germination.
Proper preparation for the procedure
At least two days before curettage, it is necessary to exclude:
- sexual intercourse;
- douching;
- washing the external genitalia using cosmetics.
Taking any medications must be agreed upon with your doctor. The fact is that many drugs can affect blood clotting, which can cause serious blood loss after surgery.
The curettage procedure is carried out in the second half of the menstrual cycle, when the woman does not have menstruation. Otherwise, the result may not be entirely correct, and surgery at the beginning of the cycle will provoke prolonged bleeding. This happens because the uterine mucosa grows before ovulation, stops developing closer to menstruation, and then is completely rejected.
If the time of curettage is chosen incorrectly, then the hormones synthesized by the ovaries will come into conflict with the endometrial layer that is unnaturally small for this time of the cycle and will not allow it to grow to the required size.
Before the procedure, you must undergo the following examinations:
- general blood analysis;
- Ultrasound of the uterus;
- ECG;
- vaginal smear;
- blood for hepatitis B and C, RW, AIDS;
- diagnostics of blood clotting.
It is also necessary to thoroughly remove all vegetation from the pubis and perineum. On the morning of the procedure, you should not eat or drink anything.
Histology analysis
After curettage of the uterus, parts of the mucous membrane from the cervical canal and the organ itself are placed in different clean test tubes, which are sent to the laboratory for research. There they accurately determine the structure of the tissue taken from the woman.
Since the material is studied under a microscope, an experienced doctor can easily recognize any abnormalities (malignant tumors, cells ready for degeneration) or the mucous membrane in a normal state.
The evaluation of the analysis lasts 5–12 days. In some cases, deadlines are accelerated, but this may affect the reliability of the results. In the course of a complex multi-level study, healthy tissue is compared with material affected by pathology.
Analysis transcript
After a qualified doctor has performed curettage and sent the material for analysis, and the laboratory assistant has correctly assessed the endometrial cells received for research, the woman receives a written report on the work done. It explains all indicators and terms, and also indicates whether any pathological changes are present in the lining of the uterus.
It is very difficult for persons without medical education to correctly understand the decoding. Therefore, with such a conclusion, you need to go to your gynecologist so that he can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
As a rule, the form indicates:
- From which part of the female genital organs was the tissue taken for analysis?
- How and with what reagents the procedure was carried out.
- Types of tissue identified, such as benign or malignant tumors, parts of an embryo (from a frozen pregnancy), polyps, cells that can develop into cancer, and much more.
Depending on what is indicated in the conclusion, further therapy is developed. Therefore, you need to read the transcript with a doctor at the clinic, and not with colleagues in misfortune on the forum.
How long does tumor histology take?
Histological examination helps to accurately determine the presence of dangerous cells and neoplasms. Histology is carried out to study tissues of different organs and systems. The difference between this research method and others is the increased accuracy of obtaining results.
Modern examinations of the body are carried out in different ways: examinations, tests, ultrasound. But these methods do not always allow an accurate diagnosis or detection of pathogenic cells and foreign formations. There is a more accurate method for this called histology. Many have heard about a smear for histology, but not everyone knows what it is.
The histological research method makes it possible to study cells and tissues and identify developmental pathologies. This method is often used in gynecology and other areas of medicine. If you do not know what a histology analysis means, how it is done, and what results it shows, we will help you figure it out.
How is a histology analysis done?
Many people do not know how to take a histology test. The study is unlike any of the usual research methods. Depending on which organ needs to be checked, the form of analysis varies: smears, prints, sections or tissue films. The analysis algorithm must be accurate and all research rules must be followed.
After the doctor receives a piece of tissue, it must be placed in formalin or ethanol, cut into a thin section and stained using special means. Methods for dyeing cut fabrics also vary. The most commonly used is hematoxylin and eosin. Due to exposure to dyes, the color of the fabric composition changes.
For example, hematoxylin colors nucleic acids blue, and with its help proteins turn red. After the procedures are completed, the specialist examines the prepared sample using an electron microscope for the presence of pathogenic and dangerous cells. But there is another way to perform histology.
