Free consultation with a doctor by phone
Gynecologist appointments are available daily by appointment!!!
LLC "Your Doctor"
Chat with the doctor
Addresses of medical centers in Moscow (unified reference) +7 (495) 255-45-59
Make an appointment at the clinic Discount on services Promotions
- +7 (495) 255-45-59
- Gynecological centers in Moscow
- Every day from 9.00 to 20.00
- call me back
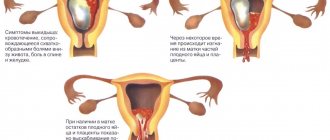
Typically, cleaning after an abortion is performed in cases where parts of the fertilized egg remain in the uterine cavity for certain reasons. This condition is extremely dangerous for a woman, as it causes infection and bleeding, which can lead to very serious consequences.
You should not waste time and try to correct the situation using traditional methods. If you notice any suspicious symptoms, you should immediately contact a good specialist. Our gynecological clinic has the most modern materials, the latest equipment and highly qualified staff.
Indications for repeated cleaning of the uterus
Women undergo the procedure of uterine curettage either at their own request for the purpose of terminating a pregnancy or as prescribed by a doctor for any pathology for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Unfortunately, in some cases, uterine cleaning is prescribed again. The cause may be bleeding from the genital tract as a result of insufficient contraction of the uterus, the accumulation of blood clots or the remains of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity, or the presence of a placental polyp. All this can happen after:
- miscarriage (spontaneous abortion);
- frozen pregnancy (failed abortion), when the fetus stops developing and dies;
- medical abortion or after vacuum aspiration performed in the early stages up to 6 weeks of pregnancy;
- unsuccessful abortion in the early stages up to 12 weeks or in the late stages from 13 to 27 weeks strictly for medical reasons;
- artificially induced premature birth, when termination of pregnancy is required beyond 28 weeks and urgent birth.
In addition, there are gynecological indications:
- recurrent bleeding in postmenopause;
- rare, but repeated curettage after removal of the tumor still occurs.
If endometrial hyperplasia is detected, separate diagnostic curettage of the uterus and cervical canal is normally performed, then repeated cleaning is prescribed:
- after 3 months when atypia is detected for control;
- if a relapse occurs during hormonal therapy;
"Miramistin"
The effect of this drug is similar to the previous one. The design of the bottle is identical. "Miramistin" is effective not only in the treatment of infections, wounds, sexually transmitted diseases, but also in the prevention of various types of pathologies. The use of the product during pregnancy is allowed, because its effect is very soft and delicate. Absorption of substances into the blood does not occur, so there will be no harm to the child.
The use of the drug during pregnancy is allowed only from the 14th week. During the procedure, a slight burning sensation may occur, which will subside over time. Do not spray more than 10 ml of product into the cavity at a time. After administration, you need to lie down for about 10 minutes. Like any other medicine, this is used only as directed by a doctor.
How does the re-cleaning procedure work?
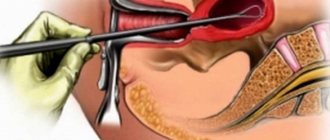
The uterine curettage procedure is an operation lasting about 20 minutes under general intravenous anesthesia. The patient falls asleep and does not feel anything. Epidural (spinal) anesthesia can also be used when the woman is conscious and does not feel the lower half of the body, but this type of anesthesia is used much less frequently. In other cases, they may limit themselves to local anesthesia, but pain still remains.
- Before and after surgery, the external genitalia and vagina must be treated.
- Then, using special instruments, the cervix is fixed, the length of the uterus is checked and the cervical canal is expanded.
- The contents of the cavity and the surface layer of the uterine mucosa are removed using a curette, hence the name curettage; or carry out vacuum cleaning with aspiration.
