Pus (purulent exudate)
- cloudy exudate resulting from purulent or serous-purulent tissue inflammation. The process of pus formation is called suppuration. Purulent bone lesions are called osteomyelitis. Pus consists of:
- purulent “serum” containing albumins, globulins, proteolytic, glycolytic and lipolytic enzymes of microbial or leukocyte origin, cholesterol, lecithin, fats, DNA admixtures dissolved in it;
- tissue detritus;
- cells, mainly living or degenerated microorganisms and neutrophilic leukocytes (purulent bodies, balls, cells). In special cases, eosinophils or mononuclear cells predominate in the pus.
The color of pus is often yellow, yellow-green, but can be bluish, bright green, or dirty gray. The color is determined by the reason that led to its formation. The consistency of fresh pus is liquid; it thickens over time. The smell is usually not strong, specific, but with putrefactive (ichorous, putrid) inflammation it becomes fetid. The color, consistency and smell of pus are very variable, depending on the location, affected tissues, communication with hollow organs, and the pathogen.
Microorganisms are almost always found in pus, which are the cause of suppuration. Suppuration is most often caused by pyogenic (pyogenic, pus-producing) bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci, meningococci, E. coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, pseudomonads, as well as putrefactive anaerobic clostridia Cl. perfringens
,
Cl.
sporogenes ,
Cl.
putrificum , etc.). At the same time, other microbes also cause suppuration, for example, salmonella, shigella, brucella, pneumococcus, mycobacteria, candida, and actinomycetes. Sometimes no microorganisms are found in the pus, which may be due to the lysis of bacteria or the non-microbial etiology of inflammation.
Staphylococcal pus is thick, white-yellow or yellow, creamy or creamy consistency, with a specific sour odor. Streptococcal pus is usually of an unpleasant odor, liquid consistency, grayish-yellow or grayish-brown, mixed with a small amount of dead tissue, streaks of blood or individual fibrin flakes. the pus from the introduction of E. coli is liquid, foul-smelling, brown in color. The pus from a tuberculous abscess is liquid and contains flakes and curdled masses. [1]
Pus, like all exudates, is subject to mandatory microbiological examination. In case of closed suppurations, it must be taken by puncture, before opening the lesion; in open processes, it must be taken from the depths of the lesion. Examination of pus should be carried out immediately after collection to avoid lysis of bacteria. Preparations from pus are examined microscopically after staining them with a Gram stain or using special methods. Sowing is carried out quantitatively on simple and blood agars, less often on special media (ZhSA, Levin, with furagin, etc.).
Purulent wounds require specific treatment, in particular to avoid sepsis (blood poisoning) caused by anaerobic or aerobic bacteria. Free outflow of pus from the source of infection or its removal (for example, surgically) is necessary.
Suppuration is a form of inflammation that produces pus, which consists of living and dead bacteria, protein-rich fluid, and dead leukocytes (white blood cells).
Inflammation is the body's protective response to various tissue damage. If the damage is caused by an internal bacterial infection, the inflammatory process (during which white blood cells fight pathogens) is usually accompanied by suppuration. Most often, suppuration is caused by so-called pyogenic bacteria.
Inflammation of the uterus
A common cause of purulent discharge in women is inflammation of the uterus. This disorder can be caused by constant stress, hypothermia and other factors that make the body more vulnerable to microbes. The severity of the symptom depends on what pathology occurs in the body:
- Vaginitis is inflammation of the uterine epithelium. Poor intimate hygiene, taking antibiotics without consulting a doctor, and unprotected sex can lead to the onset of the disease. Less commonly, the disease worsens due to the activation of opportunistic flora on the vaginal mucosa.
- Cervicitis is a lesion of the cervix and cervical canal. Inflammation is caused by fungal and infectious pathogens transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse. With the disease, discharge with an unpleasant odor of ammonia is often observed.
- Endometritis is a lesion of the cavity of the reproductive organ. The disease occurs with a clear symptomatic picture: fever, pain in the lower abdomen, copious amounts of mucous discharge. In advanced stages of endometritis, purulent discharge in women is possible, which in the photo resembles thrush.
