Lactational amenorrhea
The first month after childbirth, while the postpartum “menstruation” (lochia) lasts, the woman is considered completely sterile and incapable of conceiving. At this time, the uterus contracts, cleanses and restores itself (its surface is a huge bleeding wound).
The hormone prolactin rules the female body at this time. It is he who is responsible for milk production and indirectly contributes to uterine contractions. In addition, it suppresses the production of hormones responsible for the normal menstrual cycle. Therefore, the ovaries are temporarily “turned off” - the follicles do not mature, ovulation does not occur, and menstruation does not come.
If after childbirth a woman does not breastfeed, prolactin gradually disappears and the cycle is restored, so menstruation can come quite early - 2-3 months after childbirth. If the baby is on environmentally friendly breastfeeding, then the woman experiences so-called lactational amenorrhea - a period when she is unable to conceive due to breastfeeding.
Ecological is called feeding on demand, without supplementary feeding, complementary foods and the use of pacifiers, with the obligatory preservation of night feedings.
The period of lactational amenorrhea lasts about six months, but it is not a 100% contraceptive method, since each woman’s body is individual and everyone’s body recovers differently.
However, while a woman is breastfeeding, feeding on demand and not according to a schedule, under the influence of the hormone prolactin, her body inhibits the restoration of the cycle. If all the rules of Eco-GW are followed, then your period will come after you stop breastfeeding.
Reasons for missed periods
Stress
Regulation of the menstrual cycle is a complex process that depends on many factors in the internal environment of the body. The functioning of the hormonal system is very susceptible to stress and emotional upheaval. This feature is the result of the close interaction between the endocrine glands and the brain.
Psychological and emotional stress is an unfavorable environment for pregnancy. This is why the brain gives a signal to the endocrine system that conception should not occur. In response to this, the hormonal glands change their mode of operation, preventing the onset of ovulation.
A delay in menstruation can be caused by various stresses. Some women calmly endure severe shocks (the death of a loved one, diagnosis of an illness, dismissal from work, etc.). In some patients, the absence of menstruation may be associated with minor experiences.
Possible causes of missed periods also include severe lack of sleep and overwork. To restore the cycle, a woman should eliminate the provoking factor. If this is not possible, the patient is advised to consult a specialist. Usually, a delay in menstruation during stress does not exceed 6-8 days, but in severe cases, it may be absent for a long time - 2 weeks or more.
Heavy physical activity
By its nature, the female body is not adapted to strong physical activity. Excessive forceful tension can cause disruptions in the menstrual cycle. Such disorders of the reproductive system are quite often observed among professional athletes.
The reason for the delay of menstruation during heavy physical activity is the production of increased amounts of testosterone, the male sex hormone. Thanks to it, muscle tissue can grow in response to its tension. Normally, the female body contains a small amount of testosterone, but its increase leads to disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
High levels of testosterone affect the complex mechanisms between the pituitary gland and the ovaries, which disrupts their interaction. This leads to a lack of ovulation and delayed menstrual bleeding.
If there are disruptions in the menstrual cycle, a woman should avoid strength training. They can be replaced with aerobic exercises - dancing, running, yoga.
What are the reasons for a delay in menstruation?
https://youtu.be/d83d4nrCgDY
Climate change
Sometimes the human body has difficulty adapting to new living conditions. A sudden change in climate can cause menstrual irregularities. This feature is most often observed when traveling to hot and humid countries.
Changes in environmental conditions are a signal of the need to prevent conception. This mechanism is similar to the delay of menstruation during emotional stress and shock. The brain sends a signal to the ovaries to block ovulation.
Another reason for a missed period with a negative pregnancy test is prolonged exposure to the sun. Ultraviolet rays have a negative effect on the functioning of the ovaries. A delay may occur if you abuse the solarium.
Typically, the duration of delayed menstrual bleeding when traveling does not exceed 10 days. If it is absent for a longer period, the woman should consult a specialist.
Hormonal changes
In teenage girls, during the first 2-3 years after menarche, jumps in the cycle are possible. This feature is a normal phenomenon associated with the regulation of ovarian activity. Usually the cycle is established by the age of 14-17 years; if menstruation delays continue after 17-19 years, the girl should consult a specialist.
The reason for a delay in menstruation after 40 years is the onset of menopause, characterized by the decline of reproductive function. Typically, the menopause period lasts for 5-10 years, during which there is a gradual increase in the period between bleedings. Quite often, menopause is accompanied by other symptoms - a feeling of heat, sweating, nervousness, and surges in blood pressure.
