What should be the temperature during ovulation?
There is such a thing as basal body temperature.
It shows the minimum temperature of a person’s body during rest, especially sleep. It is approximately the same for everyone, but in women during ovulation this indicator is higher than normal by an average of 0.3-0.5°C. This is what helps to detect the moment the egg is released, which means successfully conceiving a child when planning.
Measurements are taken in the mouth, vagina and rectum. To draw up a graph, data is taken only from the rectum, which is associated with female physiology, or more precisely with the blood supply to the ovaries.
Manifestations of ovulation
The ovulatory phase is not a pathological condition, but is characterized by several signs, the presence of which allows us to judge its occurrence:
- nagging or aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- increased amount of cervical mucus;
- increase in basal temperature during ovulation;
- increased sense of smell;
- increased sexual desire.
Severe abdominal pain, discharge of an unusual color with an unpleasant odor, axillary temperature above 38 °C and other symptoms are manifestations indicating the disease.
You need to pay attention to the appearance of weakness, nausea, vomiting, which may accompany an increase in temperature during and after ovulation.
A runny nose, sore throat, combined with fever and general malaise are most often signs of an acute respiratory infection. If you experience a feverish state or deterioration in health during ovulation, it is also worth remembering that chronic diseases can worsen at any stage of the menstrual cycle.
Measurement Rules
To obtain accurate data, measurements must be taken correctly, as other factors influence the results. Let's look at the main rules:
- It is better to choose the first day of the menstrual cycle as the starting point for starting measurements.
- Temperature measurement is carried out immediately after waking up from sleep, in the rectum (rectal).
- Before taking measurements, a person must sleep for at least 6 hours.
- It is advisable to measure the temperature at the same time every day and in the same body position (deviation no more than 30 minutes).
- Before the measurement, you should not take a shower, go to the toilet, or generally engage in physical activity (stick your head in and take your temperature).
- The measurement duration is approximately 8 minutes.
- You can use an electric and mercury thermometer, but it is better to give preference to the latter (less risk of error).
- All results should be recorded in a notebook; skipping measurements is not recommended.
- It makes no sense to measure temperature in case of colds or infectious diseases, sleep disturbances, stress, depression, climate change or overwork.
- The reliability of the results is negatively affected by the following factors: taking hormonal medications, contraceptives and sedatives, as well as alcohol and drugs.
- Having sex late at night can also affect your temperature.
Important! Temperature should be measured every day for a month or more. Based on the measurements, it will be possible to create a graph that will show the moment of the highest degree of ovulation.
Pregnancy planning schedule based on basal temperature
For an example, look at the BT chart. Depending on the length of your cycle and your usual temperature, the graph may look slightly different.
Today, many applications have been developed for mobile phones, where the BT schedule is recorded. Based on the indicators, the application will independently determine favorable days of conception, and will also indicate the day the egg is released from the ovary. But this can only be reliable information if you adhere to all the rules for measuring BT.
Thus, monthly charting of basal temperature is an old, but still effective method of pregnancy planning. If the conditions necessary for a correct result are met, you can correctly determine the days of ovulation and conceive a child.
How the graph is built
You need to take a piece of paper in the box.
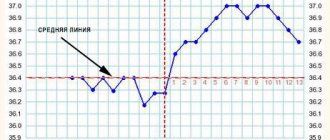
The X (abscissa) and Y (ordinate) axes are drawn on it. Each cell along the axes is marked as one division. X are days, Y is temperature 0.1°C. The temperature is taken as the starting point at 36.0°C for convenience. One graph will reflect one monthly cycle. You should also draw a line at 37°C parallel to the x-axis (X). This is the temperature limit; anything higher is considered pathological. Next, points are plotted on the graph, each day opposite the recorded temperature. At the end of the month the dots are connected.
Important! During measurements, it is necessary to take important notes that took place. For example, there was strange discharge or a headache, and so on. This is important information for a gynecologist.
Analysis
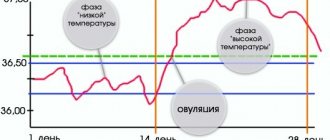
The result is a graph that is visually divided into two parts, showing the phases of low and high temperatures. It looks something like this:
At the beginning of the cycle, the readings are approximately 36.6-36.8°C. Further, from the first day of menstruation, the temperature should normally decrease by 0.2-0.5°C.