- Salpingitis and oophoritis. Symptoms of the disorder also appear clearly. They are accompanied by high fever, pain when visiting the toilet, purulent mucus with blood from the vagina. The causes of these diseases are frequent abortions, uterine cleaning, childbirth, and surgical interventions.
If the inflammation has spread to the vagina and cervix, then there is a possibility of spontaneous recovery, since during menstruation, particles of the uterine epithelium are excreted along with pathogenic flora. Often, with vaginitis, cervicitis and endometritis, a woman is cured on her own. It will not be possible to cope with salpingitis and oophoritis without the help of a gynecologist, especially if the pathogenic flora has penetrated into the lower or middle layers of the integumentary tissue.
Infectious diseases
The cause of purulent discharge in women without odor and with its presence is sexually transmitted infections that are transmitted from an infected partner to a healthy one. The nature of purulent mucus and additional symptoms accompanying it will depend on the type of infection that has entered the body:
- Chlamydia. The pathology has a hidden form of progression. The discharge takes on a slightly greenish tint and is odorless. In the chronic form of the disease, all mucous membranes of the vagina are affected. Chlamydia can be detected by examination by a doctor.
- Gonorrhea. It has a bright current. When the disease occurs, yellowish mucus with an unpleasant odor is released from the genital tract. Pathogenic microbes spread not only to the reproductive organ, but also to other parts of the reproductive system: ovaries, fallopian tubes.
- Trichomoniasis is another disease in which women may experience purulent discharge with an odor. They become foamy in consistency, causing severe itching and burning of the genitals.
- Mycoplasmosis. The disease is especially dangerous for pregnant women, as it increases the likelihood of fetal development failure, premature birth and miscarriage. You can catch an infection not only through casual sexual intercourse, but also when using someone else's underwear, after a gynecological examination with poorly disinfected instruments.
- Candidiasis. Discharge from thrush has a curd-like consistency and is white in color. Pathology affects a woman’s immunity, making it more susceptible to infectious pathogens. When a secondary infection develops, the white secretion changes its hue to yellow and green.
The time for symptoms to appear after infection depends on the immune system and the concentration of the pathogen that has entered the body. Strong immunity can cope with infectious diseases in the initial stages of their development.
Prevention
To prevent a sore throat of a purulent or other severe type, it is recommended to take preventive measures:
- avoid hypothermia;
- do not abuse cold drinks, ice cream, especially in the heat;
- strengthen the immune system with vitamins and hardening;
- promptly treat caries and other oral diseases;
- Regularly rinse your mouth and throat with boiled water or a weak saline solution.
All patients diagnosed with purulent tonsillitis should understand how serious this disease is. In case of pathology, adequate therapy is necessary, since the disease, with improper treatment or its complete absence, can easily become chronic. Follow all the doctor’s recommendations and you will recover quickly. Good health and don't get sick!
Source
Distinctive features of secretions in various diseases
Pus is not part of the secretion of healthy women. It appears due to the fact that a large number of dead leukocytes appear in the mucus. The color of the secretion in this case can vary from pale yellow to marsh. The brighter the color of the leucorrhoea, the greater the number of dead protective cells it contains and the more acute the inflammatory process.
Purulent discharge looks like green mucus in women. They have a specific smell and abundance. In addition to this symptom, other pathological signs are observed:
- discomfort and burning when urinating;
- swelling of the genitals;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- the appearance of signs of intoxication of the body (in rare cases).
For vulvitis
The pathology most often manifests itself in girls and women who do not observe basic rules of personal hygiene. It is characterized by swelling of the labia majora and minora. The color of discharge during illness depends on the type of bacterium that provoked the pathological process:
- with E. coli, the secretion will have light green or yellowish tints;
- with staphylococcus, there is a discharge of a thick consistency and dark green color that smells unpleasant;
- with a fungal infection, a white tint will appear in the mucus.
Endometriosis
Viruses, bacteria, Candida fungi and even parasites can trigger the disorder. There are several reasons why endometriosis develops: installation of an intrauterine device, abortion, unsuccessful childbirth. The main symptoms of the disease are mucopurulent discharge with an unpleasant aroma.
The initial stages of the pathology are accompanied by copious secretions of mucus, which, as the problem develops, can acquire greenish tints and no odor. Other accompanying signs of the disorder: pain in the pelvic area, false urge to urinate.