Memo to the patient after repeated cleaning of the uterus
After repeated curettage, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations so that no complications arise and you recover faster:
- continue and complete the prescribed treatment (antibacterial, hormonal, hemostatic, uterine contractions and other groups of drugs);
- watch for discharge from the genital tract. Normally, after the procedure, spotting gradually decreases in volume and lasts no more than 10 days;
- sexual rest for at least 2 weeks, and preferably up to a month and after a follow-up examination;
- do not use tampons or douche;
- eliminate physical activity;
- You cannot visit the sauna or take a hot bath.
If the following complaints occur, you must consult a doctor to exclude or identify pathology and carry out appropriate treatment:
- body temperature above 37 degrees, general weakness, dizziness;
- a few days later pain appeared in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- the volume of bleeding does not decrease or it suddenly stops;
- after 1-1.5 months, discharge does not begin, and the first menstruation may be scanty.
Consequences of repeated cleaning
Curettage of the uterus is a surgical intervention, so there may be negative consequences that occur immediately after the procedure or after some time:
- inflammation of the uterine mucosa (endometritis);
- perforation of the walls of the uterus during the procedure;
- stenosis (narrowing) of the cervical canal of the cervix;
- formation of adhesions in the uterine cavity;
- menstrual irregularities;
- infertility due to damage to the deeper layers of the uterine mucosa, which prevents the implantation of a fertilized egg in the future.
In any case, after discharge, a follow-up examination by a doctor, a dynamic ultrasound examination and, if necessary, a colposcopy are required.
For better recovery, you can undergo a course of physiotherapy (electrophoresis, mud therapy, acupuncture). Drink more fluids and healthy foods, take vitamins.
Is it painful to have a surgical abortion procedure?
If you contact a medical center when your pregnancy is more than 12 weeks, a surgical abortion is prescribed, performed in a hospital setting. Curettage, like other types of abortion, is an unpleasant and sometimes painful procedure, so the procedure is always performed under anesthesia.
Before the operation itself, the specialist administers an anesthetic. Then, with the help of a dilator, the cervix is dilated; it is at this moment that the patient most often experiences acute, but not severe pain. Next, using a curette (an instrument in the form of a sharp spoon), the uterine cavity is cleansed - the whole procedure takes no more than half an hour.
Anesthesia plays a significant role in the operation to clean the uterus; it is anesthesia that helps reduce all unpleasant and painful sensations to a minimum. When choosing an anesthetic, the doctor takes into account the woman’s age, existing allergic reactions, gestational age and other characteristics.
Many women are afraid of developing pain and discomfort during surgery, so they ask for the procedure to be performed under general anesthesia. In the absence of any contraindications, the doctor can meet you halfway. The patient need not be afraid of pain, since the entire acute part of the operation will be performed under anesthesia, which will save the woman from suffering. But it must be remembered that after the effect of the anesthetic wears off, the woman may experience pain and pain in the lower abdomen due to contraction of the uterus.
It seems completely incredible, but some time ago curettage was carried out without the use of anesthesia, the same applies to women for whom the use of anesthesia is contraindicated for one reason or another. In this case, the pain during a surgical abortion is excruciating and unbearable, from which women often lose consciousness. Now there are a large number of alternative painkillers, with the help of which the doctor makes the procedure painless and comfortable.
Some women are afraid of general anesthesia and choose local anesthesia, which is used quite rarely, since the drug acts locally. Before cleaning, an anesthetic gel is injected into the vagina, the effect of which begins after half an hour. During an abortion, the patient may experience pain and discomfort; some claimed that the procedure seemed like an eternity due to the excruciating sensations - it all depends on the degree of pain threshold. Local anesthesia is also used in patients who have an allergic reaction to anesthesia. One of the advantages of this method is the minimal list of side effects and complications, so after 1.5-2 hours the woman can leave the hospital.
What to do after an abortion for a quick recovery
The risk of possible complications depends on the method of termination of pregnancy. The risks of complications after surgery are reduced if the termination is performed by an experienced doctor. With medical termination of pregnancy, the general condition of the body is restored quite quickly. After surgery, quite serious rehabilitation is often required.
There are general rules for what to do after an abortion in order to reduce the risk of various complications. These rules are quite simple.
