What's happened
Ovarian fibroma is a benign formation, the structure of which consists of connective tissue cells. The main feature is the absence of its hormonal activity and, in rare cases, degeneration into a malignant form.
Fibrous tumors grow at a slow pace. However, they can reach up to several tens of centimeters in size.
As a rule, with the development of a pathological process, only one genital organ is affected. Bilateral pathology was recorded in only five percent of cases.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Differences between cytology and colposcopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2021
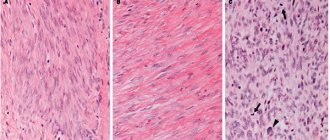
Fibroma has a smooth or nodular surface. The consistency of the contents can be hard or soft. The neoplasm is quite mobile, since it does not have a stalk, which eliminates the possibility of its twisting.
The section reveals connective tissue that has a grayish-white tint. A small number of blood vessels are also present.
If the neoplasm was formed a long time ago, over several years, but the structure will exhibit ischemic, necrotic areas, as well as pinpoint hemorrhages with random interweaving with each other.
Kinds
Depending on the structure of the tissue, fibrous tumor can be of two types:
- heterogeneous – differences in neoplasms in their structure are noted;
- homogeneous – tumors have a homogeneous structure.
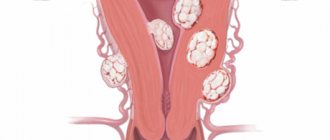
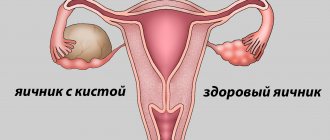
Based on the location of the pathological process, the disease is classified as fibroma of the left and right ovaries.
If we take into account the structure of the formation itself, then two types of fibromas can be distinguished.
Limited
The formation is formed in a capsule. This allows you to separate it from the tissues of the affected organ.
Diffuse
In this case, there are no capsules. There is complete damage to the ovarian tissue. This type of pathological condition is one of the most common.
Fibrothecoma of the ovary
Thecoma is a benign tumor that forms in a woman’s ovaries from stromal cells. The pathological condition occurs in 2% of women, but most often the tumor is diagnosed during menopause.
Fibrothecoma of the ovary - what is it? Fibrothecoma is a theca cell tumor of the ovary. Theca cells control the production of androgens - androstenedione and testosterone. After which androgens enter the cells of the fanulous layer of the gland, where they are produced into estrogens. Theca cells surround the follicle from the outside and begin to form in the preantral follicle.
That is, thecoma is a benign tumor that produces estrogen. The disease can occur at any age, but is more common among women over 59 who have already gone through menopause.
- 1 Reasons
- 2 Symptoms
- 3 Diagnostics
- 4 Treatment
Causes
Among all the provoking factors of the disease, hormonal imbalance comes first. In most cases, fibroma is diagnosed if the patient has a history of menstrual irregularities, as well as decreased fertility.
The development of tumor formations is facilitated by previous inflammatory pathologies and various types of trauma. It has been noted that quite often growths appear in the postoperative period after surgery on the ovaries.
Thus, we can conclude that the leading factors contributing to the development of the pathological process are a number of reasons.
Genetic predisposition
According to some experts, the tendency to develop a tumor process can be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Echosigns of adenomyosis
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2021
It was possible to prove that if cases of neoplasms affecting the uterine body, ovaries or mammary glands were found in the family, then the risk of pathology increases significantly.
In addition, the pathological process begins to develop much earlier, most often even before menopause occurs. The course of the disease will be much more complicated.
Hormonal imbalance
Against the background of hormonal failure of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus of the ovaries, especially with an increase in the concentration of gonadotropin secretion, the ovaries undergo hypoplasia, as well as cellular proliferation. This condition often leads to the formation of cystic neoplasms.
Decreased immune system
When immunity declines, the tumor grows rapidly.
Despite the fact that no cases of malignancy of the process have been identified, the disease must be treated as early as possible. Otherwise, this may lead to the development of more serious negative consequences. Therefore, timely diagnosis of the disease at an early stage is so important.
Ovarian fibrothecoma: what it is, symptoms, causes, treatment, prevention
Ovarian thecoma is considered a benign tumor-like neoplasm with hormonal activity. In most cases, the pathology affects postmenopausal women.
However, sometimes the defect is detected in girls even before puberty.
Despite its benign nature, the tumor can cause serious complications, so you need to know what alarming symptoms arise during the disease.
What's happened
The thecoma includes stromal cell structures that produce estrogen. The risk group includes older women due to the natural decline of reproductive functions. However, the defect sometimes occurs in young girls.
The tight elastic formation has a round shape. Almost always, the pathogenic process affects one of the ovaries. Sometimes liquid or jelly-like contents are found inside the tumor.