In some cases, tissue sections are placed in a special balm or paraffin, and the resulting samples can be stored.
And, if possible, conduct research using various microscopes: light, scanning, electronic, fluorescent and others.
Using a phase contrast microscope allows you to view images of samples that cannot be seen using conventional microscopy.
The required tissue sample is collected using a puncture needle, bone trephination, or aspiration.
What does the histology analysis show?
This analysis is not always required. Why is histology done? Histology is necessary in the following cases:
- To determine the presence of cancerous tumors in the body, this is the most common reason why a histological examination is performed. Studying tissues using this method allows you to determine whether there are dangerous cells in the body; To identify the causes of infertility; To study the condition of the female genitourinary system; To determine the inflammatory process in the organs of the digestive system.
How long does a histology analysis take?
To the question of how long it takes to perform histology, each clinic gives its own answer. On average, the result of the study becomes known 7-10 days after taking a tissue sample.
The time it takes to obtain the result also depends on the availability of your own laboratory on the territory of the medical institution. With the existing laboratory, the time required for performing histology is significantly reduced.
When ordering a histological examination from a third-party laboratory, delivery of the result may take 2-3 days or more. There is also express diagnostics, which is carried out in the operating room.
If during surgery a patient is suspected of having malignant tumors, a tissue sample can be examined under a microscope in a short period of time. If the result is positive, the surgeon must perform an extended operation, taking into account the rules for removing oncological formations.
Results and interpretation of histology analysis
The results of histology tests are given to the patient in the form of a written report. It will indicate whether there are abnormalities in cells and tissues.
But not everyone will be able to decipher the result. To correctly interpret histology tests, you must at least have a medical education.
Information about the study is provided in Latin using medical terms.
If you had a histological examination performed at a government institution on the direction of a doctor, you will be able to find out about the results at his appointment.
When you contact a private medical clinic, you will receive a conclusion in your hands. The form will contain the following information:
- patient's personal data; what type of tissue was taken for study; sample collection site.
Next, the method and time of the study are indicated. What solutions were used to study the tissue samples taken - information is also indicated in the form. The main conclusion about the histology parameters is described at the very end. Don't worry if you see a lot of information. This does not mean that many abnormalities or pathologies have been found.
The specialist who conducted the study lists not only possible tumors, but also the detection of all tissues. You are unlikely to read the conclusion in Latin on your own. Therefore, after receiving the test results, consult a doctor, who will also advise you on possible treatment or preventive measures.
Regardless of whether the histology results may be positive or negative, no recommendations are indicated in the conclusion.
Can a histology test be wrong?
Many patients, after receiving a histological conclusion about the presence of a malignant tumor, want the result to be erroneous. But, unfortunately, errors in histology are extremely rare. This research method is considered the most accurate and, in some studies, allows not only to determine the presence of malignant cells, but also the cause of their appearance.
Despite the accuracy of the histological method, experts do not deny that there is a small percentage of incorrect and inaccurate studies. But if the procedure for taking a tissue sample and the algorithm of action during the study were followed, then the result cannot be erroneous.
Histology - analysis
Histology
is an analysis of a tissue sample taken from an organ, which is the leading basis for making a diagnosis. In modern medicine, the method is considered one of the most reliable. It is often of paramount importance when making a diagnosis and determining the type of therapy.
What does the histology analysis show?
The examination of tissue samples is carried out for the purpose of:
- identifying inflammation in the digestive system; determining the causes of infertility; diagnosis of oncological conditions; determining the condition of the uterus and other female organs; correction of therapy for diseases of internal organs (liver, kidneys, etc.).
Source: https://gemoglobin.top/skolko-vremeni-delaetsja-gistologija-opuholi/
Recovery period
In the first few days, a woman may be bothered by bleeding after curettage. They can be minimized if you lie in bed for the first day, getting up only in extreme cases. To avoid complications after the procedure, gynecologists prescribe a course of antibiotics. For your own safety, you should not ignore this recommendation.
