Every expectant mother needs to regularly undergo a urine culture test during pregnancy. It is one of those studies that are necessary to confirm that the baby is developing safely and there are no complications.
Photos:
method of studying infection in the body Analysis during pregnancy at the doctor care pulls exercises during pregnancy
During pregnancy, tank culture of a urine smear is considered the most highly informative research method. Research is not cheap, but it cannot be ignored.
When women are prescribed a culture test during pregnancy, many do not know what it is. This is a laboratory test to determine inflammation and infection of the organ from which the doctor took the material.
Highly informational research method
During the study, bacteria are grown at a certain temperature in an area that is favorable and nutritious for them. Only under special conditions can one competently examine a variety of biological materials: bile, urine, feces, blood.
Tank seeding during pregnancy is done for certain purposes:
- identifying the presence of pathogens;
- identifying their quantity;
- determining the level of pathogenicity.
In addition, tank culture during pregnancy allows you to determine which medications microorganisms and bacteria are sensitive to. Only after this can the most safe and effective treatment be carried out.
Why take a urine culture test?
During pregnancy, research of this kind becomes one of the most important. Even if a general urine analysis reflects positive results, tank. culture can determine the chronic or asymptomatic type of infectious pathology of the genitourinary system. It is easier to stop the development of the disease than to treat its advanced form, risking the health of the baby or its loss.
Testing a pregnant woman's urine for bacteria helps:
- detect infectious pathogens;
- identify infections, identify their properties;
- carry out acceptable therapy, taking into account the stage of pregnancy. To do this, the susceptibility of the flora to antibiotics is determined;
- protect the fetus from infection and irreparable changes to its organs that are incompatible with the life of the fetus or newborn.
Testing a pregnant woman's urine for bacteria helps to detect pathology in time.
Often pregnant women are affected by pyelonephritis, which develops through an ascending pathway or due to weakened immunity. The disease can provoke abortion or intrauterine pathologies of the fetus.
In later stages, premature birth is possible. For this reason, it is necessary to undergo a therapeutic course that will help preserve the pregnancy and health of the child.
Detailed description of the study
A urine culture is a test that detects bacteria in the urine that cause a urinary tract infection (UTI). Opportunistic intestinal microorganisms, which often cause UTIs, can enter the urinary tract from the nearby anus. These bacteria include E.coli, Streptococcus spp., Haemophilusinfluenza, Klebsiellaspp., Staphylococcus spp., Pseudomonasaeruginosa, Citrobacter spp. and others. The infection has an ascending course, pathogens from the urethra enter the bladder and ureters, then, if the course of the UTI is unfavorable, to the kidneys.
UTIs are more common in women than in men. This is due to the fact that a woman’s urethra is shorter and much closer to the anus compared to a man’s. Thus, bacteria from the intestines enter the female urinary tract much more easily.
Pregnancy is another predisposing factor for the development of UTIs due to hormonal and anatomical changes occurring in the genitourinary system. Urinary tract inflammation is often asymptomatic, but can increase the risk of premature birth.
In older adults, the risk of developing a UTI increases significantly if a catheter is inserted into the urethra during an examination or hospitalization. UTI is one of the most common hospital-acquired infections.
The most common symptoms of a UTI are:
- Pain and discomfort in the lower back and lower abdomen
- Pain when urinating
- Increased body temperature, chills
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Difficulty in urine flow
- Nausea, less often vomiting
According to current recommendations of urologists around the world, urine culture is the gold standard for testing to identify microorganisms that cause UTIs.
To whom and when is tank seeding prescribed?
As a standard procedure, the test is prescribed to pregnant women upon registration and right before birth. When receiving such a referral, you should not worry or think that there are problems.
Urine testing for culture is necessary if protein was detected in general tests. A similar phenomenon indicates that there is inflammation in the urethra. Such an analysis will help detect the causative agent of infection.
Urine testing for culture is necessary if protein was detected in general tests
A urine culture tank while expecting a baby can be recommended for women affected by urolithiasis. The expectant mother must inform the doctor leading the pregnancy about the presence of existing ailments.
Such reinsurance will help prevent pathologies in the future.
How to collect and donate urine?
