After 45 years, a new stage begins in the life of women. Due to hormonal changes, she begins to worry about the deterioration of her health and the appearance of unpleasant sensations throughout her body. The reason for this is the onset of menopause - an irreversible physiological process that entails a lot of changes. Pain in the lower abdomen during menopause is quite often frightening, forcing a woman to come up with disappointing diagnoses for herself. Excruciating spasms are often felt in the lower back, as well as in the mammary glands and in all the muscles of the body. What do gynecologists recommend doing if a patient, along with other manifestations of menopause, experiences pain in the back and abdomen? How to alleviate symptoms that interfere with a full life?
The lower abdomen hurts and the back feels tight: can this happen with menopausal syndrome?
The onset of premenopause is characterized by a decrease in the production of female hormones by the uterine appendages. Initially, this affects the destabilization of the menstrual cycle. Delays begin, periods are either heavy or scanty. The psycho-emotional state worsens, insomnia appears, which causes headaches and daytime irritability. Due to constant stress, immunity decreases, the likelihood of seasonal diseases increases, and depression and psychosis develop. In addition, a slow metabolism contributes to the appearance of fat deposits. It is not surprising that in addition to everything, women suffer from pain in the lower abdomen, as well as pain in the lumbar spine.
What is the etiology of this phenomenon? Experts explain the painful sensations by a sharp drop in the quantitative indicators of estrogen in the blood. A lack of sex hormones provokes muscle spasms in the perineum and lower extremities, migraines and severe headaches, discomfort in the uterus and appendages, sacrum and lower back, and neck. Some women consider this natural and do not rush to seek help, others immediately make fatal diagnoses for themselves, self-medicate, or let things take their course. What should a lady do if she feels an unpleasant pain in her lower body? What do body spasms signal?
What happens during perimenopause
Irregularities in the menstrual cycle during this period are caused by changes in hormones . The level of progesterone and estrogen gradually decreases, and follicle-stimulating hormone increases. The number of androgens in the body decreases, but much more slowly. This imbalance leads to an excess of male hormones over female ones.
Changes in hormonal levels affect the physical and psychological health of a woman. This manifests itself in a sharp decrease in sexual desire and the appearance of the first signs of aging . Menstruation is chaotic, intermenstrual bleeding . But the opposite situation is also possible, when lean and rare critical days .
Cause and effect
With the advent of menopause, destabilization occurs in the harmonious functioning of all organs of the female body. Along with hot flashes, constant lack of sleep and problems with the cardiovascular system, the woman is tormented by pain in the back. The spine suffers from increased stress almost constantly during premenopause.
Why does the lower back, shoulder blades and sternum area hurt during menopause?
- the body lacks calcium, which has a bad effect on the spinal column and heart muscle;
- Estrogen deficiency negatively affects the organs of the excretory system, so the kidneys may hurt;
- due to hormonal imbalance, weight rapidly increases, and accordingly, the load on the lumbosacral spine increases;
- unstable operation of all systems of the female body leads to the formation of intervertebral hernias;
- age-related changes occur in cartilage and tissues, which become the causes of the development of arthritis and osteochondrosis;
- low levels of female hormones negatively affect ligaments and muscles, so after heavy physical activity, during an incline or after long walks, your back begins to hurt;
- Digestive problems and disruption of intestinal flora can cause discomfort in the back of the body.
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of pain. It is better not to postpone a visit to a specialist in order to identify the pathology in time and not aggravate the situation.
When to see a doctor
Nagging pain in the lower abdomen in women, depending on the causes of its occurrence, requires treatment by a specialist. It is advisable to make the first contact with a therapist, who will collect all the necessary data and be able to determine the further direction of diagnosis.
Based on the results of general studies, a visit to the following specialists may be indicated:
- gynecologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- proctologist;
- oncologist.
As part of the initial diagnosis, emergency conditions (for example, “acute abdomen”) may be detected that require urgent consultation with a surgeon. Some causes can only be eliminated surgically.