Attention! Each woman may have individual characteristics of her body. That is, normal indicators may differ from person to person. Only a gynecologist can detect this feature. The duration of the phases also does not have absolute values for all women.
The duration of one phase is 10-20 days. The phases determine the duration of the cycles. The graph clearly shows the moment of ovulation - the temperature rises sharply. This means the egg is mature and ready to be released.
Next, the body begins to produce progesterone to begin a possible pregnancy. The reproductive system is completely ready for conception. Thanks to this, the temperature rises even higher and remains “in readiness mode” for several days. The difference in temperature at the beginning and end of ovulation should be approximately 0.4-0.5°C.
Then the temperature drops and a new monthly cycle begins.
Important! The most likely moment of conception is ovulation on the first day.
How to use
To make calculations more likely, you should take temperature measurements and make graphs for at least 3-4 months. Then you need to find common features in them that will help determine the most likely periods of ovulation in the future. This information will help not only plan the best time for conception, but also gender.
Typically, the entire cycle lasts 28 days, and ovulation occurs on the 14th day. You are most likely to get pregnant if you conceive 12 hours before ovulation. It is difficult to predict such a moment with an accuracy of hours, which is why data for several months is needed. A gynecologist can help with the analysis.
According to research, the conception of a girl should occur 48 hours before the release of the egg. This is due to the fact that sperm from “girls” are more resilient and tenacious than from “boys”.
By the time of ovulation, male specimens will die, and female specimens will be able to fertilize the egg. To conceive a boy, fertilization should occur as close as possible to the beginning of ovulation, since sperm with “boys” are more mobile and nimble. They are the first to fertilize the egg.
Hyperthermia as a sign of conception
Gynecologists assure that a slightly elevated temperature after the release of an egg from the ovary should not be a reason for panic. As a rule, the thermometer readings do not exceed 37 °C and do not cause discomfort. A woman may accidentally discover that her axillary temperature is slightly elevated. The reason is the production of the second phase hormone - progesterone.
After the follicle has opened, a temporary gland is formed in its place. The corpus luteum produces a hormone that has a relaxing effect on smooth muscles. It also regulates blood circulation and retains fluid in tissues. The hormone of the second phase acts on the autonomic system, as a result of which thermoregulation changes.
An increase in thermometer readings after ovulation occurs in all women of reproductive age after the establishment of a cycle, but the strength of the changes varies in intensity. The temperature after ovulation lasts for 1-2 weeks. The maximum amount of progesterone in the body is observed 6-8 days after the oocyte leaves the ovary. If conception does not take place, then the hormone levels gradually decline, after which a new cycle begins.
Implantation of a fertilized egg is accompanied by another jump in progesterone and slight changes in thermometer values. The secretory activity of the corpus luteum and the high concentration of the second phase hormone do not allow the temperature to drop. Therefore, elevated values that persist for more than two weeks can indirectly be considered the first signs of pregnancy.
Gynecologists do not recommend placing high hopes on this symptom, since other circumstances may be the cause of hyperthermia. To confirm your suspicions, you need to wait until your next menstruation is missed and take a pregnancy test.
Increase in temperature and reasons for deviation from the norm
The graph can help detect various pathologies. For example, the temperature increase exceeded 37°C, sharp jumps were observed, or the graph did not show clearly defined phases of ovulation and menstruation. All this indicates some kind of disturbance in the body.
Possible reasons for deviations in temperature readings may be:
- Infectious processes.
- Previous anal sex.
- Poisoning (intoxication), for example, with alcohol.
- Experienced stress.
- Eating spicy or too salty foods.
- Diarrhea.
- Insomnia.
- Taking sedatives.
- Change of climate zone.
- Increased physical or psychological stress.
- Stormy sex the day before.
- Changing the thermometer.
Such moments must be noted and compared with facts from life. This will help eliminate errors in maintaining the schedule.
A possible cause of deviations may be hormonal disorders in the body. In this case, a schedule may arise where there is no clear moment of ovulation.