Within a month after curettage and histological examination, women are prohibited from:
- Have sex. This is necessary so that the cervix closes completely and no infection gets into the affected area.
- Douche.
- Use vaginal tampons.
- Take hot baths, visit baths or saunas.
- Lift weights.
The menstrual cycle is restored approximately 4 months after the procedure, because the ovaries are sensitive to treatment of this kind. They need to get used to the renewed endometrium and start working in sync with it.
Recovery will be faster if you rest more and strictly follow doctors' recommendations.
Histology after curettage of the uterus is prescribed to the patient in order to find out exactly what changes have appeared in the mucous membrane. This study is carried out only if there are certain indications for it. Before histology, special preparation is necessary. As for the procedure itself, its purpose is to take material for further diagnostic research.
Recovery after curettage
To ensure that the recovery process after cleaning the cervical canal is easy and without complications, a woman should follow the basic rules:
- In the first 2 months, avoid sexual intercourse.
- Do not visit the sauna or bathhouse until recovery.
- Avoid taking hot baths and visiting public pools.
- Observe personal hygiene rules and avoid using soaps and gels that have a strong odor.
- Avoid using tampons in the first 3 months after the intervention.
- Do not take blood thinners.
If the operation was performed for diagnostic purposes, after receiving the results it will be possible to give a conclusion about the diagnosis and make a prognosis for further recovery. The therapeutic procedure allows you to remove pathological tissues and growths, saving the patient from the disease. To avoid consequences, a woman must follow all doctor’s recommendations before and after the intervention.
The patient is advised to receive immediate medical attention if the following symptoms appear:
- acute pain in the lower abdomen;
- fever;
- massive blood loss;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness.
Attention! Such a clinical picture indicates the development of dangerous complications.
If there are no symptoms indicating the development of a complication, the woman should visit a doctor 2 weeks after the operation. After visiting a specialist, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the uterus.
Proper preparation for the procedure
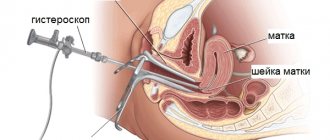
The essence of histology, which is carried out after curettage, is to study a small amount of the uterine mucosa, removed using a special instrument. This procedure, like resectoscopy, is carried out in order to diagnose various gynecological diseases in a woman’s body and cure them. Very often, curettage is performed together with hysteroscopy. The last procedure is to examine the inside of the uterus. For this, a special optical device is used.
Before curettage and histology, the patient is prescribed tests.
If a woman is taking any medications or dietary supplements, she must stop taking them 14 days before the procedure. If they are vital, this is discussed separately with the attending physician.
This prohibition before performing histology after curettage is due to the fact that some of the medications can have a bad effect on blood clotting. As a result, the risk of bleeding may increase.
If the patient is taking medications for hypertension, epilepsy, or has existing heart problems, this procedure can be performed. This will not affect the histology results in any way. But the patient must inform the doctor that the patient is taking these drugs.
Also, a few days before the histology, you should:
- stop sexual intercourse
- stop using intimate hygiene products (special gels or soaps),
- do not use vaginal suppositories,
- a ban is also imposed on douching.
When carrying out hygiene procedures, a woman is allowed to use only warm water.
Indications for use
Curettage is carried out when it is necessary to confirm the development of a pathological process in the cervix or eliminate it. The range of indications for intervention includes:
- polypous neoplasms;
- uterine fibroids;
- the presence of glandular-cystic growths;
- dysplasia;
- oncological processes;
- uterine bleeding;
- fusion of the cervical canal;
- adenomyosis.
The procedure is also carried out after spontaneous abortion in order to cleanse the uterine cavity of the fertilized egg or ensure its absence. Curettage is also carried out in cases where a woman cannot become pregnant in order to establish the cause of such a deviation. There is often a connection with pathological proliferation of endometrial tissue. Therefore, we can conclude that the operation has not only diagnostic, but also therapeutic value. To increase the information content, the method is combined with a biopsy.