“Red flags” for abdominal pain that require urgent hospitalization:
- decrease in blood pressure below 90 mmHg;
- prolonged tone of the peritoneal muscles;
- transition of nagging pain to the acute phase;
- vomiting blood;
- loss of consciousness;
- black stools or blood in the stool.
The presence of at least one symptom listed above requires an urgent call for an ambulance. You can independently alleviate the condition before the doctor arrives by ensuring rest by taking no more than 2 tablets of no-shpa and cool compresses on the abdominal area. Cold is used for no longer than 3 minutes in a row to prevent hypothermia of internal organs.
Taking any other drugs may blur the clinical picture and complicate further diagnosis. Unmotivated use of any PVS (anti-inflammatory drugs) is especially dangerous.
Why does my stomach hurt during menopause?
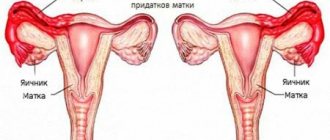
During menopause, pain in the uterus and pelvic region, unfortunately, is not uncommon. Preparing the body for menopause becomes the main reason for the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen - changes largely affect the reproductive organs. In the uterus, connective tissue replaces the muscle layer, the ovaries become smaller, and the endometrium dies. Each of these processes is reflected by pain in the pelvic area. It is sometimes completely impossible to endure it without painkillers.
When menopause occurs, the lower abdomen may hurt like during menstruation. What are the most common causes of this phenomenon?
- Slow metabolism is fraught with disruptions in the functioning of the intestines. If during menopause the lower back hurts or the lower abdomen feels tight, bloating, stomach cramps, constipation and more serious diseases of the digestive system can be diagnosed.
- Does your stomach hurt like before your period? This means that age-related disruptions occur in the reproductive system. In addition, such pain in premenopause and even at the menopause stage is a characteristic sign of the onset of menstruation, which no longer comes on schedule.
- The brain's response to decreased production of estrogen, which is responsible for many aspects of health, can manifest as pain in different areas of the body, but pain is usually localized in the abdomen.
Read
Osteoporosis during menopause: treatment, prevention
If during menopause there is a strong pull in the lower abdomen, it is necessary to help the body get rid of the unpleasant symptom. It should be remembered that self-medication in this situation can have dangerous consequences for women's health.
Ways to alleviate the condition
To get rid of pain, it is necessary to determine the cause of its occurrence. Otherwise, the chosen treatment may not be effective. A woman needs to see a doctor who will prescribe a series of tests. It is necessary to determine the state of hormonal levels, general blood and urine parameters, and perform an ultrasound of the internal organs. First of all, the doctor must exclude oncology, the presence of formations in the pelvis, and any inflammatory processes. Tests are required to detect arthritis and osteoporosis.
When unpleasant symptoms are caused solely by low estrogen levels, the doctor prescribes hormone replacement therapy. Commonly used products are Janine and Divina. But hormonal drugs have a number of side effects - the development of edema, thrombosis, and an increased risk of cancer. Therefore, in milder cases, a woman is prescribed herbal complexes - Remens, Feminal. They contain phytohormones and gently eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of menopause without side effects.
To combat pain, painkillers or antispasmodics are prescribed:
To normalize the psycho-emotional state, a woman is recommended to take antidepressants. Medicines should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor, since their use in the wrong way can further worsen your health.
Folk remedies
Simple homemade medications will help ease the condition of menopause:
- Yarrow. Effective for hot flashes, relieves excessive sweating. For treatment, the herb is dried and ground into powder. It is added as a seasoning to dishes.
- Fireweed. It helps especially well with edema and tachycardia. Used as an alcohol tincture, 20 drops daily.
- Raspberry leaves. Helps in the fight against abdominal cramps. They make simple tea, which you can take several mugs a day.
