Signs of approaching menstruation in women are approximately the same. This is pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, malaise, irritability, and digestive system disorders. Their severity depends on the characteristics of the organism.
However, there is another interesting symptom that not every woman knows about. Today we will talk about what the cervix should be like before menstruation - its density, position and other indicators.
General information about the cervix and its examination
The cervix is a part of the reproductive organ, which is a hollow body measuring 2.5 x 3 cm. It can be called the connecting link between the vagina and the uterus.
A woman can independently feel this area at home by completely immersing her middle finger into the genital tract. As soon as the fingertip touches the bulge, there is no need to move further - the desired element has been found.
By doing such diagnostics every day for several cycles, a woman will learn to determine the position of the cervix before menstruation, calculate ovulation and select days favorable for conception. Or vice versa, he will understand on which days it is necessary to strengthen contraceptive measures.
The doctor examines the patient's genital tract on a chair using a special mirror. At home, it will be convenient for a woman to examine the cervix in several positions:
- Sitting on the toilet.
- Squatting.
- Standing, but one leg placed high.
The study is not carried out during menstruation. On “clean” days, the organ is felt once a day before bed at the same time. If a gynecological disease of an infectious-inflammatory nature is suspected or with the onset of bleeding, the diagnosis is canceled.
The speed of its detection helps determine whether the cervix is high or low on a particular day. If the location is high, the area is difficult to palpate; if it is low, it can be detected immediately. The amount of openness is judged by the recess. If a small gap is felt, the uterus is closed. If the hole is round and deep, then the organ is open.
Despite the simplicity of this method, doctors do not recommend examining internal organs yourself. The ban is justified for the following reasons:
- When the hole is open, there is a risk of damage to the uterus by pathogenic bacteria. Because of them, the ovaries become inflamed and obstruction of the fallopian tubes develops. In advanced cases, the disease can result in infertility.
- Since the cervix drops slightly before menstruation, inept palpation can injure it and provoke the development of erosion. The pathological focus is susceptible to infection and is dangerous in terms of oncological degeneration.
- The woman does not see the true state of the uterus. The gynecologist evaluates the real picture visually using a mirror.
The shape of the cervix before menstruation should resemble a pupil. Deviation indicates estrogen deficiency and improper functioning of the corpus luteum.
Change of location
After fertilization, a gradual descent of the cervix occurs, its deviation towards the posterior wall. This arrangement reduces the likelihood of spontaneous miscarriage. The placement height is a diagnostic sign that helps the doctor determine how the pregnancy is developing.
A high position is an alarming signal that may indicate the development of hypertonicity. In such situations, doctors hospitalize the patient. After all, only a relaxed state of the uterus allows you to bear a child normally. Constant tension of muscle fibers in most cases provokes embryo rejection.
Sometimes the high location of the lower segment of the uterus is an individual feature of the female body. In such cases, only an intravaginal ultrasound examination of the organ will help determine the presence of a threat of spontaneous abortion.
With a high position of the cervix, women note the development of the following symptoms:
- Watery discharge in large quantities;
- Frequent urge to urinate;
- The appearance of a nagging pain in the lower abdomen, in the lumbar region;
- The appearance of blood streaks in mucous secretions.
Such symptoms should alert a pregnant woman and become a reason for urgent consultation with a specialist.
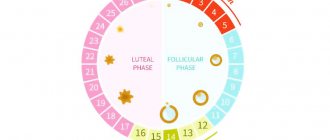
Position of the cervix in different phases of the cycle
The entrance to the uterine cavity changes in different periods of the cycle. The cyclic work of the ovaries goes through the ovulatory, follicular and luteal phases. Uterine functions change from secretory to menstrual and proliferative.
The composition of the fluid in the cervical canal also changes. It can be studied in detail in laboratory conditions. At home, a woman can analyze the consistency.
The cervix feels like this:
Its position is either high or low.
Secretory stage
The tone of the uterus in the 2nd half of the cycle decreases and after ovulation, closer to menstruation, the cervix becomes soft. The external pharynx opens to such an extent that the tip of the finger penetrates inside.
The high position of the cervix helps sperm reach the fallopian tube faster. The glandular part of the cervical canal intensively produces transparent whitish mucus. The alkaline index of the secretion reaches 8 units. The mucus doesn't stretch.
In the absence of a fertilized egg, the body begins to prepare for endometrial rejection. A plug forms in the canal, the neck hardens and falls. The pharynx closes, the cervical canal narrows. In case of pregnancy, the cervix does not change its position. It will be difficult to feel the pharynx manually at home.
