Emergency (urgent) postcoital contraception is carried out after unprotected sexual intercourse (within 1-3 days) to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
For emergency contraception, a hormonal method (antigestagens, gestatens) or intrauterine contraception (intrauterine device insertion) is usually used.
Emergency contraception is used if:
- rape has been committed;
- unprotected sexual intercourse occurred;
- interrupted sexual intercourse was performed incorrectly;
- the condom broke during sexual intercourse;
- other similar situations.
When is emergency contraception needed?
Emergency contraception methods help prevent unplanned conception. The effect of such techniques is to suppress the ovulatory process in the female body, that is, they do not allow the sperm to meet the egg.
Appropriate techniques are also used if conception has already occurred, but further development of the fetus must be urgently prevented. In this option, it is impossible for the fertilized egg to attach to the uterine wall.
Situations when a woman can resort to using contraception:
- unprotected sexual contact;
- improper use of contraception (breaking, slipping of the condom during sex);
- skipping oral contraception;
- incorrect calculation of “safe” days;
- unsuccessfully interrupted sexual intercourse;
- rape.
In all these situations, there is a high risk of unwanted fertilization. And if a woman does not plan to become a mother in the near future, then she needs to resort to using contraceptives as soon as possible (after sex).
The effectiveness of the technique depends on the duration of administration. A greater effect will be observed if the intake occurred within a period of 1 to 5 days.
Frequent use of such methods is prohibited. This can negatively affect a woman’s health and, especially, the functionality of the reproductive system. It is allowed to use emergency contraceptive methods twice a year.
Types of contraception for womeni
There are contraceptive methods in cases where unprotected sexual intercourse has occurred, as well as situations where fertilization has occurred, but it is necessary to prevent the egg from entering the uterus. In fact, the latter is a micro-abortion without harm to health.
In the first case:
- The condom broke and semen leaked into the vagina.
In the second case:
- The woman took oral contraceptives, but their effect was incorrect.
A miscarriage at an early stage can be carried out only during the first 5-7 days, when there is no threat of ectopic pregnancy. During this period, the embryo has already formed, but has not yet reached the fallopian tubes. Once the fertilized egg moves down the fallopian tubes, a medical abortion is performed.
Douching
Some women believe that douching can protect them from unwanted conception. In fact, this is a myth. Active sperm (after ejaculation) reach the cervix within 1 minute. Sperm are present in a lubricant that is able to penetrate the female genital organs, which can also result in fertilization. Douching is not capable of “eliminating” sperm from a woman’s reproductive organs.
It is necessary to point out one more important aspect. Douching has a negative effect on the vaginal microflora. Solutions injected into the genitals change the pH level of the vagina and the acidic environment to an alkaline one. It is the alkaline environment of the vagina that provokes the development of various gynecological diseases.
Cost of emergency contraceptives
How much do pills that prevent unwanted pregnancy cost? Consider the list of tablets and their average cost:
| Taking hormonal pills |
| A drug | Price, rub |
| Postinor | 410 |
| Escapelle | 480 |
| Gynepristone | 380 |
| Genale | 300 |
| Agesta | 290 |
| Marvelon | 1450 |
| Microgenone | 350 |
| Regulon | 420 |
| Rigevidon | 340 |
| Miniziston | 440 |
| Novinet | 480 |
| Logest | 810 |
Please note that the prices for drugs are average. Depending on the region of residence, the cost may vary.
Which means are better?
If we compare the installation of an IUD and the use of tablet drugs, then the first method is the safest for the female body. The effectiveness of the spiral has also been established by numerous medical studies. If a woman has contraindications to the installation of an IUD, she will have to use pills.
The use of antigestagens is safer. Such drugs are effective and not so aggressive for the female body if we compare them with gestagens.
But when choosing emergency contraception, it should be taken into account that the effectiveness and safety of the drug depends on the time of administration and the phase of the menstrual cycle. Scientific and medical research has proven that if unprotected sexual contact occurred before the ovulation period, then gestagen-based drugs can be used. In this case, they will be both safe and effective for the female body.
Taking antigestagens does not depend on the phase of the menstrual cycle. They will always be as effective as possible and relatively safe.
There have also been cases where emergency contraception methods become completely ineffective. The onset of conception (after taking appropriate medications) can be determined by the following signs:
- delay (by 1 or more weeks) of menstruation;
- The previous menstruation was accompanied by scanty bleeding and lasted less than usual.