Pain as a dangerous symptom
The lower abdomen during menopause often hurts due to dangerous provoking factors. This is not always due to physiology or psychosomatics. During menopause, the area of the uterus and appendages is disturbing due to a number of urological or gynecological ailments. They are indicated by pulling, cutting or stabbing pains that do not go away either at night or during the day.
What pathologies can cause discomfort in the body?
1. Uterine synechiae . During menopause, the size of the uterus decreases and its cavity shrinks. This physiological phenomenon is accompanied by the appearance of adhesions and fluid stagnation. Inflammations associated with atrophic phenomena often occur, hence intolerable pain in the area of the uterus and appendages.
2. Endometriosis . This disease is quite common. Women of reproductive age are susceptible to it, and with the onset of perimenopause, the likelihood of cells of the inner layer of the uterus growing beyond its limits increases significantly. Endometriosis is accompanied by heavy bleeding during menstruation, as well as pain symptoms that are localized at the site of pathological growth of the endometrium.
3. Salpingitis . Flank pain during perimenopause is often caused by inflammation of the fallopian tube. With this disease, pain is felt at the slightest movement, the body temperature rises, because the inflammatory process is actively developing in the body. Salpingitis in almost 60% of cases is diagnosed in women who have a history of ectopic pregnancies and gynecological surgeries.
4. Fibromyoma . A benign neoplasm affects the uterus as a result of a hormonal storm. It is signaled by constant nagging pain in the appendage area, often accompanied by spotting or severe bleeding. Fibroids can degenerate into cancerous tumors, and therefore require competent treatment.
Note! Hormonal imbalance can provoke the development of cancerous tumors. Ignoring the body's signals is fraught with serious consequences. If even minor symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Timely therapy will help get rid of pain, identify pathology at the initial stage and significantly improve well-being.
Preventive measures
To prevent the occurrence of abdominal pain during menopause, a woman needs to regularly visit a gynecologist. Despite the decline of reproductive function, the risk of developing many dangerous diseases does not disappear. You should consult a doctor and undergo all necessary tests at least once a year.
Disease prevention also involves following other rules:
- introduction of an active lifestyle, regular sports, walking in the fresh air;
- a balanced diet that excludes junk food (fast food, fried, fatty foods), rich in vitamins;
- weight control;
- stabilization of psycho-emotional state, fight against stress.
If there are concomitant diseases, the prescribed treatment should not be neglected. It must be remembered that with the onset of menopause, many chronic ailments worsen.
How to overcome abdominal and lower back pain during menopause?
Women of menopausal age are required to take a complex of vitamins and minerals, as well as a balanced diet. Carbonated drinks and alcohol should be completely excluded from the menu, and the consumption of strong black tea and coffee should be moderated, especially before bedtime.
If it is not possible to immediately visit the doctor's office, women can take the following medications to relieve pain:
- ibuprofen;
- tempalgin;
- paracetamol;
- diclofenac;
- analgin.
For a single dose, any painkillers with an anti-inflammatory effect are suitable. However, long-term self-medication is strictly prohibited!
It is possible to prescribe medications containing herbal components, the effect of which on the female body is identical to the effect of sex hormones.
According to reviews from mature ladies, for pain in the abdomen and lower back, as well as other unpleasant symptoms of menopause, the following help:
- Klimadinon;
- Klimakt-Hel;
- Bonisan;
- Qi-Clim;
- Femoston;
- Klimaktoplan.
They help normalize hormonal levels and emotional state, eliminate insomnia and weakness, actively fight headaches and speed up metabolism.
The use of traditional medicine recipes also gives good results. It is recommended to take herbs in the form of a decoction or tincture:
- boron uterus;
- Red clover;
- linden flowers;
- sagebrush;
- raspberry leaves.
If after taking analgesics the pain does not decrease, chills and nausea appear, the temperature and blood pressure rise, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Treatment methods
After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment, which may include antispasmodics, antibiotics, and hormonal drugs. In some cases, only surgical treatment is indicated. Traditional recipes are used as auxiliary therapy.