Experts know exactly what the cervix looks like on the eve of menstruation, and characterize it as follows:
- Located below.
- It has a loose soft surface.
- The external pharynx is open, the canal is expanded.
- Little cervical mucus is produced.
- The secretion has a sticky, thick consistency.
- pH
During the menstrual period, the cervix has other characteristics:
- She's hanging low.
- He is in low tone.
- The acidity level is approaching 7 units.
- The vaginal epithelium is slightly flaky.
- Cervical fluid is secreted in moderate volumes.
- The external pharynx is slightly open, the opening is directed towards the vaginal vault.
Menstruation occurs during the first segment of the follicular phase of the ovaries. Next, the reproductive system begins to prepare for the next ovulation.
The value of cervical palpation as a diagnostic method
Daily palpation of the cervix, including before menstruation, helps to track cyclic changes. In order not to injure or infect a delicate organ, it is necessary to cut off the nail on the desired finger and polish the edge of the plate.
For greater safety, it is better to perform the procedure with sterile gloves or a fingertip. It is recommended to record all data collected before the onset of bleeding in a notebook.
The purpose of diagnosis is to assess the position of the cervix before menstruation and during other phases of the cycle, as well as during pregnancy, if it has occurred. It is also important to know the density of the organ at the proliferative and secretory stages of MC.
The information collected over several months will help the woman with family planning and will signal the need to see a doctor if there are any abnormalities.
Before menstruation, the cervix feels different to the touch than on the other days of the cycle. Based on her condition, it is easy to calculate exactly when her period will begin (approximately how many days are left before it). Some women even conduct self-diagnosis at home for this purpose during PMS or when they want to get pregnant. But doing this without proper training is not recommended, and can even be fraught with dangerous consequences.
Normal discharge before menstruation - what is it?
Non-menstrual discharge is called leucorrhoea. In different phases of the cycle, under the influence of the hormonal system, they undergo changes. Features of secretions can indicate the presence of gynecological diseases or refute them.
The rate of discharge before the onset of menstruation is determined by the following indicators:
- Creamy consistency.
- No unpleasant odor.
- White color or slight turbidity.
- Minor bloody spotting.
- The volume of leucorrhoea increases.
The consistency and composition of discharge is influenced by estrogens and progesterone. The first type of hormones increases in the second half of the cycle, the second one decreases. The composition is modified by gram-negative microorganisms. Shortly before bleeding, they make vaginal discharge creamy or jelly-like. A yellowish tint is allowed.
Looking closely at what kind of discharge occurs before menstruation, some women observe a thick viscous mass. Its quantity increases noticeably closer to menstruation. The abundance of secretions increases the moisture content of the labia.
Before menstruation, secretions can even be released from the nipples, which is also associated with a hormonal surge. Such discharge can stain your bra a week before your period.
Yellow, odorless mucus from the genital tract is also normal. Its insignificant amount and the absence of a strange smell should not bother a woman. Yellowish or brown secretion sometimes appears due to the contraceptive device.
What does the cervix look like before menstruation?
In accordance with the day of the cycle, the cervix not only changes its position every month, but also becomes different to the touch. Its structure also changes.
What does the cervix look like before menstruation? To understand this, you need to understand what processes occur in the female body. After ovulation, which occurs in the middle of the cycle, the woman’s body and uterus prepare to fertilize the egg. Additional endometrium appears. There is a gradual change in shape and enlargement of the uterus before the onset of menstruation. Before ovulation, the cervical canal opens so that sperm can freely penetrate to their target. When ovulation ends, the canal gradually narrows and the uterus begins its preparation for a possible pregnancy.
If conception does not occur, the uterus gets rid of excess endometrium. The fundus of the uterus is drooping, the cervix dries out and hardens. Mucus appears in the cervical canal and becomes filled with vaginal discharge. The secretion changes its composition and thickens.
Immediately before monthly bleeding, the cervix opens again, and the mucus acquires a liquid consistency. Before menstruation, the uterus changes its location - it prolapses.
Before menstruation, the cervix is loose and soft, droops and opens slightly. During this period, especially careful hygiene is required because infection and bacteria can easily enter the uterus and cause bacterial or inflammatory diseases. And they are a direct path to the formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, which can cause infertility. Therefore, the uterus is most vulnerable during menstruation and is located low.
All changes are perfectly demonstrated by the image of the cervix by day of the cycle (see photo below).
Structural features
The cervix is the lower segment of the organ that connects to the vagina. It contains glands that produce mucus throughout the menstrual cycle. When pregnancy occurs, the cervix ensures that the fetus is held in its proper place, preventing the development of spontaneous miscarriage.