The nature of the green secretion will largely depend on the cause of the development of cervicitis:
- with gonorrhea, it has a yellowish tint with an unpleasant odor;
- with chlamydia and trichomoniasis, the mucus has a foamy consistency and green color;
- Candida fungi provoke the appearance of light leucorrhoea mixed with pus.
Salpingitis
Symptoms of damage to the deep organs of the female reproductive system (ovaries and tubes) differ from sexually transmitted infections. Discharge in pathologies takes on a dirty green tint, but the disease itself does not manifest itself with other characteristic symptoms (itching, burning).
When the fallopian tubes become inflamed, the secretion is released more intensely during physical activity. Along with this, signs of intoxication may appear.
Purulent discharge may appear after tumor removal. If a woman has had tumors removed in the recent past, she may develop green discharge due to a secondary infection joining the lesion. In this case, purulent leucorrhoea is accompanied by an increase in temperature to critical levels, severe pain in the pelvic area, and inflammation of the lymph nodes. Green discharge after removal of a cancerous tumor smells bad and has a thick texture.
Diagnosis and treatment
A comprehensive diagnosis is necessary to determine why purulent discharge appears in women. The doctor must identify the type of bacteria that provoked the inflammatory disease. To identify the cause of green secretion, the following is prescribed:
- smear analysis using PCR and ELISA for latent infections;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- colposcopy;
- bacteriological culture of secretions (to determine antibiotics affecting pathogenic particles).
Treatment methods
Green leucorrhoea is treated comprehensively. To eliminate the causes and symptoms of their occurrence, a number of medications are used. When the problem becomes more complicated, doctors resort to surgery. Traditional medicine is used in combination with surgical and drug treatment.
Drug therapy
In most cases, purulent discharge is eliminated with medication. There are several stages of drug treatment:
- Taking antibiotics, antifungals or antivirals. According to women's comments, the most effective antibiotics in the fight against pathology are Doxycycline and Azithromycin. Ornidazole or Metronidazole are used to relieve fungal infections.
- After a course of medications aimed at combating the pathogen, patients are recommended to restore immunity: Likopid, Immunal.
- At the final stage, medications are prescribed that restore the vaginal microflora in any pharmacological form: vaginal suppositories, probiotics, solutions for vaginal douching.
Complications
Purulent tonsillitis is dangerous due to its complications, which can be both late and early.
The early ones include:
- sinusitis;
- otitis;
- laryngitis;
- purulent lymphadenitis;
- soft tissue abscesses.
Later may develop:
- meningitis;
- rheumatism;
- glomerulonephritis;
- polyarthritis;
- pyelonephritis.
To prevent this from happening, follow simple procedures after finishing therapy:
- continue to gargle with antibacterial agents;
- take the pills prescribed by your doctor until the very end, even if the condition has already returned to normal;
- after recovery, avoid the risk of re-infection: avoid ice cream, do not drink cold water, go outside only when air humidity is low.
The prognosis for timely and high-quality treatment of the disease is favorable.
Prevention of pathologies
You can prevent green vaginal discharge if you follow a number of simple preventive rules:
- Wash and change underwear daily. During the day, a large number of bacteria and fungi accumulate on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes, which can actively multiply when the immune system is weakened.
- Place towels on seats in baths and saunas. Pathogenic microorganisms are activated under conditions of elevated temperature and humidity.
- Use condoms during contact with an unverified partner. In 95% of cases, dangerous infections are transmitted through sexual contact.
- Be checked annually by a gynecologist, even if no pathological symptoms are noted. Many sexually transmitted infections occur with hidden symptoms, and only an experienced doctor can identify them in a timely manner.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right. A similar rule prevents disruptions in the immune system.
- Do not take antibiotics unless prescribed. Many drugs in this group negatively affect the microflora of the intestine and urogenital tract.
- Stop using panty liners unless necessary.
Green discharge is a clear sign of problems in the body. If not treated in a timely manner, these problems can cause health problems for a woman and loss of her ability to conceive a child. Treatment of pathology is carried out mainly with antibiotics and medications to maintain immunity and normalize the vaginal microflora. If conservative methods of therapy do not bring results, and the woman’s well-being worsens, then surgical intervention is resorted to. Its main goal is to eliminate the source of purulent discharge.