Also, a long delay in menstruation is a natural reaction of the body after pregnancy. During breastfeeding, the pituitary gland produces a special hormone - prolactin. It causes blocking of ovulation and absence of menstrual bleeding. This reaction is intended by nature, since the female body must recover after childbirth.
If a woman does not breastfeed immediately after giving birth, her normal cycle will return after about 2 months. If a young mother begins lactation, menstruation will occur after it ends. The total duration of delayed bleeding should not exceed one year.
Natural hormonal changes occur after discontinuation of oral contraceptives. While taking them, the ovaries stop functioning, so they need 1-3 months to recover. This reaction of the body is considered absolutely normal and does not require medication adjustment.
Another reason for a delay in menstruation for a week or more is taking emergency contraception (Postinor, Escapelle). These drugs contain artificial hormones that block the synthesis of their own. Due to this effect, ovulation is blocked and the menstrual cycle shifts.
Lack of body weight and poor nutrition
Not only the endocrine glands, but also adipose tissue participate in the endocrine metabolism of the female body. Its percentage of body weight should not be lower than 15-17%. Adipose tissue is involved in the synthesis of estrogens - female sex hormones.
Inadequate nutrition causes severe weight loss, which leads to amenorrhea - absence of menstruation. With severe underweight, cyclic bleeding may not be observed for a long period of time. This feature is adaptive in nature - the brain sends signals that the woman will not be able to bear a child.
Constant delays in menstruation may be associated with insufficient intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E into the body. These substances participate in the endocrine function of the ovaries, causing the normal division of female germ cells.
To restore the cycle, a woman should gain the missing kilograms and reconsider her diet. It should include sea fish, red meat, nuts, and vegetable oil. If necessary, vitamin E supplements can be used.
Obesity
Weight gain can cause menstrual irregularities. The mechanism of pathology of reproductive function is associated with blocking ovulation due to excessive accumulation of estrogens in adipose tissue.
Also, against the background of obesity, insulin resistance occurs - a condition in which the cells of the human body become less sensitive to insulin. In response to this, the pancreas begins to synthesize increasing amounts of the hormone. A persistent increase in the amount of insulin in the blood increases testosterone levels.
An increased amount of male sex hormones disrupts the normal menstrual cycle. That is why women are advised to monitor their weight and avoid obesity.
Infectious process
Any inflammatory process disrupts the normal course of the female cycle. The body perceives it as a negative background for the onset of conception, and therefore blocks or delays ovulation.
One of the most common causes of delayed menstrual bleeding is colds and other diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Usually, with such pathologies, the cycle shifts by no more than 7-8 days.
Specific diseases of the genitourinary organs (cystitis, thrush, vaginosis) can cause prolonged absence of menstruation due to disruption of the internal organs. If a woman has pain or tightness in her lower abdomen, pathological discharge from the genital tract is observed, body temperature rises, or pain occurs during sexual intercourse, she should consult a specialist.
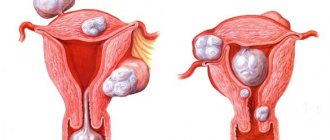
Polycystic ovary syndrome
This pathology is characterized by multiple changes in hormonal levels, causing blocking of ovulation and a shift in the menstrual cycle. In polycystic ovary syndrome, the endocrine function of the pituitary gland is disrupted. This leads to the maturation of several follicles, but none of them becomes dominant.
With polycystic ovary syndrome, an increased amount of male sex hormones is observed in a woman’s blood. They aggravate the course of the disease, further preventing ovulation. Quite often, against the background of pathology, insulin resistance is observed, which increases the secretion of testosterone.
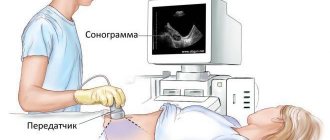
To diagnose the disease, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination. An ultrasound shows enlarged ovaries with many follicles. With pathology, an increase in androgens (male sex hormones) and their derivatives is observed in the blood. Quite often, polycystic ovary syndrome is accompanied by external symptoms - male pattern hair growth, acne, seborrhea, low timbre of voice.
Treatment of the pathology includes taking hormonal contraceptives with antiandrogenic effects. When planning a pregnancy, the expectant mother may be advised to stimulate ovulation with the help of drugs.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a disease characterized by decreased function of the thyroid gland. There are many factors that cause this condition - iodine deficiency, pathologies of the pituitary gland, trauma, autoimmune damage.