Normally, the cervix is a small, rounded formation. Its size does not exceed 4 cm in length and 2.5 cm in circumference. As part of a medical examination, a gynecologist can evaluate only the vaginal segment of the organ. The cervix has a hard consistency, a closed pharynx, which opens slightly during menstrual bleeding to allow discharge. However, the development of pregnancy leads to changes in some characteristics of the organ.
After conception, the cervix becomes soft to the touch. This is due to an increase in the production of progesterone, a hormone that is a companion to pregnancy. It leads to vasodilation, which causes swelling of the endometrium of the uterus. However, the cervix does not lose its firmness and elasticity, which allows the fertilized egg to be preserved. At the beginning of pregnancy, she gains mobility. This is due to the softening of the tissue of the isthmus, which is the part of the uterus that connects the body and the cervix.
The appearance of an embryo in the uterus leads to the activation of glands, which actively produce a thicker and more viscous secretion. A large clot of mucus appears in the cervical canal, which is called a “plug”. It performs the following functions:
- Protection of the uterine cavity from the penetration of infectious agents;
- Maintaining the balance of vaginal microflora;
- Creating optimal conditions for the functioning of the woman’s genital organs.
If after conception the consistency of the cervix remains hard, this indicates the development of hypertonicity of the organ. This pathological condition is characterized by increased tension in the uterus and can lead to rejection of the fertilized egg.
It is impossible to assess changes in the cervix yourself unless you are a specialist. Self-examinations can provoke the development of a vaginal infection and cervical injury. Therefore, only regular examinations by a gynecologist will allow pathology to be detected in time and corrected.
Is self-diagnosis allowed?
Self-examinations can be carried out, especially if a woman feels unwell or is worried about something. Learning to accurately determine the condition and position of the uterus is not an easy task. But experience comes with time. If you conduct self-examination regularly, then after just a few cycles you will be able to accurately diagnose the condition of your body and reproductive system.
Diagnosis is carried out in compliance with certain simple but very important rules. These conditions must be strictly observed:
- no examinations during the menstrual cycle, this is fraught with infection;
- First of all, remember: you should not self-examine more than once a day, it is better to do it 3 times a week;
- It is advisable to carry out manipulations at the same time;
- if there is inflammation, diagnosis will have to be postponed.
The nature of discharge before menstruation
The following female discharge is considered normal in gynecology:
- before ovulation – transparent, abundant, odorless;
- after ovulation – scanty, thick;
- 3-4 days before the arrival of menstruation – increasing in volume;
- on the first day of the new cycle - a scarlet “daub”, which gradually intensifies.
Changes in the volume and consistency of secretions are associated with regular natural fluctuations in hormonal levels. The nature of the discharge largely depends on age, intensity of sexual activity, quality of nutrition, the presence of chronic illnesses, medication use, incl. contraceptive hormonal drugs. Taking these factors into account, we can say that the norm for each woman is individual. For this reason, any deviations should be a reason for medical consultation.
What is considered normal?
White and light discharge that occurs a few days before menstruation should not bother a woman. White discharge before menstruation does not cause discomfort and is a consequence of cleansing the genital tract of mucus, dead cells and pathogenic flora. Normally, the discharge may contain cervical mucus, a small amount of leukocytes, waste products of the uterine glands, and physiological vaginal transudate.
What should premenstrual discharge be like?
The mucus of a healthy woman meets the following criteria:
- color – various shades of white and yellow;
- consistency – homogeneous, medium viscosity, with a small number of small clots;
- volume – no more than 5 ml (1 tsp) before the start of menstruation;
- smell – neutral or slightly sour.
As a rule, discharge lasts 2-3 days, but no more than 5 days. In addition, itching, burning and swelling should be absent.
Symptoms of pathology
Not all spotting can be considered natural and healthy. If they drag on for a week and appear regularly, during each cycle, you should check your women's health.
Behind spotting or insignificant discharge lie pathologies of the organs of the reproductive system, infections, and endometrial diseases. Any disease requires treatment, since the loss of women's health negatively affects self-esteem and leads to problems in their personal lives.
Self-examination technique
Before you begin a gynecological examination, you should carefully prepare:
- Trim your nails. Otherwise, there is a possibility of injury to the surface of the ball.
- Wash your hands thoroughly to avoid infection.
- Wear sterile medical gloves; they will protect the uterus from penetration of pathogenic microorganisms.