When compared with other formations that produce hormones, thecoma is the least common. Moreover, the disease has a diverse microscopic structure.
Typical epithelioid defects consist of cells similar to the inner surface of the follicle. A spindle-shaped neoplasm is often mistaken for ovarian fibroma. Fibrotekoma is capable of reaching impressive sizes. In addition, this type of thecoma is prone to relapse.
Can it develop into cancer?
Unfortunately, with ovarian thecoma there is a possibility of malignant degeneration, although minimal. The neoplasm differs significantly from cystic pathologies in that the increase in this defect occurs due to the active proliferation of cells, and not the accumulation of liquid contents.
Despite this, the tumor is not prone to invasive progression and does not cause metastases, which is typical for cancer.
Even benign thecoma sometimes causes ascites, when fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, as well as hydrothorax with filling of the pleural cavities with transudate. In addition, the disease is prone to relapse.
Most often, the tumor reappears in the same ovary 5 or more years after surgery. However, even in this case, the likelihood of malignant transformation is extremely low.
Complications
Feminizing thecoma increases estrogen production. Most often, the pathological process causes serious complications. Patients develop benign uterine fibroids when the muscle layer of the affected organ grows.
Adenomyosis is also sometimes detected. The essence of internal endometriosis is the appearance of foci of the mucous membrane in the myometrium of the uterus. In severe cases, endometrial hyperplasia is diagnosed. Excessive growth of the cervical canal leads to the fact that the tumor has to be removed along with the genitals.
All of the above complications significantly aggravate the course of the underlying disease, as a result of which, after radical surgery, a woman loses her reproductive function and becomes infertile. If the disease is started, a malignant process develops, which will be much more difficult to cure.
Forecast
The prognosis for benign formation is favorable. After eliminating the neoplasm during the postmenopausal period, bleeding disappears, pathological rejuvenation disappears, and during reproductive age the menstrual cycle normalizes.
If the ovaries are preserved, then infertility does not occur. In childhood, the severity of clinical manifestations after surgery is significantly reduced, but most girls remain short in stature.
Five years after removal, thecoma often recurs, but returns in a benign form. Even in the presence of a malignant neoplasm, the prognosis remains favorable. This is explained by the fact that a degenerated tumor does not cause metastases, so timely diagnosis and treatment will avoid serious problems.
Prevention
There are no special measures to protect against ovarian thecoma. However, following general medical recommendations will significantly reduce the likelihood of developing not only this formation, but also other pathologies of the female genital organs.
To do this, you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, eat right, constantly monitor the state of the immune system, get rid of bad habits, and regularly engage in physical activity.
Any inflammatory processes or infectious diseases of the reproductive system must be eliminated in a timely manner to prevent them from becoming chronic. The appendages should be protected from all kinds of adhesions and scars that cause malignant tumors.
Ovarian thecoma does not have a clear clinical picture, so it is important to visit a gynecologist every six months and undergo a preventive examination.
Every year you need to examine the abdominal organs using ultrasound. After this diagnosis is made, it is necessary to immediately undergo surgical treatment.
Benign ovarian thecoma extremely rarely leads to dire consequences. If the disease is detected and eliminated in time, you can quickly get rid of this problem. However, even after complete removal of the tumor, the risk of relapse always remains.
If you do nothing and the disease progresses, the tumor will gradually increase, compress neighboring organs, cause concomitant pathologies, and lead to infertility or malignant formation. To prevent the occurrence of the above complications, you should immediately visit a specialist when the first alarming signs occur.
Source: //onkologia.ru/dobrokachestvennyie-opuholi/zhenskaya-reproduktivnaya-sistema/chto-takoe-tekoma-yaichnika/
Symptoms
The symptoms of the pathological process will depend on the size of the fibrous formation. As a rule, when the disease is small in size, in most cases it is asymptomatic.
Since the growths grow slowly, they may not be noticed for several years. Pathology is detected randomly during a diagnostic examination of the pelvis.
As the disease progresses, characteristic signs begin to appear.
Soreness
As the tumor grows, severe aching pain appears in the lower abdomen, which can radiate to the lumbar region. The neoplasm does not affect the process of hormone production.
It is for this reason that pathology has nothing to do with menstrual irregularities. Discomfort occurs due to stretching of the tumor capsule or during compression of the pelvic nerve.
Disorders of urination and bowel movements
In some situations, women begin to complain of heaviness in the abdomen. As the tumor grows, it puts pressure on the bladder.
When left-sided fibroids develop, the intestines may be compressed, leading to difficulty defecating. The right-sided form of the disease can cause the development of an inflammatory process in the appendix.