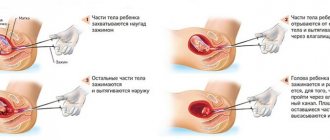
Carrying out
The histology procedure after curettage of the uterus is carried out as follows: the patient lies down on a gynecological chair in the operating room and the doctor injects anesthesia into her vein. In order to see the cervix, a special speculum instrument is placed into the patient’s vagina.
After this, the specialist will expand the cervical canal, which is located in the cervix. To perform histology, the doctor will insert a probe into the cervical canal. If necessary, such a tool will be replaced with one that has a larger diameter.
“Cleansing” the uterus is not a way to treat endometrial hyperplasia and chronic endometritis
Dmitry Lubnin obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences
“I was cleaned” or “I was cleaned” - I often hear these phrases from my patients, and they sound to me as unbearable as the movement of foam plastic on glass. We colloquially call “cleaning” curettage of the uterus - the most common procedure performed in gynecology in the vast majority of cases without any indication for it.
This very established name - “cleaning” - already reflects a rough, clumsy and primitive approach to solving the problem. By the way, the term smoothly passed from medical jargon into the vocabulary of many women who even believe that they need to “get clean” or “get clean” from time to time. Perhaps they put the same meaning into this as the notorious “cleansing the body of toxins,” suggesting that “dirt” accumulates in this organ too.
Before continuing the story, it is necessary to explain what exactly we are talking about.
After curettage of the uterus: possible risks
Curettage is an outpatient medical procedure performed under intravenous anesthesia, during which the uterine mucosa is removed (scraped) using a special curette. The procedure is called therapeutic and diagnostic, since it removes disease-modified tissue (if any), which can be examined under a microscope and an accurate diagnosis made. From the previous sentence it is clear that curettage is carried out not only in the presence of a disease, but when it is suspected, that is, for the purpose of making a diagnosis.
So far everything is clear, logical and obvious. However, there is another side to this manipulation. The procedure is performed with a sharp iron curette, with the help of which the mucous layer of the uterus is actually “torn off”, and inevitable injury to the uterus itself occurs. As a result, there is a risk of several serious complications: damage to the growth layer of the endometrium (impairing its growth in the future), the appearance of adhesions in the uterine cavity, and the development of inflammation.
In addition, this procedure contributes to the development of a disease such as adenomyosis (endometriosis of the uterus) - due to the violation of the boundary between the layers of the uterus, which contributes to the growth of the endometrium into the muscle of the uterus. As a result, curettage may lead to problems with conception or trigger the development of adenomyosis.
It is quite obvious that such a procedure must be done strictly according to indications and the benefit-risk ratio must be seriously assessed. But this is possible anywhere, but not here, and this is very sad.
What is curettage
Curettage is an invasive method that allows you to collect material for diagnostics. During the procedure, the surface layer of cells is scraped off, and then a biopsy is examined. The list of indications for manipulation is quite extensive. The procedure is used to refute the diagnosis of cervical cancer in case of inaccurate results of colposcopy and cytology in identifying oncogenic strains of human papillomaviruses.
Attention! Endocervical curettage or curettage is the mechanical removal of the surface layer using a small curette. There is a risk of complications after the intervention, but it is minimal.
The research allows:
- obtain a volumetric sample without significant tissue trauma;
- determine the depth of the foci and the area of distribution of atypical cells;
- obtain information about the ongoing process with minimal risks of receiving a false answer;
- avoid chemical or physical effects on the cervix.
The main indication for diagnostic measures is the detection of neoplasms in the cervical canal. The procedure is prescribed if the growth of atypical cells in the uterine cavity is observed. You need to understand that the detection of atypical cells in cytology after curettage is not a reason to talk about the development of an oncological process. Such a response may indicate the presence of a predisposition to the oncological process in the patient and signal the development of a precancerous condition.
Scraping “just in case”
I think that in more than 80% of cases, curettage is carried out in vain, that is, either without any indication at all, or in cases where the problem can be solved with medication or through a simple outpatient procedure.