Compliance with the recommendations for preparing for the study and proper collection of material will ensure that the results of the analysis are obtained. To do everything correctly, it is important to follow the recommendations:
- purchase a sterile plastic container from the pharmacy;
- before collecting urine, exclude exotic foods and foods that affect the color of urine (beets, carrots) from your diet, and do not use diuretic medications;
- the day before the analysis, eliminate physical activity;
- collect urine in the morning after hygiene procedures without using foam for intimate hygiene;
- After wiping the genitals, you then need to urinate into the prepared container. The labia should not touch the edges of the container;
- pregnancy is accompanied by a large volume of discharge, you need to close the entrance to the vagina with a tampon. This will help prevent foreign bacteria from entering the container;
- After filling the container, close it tightly with a lid and no later than 2 hours later, transfer it to the laboratory.
Collect urine in a sterile container
Do not touch the inside surface of the sterile jar under any circumstances. For analysis, it is better to provide an average portion of urine. After you start urinating, you need to hold the urine, then continue urinating into the container.
What infections does tank culture detect?
Bacteriological research is a way to determine the presence of such diseases:
- cystitis. The infection affects the mucous membrane of the bladder and disrupts its functioning. The disease is provoked by hypothermia, weakened immunity, bacterial vaginosis, and hormonal changes. The active stage of the disease is manifested by itching, pain when urinating, increased urge, and a feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen. The threat of cystitis when carrying a baby is the likelihood of it becoming chronic, as well as pyelonephritis. Inflammation of the bladder can cause premature birth, leakage of water, infection;
- urethritis. It occurs due to poor intimate hygiene, urological infections, and dehydration. The disease is initially detected when urine is submitted to a culture tank. The acute stage is accompanied by unpleasant discharge, swelling of the external genitalia, painful sensations when urinating, and an increased urge to go to the toilet. Not treating the disease can cause the child to suffer from pneumonia, conjunctivitis along the birth canal;
- pyelonephritis. Occurs before pregnancy; conception can worsen the course of the disease. The provoking factor is infection. The disease develops due to decreased tone of the urethra and stagnation of urine. Accompanied by headaches and lumbar pain. Pathology can provoke: fetal death, hypoxia, premature birth.
Tests ensure the identification of dangerous pathologies, help prevent it, and protect the baby from infection.
Urine culture tank during pregnancy
Bacteriological urine culture (or tank culture) is necessary to identify and identify pathogens of urinary infections, with further determination of the sensitivity of harmful bacteria to antibiotics.
The culture tank is taken twice during pregnancy - upon registration and before childbirth (at about 36 weeks of pregnancy). If leukocytes and/or protein are detected in a general urine test, as well as in cases of kidney and bladder diseases, urine testing for a culture tank is prescribed more often.
When treating urological infectious diseases, for control, a repeat urine culture is prescribed a week after stopping the antibiotic or uroseptic.
Urine collection container
Why do you need to take a urine culture test during pregnancy?
Urine culture is one of the important tests during pregnancy, so it is included in the list of mandatory tests during pregnancy.
Even with a good general urine test, with the help of a culture tank you can find a chronic or latent (asymptomatic) form of a particular infectious disease of the urinary-renal system.
It is better to prevent the development of the disease than to treat an advanced stage of the disease, risking giving birth to an unhealthy child or even losing him.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria occurs in approximately 6% of pregnant women with a normal urinalysis. Such analyzes most often reveal a significant increase in Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli), Enterococcus faecalis (fecal enterococcus), Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus), Candida type fungi and others.
In the absence or untimely treatment, the infection spreads further, affecting the kidneys. Then pyelonephritis begins - inflammation of the kidneys of bacterial etiology.
Pyelonephritis can occur under two conditions: 1) from the source of infection, bacteria spread further, reaching the kidneys; 2) the number of pathogenic bacteria, which are present in every organism in small numbers, begins to increase under conditions favorable for reproduction, for example, with a decrease in immunity “plus” stagnation of urine.
Pyelonephritis during pregnancy most often occurs for the following reasons:
- a decrease in the tone of the ureters and an increase in their length and width under the influence of pregnancy hormones, which can lead to stagnation of urine, where pathogenic microorganisms begin to develop;
- enlargement of the uterus, which can lead to compression of the urinary tract (this picture is especially often observed in pregnant women with a narrow pelvis), which also causes stagnation of urine;
- hormonal changes during pregnancy, which can lead to dilation of the ovarian veins, compressing the ureter, thereby disrupting the outflow of urine, etc.
Pyelonephritis can cause intrauterine infection of the fetus, spontaneous abortion, and in the third trimester cause premature birth.
Therefore, it is necessary to carry out treatment on time in order to preserve the baby’s health.