After the operation, you must abstain from sexual activity for at least three weeks, until the end of the first menstrual cycle. After all, sexual contact can provoke bleeding and rejection of the mucous membrane of the cervix. During sexual intercourse, an infection can enter the uterine cavity.
It is prohibited to engage in sports or carry heavy loads for two weeks after the procedure. Only in this case can complete rest be ensured for the muscle mass in the abdominal area. Complete rest is all that is needed after an abortion. After the operation, enough time must pass for the woman’s body to restore physical health without external irritants.
Swimming in pools, open reservoirs, and taking baths is prohibited. You can only wash in the shower. Then bacteria will not be able to enter the body, and this will prevent infection.
It is very important to eat right while recovering from an abortion. After all, abortion is very depleting to the body, so during the recovery period you will need a lot of fiber and protein.
It is very important to know what to do after an abortion in order to notice alarming symptoms in time and prevent the development of complications. It is necessary to check pulse, temperature, blood pressure, and assess the general condition of the body.
It is equally important to maintain personal hygiene. Panty liners should be changed every three hours, and you should wash yourself several times a day. Tampons cannot be used.
When talking about what is needed after an abortion to rehabilitate the body, we must not forget about visiting a gynecologist. Seven to ten days after the abortion, the attending physician sends the patient for an ultrasound to identify possible remnants of fetal particles. It is also advisable to undergo an ultrasound of the mammary glands after an abortion to prevent the development of tumors.
If after an abortion a woman has more frequent breakdowns, stress, and depression, then it is advisable for her to visit a psychologist. At a consultation, a psychologist will help you find a way out of this state.
When is chlorhexidine douching necessary?
Douching with chlorhexidine has recently become quite popular. This drug contains the component bigluconate, which can fight chlamydia, gonococci, ureaplasma and treponema pallidum. Also, chlorhexidine can destroy yeast, herpes simplex virus and dermatophytes, but has no effect on bacteria and fungi.
The pharmacy sells a ready-made solution of chlorhexidine for douching, which does not need to be diluted. Moreover, a syringe is also not required to use it, since the packaging of the medicine itself is a pear. The printed package should be inserted with the tip into the vagina (it is best to take a lying position for this) and, pressing on the bottle, slowly introduce the drug inside. You can’t get up right away - you need to lie down for a few minutes.
It is strictly forbidden to douche with chlorhexidine during pregnancy. If unprotected sexual intercourse has occurred with a new partner, chlorhexidine can serve as a prevention of sexually transmitted diseases, but it is better not to postpone subsequent examination. Frequent use of the solution is fraught with bacterial vaginosis.
Treating thrush with chlorhexidine douches may not be useful. The fact is that candidiasis is usually provoked by fungi, against which the drug in question is powerless. Therefore, such douching for thrush can only be recommended by a doctor who, upon examination, will find concomitant diseases in the woman that chlorhexidine can treat.
Cleaning after abortion
Incomplete release of the fertilized egg is one of the very first complications that many women have to face. In this case, additional cleaning is carried out after the abortion, which increases the risk of damage to the cervix and uterine lining. As a result of damage to the uterine mucosa, bleeding may occur. What to do after an abortion if heavy bleeding occurs? Naturally, consult a doctor immediately.
After all, if you do not clean up after an abortion in a timely manner, then pathogenic bacteria will rapidly begin to multiply in the uterine cavity. And the proliferation of bacteria can lead to the rapid development of endometritis, purulent inflammation, and salpingitis.
Therefore, in case of high fever, heavy bleeding with blood clots, pain exceeding the pain threshold during the menstrual cycle, discharge with an unpleasant strong odor, fainting, nausea, dizziness, vomiting, you should immediately call for medical help.
Found an error in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Uterine curettage surgery
[contents h2] In addition to the diagnostic procedure intended to conduct a detailed examination of the tissues of the uterus, curettage is also performed for the purpose of terminating pregnancy. Women are better known and understand the term “abortion,” which often means instrumental curettage of the uterus. If in the early stages it is possible to stop the development of an unwanted pregnancy using more gentle methods, then after 6-8 weeks surgical intervention will be required to remove the fetus and membranes from the uterine cavity.