Thyroid hormones are responsible for all metabolic processes in the human body. With their deficiency, a decrease in reproductive function is observed due to blocking ovulation. That is why, with hypothyroidism, long delays in menstruation, even its absence, are often observed.
To diagnose pathologies of the thyroid gland, ultrasound examination and calculation of the amount of hormones in the blood are used. Treatment is based on the type of disease and may include iodine supplementation, replacement therapy, or surgery.
Hyperprolactinemia
This disease is characterized by increased synthesis of the pituitary hormone prolactin. Its excess quantity blocks ovulation and disrupts the menstrual cycle. Hyperprolactinemia occurs due to injury, pituitary tumors, medications, or disruptions in hormonal regulation.
Diagnosis of pathology includes a blood test for hormones, as well as an MRI or CT scan of the brain. To treat this disease, medications called dopamine agonists are used.
Hyperprolactinemia: the main mechanism for the development of PMS
Pregnancy
Delayed menstruation is considered one of the very first signs of pregnancy. To confirm conception, the expectant mother can use test strips that determine the level of hCG in the urine. The most modern of them can detect pregnancy even before a missed period.
In addition to pregnancy, delayed menstruation can be caused by more rare pathologies and diseases:
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease (overproduction of adrenal hormones);
- Addison's disease (underproduction of the adrenal cortex);
- tumors of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland;
- damage to the endometrium of the uterus (as a result of surgery, cleaning, abortion);
- resistant ovarian syndrome (autoimmune disease);
- ovarian wasting syndrome (premature menopause);
- ovarian hyperinhibition syndrome (due to long-term use of oral contraception, radiation exposure).
When does your period come after breastfeeding?
After breastfeeding, periods can be restored in different ways. Sometimes they come immediately after the woman has finished breastfeeding, sometimes only after 1-2 months. This is due to the fact that for some time the hormone prolactin can be produced in fairly large quantities, so to speak, by inertia.
If the child refuses the breast on his own, menstruation will begin earlier, since this usually happens gradually - the baby eats less and less, and in the end does not ask for more breast. The body reacts sensitively to this and the amount of prolactin and milk also gradually decreases, which means that the restoration of the cycle is not delayed.
If the child had to be weaned for external reasons, then after breastfeeding is discontinued, in this case, menstruation may be delayed. It will take time for the body to understand that milk is no longer needed. Normally, such a delay lasts a month or two.
It also happens the other way around - breastfeeding continues, but the cycle has already been restored. This is usually associated with the introduction of complementary foods and the abandonment of night feedings. The child eats less milk during the day and does not stimulate prolactin at night, so the cycle is restored earlier. Read a detailed article about periods while breastfeeding.
Many women believe that they are unable to become pregnant before their first period. But you should understand that before your period, as a rule, ovulation occurs - and if the “stars align”, then it is absolutely enough to get pregnant and not wait for your period. And become the mother of charming weather.
However, the restoration process does not end there. After lactation, periods may differ significantly from the usual picture for some time.
Will menstruation become regular immediately?
The first periods after breastfeeding are often irregular and unstable. In some women they are abundant, in others, on the contrary, they can be scanty. There can be quite long intervals between them. This is especially true in those cases when a baby, who has almost given up breastfeeding, suddenly begins to breastfeed more often again.
Hormonal levels after feeding are usually restored within 2-4 cycles. At this time, the menstrual cycle is gradually restored. This process can be compared to trying to start a car - the engine starts and stalls, stalls again and again, and so on until it finally starts. Likewise, the female body, during feeding and after completion of breastfeeding, makes attempts over and over again to restore the cycle, until it fails - until estrogen and other hormones outweigh prolactin.
After cessation of lactation, you need to carefully monitor your body, notice when your periods come, how regular, heavy they are, etc., so as not to miss an alarm bell about possible “problems” in the body.
When to visit a doctor
If feeding took place on demand and also ended at the baby’s request, then periods after the end of lactation will come early and will immediately become quite regular. Moreover, after childbirth, the nature of menstruation often changes - they may become more abundant than before, or shorter/longer. Very often they become less painful than before childbirth.
If your period takes too long to return after breastfeeding, you should consult a doctor. Reasons for seeking help may include:
- too long breaks between menstruation (in the absence of reasons such as ongoing or intensified feeding);
- too much discharge;
- if two months after completion of breastfeeding there are no periods.
The doctor will be able to determine the cause of the disorder and tell you how to eliminate it in order to establish the cycle. This will most likely require an ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries, as well as a blood test for hormones. Excess prolactin after the end of breastfeeding may be a sign of the formation of a benign tumor - prolactinoma.