That is, the temperature remained virtually unchanged throughout the monthly cycle (the deviation in this case is only 0.1-0.3°C). This means that for some reason the estrogen level did not change, so the woman could not get pregnant.
Where to buy an ovulation thermometer?
It's worth going to a pharmacy to buy an ovulation thermometer, although you can also buy one online. Prices start from 12-14 zlotys, but if we want decent equipment, it is better to invest about 40 zlotys in it. Interestingly, the cheapest ovulation thermometers are usually electronic, but they are of low quality. For 40-50 zlotys we will buy a glass thermometer or a battery-powered thermometer, which will last us much longer.
Bibliography
- “Statement of the expert group of the Polish Gynecological Society on the use of natural methods of family planning for contraception”, expert group of the Polish Gynecological Society, published in: Gynecology Polska, 2010, 81, 947-94
- https://pl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Owuła
- https://pl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Termometr_owulacyjny
Vorobyova Marina
Neurologist of the highest qualification category (work experience 14 years), doctor of neurofunctional diagnostics (work experience 12 years);
author of scientific publications on vertebroneurology; participant of scientific conferences on neurology and functional diagnostics of all-Russian and international significance. About
Prevention
To prevent various female diseases, as well as infertility, it is recommended to maintain a BT calendar for at least 3 cycles. If observations are carried out correctly, they can provide a qualified doctor with a lot of useful information in case of suspicion of any pathologies in a woman’s body.
It should be remembered that one or two cycles without ovulation per year is the norm. But if BT levels periodically increase before menstruation or at the beginning of the cycle, this will be a signal to contact a gynecologist even before other symptoms appear (itching, pain, cycle disorders, urinary problems).
In addition, it is recommended to undergo a preventive gynecological examination every six months.
Thus, increased BT in the first half of the cycle and on the eve of menstruation is a pathology and indicates the need to see a doctor.
In some cases, a high core temperature may indicate pregnancy. But if a temperature difference of at least 0.4 ° C between the two phases remains, perhaps we are talking about an individual norm.
Source
Signs and sensations of ovulation in a woman
In 90% of women of childbearing age, the menstrual cycle lasts from 28 to 32 days and is divided into three main phases: follicular, ovulatory and luteal.
Follicular phase
The first phase begins from the onset of menstrual bleeding and lasts for 10-14 days. Under the influence of hormones in the ovary, a certain number of primary follicles are activated and their maturation begins. At the same time, the uterus begins to prepare for pregnancy, initiating the formation of a new layer of the endometrium.
During the last five days of the follicular phase, one (in rare cases two) of the follicles separates from the cohort and continues its maturation to a dominant state. It is he who will subsequently release the egg for its passage through the fallopian tubes and subsequent fertilization.
Ovulatory phase
The levels of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones, which reach maximum values at the end of the follicular phase, lead to the rupture of the dominant follicle and the release of the egg from the ovary into the fallopian tubes, from where it begins its journey to the uterus with the help of cilia pushing it. At the site of the burst follicle, a corpus luteum forms, which begins to produce progesterone and prepare the uterine mucosa for possible pregnancy.
The timing of ovulation varies from cycle to cycle and woman to woman, but usually occurs 14 days before the next period.
The fertile period, taking into account the lifespan of sperm and egg, ranges from 12 to 24 hours from the moment the egg is released.
The exact time of ovulation can be determined by charting your basal temperature and using an ovulation calendar.
Luteal phase
The fertilized egg moves to the uterus within 7-10 days, where implantation and development of the embryo occurs during its attachment to the wall. The corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone to maintain the pregnancy and prevent the release of new eggs. By 10-12 weeks, its main functions are taken over by the placenta, and it disappears.
If fertilization fails, the egg dies within 12-24 hours after ovulation. Hormone levels return to normal, and the corpus luteum gradually disappears.
In approximately 1-2% of cases, two eggs are released into the fallopian tubes during ovulation. This condition is usually observed in women over 35 years of age. Fertilization of two different eggs by two different sperm results in the birth of twins.
Signs of ovulation
Symptoms of the process vary from woman to woman and may not always be repeated during each cycle. Only two signs remain unchanged: an increase in basal body temperature and changes in the structure of cervical mucus. A small proportion of women do not experience any symptoms at all; in this case, the only reliable method for determining ovulation is ultrasound.