During pregnancy, for the treatment of pyelonephritis, a gentle antibiotic is usually prescribed, for example, Amoxiclav or Monural, in combination with an antispasmodic, a sedative, and vitamins B, PP and C.
How to properly collect urine for tank culture analysis?
Often test results are distorted due to improper urine collection. Prepare a sterile, dry container with a tight-fitting lid for collecting samples (preferably transparent). Special jars for collecting urine tests can be purchased at pharmacies for almost nothing.
Immediately before collecting urine, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the external genitalia using toilet soap. It is recommended that pregnant women cover the vaginal opening with a piece of sterile cotton wool when collecting urine, so that nothing from the genital tract is brought into the urine collection. Don't forget to wash your hands too, so you don't accidentally transfer bacteria from your hands.
For the study, it is necessary to collect an average portion of morning urine (excreted immediately after waking up) in an amount of at least 70 ml. To do this, you need to skip the first and last stream of urine when urinating.
Those. start urinating, then hold the flow and place the jar, continue urinating into the jar, towards the end of the process hold the flow again, set the jar aside, screw it on with a lid, and finish urinating.
- A urine test must be submitted to the laboratory within 1.5-2 hours after collection.
- Remember that a day or two before taking a urine test, it is not recommended to consume foods that can color urine, such as beets and carrots, as well as diuretics and other medications that can affect the test result.
- Please note that excessive physical activity can increase the concentration of protein in the urine, so the day before the test, reduce physical activity to a minimum.
Analysis results
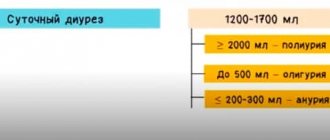
The answer is ready 5, maximum 10 days after donating the liquid. Indicators are detected in colony-forming units per 1 ml of liquid (CFU/ml). For women, this figure should not exceed 1000 units. If the culture result is between 1,000 and 100,000 CFU/ml, they are suspicious to the doctor, who may order a repeat test.
An indicator exceeding 100,000 CFU/ml indicates the presence of a pathogenic process that requires urgent treatment. This amount of bacteria in urine is due to inflammation and infections. Antibiotics are prescribed for treatment.
The results of studies of urine from pregnant women contain a list of detected microorganisms - protozoa, fungi, bacteria. To identify their susceptibility to drugs, an antibacterial test is performed.
The study allows you to determine sensitivity to medications for effective treatment.
What research needs to be done?
During pregnancy, materials for analysis for tank culture are taken from different organs of the woman: vagina, nose, bladder. This allows you to get the most complete picture of a woman’s health status.
Analysis of culture from the cervical canal, carried out during pregnancy, allows us to identify various genitourinary infections in the body (trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis), sexually transmitted diseases, which are very dangerous for expectant mothers. Infections can threaten the baby's life and cause miscarriage.
Can detect various genitourinary infections
When you take a culture test from the cervical canal during pregnancy, be prepared for the results to come in at least 5 days. This is how long it takes for bacteria to grow.
During pregnancy, urine culture must be performed. This analysis is included in the list of main ones.
Even if the general examination showed a good result, this does not mean that you do not have an asymptomatic (hidden) or chronic form of any infectious pathology of the genitourinary system.
It is better to prevent the onset of the disease than to treat its advanced stage later. In addition, there is a risk of either losing the child or giving birth to an unhealthy one.
During pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a urine culture, since approximately 6% of expectant mothers have asymptomatic bacteriuria, although their general urine test is normal. When you take a urine culture test during pregnancy, the doctor usually tells you exactly what it shows. It may contain large amounts of E. coli, fecal enterococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida fungi, etc.
Also read about the sensations during pregnancy after a cesarean section and increased heart rate during pregnancy.
When treatment is untreated or delayed, the infection begins to spread and can affect the kidneys. This will cause inflammation of the kidneys - pyelonephritis.
During pregnancy, the doctor may recommend not only a smear or urine test, but also a nasal culture test. This allows the presence of Staphylococcus aureus to be detected, since the disease can pass from an infected woman to her unborn child.
The test must be taken as early as possible in order to have time for treatment if necessary. The material is collected in a laboratory or clinic and does not require special preparation. When the results show bacteria, the doctor immediately prescribes treatment to the patient, because ignoring therapy risks infecting the fetus in the womb or through the birth canal during childbirth.
We rent early to have time for treatment.
Such studies are also paid. However, it is necessary to take them, because it is timely diagnosis and proper treatment of infections that help save the child and safely carry him to term.