Incubation period
The incubation period of purulent tonsillitis is the time from the entry of the pathogen to the appearance of the first signs of the disease. The duration of the period varies from several hours to 2-4 months.
Is purulent sore throat contagious?
Of course, yes, if you do not adhere to the rules of hygiene and do not wear a protective bandage when in contact with a sick person. The risk of getting a sore throat increases if a person is hypothermic, if he has a low immune system, and also if he has bad habits: smoking and alcohol abuse.
Causes of pus from the vagina
Pus from the vagina can be the result of both specific and nonspecific inflammation.
Therefore, there can be a lot of reasons.
The most common is unprotected sexual intercourse.
If pus from the vagina is caused by a specific infection, the most likely pathogen is gonococcus.
Therefore, with a high degree of probability, the woman will be diagnosed with gonorrhea.
Gonococcal infection can occur with the release of purulent secretion from the genitourinary tract, with itching and redness of the vulva, burning during urination, but often this sexually transmitted infection in women occurs mildly, latently.
The acute course of the disease in most cases is observed with weak immunity and concomitant urogenital infections.
In addition to gonococci, trichomonas and chlamydia can provoke a purulent inflammatory process in the vagina.
With trichomoniasis, the pus from the vagina is extremely abundant, has a foamy liquid consistency, and a greenish-yellow color.
In this case, an unpleasant odor of pus may be felt from the vagina.
The inflammatory and infectious process is accompanied by unbearable itching of the vulva and vestibule of the vagina.
Abundantly secreted pus gets on the skin of the groin, perineum, and inner thighs, causing irritation, redness, burning, soreness, and itching.
With chlamydia, there may also be pus discharge from the vagina.
Compared to trichomoniasis, its amount is insignificant; it has a transparent liquid consistency and a yellowish-white color.
Itching, burning, and pain in the genital area are usually absent.
Most often, this infection is subclinical or completely asymptomatic.
The more pronounced the pathological secretion from the vagina, the more acute the infectious process, the more pathogenic the pathogen is.
But if a woman, on the eve of the onset of genital symptoms, did not have unprotected sexual contact with unfamiliar sexual partners, most likely the inflammatory process in the vagina is caused by nonspecific flora.
This can be E. coli, staphylococcus, Proteus and many other bacteria.
There are many causes of nonspecific inflammatory process in the vagina or cervix, including:
- chemical, thermal, mechanical damage to the vaginal mucosa, including during medical procedures;
- deterioration of local immunity;
- self-treatment with antimicrobial drugs;
- violation of genital hygiene.
There are many risk factors that increase the likelihood of purulent lesions of the female genital organs:
- menstruation,
- diabetes,
- hypovitaminosis,
- taking glucocorticoids.
Associated symptoms of purulent vaginal discharge
Usually, the discharge of pus from the vagina is not the only symptom that worries a woman.
It is accompanied by the following signs of the inflammatory process:
- itching, pain, burning in the genitals;
- redness of the mucous membrane of the genital organs;
- unpleasant smell of pus from the vagina;
- urinary disorders;
- increased body temperature;
- signs of intoxication of the body.
The exact cause cannot be determined based on the symptoms.
To do this, you should go to a medical institution, take smears and blood tests.
The pathogen can only be detected during laboratory diagnostics.
Purulent vaginal discharge.
The gynecologist tells
Garyaeva Irina Vladimirovna
The contents of this article have been checked and confirmed for compliance with medical standards by a gynecologist
Garyaeva Irina Vladimirovna
Complications of pus from the vagina
A woman who has pus coming from her vagina should see a doctor immediately.
Otherwise, with a high degree of probability, the infection will spread further - to the uterus, bladder, kidneys.
- cystitis - inflammation of the bladder;
- pyelonephritis – inflammation of the kidneys;
- endometritis – inflammation of the uterine mucosa.
If the function of the immune system is impaired and there is no treatment, generalization of the pathological process is possible.
This condition is dangerous not only for a woman’s health, but also for her life.
Symptoms of purulent sore throat in adults
The infection, having penetrated the human body, settles on the tonsils and begins to multiply intensively. Already on the fifth day, signs of sore throat are usually noticeable. The weaker the body's immune defense, the stronger the impact of infection and the greater the likelihood of complications.