The best position for the examination is sitting. To make it more comfortable, you can sit on the toilet or bidet. But it’s better to squat down or simply raise your leg and fix it on a hill. If it is more convenient to feel the cervix while lying down, you can conduct a self-examination in this position. Two fingers (middle and index) are inserted into the vagina. Watch your movements; they should not be sudden, so as not to cause injury to the mucous membrane.
During the examination, you will find a dense tubercle under your fingers; this is the cervix. If you have the appropriate experience, you can easily determine whether it is hard or, conversely, soft. It is also easy to understand the state of the cervical canal - closed or open - this indicates ovulation or other conditions.
What is this?
Cervix
is the organ connecting the uterus and vagina. It has a trapezoidal shape. Among women, an abbreviation term appeared - ShM. It is convenient to use when filling
The size of the neck varies for each individual woman. They depend on age, pregnancy experience and physiological characteristics. Position of the organ
just like the structure changes depending on. It can be hard or soft.
the external os is located on the cervix
.
Through this opening, secretions from the uterus enter the vagina. The pharynx takes on different states, depending on cyclical processes
. It can be closed, semi-closed and open.
Determination of the position of the cervix is regularly carried out by touch with mandatory compliance with the conditions. The woman enters all the data in a separate notebook. Information helps to recognize or pregnancy. The most revealing studies will be in combination with the use of tests for.
ON A NOTE!
Examinations of the cervix should be carried out with clean hands, as there is a possibility of infection.
Examination of a pregnant woman
By examining herself during pregnancy, a woman will be able to determine the likelihood of miscarriage in the early stages. So, in an interesting position, the ball is long and dense. If it is shortened (less than 2.5 cm), this becomes a serious reason for early contact with a specialist, undergoing examination and even hospitalization.
Before the expected date of delivery, such medical examinations make it possible to determine the readiness of the cervix for labor, this is especially true when the third part of pregnancy begins. It becomes shorter, smoothes out and allows 1-2 fingers into its throat. The stomach may drop. At different stages of pregnancy, the cervical tumor looks and feels different.
How to find out if everything is okay with women's health by discharge
When medicine was not yet so developed, grandmothers advised girls to carefully look at their discharge and remember its appearance and smell during the period when they were not sick. Any deviations in odors, consistency, or color should have been a reason for examination. Modern girls can also follow this advice. Then, at the first doubts and signs of “something is wrong,” it is better to consult a doctor, get tested and live in peace. In addition, it is very important to visit a gynecologist every six months - it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it.
A doctor is like a priest; you can trust him with all the secrets concerning your health. Only in this case will you receive competent, qualified help.
So, the consistency of a healthy woman’s discharge before menstruation can be:
- creamy;
- slightly curdled;
- mucous membrane transparent, like the white of an egg;
- slightly white mucous membrane;
- thick milky white;
- whitish with brown spots;
- yellowish-rusty-brown a day or two before menstruation;
- lumpy white;
- abundant;
- scanty;
- the day before menstruation, scarlet inclusions in a white clot of discharge;
- Absent at all (not visible on underwear).
In each of these cases, either a complete absence of odors or the presence of hints of sour milk is allowed. There should be no unpleasant sensations, itching, or irritation either.
Doctors' opinion
Although self-examination of the vaginal fundus and cervix can be very informative, experts do not recommend that women palpate the cervix on their own. And there are a number of reasons for this, which are the subject of many new articles. There is always a risk of infection, which can ultimately lead to infertility. Inaccurate examination can result in traumatization of the mucous membrane, and this is a path to the development of erosion.
In combination with infections, this condition can be very risky and can even result in the development of oncological processes.
Pathological discharge
A distinctive feature of pathological leucorrhoea is its bright, rich color. Mucus often contains discharge with foam, lumps and clots, pus and blood. In addition, there is an unpleasant odor. A woman experiences pain in the genital area and lower abdomen. The appearance of pathological discharge of various types is due to the development of serious diseases that require treatment.
Among the reasons for such changes are the following:
- hormonal disbalance;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- the formation of tumors in the cervix or its cavity.
It is worth separately noting what kind of discharge before menstruation is observed in the case of taking oral contraceptives and when installing an intrauterine device. In the first three months after this, the mucus becomes bloody, sometimes there is even a black secretion. With the onset of the fourth cycle, everything should return to normal. If this does not happen, you should seek help from a gynecologist.
White mucus released throughout the cycle indicates diseases of the genital organs:
- Thrush. The area around the vagina itches, itching appears, the discharge becomes cheesy in consistency and acquires an unpleasant sour smell.
- Cervicitis. There is profuse leucorrhoea, accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the lumbar and abdominal areas.