Heavy periods after breastfeeding may be a sign of uterine fibroids or endometriosis. During lactation they practically do not appear, but after its end they can make themselves known.
Restoring the cycle and the entire body as a whole is a delicate and lengthy process. You should make this work easier for your body as much as possible by carefully monitoring your diet, allowing yourself to rest and maintaining a good mood.
When did you start your period after giving birth?
When will your period come?
One of the questions that often arises in women after childbirth is the question of when the menstrual cycle should normally resume, and what is associated with either early or late onset of menstruation after childbirth. The absence of menstruation during pregnancy is due to hormonal changes in the woman’s body. From the moment of delivery, regardless of whether the birth took place naturally or through a cesarean section, the restoration of hormonal status begins. One of the signs of the end of the process is the first menstruation after childbirth. An important factor influencing the timing of restoration of menstrual function is breastfeeding. Prolactin, a hormone that ensures milk production in the mother's breast, suppresses the production of other ovarian hormones, and therefore menstruation may be delayed during breastfeeding. This has a certain biological meaning. While a woman is breastfeeding, she is not ready for another pregnancy, and prolactin protects her from untimely conception. However, unfortunately, this protection is not absolute, and when you have sex again, you will most likely need additional contraception.
The relationship between prolactin and sex hormones is individual for each woman, so if you have your period 2-3 months after giving birth, this does not mean that you have little milk, but it means that your body has recovered from pregnancy and you can get pregnant again. If discharge appears earlier, especially heavy or accompanied by pain and fever, it is better to consult a gynecologist. Some particularly sensitive babies begin to turn their nose up at the breast during their mother's period - they believe that the taste of the milk is changing. If the child is still small, and the mother already has problems with milk, these whims may be very inappropriate. However, most mothers manage to save milk in this situation. Try pumping your baby's milk every three hours and breastfeeding when he's dozing - he'll probably be less fussy when he's half asleep. If you don't get your period within a year of giving birth or when you stop breastfeeding, you should still see a gynecologist. He will prescribe hormonal tests and decide whether such a long absence of periods is normal for you or whether treatment is necessary. Unfortunately, secondary infertility (infertility that occurs after the first birth) is by no means uncommon, so treat yourself carefully. There is another situation in which the absence of menstruation for a long time after childbirth indicates pathology. Sometimes, if there was heavy bleeding during childbirth, the areas of the brain responsible for regulating the production of hormones suffer, and real hormonal hunger begins in the body. There is no menstruation, but there is also no milk production in the breast. Later, the woman notices that she begins to lose weight, has dry skin, hair loss, gets tired quickly, suffers from dizziness and even loses consciousness as a result of a sharp drop in blood pressure. All of these changes can be mistaken for normal postpartum fatigue or symptoms of anemia. However, it is necessary to be examined by an endocrinologist, since only hormonal treatment in such a situation can save both the health and life of a woman. Fortunately, such cases do not occur often, but that is why they are worth thinking about.
There is also an opinion among women that if before childbirth menstruation was heavy, long and painful, then after childbirth this problem should disappear. In fact, often after childbirth the nature of menstruation changes. Your periods after giving birth may become more regular than they were before pregnancy, as well as less painful or completely painless. The fact is that the pain of menstruation, as a rule, is caused by a bend of the uterus, which impedes the outflow of menstrual blood. During childbirth, the curvature of the uterus naturally disappears, the relative position of organs in the abdominal cavity changes, as a result of which the position of the uterus becomes more physiological and pain during menstruation disappears.
Vaginal discharge - why is there bleeding and when will it end? Perineum - perineal care, Kegel exercises. Cervical erosion What is cervical erosion. Symptoms, treatment Sexual relationships How to resume sex after the birth of a baby without any problems?
Menstruation after childbirth - irregular cycle, delay, features
Zhanna Fedotova
If they don't notice you, it means they are seriously interested in you
calendar_today December 27, 2021 visibility
One of the most important questions that women ask about their health after pregnancy and childbirth is the establishment of the menstrual cycle, because menstruation is perhaps the main indicator of women's health.
After the birth of a child, against the background of renewal of processes occurring in general in a woman’s body, changes occur in her menstrual cycle.
Your periods may be delayed, irregular, or even disappear for a while. But you don't need to panic because this is all natural and normal. The speed of restoration and establishment of a woman’s menstrual cycle after childbirth depends on her physiological parameters, hormonal levels, the presence or absence of breastfeeding, stress, etc. In our article we will discuss menstruation after childbirth - irregular cycle, delay, features.