Here are situations in which you may be asked to perform curettage.
- You have been bleeding for a long time or have uterine bleeding.
- An ultrasound revealed that you have an endometrial polyp, endometrial hyperplasia, adenomyosis, uterine fibroids, or chronic endometritis.
- You are planning to undergo surgical treatment for uterine fibroids.
- You suspect an ectopic pregnancy.
- You complained that you have heavy menstruation, intermenstrual spotting or brown “spotting” before and/or after menstruation.
In general, people are sent for “cleaning” very often, even in the absence of the reasons that I listed above. Curettage often accompanies any surgical treatment in gynecology. It’s as if they are always trying to do it “at the same time”, in order to “check, just in case,” whether everything is normal. It shouldn’t be this way; this is too frivolous an attitude towards a rather traumatic procedure.
When not to agree to scraping
So, instructions on how to avoid scraping.
- If you do not have heavy uterine bleeding (as they say, “it pours down your legs”), but just prolonged bleeding and pregnancy (uterine and ectopic) is excluded, ask your doctor about the possibility of stopping the bleeding with medication. Yes it is possible. While taking the drug (I will immediately warn you that this is a hormonal drug, but it is safe), the bleeding may stop, and your condition will need to be re-evaluated after the next menstruation. In many cases, the treatment provided will be sufficient and nothing more will need to be done.
- If during an ultrasound you are found to have a polyp or endometrial hyperplasia, do not rush to agree to curettage. Ask your doctor about the possibility of prescribing the drug for you this cycle and then repeat the ultrasound after the end of the next menstruation. If a polyp or hyperplasia is confirmed, alas, curettage must be done under hysteroscopy control. But you have a very high chance that after menstruation there will be no indication for the procedure.
A polyp is a growth on the lining of the uterus (looks like a finger or mushroom), most often benign. There are polyps that are rejected during menstruation, and those that grow from the germ layer. The latter require removal.
Hyperplasia is a thickening of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity. There are two types: simple and complex. Simple hyperplasia occurs most often, it is not dangerous, for its development there must be a mandatory reason (functional cyst in the ovary, polycystic ovary syndrome and several more). Usually, 10 days of taking the drug is enough for it to go away and not recur.
Complex hyperplasia - bad hyperplasia, an error in the structure of the endometrium, usually occurs after 35 years, more often against the background of excess body weight. It is treated first by removing the mucous membrane (scraping) and then by a multi-month course of hormonal drugs or by installing a Mirena intrauterine hormonal device. An accurate diagnosis is only possible with histological examination.
- If you are asked to do curettage only for diagnostic purposes before surgery or to clarify the condition of the mucous membrane, ask the doctor to start with an endometrial biopsy (also called a “pipe biopsy” or “aspiration biopsy”). This is a simple outpatient procedure that does not require any anesthesia. A thin tube is inserted into the uterine cavity and a small amount of tissue is sucked in, which is then sent to the laboratory for examination. This is a fairly informative analysis.
Important: the material obtained as a result of curettage or biopsy is only the mucous membrane of the uterus; it does not carry any information about other diseases. The fact is that curettage is often prescribed for the purpose of assessing uterine fibroids for its characteristics; So, scraping will not give any information.
- Remember, almost all modern ultrasound machines allow you to evaluate the uterine mucosa and identify signs of pathology in it. If the doctor writes during an ultrasound that the endometrium is not changed, and you do not have heavy menstruation or intermenstrual bleeding, then the likelihood that you have a pathology that requires curettage is close to zero.
- In general, the main manifestations of endometrial pathology (curettage is aimed only at this tissue) are bleeding, heavy menstruation and intermenstrual spotting. Thus, if you do not have this, discuss with your doctor whether his desire to perform curettage is justified.
- “Chronic endometritis” is a common diagnosis on ultrasound and in the results of histological findings after curettage. We are talking about chronic inflammation of the uterine mucosa. However, there are no generally accepted criteria for making this diagnosis using ultrasound in evidence-based medicine. Simple histology also cannot reliably confirm this diagnosis. Often this diagnosis is made where it does not exist, since they focus on “leukocytes”.