Postcoital contraception - principle of action and effectiveness
All drugs in this group are hormonal. The principle of their work is based on the periodic release of doses of a hormone that upsets the standard changes in the female body that pregnancy brings. The state in which the body finds itself after using drugs is called menstrual chaos .
You need to understand that such a technique can only work once, after a single sexual intercourse without protection. In no case can this serve as a means of regular birth control. On the one hand, the effectiveness of postcoital contraception, and on the other hand, the harm to the body may be incomparable compared to the use of other means.
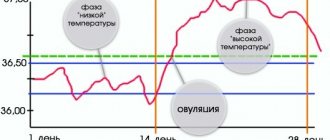
The very effectiveness of postcoital contraception depends on the moment at which copulation occurred. For the menstrual cycle, it is 74-100% if used immediately after intercourse, and 70-93% if used during the periovulatory and/or ovulatory period .
Navy
The installation of an IUD is one of the most common and most effective means of emergency contraception.
In terms of external parameters, a spiral is a special small-sized tool made of plastic with the presence of alloys of gold, copper or silver.
The IUD is inserted no later than 5 days after unprotected sexual intercourse. The procedure for installing the spiral is carried out by a gynecologist in a medical institution. The installation of a spiral is allowed only for women who do not have contraindications to the corresponding procedure.
The IUD effectively prevents the onset of unwanted fertilization, but it is not able to protect the female body from the invasion of various types of infections (including sexually transmitted infections).
Menstruation after the installation of an IUD always becomes more abundant, lasts longer than usual and is accompanied by physical discomfort.
If the IUD was used only as an emergency contraceptive, it must be removed one month after installation. The IUD is removed by a gynecologist. It is forbidden to remove the IUD yourself, as this may result in adverse consequences for the female body.
STD prevention
The main sexually transmitted infections are divided into bacterial and viral. Bacterial infection after unprotected sex can be prevented if treatment is started on time; viral infection cannot be stopped.
We recommend reading: Hormonal acne: causes, treatment methods in women and men
Bacterial STDs include:
| Type of infections | Disease |
| Common | Gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, trichomoniasis |
| Opportunistic flora | Gardnerellosis, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis |
| Rare tropical | Donovanosis, chancroid, lymphogranuloma venereum |
Viral infections include:
- genital herpes;
- HIV;
- hepatitis B and C;
- human papilloma virus.
Through unprotected sexual intercourse, you can also become infected with non-venereal skin diseases (lice, scabies, molluscum contagiosum).
Necessary actions
The measures that need to be taken to avoid infection depend on the time that has passed:
- In the first 2 hours, emergency preventive measures are used. In the period from 2 to 4 hours their effectiveness will be lower. After 4 hours, such measures make no sense.
- In the next 72 hours, prophylaxis with medications is carried out.
- After 3 days, any manipulations will be not only ineffective, but also harmful. Medicines will “blur” the picture of the disease, cause resistance to antibiotics and transfer the infection to a latent form.
If there are no symptoms, after 14 days they are tested for major bacterial infections. After 1.5 months - for syphilis, after another month and a half - for HIV, hepatitis and herpes.
If symptoms appear and a certain infection is suspected, it is not recommended to select medications on your own. First, you need to get test results, take a bacterial culture to determine sensitivity to antibiotics (if there is a bacterial infection), or immediately consult a doctor.
Emergency prevention
It is carried out independently or by contacting an individual STD prevention center. Such points operate around the clock; you can find out their location at the city dermatovenereal dispensary. Most often they are organized near the train station, hotels, large car parks, recreation areas and markets.
The prevention center is an office with an examination chair and a separate toilet. First of all:
- It is necessary to wash your hands with soap, empty your bladder, and rinse your genitals with warm water.
- Next, the doctor wipes the intimate areas with sterile gauze wipes and treats them with a cotton ball with an antiseptic solution.
- Douching of the vagina and urethra is performed. The vagina is washed with 150-200 ml of an antiseptic solution (Chlorhexidine or Miramistin is used). 1 ml is poured into the urethra, 2 ml for a man. An alternative to drugs are potassium permanganate (for vaginal douching) and silver nitrate (for the urethra).
- After treating the genitals, you must refrain from urinating for two to three hours.