Purulent tonsillitis in adults lasts no more than a week (the chronic form is an exception), after which a period of convalescence begins.
Medical experts have identified a number of the most characteristic signs of purulent tonsillitis:
- chills, heat, fever, elevated temperature (39-40 ° C);
- increasing soreness of the throat, intensifying during swallowing movements;
- when palpated, painful and enlarged mandibular lymph nodes;
- enlargement and redness of the tonsils;
- areas of pus and white plaque in the tonsil area, which can be easily removed using a medical instrument without damaging the mucous membranes;
- vivid symptoms of intoxication, with headaches, a feeling of weakness and loss of appetite.
Patients may also be concerned about:
- pain in joints and muscles, in the abdomen;
- cardiopalmus;
- cough;
- runny nose.
Purulent tonsillitis in adults can occur without a significant rise in temperature. In this case, the main and defining signs are a sore throat, a change in the appearance of the tonsils: redness, swelling of the mucous membrane, pustules and plaque on the tonsils.
| Purulent sore throat | Characteristic signs |
| Catarrhal |
|
| Follicular |
|
| Lacunarnaya |
|
What does it look like in the photo?
Almost always, purulent tonsillitis looks in the photo as yellow or dirty yellow dots, spots or streaks on the surface of the tonsils. In some cases, the plaque forms a continuous film on the tonsils.
Stages of disease development
Purulent sore throat develops within one to two days from the moment of infection. Especially in people with weakened immune systems. The development of bacteria occurs very quickly, so do not delay treatment. The main thing is to follow all doctor’s orders.
| Symptoms and course at different stages | |
| 2-3 day | manifestations of the disease become expressed as clearly as possible:
Body temperature remains high, appetite disappears, symptoms of intoxication are pronounced; |
| 4 day | The ulcers begin to go away on their own. Most of them are opened; with lacunar angina, the pus is simply separated from the tonsils, in its place there remain noticeable perforations of the surface, which quickly heal; |
| 5-6 days | the patient’s temperature and general condition normalize, appetite appears; |
| 7-8 days | sore throat disappears; |
| 10-12 days | The size of the lymph nodes returns to normal and their pain disappears. |
What does pus smell like?
Macroscopic and microscopic characteristics of pus
are of great importance, as they allow us to roughly determine the type of microorganism that caused suppuration. Taking this into account, it is possible to tentatively select the appropriate antibiotic, then clarifying the correctness of the choice with a disk test of the sensitivity of microbes contained in the purulent exudate to it.
Pus
consists of serum and a huge number of predominantly neutrophilic leukocytes, most of which died during the process of phagocytosis, under the influence of microbial toxins and histolysis products. Purulent serum contains a large amount of predominantly proteolytic enzymes, proteins and various tissue breakdown products (peptones, amino acids, ketone bodies, fatty acids, etc.). In horses, as a rule, and in dogs there is always no fibrin in the serum of pus, but in cattle and pigs there is a small amount of fibrinogen, which turns into fibrin, which falls out in the form of a mesh on the walls of the forming purulent cavity.
Staphylococcal pus
in all animals it is thick, white-yellow or yellow, creamy or creamy consistency, with a specific sour odor. In cattle and pigs it may contain fibrin flakes. In rabbits, the pus is thick, white or white-yellow, like thick sour cream; in birds it is cheese-like, gray-white in color.
Streptococcal pus
usually of an unpleasant odor, liquid consistency, grayish-yellow or grayish-brown, mixed with a small amount of dead tissue, streaks of blood and individual fibrin flakes. With hemolytic streptococcus, the pus is liquid, yellowish in color, with a bloody tint and streaks of blood; in cattle and pigs it contains fibrin impurities.
The pus from the introduction of E. coli is liquid
, foul-smelling, brown in color; Pseudomonas aeruginosa - thick, pale green or gray-green in color; necrotic tissue and cartilage are painted emerald green.
The pus from a tuberculous abscess is liquid
, contains flakes and cheesy masses, with brucellosis - purulent-bloody, liquid, sometimes mixed with a small amount of whitish-yellow cheesy mass;
later it may take on a grayish-yellow oily appearance. The pus in
chronic abscesses is often thick and resembles a caseous (cheesy) mass.