Features of menstruation after childbirth
As practice shows, the menstrual cycle after childbirth can become somewhat unpredictable and have a number of features. There is no specific time frame within which menstruation should begin after the birth of a child. The time of its onset is purely individual.
Many women note that for several months after giving birth they experience irregular menstrual cycles, and the periods themselves are sometimes very difficult. This is due to the fact that the female body needs some time to return to normal functioning.
Bloody discharge in healthy women should last no more than 3-7 days. Very short (a couple of days) or, conversely, too long menstruation, ending in bleeding, can indicate problems in the woman’s reproductive sphere - uterine tumors (fibroids), endometriosis (proliferation of endometrial tissue outside the uterus).
The volume of menstrual blood also matters. Normally it is 50-150 ml. Too much or too little menstrual flow also indicates pathology. The length of your cycle after childbirth may change. If before the birth of a child a woman’s cycle was, for example, 20-30 days, then after childbirth this figure can average out and amount to 25 days.
Often, mothers who have recently given birth develop the so-called premenstrual syndrome, in which the woman becomes very irritable, tearful, sometimes experiences dizziness, insomnia, increased hunger and even bouts of nausea.
Some women notice the appearance of menstrual pain that they did not experience before giving birth. These pains are usually caused by the body's unpreparedness for full recovery, psychological instability, inflammatory processes in the pelvis or strong contractions of the uterus. If during menstruation a woman constantly has to take painkillers and antispasmodics, she should definitely see a gynecologist.
Quite often the opposite situation occurs. After childbirth, women who previously suffered from severe pain during menstruation become painless. This is due to a change in the position of the uterus in the pelvis, which removes obstacles to the normal outflow of blood.
If a woman has any concerns about her period after childbirth, she should contact her gynecologist, but, as a rule, all the borderline conditions described above go away on their own within a few months.
Restoring menstruation after childbirth
Menstrual cycle and its phases
The menstrual cycle is one of the manifestations of a complex biological process in a woman’s body, which is characterized by cyclic changes in the function of not only the reproductive (reproductive) system, but also the cardiovascular, nervous, endocrine and other body systems.
More specifically, the menstrual cycle is the period of time from the first day of one period to the first day of the next period. The length of the menstrual cycle varies among women, but on average ranges from 21 to 35 days. It is important that the duration of a woman’s menstrual cycle is always approximately the same - such a cycle is considered regular.
Each normal menstrual cycle prepares a woman’s body for pregnancy and consists of several phases:
During the first phase
The ovaries produce the hormone estrogen, which promotes swelling of the inner layer of the uterus, and the follicle (the vesicle in which the egg is located) matures in the ovaries. Then ovulation occurs - the mature follicle bursts and the egg is released into the abdominal cavity.
In the second phase
The egg begins to move through the fallopian tubes into the uterus, ready for fertilization. This process lasts on average three days; if fertilization does not occur during this time, the egg dies. In the second phase of the menstrual cycle, the ovaries predominantly produce the hormone progesterone, thanks to which the endometrium (the inner layer of the uterus) prepares to receive a fertilized egg.
If fertilization does not occur, the endometrium begins to be rejected, which occurs due to a sharp decrease in progesterone production. Bleeding begins - menstruation. Menstruation is bloody discharge from a woman's genital tract, the first day of which marks the beginning of a new menstrual cycle. Normal menstruation lasts 3-7 days and during this process 50-150 ml of blood is lost.
During pregnancy, the expectant mother's body undergoes changes associated with hormonal changes, which are aimed at maintaining pregnancy, which causes physiological amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
The sequence of restoration of menstrual function
After the birth of a child, the work of all endocrine glands, as well as all other organs and systems, returns to its pre-pregnancy state. These important changes begin from the moment the placenta is expelled and last approximately 6-8 weeks. During this time, important physiological processes occur in a woman’s body: almost all changes that occur in connection with pregnancy and childbirth in the genitals, endocrine, nervous, cardiovascular and other systems undergo; the formation and flourishing of the function of the mammary glands occurs, which is necessary for breastfeeding.