After you receive the research results, you should definitely make an appointment with a doctor for a consultation and interpretation. Do not panic if the doctor finds abnormalities in you. This is not always a sign of any pathology. The results depend on a large number of factors, so only a specialist can give an accurate assessment.
The doctor does not always prescribe the necessary treatment immediately; sometimes he refers you for a repeat test. Let's figure out how to take urine culture tests necessary during pregnancy.
How to donate urine?
When you have received a referral for a urine culture, check with your doctor about how to do it. There's nothing complicated about it.
- Insert the cotton swab into the vagina.
- Collect an average portion of morning urine.
- Deliver the jar to the laboratory within a maximum of two hours.
The container for collecting material must be extremely sterile. It will be very difficult to sterilize any jar at home, so it is best to buy it at a pharmacy.
In the morning you need to wash yourself thoroughly with soap. To prevent bacteria from the vagina from getting into the container with urine, you should insert a cotton swab into it and only then start collecting urine. It is best to take medium urine. To do this, you need to urinate a little into the toilet and only then collect a small amount of material into the container.
It is advisable to deliver the container to the laboratory within an hour. The maximum allowed time is 2 hours. Only in this case will the results be accurate. Your doctor will make treatment decisions based on the results, so if you're pregnant, it's important to know how to collect your urine culture.
Decoding the results obtained
As already mentioned, when you donate a urine culture during pregnancy, you must definitely ask your doctor for a transcript.
Test results are determined in CFU/ml - colony-forming units per 1 ml of liquid:
- when during pregnancy you have your urine tested for culture and the indicator turns out to be less than 1000 CFU/ml, then you are healthy, this number of bacteria does not need treatment.
- if the readings are from 100 to 100,000 CFU/ml, then these are questionable tests; the doctor will most likely refer you for a repeat test.
- if the analysis results show a value above 100,000 CFU/ml, then you are infected with an infection that requires urgent treatment (such a large number of bacteria usually cause infections and inflammation, so the woman is prescribed antibiotic treatment).
The results usually list all the microorganisms that are in the urine. These may include various bacteria, fungi or protozoa. To determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to various medications, the doctor prescribes another study called an antibactogram.
Finds out the doctor's diagnosis
During it, the sensitivity of bacteria to drugs is tested so that the prescribed treatment is as effective as possible. The results obtained must also be deciphered so that the woman can receive detailed explanations and precise instructions for further actions.
When you receive a smear culture form during pregnancy, it usually lists the microorganisms that inhabit the cervical canal. In the normal state, there are no fungi, but at least 107 bifidobacteria and lactobacilli are present. A large number of enterococci and E. coli are very dangerous. Yeasts are also dangerous, especially those with mycelium.
The analysis allows us to detect the presence of Leptothrix, Gardnerella, Trichomonas, Gonococcus, Proteus, Citrobacter, Staphylococcus aureus, epidermal. It is worth knowing that chlamydia, mycoplasma and ureaplasma are intracellular parasites, so a regular study will not be suitable for identifying them. It is necessary to perform PCR of the cervical canal.
| Term | Quantity of content | Consequences |
| 1st trimester | Less than 1000 CFU/ml | There are no consequences for the health of the woman and child. This indicator is considered normal. The expectant mother is not prescribed treatment. |
| 2nd trimester | From 100 CFU/ml to 100,000 CFU/ml | In this case, there is a risk of serious infections, but the doctor usually prescribes repeat tests to exclude errors during the study. |
| 3rd trimester | More than 100,000 CFU/ml | There is an infectious focus in the urinary tract. It threatens possible pathologies for both the woman and the fetus. The baby can become infected in the womb or during the birth process. |
Decoding
Only the doctor leading the woman’s pregnancy deciphers the received data. The presence of various pathogenic microorganisms and rods in the human body is considered normal. An increase in their number provokes the development of diseases, so treatment is required.
Refusal of therapy is fraught with serious consequences not only for the health of the expectant mother, but also for the health of the fetus. This becomes a reason to donate a urine culture during pregnancy. Analyzes indicate the presence (“+”) or absence (“-”) of the growth of pathogenic bacteria. If the growth of microorganisms is detected, a test is performed to determine their susceptibility to antibiotics.
If a gynecologist reports a poor urine culture in a pregnant woman, then an increase in infectious agents has been detected that requires treatment. Antibiotics are involved; Canephron and cranberry juice are certainly not suitable. It is possible to use other medications.