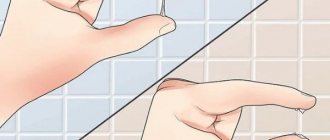
When examining acute superficial abscesses
a hemispherical swelling is established, fluctuating upon palpation, with increased local and general temperature and a moderate pain reaction. To determine the fluctuation, place the thumb and index finger on opposite sides of the swelling. When you alternately apply pressure with your fingers on the swelling, you feel the oscillating movement of the liquid (ripple). The more superficial the abscess and the thinner its wall, the better the fluctuation is determined; with a deeply located abscess - it is worse, and sometimes it is not detected at all if the wall of the abscess is very tense or thickened due to encapsulation.
Acute deep abscesses
Diagnosed by the presence of increased general and local temperature, increased heart rate, respiration and depression of the animal, dysfunction of the corresponding organ or part of the body, as well as sometimes established signs of deep fluctuation (ripples under a thick layer of tissue). In this case, it is necessary to exclude false fluctuation, which is felt during bimanual palpation of muscles that are in a relaxed state or moderate tension. To distinguish deep fluctuation from false, it is necessary to conduct a palpation study of adjacent areas and compare with the results of fluctuation of the area of the supposed deep abscess.
True deep fluctuation
It differs from the turn-down one in that when palpating the intact zone it is not possible to obtain the same sensations as when palpating the zone of a deep abscess. Often this reveals collateral swelling of the subcutaneous tissue and a strong pain reaction when pressing on the skin under the center of the projection of a deep abscess.
In order to clarify the diagnosis
They perform a puncture, which is absolutely necessary when diagnosing deep abscesses. Puncture of the superficial abscess is performed with an injection needle in the center of the swelling in an oblique direction; deep abscess - perpendicularly with a needle of significant diameter with a mandrel at the point of maximum pain. Having reached the expected depth of the abscess, the mandrin is removed, a syringe is attached and the piston is pulled back.
If pus
does not get sucked in, reinsert the mandrin into the needle and evenly move it deeper. When the wall of an acute abscess is punctured, the needle “failure” is felt, and when an encapsulated abscess is punctured, increasing resistance is noted, sometimes with a crunch, and then the needle “failure”. Thick pus from chronic abscesses is first liquefied with furatsilin or chloramine. After aspiration of pus and thorough washing, the abscess is opened.
It must be taken into account that the abscess
forms within a few days, and a hematoma forms after an injury within a few minutes or hours; its puncture is accompanied by the release of blood from the needle. With pulsating hematomas, pulsation is detected, and upon auscultation, noise is detected. The aneurysm is located along the main blood vessel, the swelling is elongated-oval, when pressed it decreases and pulsates well, noises associated with the pulse wave are heard, puncture produces fresh blood.
Properties
Pus is alkaline; when fatty and other acids are formed in it, the reaction can become neutral or acidic. The specific gravity of pus ranges from 1.020 to 1.040. Serum consists of 913.7 parts of water, 78.57 parts of organic and 7.73 parts of inorganic compounds, that is, close to blood serum.
The pus in the body cavity, without “finding a way out” for a long time, undergoes significant changes: purulent bodies and other cells disintegrate into fine-grained detritus (partly protein, partly fatty), while the liquid part is only slightly absorbed, which is explained by the presence of a pyogenic membrane around the accumulations of pus, and partly by compression of the draining lymphatic tracts.. Proteins disintegrate and can become the basis for the formation of cholesterol crystals. Bacteria in old pus also undergo dissolution, probably due to the isolation of purulent accumulations and the weak ability to renew nutrient substrates; sometimes in old abscesses changes in the cultural and biological properties of bacteria are observed, for example. — Reducing their virulence.
Why do pimples smell like pus on the face?
According to the American Academy of Dermatology and Acne, acne is the most common and complex inflammatory skin disorder, affecting at least 50 million American adults and teenagers. The inflammatory condition involves problems with the skin's sebaceous glands, which become clogged with dead skin cells and excess oil, trapping bacteria in pores This causes an inflammatory response and leads to the development of pimples, some of which contain pus. Pus can emit a foul odor due to the byproducts of bacteria feeding on the skin's oil.