The normal menstrual cycle is a coordinated mechanism of the ovaries and uterus, so the process of restoring the functioning of these organs is inseparable from each other. The process of involution (reverse development) of the uterus occurs quickly. As a result of contractile muscle activity, the size of the uterus decreases. During the first 10-12 days after birth, the fundus of the uterus drops approximately 1 cm daily. By the end of the 6-8th week after birth, the size of the uterus corresponds to the size of a non-pregnant uterus (in nursing women it may be even smaller). Thus, by the end of the first week the weight of the uterus is reduced by more than half (350-400 g), and by the end of the postpartum period it is 50-60 g. The internal os and the cervical canal are also quickly formed. By the 10th day after birth, the canal is completely formed, but the external pharynx is still passable for the tip of the finger. The closure of the external pharynx is completed completely in the 3rd week after birth, and it takes on a slit-like shape (before birth, the cervical canal has a cylindrical shape).
The speed of involution may depend on a number of reasons: general condition, woman’s age, characteristics of pregnancy and childbirth, breastfeeding, etc. Involution can be slowed down in the following cases:
- in weakened women who have given birth many times,
- in primigravidas over 30 years of age,
- after pathological childbirth,
- with the wrong regimen in the postpartum period.
After the separation of the placenta and the birth of the placenta, the uterine mucosa is a wound surface. Restoration of the inner surface of the uterus usually ends by 9-10 days, restoration of the uterine mucosa - at 6-7 weeks, and in the area of the placental area - at 8 weeks after birth. During the healing process of the inner surface of the uterus, postpartum discharge - lochia - appears. Their character changes during the postpartum period. The nature of lochia during the postpartum period changes in accordance with the processes of cleansing and healing of the inner surface of the uterus:
- in the first days, lochia, along with decaying particles of the inner lining of the uterus, contain a significant admixture of blood;
- from the 3-4th day, lochia acquires the character of a serous-sucrose fluid - pinkish-yellowish;
- by the 10th day, the lochia become light, liquid, without any admixture of blood, their number gradually decreases;
- from the 3rd week they become scanty (contain an admixture of mucus from the cervical canal);
- at 5-6 weeks, discharge from the uterus stops.
The total number of lochia in the first 8 days of the postpartum period reaches 500-1400 g, they have a specific smell of rotten leaves.
With slow reverse development of the uterus, the release of lochia is delayed, and the admixture of blood lasts longer. When the internal pharynx is blocked by a blood clot or as a result of a bend in the uterus, an accumulation of lochia may occur in the uterine cavity - lochiometer. The blood accumulated in the uterus serves as a breeding ground for the development of microbes; this condition requires treatment - the use of medications that contract the uterus or, at the same time, washing the uterine cavity.
In the postpartum period, the ovaries also undergo significant changes. The reverse development of the corpus luteum, a gland that existed in the ovary during pregnancy at the site of the egg released into the abdominal cavity and then fertilized in the tube, ends. The hormonal function of the ovaries is restored completely, and the maturation of follicles - vesicles containing eggs - begins again, i.e. the normal menstrual cycle is restored.
Time frame for the restoration of the menstrual cycle
Most non-breastfeeding women experience menstruation between 6 and 8 weeks after birth. Breastfeeding women generally do not menstruate for several months or during the entire period of breastfeeding, although in some of them menstrual function resumes soon after the end of the postpartum period, that is, 6-8 weeks after birth. Here you should not look for either a norm or a pathology, since the timing of the restoration of the menstrual cycle after childbirth is individual for each woman. This is usually associated with lactation. The fact is that after childbirth, a woman’s body produces the hormone prolactin, which stimulates milk production in the female body. At the same time, prolactin suppresses the formation of hormones in the ovaries, and, therefore, prevents the maturation of the egg and ovulation - the release of the egg from the ovary.
If the baby is entirely breastfed, that is, eats only breast milk, then his mother’s menstrual cycle is often restored after the start of complementary feeding. If the child is mixed-fed, that is, in addition to breast milk, the baby’s diet includes formula, then the menstrual cycle is restored after 3-4 months. With artificial feeding, when the baby receives only formula, menstruation is restored, as a rule, by the second month after birth.
First menstruation after childbirth
The first menstruation after childbirth is often “anovulatory”: the follicle (the vesicle in which the egg is located) matures, but ovulation—the release of the egg from the ovary—does not occur. The follicle undergoes reverse development, and at this time the disintegration and rejection of the uterine mucosa begins - menstrual bleeding. Subsequently, the ovulation process resumes and menstrual function is completely restored. However, ovulation and pregnancy may occur during the first months after birth.
The restoration of menstrual function is influenced by many factors, such as:
- the course of pregnancy and complications of childbirth,
- woman’s age, proper and nutritious nutrition,
- adherence to sleep and rest patterns,
- presence of chronic diseases,
- neuropsychic state and many other factors.
Possible complications after childbirth
What problems do young mothers face when restoring menstrual function?