If it is not possible to visit a preventive clinic in the next 2 hours, the procedure is carried out at home. Algorithm of actions:
- Urinating immediately after coitus will help flush out harmful bacteria from the urethra.
- Rinse the external genitalia, treat with antiseptic solutions containing chlorhexidine, miramistin or povidone-iodine.
- Inject the medicine into the urethra (1-2 ml) and into the vagina (10 ml). Effectively use antiseptics in the form of vaginal suppositories and tablets.
The best option is to treat the genitals and urethra with an antiseptic in the first minutes, and then contact a preventive center.
Medicines
This group includes tablets that contain a large dosage of hormonal substances.
Depending on the active hormone that is part of the product, there are several methods of using emergency contraception:
- The Yuzpe method is taking twice a day (every 12 hours) equal dosages of drugs based on Ethinyl estradiol (200 mg) and Levonorgestrel (1.5 mg).
- Taking medications that contain Levonorgestrel (1.5 mg). It can be taken twice a day, and the total dosage is divided into 2 equal parts. Another way is to take a high dose once.
- Taking pills based on Mifepristone or a progesterone hormone antagonist. It is taken once at a dosage of 10 mg.
When comparing methods, it is necessary to point out that the Yuzpe method is less effective.
The use of Levonorgestrel is aimed at suppressing ovulation, but it does not affect the process of implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterine wall. This feature must be taken into account when using the drug after the ovulation period. If these nuances are not observed, then Levonorgestrel-based tablets become completely ineffective and do not in any way protect a woman from unwanted conception.
Mifepristone-based drugs inhibit the ovulation process and prevent the implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterine mucosa. Scientific research has also proven that they are able to “delay” the onset of ovulation for 4 or more days.
This feature of Mifepristone is very important, since the vital activity of sperm in the female genital organs is 3-5 days. If you take Mifepristone-based tablets on the date of ovulation, the drug will be effective and will continue to be active for another 3-5 days.
Side effects
All medications can cause a number of side effects:
- aching headache;
- urge to vomit;
- diarrhea;
- discomfort or acute pain in the lower abdomen;
- discharge mixed with blood;
- allergic reactions (nasal congestion, skin rash, shortness of breath, etc.).
Menstruation after emergency contraception tablets changes slightly. Often there is a change in the date of menstruation (up or down). Some women note that after taking medications they experience slight spotting between periods. This feature is not a pathology or a cause for panic.
After using the chosen method of contraception, a visit to the gynecologist is recommended. This is necessary to confirm the effectiveness of the drug and eliminate the risk of pregnancy.
Interaction with other drugs
The simultaneous use of certain medications and emergency contraception is unacceptable. To avoid causing side effects:
- Concomitant use with Ampicillin, Tetracycline, Barbiturates, Tacrolimus, and Griseofulvin reduces the effectiveness of contraceptive action.
- Taking contraceptives simultaneously with drugs to normalize glucose levels, as well as anticoagulants, reduces the effectiveness of the latter.
- The combined use of contraceptives and glucocorticosteroids leads to the accumulation of the contraceptive effect of the corresponding drugs in the blood.
- The simultaneous use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and Mifepristone is prohibited.
- It is not recommended to take Mifepristone and Levonorgestrel before responsible work.
Pregnancy after taking
No contraceptive drug provides a 100% guarantee against unwanted conception. And if, after taking appropriate medications, pregnancy does occur, then gynecologists advise women to terminate it.
The effect of hormonal drugs on the fetus has not been fully studied, so abortion is necessary to avoid negative consequences.
Ectopic pregnancy
It is important to clarify that the risk of ectopic pregnancy occurs only after taking Levonorgestrel-based tablets. This feature is explained by the fact that the hormone inhibits the “movement” of the egg after the period of ovulation through the fallopian tube. On the one hand, this feature provides protection against unwanted conception, but on the other hand, it contributes to the development of ectopic pregnancy.
When taking medications based on Mifepristone, the risk of ectopic pregnancy is reduced to 2%. On the contrary, it accelerates the “movement” of the egg through the fallopian tube. Moreover, scientific studies have proven that Mifepristone can be used as a comprehensive treatment for ectopic pregnancy.