Douching for unwanted pregnancy
Douching is done using a wide variety of solutions. Depending on them, certain goals are achieved. Let's consider two options - douching as a means of preventing pregnancy or vice versa, increasing the chances of conception.
If pregnancy is not currently needed by a young couple, then agents that oxidize the vaginal environment are used. Even in ancient times, priestesses prevented pregnancy by inserting a piece of lemon into the vagina before sexual intercourse. Grape vinegar also helps. We strongly do not recommend using such tools. Douching for an unwanted pregnancy can lead to the loss of the chance not only of conception, but also of a normal sex life. After all, without calculating the concentration of the solution, a woman can burn her entire mucous membrane.
How is curettage performed?
[ads1]Before surgery, a vaginal examination is performed to accurately determine the position, size and shape of the uterus.
You will also need to consult an anesthesiologist to find out contraindications to anesthesia and select its method. Most often, the patient is given instant intravenous anesthesia directly on the operating table, having previously installed a catheter for the possible addition of a portion of the drug during manipulation. In rare cases, abortion is performed using spinal anesthesia or endotracheal anesthesia.
The sequence of actions of the doctor during curettage:
1. Treating the genitals with alcohol or iodine solution. 2. Opening the vagina using gynecological speculum, cleansing the internal genital organs with an alcohol solution. 3. Expansion of the cervical canal by introducing tubes of different diameters (Hegar dilators). 4. Insertion of a curette into the uterine cavity, detection of the fertilized egg. 5. Destruction of fetal tissue by the curette. Additionally, it may be necessary to use an abortion forcemer, which easily grasps the fetus. This tool is used especially often during late pregnancy (13 weeks or more). 6. Removal of the fetus whole or in parts. 7. Curettage of the mucous membrane of the uterus and the remaining membranes of the fertilized egg until the walls of the organ are smooth. 8. Retrieving instruments. The success of the operation is determined by the cessation of bleeding and the appearance of bloody foam. 9. All parts of the fruit are placed in a tray to confirm its integrity and complete removal. Operations controlled using ultrasound sensors are considered more successful and faster. An examination using ultrasound or a hysteroscope is also required after surgery to avoid complications.
Is it possible to douche with hydrogen peroxide?
If a woman has developed vaginal dysbiosis due to taking antibiotics or for some other reason, douching with hydrogen peroxide can help. This is very important for women’s health, since a sharp decrease in the number of lactic acid bacteria, inevitable with dysbacteriosis, can provoke colpitis. A set of therapeutic measures, including douching with a peroxide solution, will help restore normal microflora. Attention! For these purposes, use only a 3% pharmaceutical solution of hydrogen peroxide, which should be diluted with chilled boiled water in a ratio of 1:3 before use. The rules for douching are similar to those recommended for procedures with other solutions.
How to prepare for the procedure?
In order for curettage to take place without unpleasant complications from the gastrointestinal tract, you should not eat 12 hours before the operation (especially if it is performed under general anesthesia). You should also empty your bowels and bladder immediately before the procedure, perform a cleansing enema at home, and carefully shave your pubic and perineal hair.
To perform curettage, you will need a consultation with an anesthesiologist and a number of tests and studies:
1. Gynecological examination. 2. Smear for oncocytology. 3. Smears for infectious diseases of the genital area to exclude infection of the appendages during surgery. 4. Ultrasound of the uterus to determine the gestational age and the nature of the location of the fertilized egg. 5. Tests for HIV, hepatitis B, C, syphilis. If STI pathogens are detected in smears, a course of intensive therapy is carried out before the abortion to eliminate the disease.
Surgical abortion in late pregnancy
Late abortion is performed surgically at 13-28 weeks, which poses a serious danger to a woman’s reproductive health. For each medical center and specialist, different pregnancy periods are established; for some, the period is up to 20 weeks, while others do late-term cleansing no earlier than 22 weeks, believing that this period is safer for a woman’s health.