A reliable diagnosis is possible only by conducting a special type of study - immunohistochemistry. This study is not available in all laboratories, and the material for it can be obtained by biopsy rather than by curettage. I think it is now clear that curettage is not necessary to confirm the diagnosis of chronic endometritis. In general, the diagnosis and treatment of this endometrial disease makes sense only within the framework of the problem of infertility and miscarriage.
Histology of the neoplasm
Histological examination of neoplasms is an analysis of tissue taken from the patient under a microscope.
This procedure allows you to make the most accurate diagnosis if the disease is associated with the occurrence of neoplasms. Consequently, the effectiveness of the selected treatment depends on the correct diagnosis. For example, a visually ordinary mole does not cause concern, but it can become malignant at any time, therefore, in order to determine the type of mole and understand what to do with it next, a histological examination is prescribed.
Purpose of prescribing histological examination
Histological examination of neoplasms is prescribed to analyze the dynamics of the growth of a malignant tumor, changes in tissues that occurred after therapy (the effectiveness of treatment is checked), establishing indications for radical surgery, differentiating malignant and benign neoplasms, the presence of a tumor in the early stages of its development, staging the maximum accurate diagnosis.
If the results of the study demonstrate the presence of a pathological process, the doctor selects an effective treatment package in accordance with the diagnosis. It is important to remember that timely diagnosis is the key to successful and short-term treatment, which is possible without surgical intervention.
Two methods are used for research: studying tissues that were obtained during surgery and biopsy (targeted excision of a small piece of tissue for research).
It is important to understand that any wart can be cancer, and a mole can be a malignant tumor, and only histological diagnosis will determine the type of tumor.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
Among the contraindications it is worth noting:
- the presence of blood diseases (including poor blood clotting);
- diabetes;
- acute viral and infectious diseases;
- serious central nervous system disorders (congenital or acquired);
- stage 4 cancer.
It is also necessary to tell your doctor about the presence of drug treatment and allergies to anesthesia.
This type of diagnosis is prescribed if the presence of a tumor has already been established and it is necessary to determine its type and stage, if cosmetic removal of tumors on the skin is necessary, as well as to determine the etiology of tumors, etc.
In other words, histological examination of neoplasms makes it possible to establish the diagnosis as accurately as possible. An analysis is also prescribed if there is a suspicion of polyposis.
Polyps can form in the body of the uterus, small and large intestines, stomach, nose, and other places where there are mucous membranes.
Algorithm for histology of neoplasms
The first thing you need to do is consult a doctor (gynecologist, gastroenterologist, ENT specialist, therapist, dermatologist, surgeon) - the choice of doctor depends on the symptoms. The doctor collects the necessary biological material (aspiration, suction, puncture, collection of secretions from the tumor, mucosal smear).
The resulting biological material is placed in formaldehyde (the solution in volume should be ten times the volume of the material being tested).
The jar with the formaldehyde solution is marked, indicating the patient's data, the date and area of collection of the histological sample. The doctor issues a referral for histology, in which he indicates all the necessary data, including bad habits.
On the day of tissue collection, after all documentation has been completed, the excised tissues in formaldehyde solution are transferred to the pathologist. The doctor first stains the obtained samples (special dyes are used), then the process of complete dehydration occurs. After dehydration, the samples are placed in paraffin.
The cube of the resulting paraffin is cut into thin slices, which are then placed on glass and examined by a specialist under a powerful microscope.
If no errors were made during the collection of tissues and cells, as well as in the histology algorithm, the results are as accurate as possible and allow you to diagnose the type and stage of the tumor.
Taking materials for research will in no way speed up or stop the development of the tumor.
A great danger to the human body is the constant traumatization of the neoplasm, as well as late diagnosis.
The average duration of histology of neoplasms after tissue sampling is three days. The doctor may also prescribe an emergency diagnostic test. It is usually prescribed during the operation.