Medications
Each group of diseases, which has pain in the lower abdomen as a symptom, requires the prescription of different groups of drugs. In each case, the course is selected individually, which often depends on the severity of the pathology.
Main directions of drug therapy:
- Pyelonephritis, cystitis - antibiotics and diuretics.
- Endometriosis – hormonal drugs, surgical curettage.
- Inflammation of the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes - complex treatment with antibacterial drugs and NSAIDs with the mandatory prescription of vitamin complexes.
- For functional pain – hormone replacement therapy, antispasmodics for pain relief.
Twisting of the cyst stalk, ovarian apoplexy, profuse bleeding, ectopic attachment of the fetus requires exclusively surgical treatment. Resection of uterine fibroids is carried out after careful therapeutic preparation.
Some methods of universal symptomatic treatment:
- In addition to no-shpa, ketonal may be prescribed to alleviate the condition. For nagging pain in the lower abdomen, take 1/2 tablet no more than 3 times a day.
- To relieve hyperemia, edema, and allergic reactions to basic medications, take 1 tablet of Suprastin up to 2 times a day. If ineffective, use a stronger antihistamine - loratadine: 1 tablet no more than 1 time in 24 hours.
- Papaverine for nagging pain is prescribed to normalize pressure and relax smooth muscles. The drug relieves pain and calms the nervous system. Take ½ tablet up to 3 times a day.
For any diagnosis, together with drug therapy, vitamin complexes and individual vitamins are prescribed: C, K, PP and D.
Traditional methods
Herbal remedies can help relieve pain in mild functional disorders and some diseases.
The following traditional medicines are used as additional therapy:
- For accumulation of gases and bloating of the intestines - water infusions of anise, dill, caraway (1 tsp of seeds per 200 ml of boiling water). Take a few sips every hour.
- Teas from mint, chamomile, and St. John's wort are used for antiseptic, sedative, and analgesic effects. Wormwood has an antispasmodic effect. Herbs are used both separately and in mixtures. Prepare based on the proportion: for 1 tbsp. l. herbs - 250 ml boiling water.
- The herbs red brush and boron uterus have a pronounced estrogen-replacement effect. Such herbs are prepared by boiling 1 tbsp for up to 10 minutes. l. raw materials in 250 g of water. Take the entire amount per day during the entire cycle, excluding the bleeding period.
- Yarrow and knotweed have a strong hemostatic effect and help reduce pain. Herbs are used in the form of infusions and decoctions.
Medicinal plants can be used as concomitant therapy, along with official treatment
An important rule for such use is a mandatory consultation with a doctor to avoid duplication and cross-reaction of medicinal substances.
Other methods
Nagging pain in the lower abdomen in women, the causes of which have been accurately diagnosed, responds well to physiotherapeutic treatment. Electrophoresis is most often used for precise delivery of drugs using microcurrents to the sites of inflammation. The procedure delivers substances deep into the tissue, allows you to reduce the dosage of drugs, and does not harm the gastrointestinal tract.
For various indications, ultrasound treatment, radio wave therapy, laser and cryogenic procedures may be prescribed as a replacement for traumatic procedures or surgical methods.
Prevention of pain syndrome
In order not to suffer from pain in all parts of the body during menopause, women are advised to constantly maintain good physical shape, strengthen the muscle corset and always be in good shape. Light exercises that should be performed daily will help prevent blood stagnation in the pelvic organs and stop degenerative processes:
- while lying on your back with your knees bent, lift your pelvis up 10-15 times in 3 sets;
- do a “cat”: standing on all fours, bend your back and stretch your neck as far forward as possible;
- spin the “bicycle” while lying on your back;
- tilting to the side and turning the head;
- pump the press - at least 30 times in 1 approach.
A 15-minute exercise will allow the muscles to receive enough oxygen to maintain tone. In addition, you should take medications containing calcium - this is a necessary prevention of osteoporosis.