- Vaginosis. A fishy-smelling discharge is observed. The woman notes that they have increased in volume, this is especially noticeable after sex. The disease is provoked by a violation of the microflora of the vaginal mucosa and the presence of a large number of pathogenic microorganisms in it.
Brown spotting or heavy vaginal discharge is caused by the following pathologies:
- Endometriosis. Both spotting mucus and severe bleeding may appear.
- Dysplasia, erosion or leukoplakia of the cervix. As a result of damage to the mucous membranes, leucorrhoea of an uncharacteristic color may appear.
- Tumors, cysts and polyps of the ovaries. Smearing brown mucus appears before menstruation and after it ends. There is a risk of bleeding.
Yellow and green discharge in women appears due to various inflammatory processes occurring in the genitourinary system and sexually transmitted diseases.
In order to establish the cause of pathological discharge, laboratory tests are carried out, and hardware and instrumental diagnostic methods are also used. Only after this a course of treatment is prescribed.
Leucorrhoea before menstruation is considered normal and is observed in all women. However, you need to carefully monitor the nature of the mucus, its consistency and smell. Any changes are a reason for a full examination. Often, such symptoms indicate the development of diseases that can cause serious complications. Only if there is no discomfort, no unpleasant odor, and the color of the mucus has not changed, there is no cause for concern.
"Pros" and "cons" of self-diagnosis
Self-examination of the uterus does not give a complete picture of its condition, but will only help make some assumptions. Perhaps this is the only positive side of this procedure. But there are many more negative aspects. This is also the possibility of infection, trauma, which threatens inflammation, complications that lead to infertility.
A photo of what the cervix looks like before menstruation and during pregnancy cannot help analyze the condition of the organ. You should be guided only by tactile sensations.
If you have any questions, you can always ask your gynecologist. If necessary, a woman can conduct an independent examination of the cervix, but this should be done only in extreme situations and no more than three times a week.
To determine the condition of an organ, considerable experience is required, which means that in its absence, the examination will be uninformative and will not yield any results. Only an experienced doctor is able to recognize changes, evaluate them and prescribe additional examination methods, because the position of the cervix is constantly changing by day of the cycle, and these features must be taken into account.
Menstruation is a natural physiological process that is evidence of the onset of puberty. The duration of the menstrual cycle generally ranges from 21-30 days. Everyone's periods are completely different. However, the vagina before and during menstruation is vulnerable and sensitive in all women.
Read in this article
Position
The normal position of the uterus in a healthy woman is the center of the pelvis. The CMM analysis method is used. It helps to most reliably determine the fertile period.
This increases the chances of conception. At each organ, the organ takes a special position. Under the influence of hormones, it changes its structure.
A gynecologist can easily determine the position of the cervix most accurately. But some women are able to do this on their own. The main thing is to comply with the basic requirements and adhere to regularity. To the rules for conducting research
include:
- The analysis should be carried out in the same position. The best position is lying on your back with your knees bent or squatting.
- For convenience, you can use a specially targeted lubricant.
- The index finger should be inserted into the vagina until it rests on the tip of the cervix.
- It is necessary to pay attention to the nature of the discharge
and the degree of openness of the external pharynx.
IMPORTANT!
During menstruation, it is better to refuse research. If this is not possible, then additional measures must be taken to protect against bacteria.
Before ovulation
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle of the study, the position of the cervix will be low. Its surface is dry and hard to the touch. The external os is tightly closed.
REFERENCE!
When analyzing the degree of hardness of an organ, you should imagine the tip of the nose. The neck will resemble this part of the face.
During ovulation
On days of increased fertility
Significant changes occur in a woman’s body. The characteristic features of this period include:
Fertilization of an egg triggers numerous physiological processes in a woman’s body that are aimed at maintaining pregnancy. First of all, this affects the condition of the organs of the reproductive system. It is necessary to consider in more detail possible changes in the cervix after conception, which are the main diagnostic criterion in determining pregnancy.
Vagina before menstruation: features of structure and position
Any specialist knows that the cervix should be slightly softened before menstruation, and if a woman has already given birth, it should be slightly open. But during pregnancy, it is located high in the vagina and has a characteristic dense consistency.
Before the onset of menstruation, the cervix of the organ changes position and moves slightly lower in the vagina. Only a gynecologist should examine the position and consistency of the uterus. With an incompetent examination, there is a risk of infection of the woman’s reproductive system, ovaries or fallopian tubes, since the uterus opens slightly before menstruation. When the cervix is injured, erosion appears upon examination, which quickly heals if there is no infection.