Forms of the disease
In fact, all 3 types of purulent tonsillitis (as in the photo) represent stages of the same inflammatory process, which can transform into one another as the disease progresses:
Catarrhal form
Catarrhal tonsillitis is considered the original form of tonsillitis. When therapy is chosen correctly, purulent processes can be avoided.
Follicular tonsillitis
In this case, pus accumulates in the parenchyma of the tonsils, they become inflamed and covered with ulcers. This form has a high risk of the pathogen entering the blood due to densely concentrated blood vessels in the tonsils. Characterized by intense pain, intoxication and swelling. Often the pain radiates to the ear.
Purulent lacunar form
The gaps in the tonsils are filled with pus (see photo). Lacunae are canals in the tonsils that are lined with epithelium and open towards the pharynx. This form of purulent tonsillitis is almost identical to the follicular one, but still has its own characteristics. At first, the adult experiences severe hyperthermia. The pain in the throat is so severe that patients refuse water and food.
Causes of unpleasant odor from acne
Acne - bacteria
A type of bacteria called Propionibacterium acnes (P acnes) usually lives deep in the oily pores of the skin because it feeds on the skin's oil, also known as sebum. People with acne usually have an overgrowth of P acnes, likely due to excess sebum production. People with acne also have an exaggerated immune response to P acnes, which leads to inflammation of the pores and a buildup of white blood cells. An inflammatory response to trapped bacteria, as well as a buildup of sebum, dead skin cells, and white blood cells in the pores, leading to the appearance of pus. People with moderate or With severe acne, these pimples can grow into larger nodules or cysts and even develop an unpleasant pimple odor.
Odor associated with bacteria:
Many types of bacteria produce odors as they grow. These odors come from the by-products produced by the bacteria feeding on various substances. P acnes has specialized enzymes that allow the bacteria to break down and feed on sebum. This breakdown results in the formation of propionic acid and chemicals called short-chain chemicals. fatty acids While sebum is odorless, side effects from the breakdown of sebum oil P acnes release an odor that many patients describe as a bitter or sour body odor.
Types of Bacteria that Infect a Pimple and Cause Bad Odor
There are different types of bacteria that can harm hair follicles, causing clogged pores that can result in zits. These different types of bacteria have a completely different effect on how these odors smell. Aerobic bacteria, which depend on the growth of oxygen, usually do not cause a foul smell with rot. zit, while those anaerobic bacteria that produce sulfur can cause zit to smell bad.
Bacteria are usually present on the skin, and some of them are beneficial. But harmful bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, may also be present. Blocked pores provide a breeding ground for bacteria and can become infected as the bacteria attack the biological building materials in them. The odor is unlikely to be very noticeable. If the smell is very noticeable, then this may indicate a more serious infection, and you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Pimple pus smell
When small, common pimples produce a small amount of pus, it is unlikely that you will notice any odor. In this case, the amount of odor-producing chemicals is usually too low to cause a noticeable odor. However, because large nodules of dead cells and cysts contain a large amount of pus and bacterial debris, you may notice an unpleasant odor from these types of pimples as well.
Dead skin cells
As new skin cells develop in the dermis, old skin cells are forced out. The outermost layer of skin cells, the stratum corneum, is made up of about 20 layers of dead skin cells that gradually slow down. But in acne, dead skin cells can get trapped in the pores, and instead of peel off, they form a fork with sebum. They can begin to disintegrate in the pores, which contributes to the problem of foul-smelling pus from the pimple.
Although the foul odor caused by pus usually affects severely infected skin that contains a large amount of pus, it is not a major problem for your health. Instead of trying to determine what your pimple smells like, it is better to pay close attention to the symptoms of its development. skin disease and as accurately as possible in the future explain to the dermatologist the entire course of the disease.