Monitoring sensations during ovulation not only increases the chances of pregnancy, but also helps a woman identify complications associated with the reproductive system.
Increase in basal temperature
Basal body temperature is the lowest body temperature at rest after prolonged sleep.
In the first phase of the menstrual cycle, the indicator is just below 37 °C and, as it approaches ovulation, it gradually decreases to values of 36.3-36.5 °C.
The process of egg release and a surge of progesterone increase the temperature to 37.1-37.3 ° C, and the fertile period begins.
Charting your basal body temperature is one of the most popular methods for tracking ovulation.
Measurements should begin to be taken every morning before getting out of bed several months before the expected conception by inserting a digital thermometer into the rectum.
The data is entered into a special chart, information from which helps determine the onset of ovulation in subsequent cycles.
Read more: [Basal temperature during ovulation]
Change in cervical mucus
Cervical mucus is a natural fluid in the female body that is produced in the cervix during the menstrual cycle.
At the time of ovulation, under the influence of estrogen, the mucus acquires an elastic and transparent consistency, reminiscent of egg white.
Thus, the body creates a favorable environment for sperm, which easily penetrate the barrier between the vagina and cervix.
The best way to test the consistency of cervical mucus is to stretch it between your index finger and thumb. Transparent, slippery and elastic consistency is a clear sign of ovulation.
As you get older, the amount of cervical mucus decreases and the duration of its change during ovulation. A woman at the age of 20 retains fluid for up to five days, but at the age of 30 the number of days is reduced to 1-2.
Signs of ovulation and its end
Changes in cervical position
The cervix plays a large role in the female reproductive system. It connects the vagina to the uterus and acts as a barrier that opens during the most fertile period, allowing sperm to enter the fertilization site. During ovulation, the cervix becomes soft, high and moist.
It is quite easy to determine and interpret this sign of ovulation. Before the procedure, you should wash your hands, take a comfortable standing position and insert two fingers inside the vagina.
The longest finger should reach the neck. If the cervix is low and feels like touching the tip of the nose, ovulation has not occurred.
If the cervix is high and soft to the touch, the ovulatory phase has begun.
Minor bleeding
Brown or light spotting during ovulation is normal. The symptom can be detected when a mature egg leaves the follicle and the level of estrogen in the body drops.
There is no need to worry, but if the spotting persists for a long time, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will check for signs of infection and conduct an examination to rule out an ectopic pregnancy.
Increased libido
Some women note that during ovulation their sexual desire for their partner increases.
Doctors associate this phenomenon with signals from the body, which strives to preserve and procreate.
However, according to other experts, girls should not always trust this symptom, since changes in libido can also be triggered by other factors: a glass of wine or just a good mood.
Increase in breast volume
During ovulation, under the influence of hormones, painful sensations occur in the breast area, its volume and sensitivity of the nipples increase. The sign is not the main one, so it should only be considered together with others to determine ovulation. Some women continue to experience mild breast pain until the end of their menstrual cycle.
Pain in the lower abdomen
During ovulation, some women experience pain that resembles short cramps or a sharp tingling sensation in the lower abdomen.
Typically, discomfort occurs at the level of the ovary on one side and in a small number of cases in the kidney or lumbar region.
During a normal menstrual cycle, the pain goes away within one day, but in some women it can continue for several days, resembling menstrual cramps.
The cause of pain is a mature dominant follicle measuring 20-24 mm, causing stretching of the peritoneum and irritation of its pain receptors. When the follicle ruptures, releasing the egg and the follicular fluid that protects it, the pain disappears.
Read more: [Why does the lower abdomen hurt during ovulation? ]
Heightened sense of smell
For some women, a heightened sense of smell and changes in taste preferences in the second phase of the menstrual cycle may be symptoms of ovulation. The sense of smell increases so much that the male pheromone androstenone, the smell of which causes a negative reaction in women on normal days of the cycle, on the contrary, begins to attract them during the period of ovulation.