Traditional methods: more harm than good
In addition to modern contraception, some women use traditional methods. However, most of them do not help prevent conception and pregnancy at all, and some are completely unacceptable because they can be harmful to health. The most famous are:
- douching with water and lemon juice, vinegar or herbal decoctions immediately after intercourse. The principle of operation is that sperm will be removed from the vagina along with the fluid, and acidic water has a detrimental effect on male cells, destroying them. However, this method is not effective. Doctors also warn: frequent douching negatively affects the microflora of the vagina, which leads to inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane;
- douching with manganese water. It will not be possible to achieve a positive effect, but a woman risks getting a burn to the vaginal mucosa if the concentration of manganese in the liquid is too high;
- inserting a piece of laundry soap or a slice of lemon into the vagina before sexual intercourse. The sperm will not die, but the balance of the vaginal microflora will be disrupted. Gynecologists insist: the use of this method can lead to serious diseases of the woman’s genital area;
- hot bath with mustard. Some women take such a bath immediately after sexual intercourse. The method does not lead to a positive result, but there is a risk of developing a severe allergic reaction.
Doctors recommend that women not risk their health and use proven methods of contraception to protect against unwanted pregnancy.
Modern medicine offers a large selection of contraceptives. Depending on individual preferences and the presence of contraindications, each couple can choose the most suitable method that will prevent the occurrence of an unwanted pregnancy, as well as enjoy each other without worrying about the risk of conception. There is no need to listen to the advice of friends or acquaintances. The best option for choosing a contraceptive would be a consultation with a gynecologist. Based on the examination results, the doctor will select an effective drug or product that is right for you.
Learning new things and self-improvement are the main criteria in work, which I always try to do efficiently!
Emergency contraceptive pills
Tablet preparations of emergency contraception are classified depending on the active component into several forms:
- Levonorgestrel-based drugs - Postinor, Escapelle, Levonelle.
- Based on Mifepristone - Agesta, Ginepriston, Zhenale.
- Oral contraceptives - Ovidon, Marvelon, Ovret, Microgynon.
Postinor
One of the most well-known emergency contraceptives contains 0.75 mg. Levonorgestrel.
Method of administration:
- the total dosage is divided into 2 doses;
- Take the first tablet no later than 3 days after unprotected sexual intercourse;
- the second - no later than 12 hours after taking the first tablet.
The effectiveness is 94% if taken within the first 24 hours after unprotected sex. The effect will be equal to 86% if Postinor is taken on the 2nd day and 57% - on the 3rd after unprotected sexual intercourse.
Escapelle
It is an analogue of Postinor. Escapel contains 1.5 mg of active Levonorgestrel.
Method of administration: single use of 1 tablet no later than 4 days after unprotected sexual intercourse.
The effectiveness of Escapel (subject to the basics of application) reaches 98.9%.
Gynepristone (Agesta)
The base contains 10 mg. Mifepristone.
Method of administration: a single dose of 1 tablet of the appropriate remedy no later than 3 days after sexual contact.
Numerous studies have proven that it is drugs based on Mifepristone that most effectively protect against unwanted conception.
Oral contraceptives
The active component of such drugs is ethinyl estradiol. Oral contraceptives can replace emergency contraception. They perform the same functions and have approximately the same effect.
Method of administration:
- the total dosage of the product is divided into 2 parts;
- Take the first tablet no later than 3 days after unprotected sex;
- the second - 12 hours after taking the first tablet.
Depending on the name of the drug, the content of the active hormone may vary. This is important to consider when determining the dosage of an oral contraceptive.
For example, if you use Microgynon or Marvelon as an emergency contraceptive drug, the total dosage of tablets will be 8 pieces, respectively, a single dose will be 4 tablets, and the remaining 4 of the total dose will need to be taken after 12 hours.
When using Ovidon or Ovulene, the total dosage of tablets is 4 pieces, respectively, 2 tablets for each dose.
EllaOne
Included in the group of new generation products. Can be used as an abortifacient.
Directions for use: once, no later than 5 days after sexual intercourse.