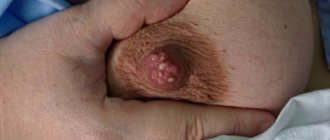
Education
Pus is formed as a result of the accumulation of a large number of leukocytes in a certain area of the human body in response to the penetration of bacterial infection agents into the tissue. The main role in its formation is played by neutrophil leukocytes - the most common type of leukocytes in human blood (40% - 75% of all leukocytes), which are formed in the bone marrow and constantly enter the blood. In response to microbes entering the sterile (normal) tissues of the body, neutrophils begin to actively move to the site of the infectious process. This active migration of leukocytes to the site of inflammation is called "chemotaxis" and is caused by specific cytokine proteins that are released by macrophages - white blood cells that phagocytize (engulf and digest) cell debris and pathogens, and also stimulate lymphocytes and other immune cells to respond to the invading pathogen. Consequently, neutrophils, when destroyed, kill bacteria, resulting in the release of chemicals that destroy bacteria (mediators of inflammation, and also cause dilation of blood vessels (inflammation) and attract even more leukocytes to “fight" the infection. In turn, neutrophils die and are phagocytosed macrophages, stimulating the formation of new active neutrophils to fight infection.Actually dead neutrophils (“purulent bodies”) form the viscous part of the pus.
Subcutaneous pimple with an unpleasant odor
Poll: When did your acne appear? (Number of votes: 4295)
I've been suffering all my life
It's been a couple of years now
About a few months
To vote, click on the desired answer. results
A subcutaneous pimple with an unpleasant odor usually appears as a sebaceous cyst - a small lump of oil and pus located under the skin. This type of cyst is not cancerous.
They most often occur on the face, neck, and upper back, but can occur on other areas of the body.
Typically, a sebaceous cyst grows very slowly and does not cause pain.
However, they can become inflamed or infected, with the overlying skin becoming red, tender and painful to the touch.
How to get rid of acne with an unpleasant odor
Most recommended acne treatments directly or indirectly reduce the overgrowth of P. acnes in the sebaceous glands, thereby reducing the likelihood of foul-smelling pus. Topical benzoyl peroxide products, for example, kill some of the P. acnes on the skin.
These products are recommended for use either alone or in combination with other acne treatments Oral antibiotic therapy also reduces P. acnes populations and is recommended for some people with acne Topical retinoids such as tretinoin (Retin-A), adapalene (Differin) and tazarotene (Tazorac ), in the form of a gel or lotion.
Zits, or foul-smelling pimples, are usually more common in men, although women can experience them too. Although this skin breakout usually occurs on the facial skin, zits can also spread throughout the skin of the body. Zits are always filled with pus, which is usually solid white or yellow. color Pus is dead white blood cells that fight off infecting bacteria. As anaerobic bacteria, these bacteria do not require oxygen to survive. Instead, they produce their own sulfur compounds when they grow and spread through the internal channels of the skin.
A strong odor may be noticed if the zit is infected with an anaerobic type of bacteria. On the other hand, bacteria growing and spreading with oxygen usually does not cause a foul odor. A mild zit problem usually does not lead to that foul odor, while a severe infection tends to result in an odor. , as the body produces more of the pus contained in the zits.
The stronger the odor, the more likely the zit will be contagious. This means that if you detect a foul odor, the infecting bacteria will enter other skin pores, causing another similar pimple. Therefore, it is important to clear any purulent zit to prevent further infection and bacterial infestation Therefore, it is important to clean any purulent abscess to prevent further spread of infection and bacterial infestation.
Home remedy for treating and preventing suppuration
The indoor aloe plant is used to draw out pus from a pimple or boil, to suppress the growth of skin microflora. Juicy leaves are rich in antioxidants, enzymes and vitamins; condensed and cooled juice has an even richer composition. Therefore, it is better not to use fresh raw materials, but to keep the cut plant for two weeks in the refrigerator.
Aloe has an antiseptic effect; its phytoncides have a natural antibacterial effect, eliminating germs and inflammation.
The leaves are crushed, the juice is squeezed out, and used several times a day as a lotion on the area of a wound or pimple. Aloe pulp is applied to the affected area to get rid of its putrefactive contents. Acne and furunculosis are wiped with pure juice or tincture of aloe in alcohol (1:4).
You can quickly remove pus from a wound without wasting 10 days preparing the leaves at home by using aloe juice and liniment from a pharmacy. They treat abrasions, small wounds, and burns to speed up healing. In addition, aloe softens and moisturizes the skin and prevents the formation of wrinkles.