Regularity of the menstrual cycle:
after childbirth, menstruation may immediately become regular, but it may take 4-6 months to establish itself, that is, during this period, the intervals between them may vary somewhat, differing from each other by more than 3 days. But, if 4-6 months after the first postpartum menstruation the cycle remains irregular, then this is a reason to consult a doctor.
The length of your menstrual
cycle
may change after childbirth. So, if before childbirth the cycle was 21 or 31 days, then there is a high probability that after childbirth its duration will become average, for example 25 days.
Duration of menstruation
that is, bleeding should last 3-5 days. Too short (1-2 days) and, especially, too long periods can be evidence of some pathology - uterine fibroids (benign tumor), endometriosis - a disease in which the inner layer of the uterus, the endometrium, grows in uncharacteristic places.
The volume
of menstrual flow can
Although in the first few months after the first postpartum menstruation there may be some deviations, they must still correspond to the physiological norm: for example, on the heaviest days, one medium pad should be enough for 4-5 hours.
Prolonged
spotting
at the beginning or end of menstruation is also a reason to consult a doctor, since most often it indicates the presence of endometriosis, inflammatory diseases - endometritis (inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus), etc.
Sometimes menstruation is accompanied by pain.
They can be caused by the general immaturity of the body, psychological characteristics, concomitant inflammatory processes that arise after childbirth, and strong muscle contractions of the walls of the uterus.
If the pain is such that it bothers a woman during menstruation, forces her to repeatedly take painkillers, antispasmodics, and disrupts the normal rhythm of life, this condition is called algodismenorrhea
requires consultation with a doctor.
Although often after childbirth the opposite happens, that is, if before pregnancy menstruation was painful, then after childbirth they pass easily and without pain. This is due to the fact that pain can be caused by a certain position of the uterus - the uterus is bent backwards; after childbirth, the uterus acquires a normal position.
Chronic inflammatory diseases often worsen during menstruation
- endometritis (inflammation of the uterus), salpingo-oophoritis (inflammation of the appendages). In this case, significant pain appears in the lower abdomen, the discharge can become very abundant, with an unpleasant, uncharacteristic odor. You should especially monitor the presence or absence of these symptoms if inflammatory complications were observed after childbirth.
Some women complain of so-called premenstrual syndrome.
This is a condition that is manifested not just by irritability, bad mood or a tendency to cry, but by a whole complex of symptoms. Among them: engorgement and tenderness of the breast, headache, fluid retention in the body and swelling, joint pain, allergic manifestations, distracted attention, insomnia.
There are many theories regarding the reasons for the development of premenstrual syndrome, but there is no single reason underlying it, and therefore there is no specific drug that would cure it completely. If a woman is concerned about such symptoms, she should consult a doctor who will prescribe appropriate treatment.
After childbirth, especially complicated ones (bleeding, severe gestosis with severe edema, a significant increase in blood pressure, up to the development of convulsive syndrome, so-called eclampsia), ovarian dysfunction may occur, which is associated with a violation of central regulation - regulation of the production of pituitary hormones (glands of the internal secretion located in the brain). In this case, the development of eggs in the ovaries is disrupted, hormonal changes occur and, as a result, menstruation is disrupted in the form of delays, which can be replaced by bleeding. With such manifestations, you should definitely seek the help of specialists.
It is important for a young mother to know that pregnancy can occur even in the absence of normal menstruation. This happens because ovulation begins on average two weeks earlier than your period. Therefore, in order not to be faced with the fact of an unplanned pregnancy, it is necessary to discuss contraception issues at the first appointment with a doctor after childbirth or consult about this before giving birth.
Restoring menstrual function after cesarean section
Complicated labor can also lead to various menstrual irregularities. In this regard, I would especially like to note the peculiarities of restoration of menstrual function in women after cesarean section. Their menstruation usually occurs at the same time as after normal childbirth. However, with complications in the postoperative period, menstrual function may not be restored for a long time due to a longer period of uterine involution due to the presence of a suture, as well as a longer process of normalization of ovarian function in infectious complications. Most likely, in this case, you will need to consult a gynecologist who will select the necessary therapy.
Useful tips after childbirth
After the birth of a baby, a young mother’s load on the endocrine and nervous system increases. When breastfeeding, the need for vitamins, minerals and microelements increases, which a woman needs for the proper functioning of the ovaries and their production of hormones. If they are deficient, problems such as scanty or painful menstruation may occur. Therefore, women after childbirth are recommended to take multivitamins with a complex of microelements for nursing mothers and a nutritious diet, including dairy products, meat, vegetables and fruits.