Contraceptive methods used before sexual intercourse
Barrier contraception
This method involves placing some kind of barrier between the sperm and the egg. It includes the following varieties:
| Method | Description |
| Contraceptive sponge | This is a soft disc-shaped product containing spermicide (a substance that kills sperm). You wet it with water and insert it into your vagina before having sex. The sponge must be left in place for six to thirty hours to ensure effective protection. |
| Diaphragm and neck cap | The diaphragm and the cervical (uterine) cap are similar to each other, but the second one is smaller in size. They block sperm and prevent sperm from entering the cervix, where they can reach the egg. You need to add spermicide to the product before use, and then leave it for 6-8 hours to 24 (diaphragm) -48 (cap). |
| Female condom | It is worn inside the vagina and should not be used in conjunction with a male condom. Suitable for single use. |
| Male condom | It is put on the penis. Made from latex, polyurethane or sometimes even natural material (sheep), it can be with or without lubricant. |
Hormonal method
Hormones prevent fertilization, ovulation, or implantation of a fertilized egg. The method includes:
- Oral contraceptives (OC). Oral contraceptives are commonly called birth control pills and come in several varieties available. Your doctor can help you choose the right one.
- Contraceptive patch. You wear the patch for three weeks (week four off). Hormonal substances from it enter the ovaries through the bloodstream, and the eggs lose their ability to fertilize.
- Injections / Shot. You can use the injections every three months, but not more than two years in a row.
- Vaginal ring. You insert it inside your vagina and wear it for three weeks (week four off).
Implantation method
Implantable contraceptives are inserted into the body and remain there for several years. These include:
- Subcutaneous implant. This rod is the size of a matchstick and is inserted into the shoulder. There it releases the hormone progestin, which prevents pregnancy. The most famous brands are Northplant and Northplan.
- IUD (intrauterine device). They can be copper (plastic inside) or hormonal, most often T-shaped. Copper ones inhibit sperm production and reduce the lifespan of eggs, while hormonal ones act in a similar way to other contraceptives containing progestins. There are also inert IUDs, but they are less effective.
Permanent, including surgical method
The effects of these methods cannot be undone and include*:
- Implants such as Essure. They are products placed into the fallopian tubes without surgery, which are subsequently overgrown with scar tissue.
- Surgical sterilization. Women's fallopian tubes may be tied or severed. In men, a vasectomy involves ligating or disconnecting the vas deferens in the scrotum.
*Although there are operations to restore reproductive capacity after such procedures (when possible), but given their cost, complexity and reduced chances of conceiving in the future, this is in most cases an irreversible method.
Precautionary measures
You can preserve women's health only if you adhere to the following basics:
- Before taking the drug, carefully study the instructions for use, especially contraindications.
- Strictly follow the recommendations specified in the instructions.
- It is recommended to take the tablets on an empty stomach (or 2 hours after meals). In this way, the maximum contraceptive effect is achieved.
- Be sure to take the tablets with plenty of cool water.
- If the instructions say to divide the total dose of the drug into 2 parts, then you need to do so. Ignoring this point may result in the development of serious side effects.
Only high-quality, protected sex can protect a woman from unwanted pregnancy.
Levonorgestrel-based birth control pills
Emergency contraceptives that contain levonorgestrel prevent fertilization of the egg. After taking the pill, ovulation is delayed due to cervical mucus, which prevents sperm from entering the egg.
Whether these birth control pills will help after intercourse depends on the time that has passed since sexual contact :
- up to 24 hours - 95% efficiency;
- 25 - 48 hours - efficiency 85%;
- 49 - 72 hours - effectiveness 58%.
The principle of action of contraceptive injections
Birth control injections Depo-Provera and Noristerat are usually injected intramuscularly into the buttock or forearm. The Sayana Press injection is given subcutaneously, not in the muscle, in the abdomen or thigh.
The contraceptive injection works in the same way as the implant. It constantly releases the hormone progestogen into the blood. Progestogen is similar to the natural hormone progesterone, which is produced in a woman's ovaries during menstruation.
Release of the progestogen hormone:
- stops women's monthly production of eggs (ovulation)
- thickens/makes the mucus from the cervix more viscous, which makes it much more difficult for sperm to penetrate through it
- makes the lining of the uterus thinner so that it cannot hold a fertilized egg
The injections can be given at any time during your menstrual cycle, as long as you and your doctor are sure you are not pregnant.
Injection contraception after childbirth
The injection can be given at any time after giving birth, as long as you are not breastfeeding. If you are breastfeeding, the injection is usually given after 6 weeks.
- If the injection is given before or on the 21st day after birth, you will be immediately protected from becoming pregnant.
- If it is later than day 21, you will need to use additional contraception for the next seven days.
If the injection is given in the first few weeks after birth, heavy and irregular bleeding may occur. The injection is safe to use while breastfeeding.