Meigs syndrome
From the fibrous neoplasm there is a release of fluid, which at the very beginning fills the peritoneal cavity. Through the diaphragm, the contents can penetrate into the pleural cavity.
Against the background of this condition, hydrothorax begins to develop. The hemoglobin concentration also decreases, indicating anemia. The process is accompanied by an increase in the size of the abdomen, pallor of the skin, weakness, and tachycardia.
It is possible that this syndrome may indicate the development of a malignant tumor, which requires an immediate visit to a specialized specialist.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Do I need to remove an ovarian cyst if it doesn’t bother me?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2021
According to medical workers, right-sided fibroma is more often diagnosed, since it is on this side that there is improved blood supply to the organ and good development of the lymphatic system.
In the case of a complicated course of the pathological process, the condition is accompanied by:
- cold sweating;
- acute abdominal pain
- nausea and vomiting;
- decreased blood pressure;
- the appearance of pain when touching the abdominal area;
- an increase in temperature ;
- constipation
In this condition, emergency surgery is required.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, you must first of all be examined by a gynecologist. Upon palpation, he can already detect a formation that has good mobility and elastic consistency. As a rule, no pain is observed when palpating.
If a tumor is suspected, the patient is sent for a diagnostic examination, which includes a number of activities:
- taking vaginal smear
- blood test for hormones;
- ultrasonography ;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- puncture ;
- diagnostic laparoscopy.
It is also necessary to differentiate fibroids from ovarian cancer, functional cysts or uterine corpus fibroids.
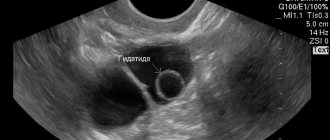
Ovarian fibroma on ultrasound
On ultrasound, fibroma appears as an oval or round formation with clear and smooth boundaries. During tumor growth, a hypoechoic contour may appear; fibroids are characterized by reduced echogenicity. Diagnosis and treatment of fibroids is carried out at the Yusupov Hospital. Diagnosis of ovarian fibroids is carried out during an examination by a gynecologist or oncologist. If there is a suspicion of an ovarian tumor, the doctor refers the patient for further studies: analysis for tumor markers, general blood test, transvaginal ultrasound, MRI, CT; if a tumor is detected, a biopsy and histological examination of the tumor tissue is performed. You can make an appointment with a doctor by phone.
Treatment
It’s worth saying right away that fibroids can only be removed through surgery. With drug therapy, resorption of the tumor tumor will not occur.
For very small tumors (about 8 mm), observational tactics are prescribed. The woman is constantly under the supervision of a doctor who monitors the dynamics of the pathology.
When carrying out therapy, specialists use two types of surgery, and, if we are talking about a young woman, they try to carry out an organ-preserving procedure, which allows preserving reproductive function.
Laparoscopy
Refers to minimally invasive operations. The essence of the procedure is to puncture the peritoneum, through which access to the tumor is achieved. The laparoscopic method is used in cases where the fibroma has a small diameter.
Laparotomy
Prescribed for tumors larger than 6 centimeters. Depending on the stage of the pathological process, the ovary can be removed completely or partially (only the affected part).
If the patient has reached menopause, it is recommended to undergo radical surgery, when the tumor and appendages are excised.
In conclusion
Now you know what ovarian fibrosis is, how it manifests itself and what consequences it leads to. Therapy for this disease is carried out only through surgery. Alternative medicine is simply useless in such a situation. Since there are no preventive measures for the disease, a woman should undergo a thorough examination by a gynecologist annually, as well as an ultrasound examination. This is the only way to diagnose ovarian fibroma and prevent its further development.
Complications
When a fibroid tumor is diagnosed, women should undergo regular examination until it is removed. Often such a symptom becomes a sign of a malignant process.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Can there be a delay and a positive test for an ovarian cyst?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 4, 2021
Possible negative consequences may include the following:
- torsion ;
- formation of adhesions of the fallopian tubes;
- rupture of tumor formation;
- suppuration;
- peritonitis;
- severe bleeding.
To prevent the development of complications, at the first suspicion of pathology, you must immediately seek medical help.
Prevention
Since no special preventive measures have been developed to prevent the disease, experts recommend adhering to certain rules:
- maintaining a correct lifestyle ;
- regular exercise ;
- healthy and balanced diet;
- rejection of bad habits;
- normalization of emotional state;
- regular gynecological examination for preventive purposes;
- strengthening immune system.
Who to contact?
At the first symptoms of the disease, a woman should undergo a thorough examination. First of all, you should visit a gynecologist. In such cases, the doctor conducts an examination using a two-handed method. In this case, a specialist can determine not only the location of the neoplasm, but also determine its surface structure, rocky consistency, density, pain and mobility.