In only 15% of cases, a woman needs to undergo a late-term abortion, and this requires compelling reasons, since such an interruption is fraught with complications. The main indications for late-term surgical abortion include:
- If a woman had no idea about her pregnancy: menstruation was present or its absence was regarded as a hormonal disorder. When contacting a specialist for a fairly long period, an abortion must be supported by medical indications.
- Social grounds: rape, divorce, inability to support a child, disability of a partner, lack of housing, imprisonment, deprivation of parental rights.
- If the examination revealed serious abnormalities in the development of the fetus, which after birth can be painful or fatal. For example, developmental defects, anomalies, absence of one or more limbs, Siamese twins, etc.
- During pregnancy, a woman was diagnosed with a serious illness, which may threaten her health or life during further pregnancy. Such diseases include: exacerbation of diseases of the central nervous system and cardiovascular system, infectious diseases, mental disorders, etc.
Which method of late-term surgical abortion to use is considered by a commission of specialists, a social worker and a lawyer, and the doctor can also take into account the opinion of the patient herself.
Late abortion can be performed using the following surgical methods:
- C-section. This type of late pregnancy termination is the safest and is used in most cases at the request of the patient, as well as for existing social and medical indications. These include: a serious illness in a woman that threatens her life, fetal defects associated with mental or physical disabilities. In addition, such surgical intervention is used if urgent extraction of the fetus is required in case of severe bleeding in the case of placental abruption or if natural delivery is contraindicated. During the operation, the doctor makes an incision on the anterior abdominal wall, spreads the muscles and makes an incision on the uterus. The fetus is removed from the organ cavity manually, then the uterus is cleaned of the placenta and blood. Less commonly used is a vaginal cesarean section, in which the lower part of the uterus is cut and the fetus is delivered through the vagina. Caesarean sections for social reasons are quite rare.
- No later than 15 weeks, pregnancy can be terminated by simultaneously removing the embryo from the uterine cavity. This method refers to curettage using metal instruments and is used only in case of emergency abortion after a previous unsuccessful surgical intervention. This method is traumatic and dangerous due to the risk of damage to the uterus, severe bleeding and protracted abortion.
- Dilatation of the cervix. After anesthesia, the specialist dilates the cervix, then the doctor uses special forceps with a weight. This type of abortion is dangerous and carries many risks, so it is used quite rarely.
- Instrumental curettage. After putting the woman under anesthesia, the doctor opens the uterus using dilators, and then cleans the organ cavity with a loop instrument, removing fragments of the fertilized egg and placenta. This operation is accompanied by light bleeding, the duration of which should not exceed 10-14 days.
Each of the methods of late surgical abortion has its own disadvantages and advantages, but all of them are traumatic for the reproductive organ, so it is very important to follow the recovery recommendations as closely as possible.
What discomfort might a woman experience?
If the operation is performed under general anesthesia, pain is completely eliminated. Nowadays, private and municipal clinics do not practice operations with local anesthesia with lidocaine, which was previously the norm.
After curettage, pain often occurs, which is associated with the contraction of the uterine walls to their original size. The pain is aching or characterized by mild cramping attacks, similar to the sensations during menstruation. Only a small percentage of women need medication to relieve discomfort; for the rest, it does not exceed that during menstruation and lasts 1-5 days.
Signs of bleeding often appear, which normally ends quickly. Sometimes pain in the mammary glands develops - the result of changes in hormonal levels, which can be potentially dangerous due to the occurrence of mastopathy and fibrocystic pathologies.