When ovulation occurs, the cervix of the organ is slightly softened, and characteristic mucus is released from the vagina. The pharynx is somewhat reminiscent of a pupil (“pharynx symptom”). Gradually, this symptom disappears after ovulation. However, if the doctor, during an examination before menstruation, observes a weak expression of the pupil, then it can be assumed that there is a lack of estrogen or the appearance of disturbances in the functioning of the corpus luteum.
Color after conception
Immediately after fertilization, the body begins to create all the necessary conditions for bearing a child. In the early stages of pregnancy, the uterus rapidly increases in size. The growth of her body occurs due to the intensive growth of the mucous membrane (endometrium) and muscle layer (myometrium).
Along with the growth of layers, the area of the network of blood vessels penetrating the body of the organ increases. The vessels fill with blood and dilate. Blood circulation in the uterus is significantly enhanced. The body prepares to supply nutrients and oxygen to the growing fetus.
An increase in uterine blood flow causes a change in the color of the cervix. From light pink it turns into bluish-purple. Increased blood circulation causes swelling and darkening of the mucous membrane of a woman’s external genitalia. It may also be observed on the walls of the vagina and the surface of the vaginal part of the cervix.
The uterus changes dramatically during pregnancy. This is understandable, because this is where the fetus develops for 9 months. And a lot depends on the health of this organ. How does it change and later? What is considered normal, and what is a reason to consult a doctor?
Physiological changes
In its normal state, the uterus has a height of 4.5-5.5 cm, while the size of the uterus during pregnancy reaches 38 cm in length (at the end of the third trimester, before childbirth). No other organ has the ability to stretch like this. That is why an ectopic pregnancy, when the fertilized egg begins to develop in the ovary, fallopian tube or abdominal cavity, cannot be carried to term and, if diagnosed untimely, has dire consequences.
The position of the uterus changes during pregnancy as it grows. But the most favorable situation is when the uterus is located approximately on the same plane as the cervix and vagina, without bending or deviation to the side. This makes it easier to conceive and give birth.
Dense, long, closed, located deep in the vagina and has a bluish tint - this is one of the early signs that a woman is pregnant. The gynecologist examines the cervix with his fingers and using a special mirror.
If the cervix is short (less than 30 mm), or slightly open, the woman may be advised to have sutures to avoid further dilatation and miscarriage, or a removable ring pessary.
Uterine tone
There is probably no woman whose pregnancy proceeds ideally. Hypertonicity, expressed in nagging pain and uterine tension, is one of the most common complaints, especially in the first trimester. And this is also the reason for most hospitalizations. In fact, periodic is the norm, since this organ has a muscle layer. Any muscle in our body contracts. Hypertonicity is dangerous if it is accompanied by dilatation of the cervix and bleeding.
When examined by a gynecologist, it is not often that the uterus is soft during pregnancy, since even touching can tone the muscle. The same thing happens when an ultrasound probe is passed over the abdomen. However, most doctors continue to write in their reports “local hypertonicity along the anterior wall of the uterus” in such cases. Perhaps it exists, but it is completely harmless and usually lasts only a few seconds.
If the uterus during pregnancy is almost always hard to the touch, and in addition, the tone is painful, the doctor may prescribe antispasmodics.
Observation by a doctor
All those weeks and months while a pregnant woman is under the supervision of a gynecologist, he monitors the condition of the child and the uterus. Gynecological examinations are carried out no more than 2-3 times during the entire pregnancy (if there are no deviations). And measurements of the uterus (its length and abdominal volume) at each woman’s visit. The received data is recorded in its exchange card. And if the records show that the uterus has not enlarged at all in 1-2 weeks, and a woman at more than 20 weeks does not feel or rarely feels the baby moving, she is urgently sent for an ultrasound. This can occur when the fetus dies or there is a lack of oxygen and nutrients. In the second case, the doctor will be able to help.
This is why observation by a gynecologist is so important. Don't miss your appointments.
In adolescence, every girl begins her period, and with its beginning the menstrual cycle. From this age, young ladies need to regularly visit a gynecologist so that the doctor can monitor the condition of the reproductive organ.
Condition of the vagina during menstruation
During menstruation, the uterus is influenced by female sex hormones. If the uterus is not fertilized, then after a certain period the level of hormones decreases and menstruation begins. During menstruation, the uterus is freed from the endometrium, which is prepared after ovulation to receive a fertilized egg. If conception does not occur, it peels off. With a regular cycle, if there are no deviations from the norm, ovulation cannot begin on the days of menstruation. During menstruation, constant contractions of the uterus occur, so a woman may experience characteristic pain in the lower back or ovaries.