Bloating
In rare cases, a sign of ovulation is mild bloating. It, like many other symptoms, occurs as a result of increased estrogen levels, which leads to water retention in the body. If a woman has a hormonal imbalance, when the level of estrogen prevails over the level of progesterone, the symptom manifests itself more clearly.
Crystallization of saliva
Two days before ovulation, saliva crystallizes due to an increase in luteinizing hormone in a woman’s body. You can determine the sign at home using a regular microscope - the image of saliva resembles the formation of frost on glass.
Test strips for determining ovulation
The easiest way to determine ovulation is to use special test strips that detect high levels of luteinizing hormone in a woman’s body and signal the onset of a fertile period. Most tests are presented with paper or plastic strips; more expensive options are equipped with a digital display.
Manufacturers advise not to urinate 4 hours before testing to ensure sufficient levels of the hormone are concentrated in the urine. Therefore, many women prefer to use strips in the morning.
If the result is positive (increased levels of luteinizing hormone), the test strip will take on the same color or slightly darker as the control. Typically, ovulation occurs 1-2 days after the level of luteinizing hormone begins to increase. This period of time is the most favorable for conceiving a child.
The start of testing depends on the cycle length:
FAQ
How to understand that ovulation has occurred? Two main signs of ovulation: an increase in basal temperature and a change in cervical mucus. When using the test, the test strip will take on the same color or a little darker as the control strip. When does ovulation occur after the end of menstruation? After the end of menstruation, ovulation occurs in the middle of the cycle, with a normal menstrual cycle on days 14-16 after the end of menstruation. Ovulation calculation online . Press!
Source: https://mymammy.info/ovulyatsiya/25-priznaki-ovulyatsii.html
Consequences
With a high BT in the first half and a slight temperature difference in the two phases (for example, 0.2 °C), the chances of fertilization are reduced. A lack of estrogen leads to the fact that the body does not have the conditions for normal maturation of the egg.
Even if a follicle begins to grow in the ovaries, ovulation still does not occur, and the follicle degenerates into a cyst. As a result, the woman suffers from infertility. Infertility also develops against the background of adhesions formed during chronic endometritis.
In addition to the impossibility of conception, ignoring abnormally high BT in the first phase leads to the progression of the listed diseases of the genital organs, which can affect not only reproductive health, but also threaten the life of a woman.
Special cases
A sharp increase in BT for just 1 day in the first phase does not indicate anything, since it may be the result of inaccurate measurements, violation of the rules for measuring basal temperature, or an illness accompanied by elevated body temperature. The inflammatory process also does not go away in one day.
Therefore, it is possible to determine the probable cause of the increased basal temperature in the first phase only based on an analysis of the entire graph for at least 3 to 4 cycles. So, it was said above that in case of insufficient secretion of estrogen by the body, BT usually increases in the second phase of the cycle to more than 37.1 ° C (and this happens more slowly than usual, about 3 days).
You cannot trust the BT schedule for diseases associated with an increase in body temperature if the principles of BT measurement are not followed.
Some women may have consistently high BT in both phases of the cycle (more than 36.8 °C in the first half of the cycle and, for example, 37.2 °C in the second). But if at the same time a difference of at least 0.4 °C remains, it means that there is no pathology and, most likely, the matter is in a hyperthermic state, which is an individual norm. But just in case, it is better to consult with a specialist, undergo an examination and get tested.
Useful video on the topic
It is recommended that every woman keep a chart of basal temperatures at least from time to time. It allows you to indirectly judge the state of the reproductive and endocrine systems; its readings can warn a woman about a possible pregnancy, hormonal disorders, and the development of certain gynecological diseases. Thus, maintaining basal temperature at high levels during menstruation is considered a sign of endometritis.
However, most often basal temperature is measured to determine ovulation when planning pregnancy. Keeping this chart allows you to calculate the most favorable period for conception or diagnose anovulation, when the egg does not mature. Every healthy woman can normally have several anovulatory cycles per year, but if ovulation does not occur from month to month, then we are talking about a serious disorder.
As you know, the duration of the menstrual cycle is different for each woman, and the basal temperature schedule is also very individual. But no matter what, ovulation almost always occurs 14 days before the expected date of the next period. For example, if your next menstruation should begin on the 15th, then expect ovulation on the 1st.