In addition, caring for a newborn takes a lot of effort and time from a young mother, and it must be remembered that the lack of a full night’s sleep and lack of sleep can lead to increased fatigue, weakness, and sometimes even depression, which also negatively affects the development of menstrual function; In this connection, it is necessary to create your own regime so that the young mother has time to rest during the day, and, if possible, save night time for proper rest.
As mentioned above, the presence of chronic diseases can also negatively affect the development of menstrual function, especially diseases of the endocrine system (thyroid gland, diabetes, etc.). Therefore, in the postpartum period, it is necessary to correct these diseases together with specialists, which will avoid menstrual irregularities.
In conclusion, I would like to note that restoration of normal menstrual function after childbirth is one of the main conditions for a woman’s future health. Therefore, any problems associated with its violations should be resolved together with a doctor.
Features of menstruation after childbirth while breastfeeding
Breastfeeding has a great influence on the menstrual cycle after childbirth. A woman’s body begins to function in previously unknown conditions. The pituitary gland sharply increases the production of the hormone prolactin, which is responsible for the secretion of breast milk and the lactation process.
It is because of the high content of prolactin that menstruation may be absent for a long time after childbirth. Nature, thus, takes care of the mother and baby and devotes all the body’s strength to feeding the child, suppressing ovarian function, blocking ovulation and thereby making it impossible for a new pregnancy to occur in an exhausted body.
A peculiarity of menstruation after childbirth with regular breastfeeding is that menstruation may not occur until breastfeeding is completed. The arrival of menstruation is delayed due to the fact that during breastfeeding the pituitary gland produces the hormone prolactin, which suppresses ovarian functions, for example, ovulation, which prevents the onset of a new pregnancy during breastfeeding. Prolactin can act as a cause of irregular menstrual cycle after childbirth.
Irregular menstrual cycle after childbirth
If a woman does not breastfeed her baby, then her first period after giving birth comes in about 2-3 months. In mothers whose children are mixed-fed, i.e. lactation is present, but not on demand; menstruation begins on average after 4-5 months.
The method of delivery does not affect the time of arrival of the first menstruation and the establishment of the menstrual cycle. True, in women who have suffered postpartum complications in the form of bleeding, sepsis, endometritis, etc., menstruation may come a little later than due, since these processes inhibit the restoration of the uterus due to damage from inflammation.
Irregular menstrual cycles after childbirth are quite common. Often after the birth of a child, menstruation becomes irregular: periods sometimes come, sometimes they don’t come, sometimes they are delayed for several days, sometimes they begin earlier than before.
The cycle can be established up to 4-6 months, but if after this period the interval between the arrival of menstruation varies by more than 5 days, this is a reason to consult a doctor for advice. The resumption of regular menstruation after childbirth is a sign that the female body has fully restored its reproductive function and is ready for a new pregnancy.
Lochia after childbirth: what is it?
The moment a child is born is not the end. Then the woman should try to give birth to the afterbirth (placenta). And after this, the birth process can be considered complete.
But the inner surface of the uterus has a very unpresentable appearance and it needs some time to heal. Basically, complete healing ends on the 10th day. After 7 weeks, the mucous membrane is restored, and after 8 weeks, the placental area is restored.
And this whole process is characterized by the appearance of lochia. This is postpartum discharge.
Some women mistakenly believe that this is their period. In fact, lochia comes with an admixture of blood, which gradually becomes less.
In the last days of postpartum discharge, it becomes transparent. Slightly cloudy and yellowish color is acceptable. They appear in abundance, but can and should change during the healing of the uterine surface.
Conventionally, lochia can be described as follows:
- in the first days they are abundant and how many different extra particles that were needed during pregnancy come out is unknown. Their contents come out with blood clots, and the smell may be similar to rotten fallen leaves.
- After 4 days, the lochia becomes pink-yellow.
- On the 10th day, the lochia become free of impurities and begin to decrease in volume.
- Starting from the 3rd week, their abundance decreases to scanty discharge.
- And somewhere in the 6th week, the lochia stops.
During such a period, it is very important to adhere to hygiene and ensure that the health of the newly baked mother is normal.
It is important to know what happens when lochia accumulates inside the body and then there will be trouble. No, you cannot self-medicate here under any circumstances, but you need to undergo treatment from a specialist.
It happens that additional lavage of the uterine cavity is prescribed. The main thing is not to launch it. In principle, after giving birth, every woman will be told this by her doctor, but as they say: “forewarned is forearmed.”