What to do if there is pain, pulling
Pain in the vagina during menstruation or on the eve of it is usually associated with diseases or changes in the body that do not stem from the condition of the vagina itself. The following may lead to this:
- Ovarian cysts . These neoplasms will put pressure on the pelvic and vaginal organs; this is possible if they are larger than 3 cm.
- Endometriosis . When lesions are located on the peritoneum between the uterus and the bladder or rectum on the eve of or during menstruation, the pain syndrome worsens; sharp and even dagger-like pains can radiate to the vagina.
- Diseases of the rectum and bladder . Due to the close anatomical location of the organs, pathological processes in them can give off unpleasant sensations to the rectum.
- Adhesive process in the pelvis . It can occur after removal of the uterus or after ovarian surgery.
Pulling in the vagina can also be due to an incorrectly selected hygiene product. If, during light discharge, you use highly absorbent tampons, this can lead to dryness of the mucous membrane and unpleasant sensations.
In any case, discomfort and pain in the vagina should be a reason to consult a doctor for a routine examination in order to detect serious pathological processes in time.
In addition, acute surgical conditions can be causes of pain in the vagina. For example, ovarian apoplexy or cyst rupture, ectopic pregnancy. All these conditions are accompanied by intra-abdominal bleeding. Blood accumulates in the deepest place in the pelvis - the “pouch of Douglas”. In front it is limited by the uterus and vagina, in the back by the rectum.
The accumulation of fluid here leads to a feeling of pressure on the perineum, vagina and rectum. Along with this, the following symptoms occur:
- sharp or aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- weakness, lethargy, dizziness;
- nausea.
Ectopic pregnancy
Condition of the uterus after menstruation
Some changes occur in this organ after menstruation. A healthy cervix after menstruation is thus prepared for possible fertilization. And if the uterus opens slightly before menstruation, then the next menstrual cycle begins with the closing of its pharynx after the bleeding stops.
The organ gradually pulls up, the endometrium begins to grow, into which, in turn, an egg can be implanted during fertilization. Before and after menstruation, the cervix has the same tissue consistency and degree of dryness. After menstruation, it is filled with thick mucus, which protects the organ from the penetration of pathogenic infections.
With the arrival of ovulation, the surface of the organ becomes loose and moist. The mucus acquires a less thick consistency, which allows sperm to pass through it unhindered.
Normally, the uterus should be contracted. If it remains enlarged, then additional examinations should be carried out - an appropriate analysis for the hCG value or an ultrasound procedure.
If the uterus is not positioned correctly in the abdominal cavity, nagging pain may occur after menstruation. Stress and nervous tension can also be causes of postmenstrual pain. If pain persists for more than 3 days, you should consult a specialist to rule out possible pathology.
How is the organ examined after fertilization?
If pregnancy occurs, the woman should consult a gynecologist. The doctor will perform a gynecological examination using speculum and two-handed examination. Additionally, a study of the vaginal microflora will be required to ensure the absence of sexually transmitted infections that could threaten the fetus.
It is necessary to conduct cytology - a histological examination of the cells of the cervix. This is necessary to prevent the development of cancer. The fact is that during pregnancy, a woman’s immunity is suppressed in order to prevent fetal rejection. This process can trigger the rapid growth of cancer cells that are in the body.
When pregnancy occurs, the development of the following diseases should be additionally excluded:
- Endocervicitis. This is an infectious lesion of the cervix, which can provoke the penetration of bacteria into the uterine cavity, infection of the fetus, decreased tone of the organ and spontaneous abortion. Therefore, it is necessary to promptly determine the presence of infection and begin therapy;
- Erosion (small ulcer on the uterine mucosa). The cause of the pathological formation may be pregnancy or infection. The disease requires constant monitoring by a specialist, but treatment is carried out only after delivery.
The listed changes in the cervix allow the gynecologist to draw a conclusion about the occurrence of pregnancy, its duration, and the development of threatening factors. You should not engage in self-diagnosis, because it can lead to the development of dangerous diseases and termination of pregnancy. Regular examinations with a doctor will allow you to monitor any changes in the process of bearing a child and stop pathologies in a timely manner.
How is the examination carried out?
First of all, the gynecologist interviews the patient. The doctor analyzes the symptoms and examines the patient on the gynecological chair. Bring a special medical examination kit with you to your appointment.
If necessary, a woman is given a referral to:
- blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- ultrasonography.