Possible complications
Unfortunately, many women experience various complications after instrumental abortion. Among the primary, or early complications, the following are distinguished:
The most dangerous, life-threatening consequence is perforation of the uterus (perforation). It can occur when curettage is performed by an unqualified doctor in the form of mechanical damage to the walls or their thinning due to the removal of an excess layer of mucosal tissue during surgery. If the contents of the uterus penetrate the peritoneum, there is a high probability of peritonitis and death. Perforation of the uterus often becomes the reason for its emergency complete removal. Damage to the cervix from abortion instruments. Threatens infertility or problems with subsequent pregnancy. Bleeding . Instrumental abortion is especially dangerous for women with bleeding disorders. In this case, continuous bleeding can lead to anemia, fainting and even death. Excessive bleeding after curettage is a reason to sound the alarm. After numerous curettages, bleeding may intensify while still on the operating table, which is often an indication for blood transfusion and removal of the uterus. A consequence of abortion is often infection of the genital organs due to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria onto the wound surface. An infection can be suspected by prolonged aching pain, unpleasant-smelling discharge, and an increase in body temperature. They can be symptoms of endometritis, salpingitis and even thrombophlebitis of the uterine vessels. Leaving part of the fertilized egg in the uterus . A rare complication, but one that occurs in medical practice. It manifests itself as pain, putrefactive discharge, inflammation of the uterine tissue and requires an urgent repeat abortion. Proliferation of placental remnants that have not been removed. The pathology is typical for curettage in late pregnancy and is very serious. Treatment is only surgical. In addition to early disturbances in the body that appear in the first weeks, there are also late complications of curettage. You can expect them even years after an abortion, since they are caused by trauma to the walls of the uterus and severe hormonal disruption in the woman’s body. These include:
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital area and the problems they cause with bearing a fetus in the future.
- Adhesions in the fallopian tubes (potential risk of infertility or ectopic pregnancy due to tubal obstruction).
- Habitual miscarriage, miscarriages due to damage to uterine tissue.
- The need for a caesarean section in subsequent pregnancies, which is associated with deformation of the cervix during an abortion.
- Endocrine pathologies, mastopathy, breast tumors.
- Uterine fibroids, endometrial hyperplasia, ovarian cysts.
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle, prolonged absence of menstruation.
- Menstruation after curettage
Until what time can you have a surgical abortion?
Curettage can be done up to 22 weeks; this usually occurs for medical reasons, if fetal development is impaired. For the same reasons, surgical abortion can be performed at a later date, which can only be determined by a doctor. The operation is performed in a hospital setting by an experienced specialist, which guarantees the absence of postoperative complications.
When deciding to undergo surgical curettage, a woman must undergo a number of examinations, such as:
- examination on a gynecological chair with taking a smear,
- Ultrasound,
- take tests for blood clotting, the presence of infectious diseases, blood type, hCG level.
Only after a preliminary examination, the doctor prescribes the time for the operation. If there are no complications, the patient can leave the hospital on the same day.
Pregnancy after curettage
Irregularity of the menstrual cycle is one of the reasons for repeated unwanted pregnancies. In this regard, careful protection after curettage is necessary. More often it comes down to barrier contraception or taking hormonal drugs. Planning offspring immediately after an abortion is a rash step: the genitals have not had time to recover, and the uterine tissue and hormonal system are still in a depressed state for a long time, so the risk of miscarriage or premature birth is very high. The optimal time for subsequent conception is six months after curettage.
Failure to conceive is a common complication of abortion, which is caused by inflammatory diseases and adhesions. Moreover, the likelihood of infertility increases with the number of operations performed. It has been established that up to half of cases of inability to have offspring are caused by abortion, so you should think carefully before deciding to have the uterus curetted.
Douching during pregnancy
Obstetrician-gynecologists categorically prohibit douching during pregnancy for the following reasons:
- During pregnancy, the number of blood vessels on the inner surface of the uterus increases, and accordingly, the risk of air entering through the cervical canal during the douching procedure increases.
- Douching can deliver chemicals to the fetus that can have a negative effect on the growing body, and also increases the risk of damage to the amniotic sac.
- The risk of thrush - vaginal candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis (discharge with a fishy smell) and other vaginal infections due to douching during pregnancy is very high and this can provoke transmission of infection from mother to fetus, which increases the likelihood of premature birth and other pregnancy pathologies.