Often the outcome of the operation will depend on the result obtained. Emergency diagnostics do not involve drying samples; they are simply frozen. The patient can receive the results in the form of a conclusion, or they will be transferred directly to the attending physician.
In any case, the attending doctor will decipher the conclusion in order to decide on further actions. Often, after receiving the results, the patient is referred for additional studies. The doctor can also refer you to other specialists in this field.
What can the analysis show?
Histology analysis is not prescribed in all cases. Histology of neoplasms is necessary to determine the inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract, to diagnose pathological changes in the female genital organs, to determine the causes of infertility, and to diagnose cancer.
In rare cases, analysis shows false results; according to statistics, 98% of histology shows true results, which makes it possible to establish a diagnosis and determine further actions.
Histology of the neoplasm
updated:
June 8, 2018
Source: https://FoodandHealth.ru/meduslugi/gistologiya-novoobrazovaniya/
In what situations should you agree to scraping?
- Heavy uterine bleeding: yes, curettage is a way to stop it.
- Suspicion of ectopic pregnancy (difficulty in making a diagnosis).
- Polyp or endometrial hyperplasia that has not disappeared after menstruation or drug treatment.
- Remains of membranes (after abortion, miscarriage, pregnancy).
- Any spotting after menopause.
Now, I hope you have reliable instructions on how to avoid possibly unnecessary surgery for you. Don't be afraid to ask your doctor questions. Offer alternatives (endometrial biopsy, medication). Ask to justify the need for curettage. The answer “that’s how it is with us” should not be accepted. Of course, all this applies only to those situations in which there is no threat to your life and health (excessive bleeding).
Histology after curettage of the uterus is prescribed to the patient in order to find out exactly what changes have appeared in the mucous membrane. This study is carried out only if there are certain indications for it. Before histology, special preparation is necessary. As for the procedure itself, its purpose is to take material for further diagnostic research.
Proper preparation for the procedure
The essence of histology, which is carried out after curettage, is to study a small amount of the uterine mucosa, removed using a special instrument. This procedure, like resectoscopy, is carried out in order to diagnose various gynecological diseases in a woman’s body and cure them. Very often, curettage is performed together with hysteroscopy. The last procedure is to examine the inside of the uterus. For this, a special optical device is used.
Before curettage and histology, the patient is prescribed tests.
If a woman is taking any medications or dietary supplements, she must stop taking them 14 days before the procedure. If they are vital, this is discussed separately with the attending physician.
This prohibition before performing histology after curettage is due to the fact that some of the medications can have a bad effect on blood clotting. As a result, the risk of bleeding may increase.
If the patient is taking medications for hypertension, epilepsy, or has existing heart problems, this procedure can be performed. This will not affect the histology results in any way. But the patient must inform the doctor that the patient is taking these drugs.
Also, a few days before the histology, you should:
- stop sexual intercourse
- stop using intimate hygiene products (special gels or soaps),
- do not use vaginal suppositories,
- a ban is also imposed on douching.
When carrying out hygiene procedures, a woman is allowed to use only warm water.
Carrying out
The histology procedure after curettage of the uterus is carried out as follows: the patient lies down on a gynecological chair in the operating room and the doctor injects anesthesia into her vein. In order to see the cervix, a special speculum instrument is placed into the patient’s vagina.
After this, the specialist will expand the cervical canal, which is located in the cervix. To perform histology, the doctor will insert a probe into the cervical canal. If necessary, such a tool will be replaced with one that has a larger diameter.
Conditions for which histology is used
The information obtained through histological analysis makes it possible to promptly begin treatment in the early stages of the disease. Sometimes it even helps prevent unnecessary surgery. Most often, histology is performed after curettage, but is mandatory in other cases:
- Stillbirth or frozen pregnancy.
- The endometrium or cervix is in a hyperplastic state.
- Chronic form of endometritis.
- Unclear picture after colposcopy.
- Neoplasms on the uterus.
- Negative results of cytological analysis.
- Bleeding that is acyclic in nature.
- Miscarriage or infertility.
- Bleeding during menopause.