Only after receiving the diagnostic results is effective treatment selected. Independent selection of drugs is strictly contraindicated.
Causes of vaginal swelling
Below are reasons that may lead to vaginal swelling and the treatment options available.
Allergy
A reaction to certain chemicals may cause the vagina to swell
Vaginal swelling may result from an allergic reaction. The vagina is a sensitive area of the body that can react to any personal hygiene products. Such means include the following:
- soap;
- lubricants;
- vaginal cleansers and douching solutions;
- tampons and pads;
- vaginal contraceptives;
- body lotions and creams;
- latex condoms.
Sometimes swelling is a reaction to new products, but products the body is already familiar with can also cause irritation. If a woman suspects she has an allergic reaction to a specific product, then it is better for her to stop using it and discuss options for dealing with the situation with a dermatologist.
Irritation
If a woman does not have allergies, her body may react differently to skin contact with specific products. Even the most popular and widely used chemicals can cause the vagina to swell.
Doctors often blame fragrances for irritations. They are found in many products that come into contact with the vagina. Such means include:
- washing powders;
- perfume;
- toilet paper;
- body washes;
- bath bombs and soaps.
Certain tissues can also cause vaginal irritation and swelling. In particular, lace underwear or polyester underwear sometimes irritate this area.
Irritation often occurs when a woman refuses to wear underwear. In addition, thongs may not completely cover the labia, which often leads to unnecessary rubbing of the intimate area throughout the day and ultimately results in swelling.
When edema appears, it is important to identify irritants and avoid them in the future. If a woman stops using a specific product and the swelling goes away, this may mean that the culprit of the irritation has been found.
If a woman cannot identify the cause of vaginal swelling, then she needs to consult a dermatologist about this issue.
Rough sexual contact
Sexual contact can also cause swelling of the vagina. If the vagina is not adequately lubricated, excessive friction can lead to discomfort or pain during sex, as well as vaginal swelling after intimacy.
Rough sexual contact can also damage the vaginal tissue and thus increase the risk of developing an infection.
If a woman suspects that her vagina is swollen due to rough sexual contact, then she needs to either use additional artificial lubricant or spend more time on foreplay.
Over-the-counter pain relievers or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help if vaginal swelling is accompanied by pain.
Gartner's canal cysts
The canal, which forms in the fetus during the development of the reproductive and urinary systems, usually disappears after birth. If part of this channel remains, it is usually called the Gartner channel. The remaining tissue can attach to the vaginal walls and develop into cysts.
Gartner's canal cysts usually do not pose a threat to health, but if they increase in size, they can cause problems for a woman. In particular, these formations can become infected and cause pain and swelling in the vagina.
In some cases, cysts appear as growths outside the vagina.
Surgery is sometimes required to remove problematic Gartner's cysts. When the cysts are removed, the symptoms go away.
Bartholin cysts
Bartholin's glands are located on both sides of the vaginal opening. They secrete a natural lubricant and thus help provide lubrication to the organ.
Cysts in one of these glands may not be noticeable to a woman until they become inflamed. When they become inflamed, abscesses sometimes form. In addition, the skin around the vagina may also become inflamed and painful. In some cases, this condition causes a burning sensation and even bleeding.
If the cysts or abscesses are small, they may dry out and disappear on their own. Warm baths usually relieve pain. Over-the-counter medications can also help reduce pain and swelling.
In more severe cases, doctors recommend antibiotics, surgical drainage, or removal of the cysts.
Cellulite
Cellulite is a bacterial infection in the inner layers of the skin that causes it to become swollen, red, and painful. In the vagina, cellulite can develop when bacteria gets into cuts in the skin, such as when shaving the pubic area.
Cleaning cuts regularly helps fight infection. In some cases, the doctor may suggest taking antibiotics.
Bacterial vaginosis
Antibiotics are commonly used to treat bacterial vaginosis.
Overgrowth of harmful bacteria in the vaginal area can lead to bacterial vaginosis. Symptoms of this condition include vaginal swelling, as well as a grayish discharge and a strong odor.
In many cases, vaginosis goes away on its own, but to speed up recovery, your doctor may recommend antibiotics.
Regular cleaning of the vaginal area and avoiding products that cause irritation can help prevent bacterial vaginosis.
In addition, women are advised not to douche, since this procedure often causes a bacterial imbalance in the vagina.
Yeast infections
Yeast infections are caused by overgrowth of a fungus such as Candida. This condition can cause vaginal swelling as well as other symptoms, such as:
- vaginal burning;
- pain during sex and urination;
- redness;
- thick, lumpy discharge;
- skin irritation.